Bangladesh Logistics and Warehousing Market Outlook to 2029
By Mode of Transportation (Road, Rail, Air, Sea), By End User (Retail, FMCG, E-commerce, Pharmaceuticals, Manufacturing), By Warehousing Type, By Region
- Product Code: TDR0176
- Region: Asia
- Published on: May 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Bangladesh Logistics and Warehousing Market Outlook to 2029 – By Mode of Transportation (Road, Rail, Air, Sea), By End User (Retail, FMCG, E-commerce, Pharmaceuticals, Manufacturing), By Warehousing Type, By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the logistics and warehousing industry in Bangladesh. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer-level profiling, issues and challenges, and comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the logistics and warehousing market. The report concludes with future market projections based on revenue, segmented by transport mode, industry verticals, regions, and success case studies highlighting major opportunities and risks.
Bangladesh Logistics and Warehousing Market Overview and Size
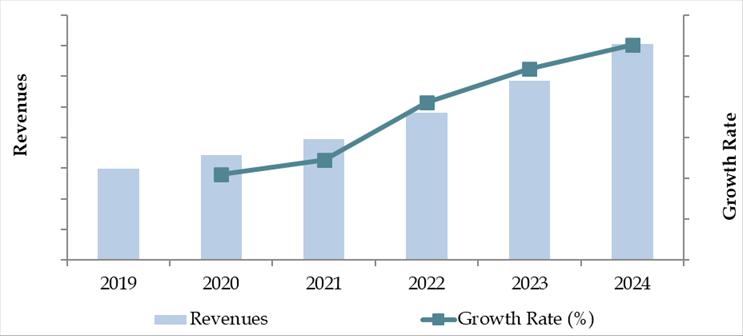
The Bangladesh logistics and warehousing market reached a valuation of BDT 62,000 Crore (approx. USD 5.7 Billion) in 2023, fueled by rapid urbanization, the expansion of e-commerce, government investments in transport infrastructure, and increasing manufacturing and export activities. Key players in the market include Kuehne + Nagel Bangladesh, DHL Express, DB Schenker Bangladesh, Maersk Bangladesh, APL Logistics, and Runner Logistics. These firms are recognized for their robust transport fleets, multimodal connectivity, and growing warehousing footprints across Dhaka, Chattogram, and emerging SEZs.
In 2023, DHL launched a new 100,000 sq. ft. bonded warehouse near Chattogram Port to handle growing demand for just-in-time logistics. The initiative supports Bangladesh’s vision to become a regional logistics hub and enhance efficiency in export-import activities. Dhaka and Chattogram remain critical logistics corridors due to their proximity to industrial clusters and maritime gateways.
Market Size for Bangladesh Logistics and Warehousing Industry on the Basis of Revenue in USD Billion, 2018-2024
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Bangladesh Logistics and Warehousing Market
Infrastructure Development: Major government investments in Padma Bridge, Dhaka Elevated Expressway, and upgrades at Chattogram and Mongla ports have dramatically improved logistics efficiency and connectivity. These projects reduce travel time and lower operational costs, driving growth in freight and warehousing demand.
Boom in E-commerce and Retail: Online retail growth at 25% CAGR has significantly increased demand for last-mile delivery, third-party logistics (3PL), and cold chain infrastructure. Dhaka, Gazipur, and Narayanganj are emerging hotspots for fulfilment centers due to population density and high order volumes.
Export-Oriented Manufacturing: With RMG, leather, and pharmaceuticals driving Bangladesh’s exports, logistics providers are building specialized infrastructure for containerized transport and bonded warehousing. In 2023, the logistics sector handled over 80% of garment-related exports with dedicated customs clearance facilities.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for Bangladesh Logistics and Warehousing Market
Infrastructure Bottlenecks: One of the major barriers to growth in Bangladesh’s logistics sector is the inadequate infrastructure, including poor road conditions, congestion at key ports (like Chattogram), and limited railway connectivity. As of 2023, logistics costs in Bangladesh accounted for nearly 15% of GDP—one of the highest in Asia—mainly due to inefficiencies in transport and warehousing.
Regulatory Complexity and Bureaucracy: A fragmented regulatory framework and multiple government agencies overseeing logistics operations result in delays, especially in customs clearance and cargo handling. In 2023, the average dwell time at major ports exceeded 4.5 days, significantly above global standards, adding delays and costs to supply chains.
Lack of Skilled Workforce and Technology Adoption: The logistics sector struggles with a shortage of trained personnel, particularly in cold chain and warehouse automation. Only about 25% of warehousing operators reported having access to trained staff for handling digital inventory systems or temperature-sensitive goods. This limits operational efficiency and scalability for logistics service providers.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market
National Logistics Policy 2021 (Draft Stage): The Government of Bangladesh has introduced a draft National Logistics Policy aimed at streamlining regulatory oversight, boosting infrastructure investments, and creating a one-stop service platform for logistics stakeholders. If implemented effectively, this is expected to reduce logistics costs by 4-5% of GDP over the next 5 years.
Bonded Warehouse Licensing and SEZ Expansion: The Bangladesh Export Processing Zones Authority (BEPZA) and the Bangladesh Economic Zones Authority (BEZA) have streamlined rules to allow faster approval for bonded warehouse operations in export zones. In 2023, more than 50 new warehouse licenses were issued across the country, encouraging private investment in logistics parks and cold chain facilities.
World Bank-Backed Infrastructure Programs: Under the Western Economic Corridor & Regional Enhancement Program (WeCARE), Bangladesh has initiated multi-billion dollar projects aimed at upgrading highways, rural roads, and inland ports. The first phase, focusing on the Dhaka-Khulna corridor, is expected to reduce transit times by 30% once operational by 2026.
Bangladesh Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
By Market Structure: The logistics market in Bangladesh is predominantly unorganized, comprising small transporters and local storage providers who dominate due to cost competitiveness, informal business models, and long-standing client relationships. However, the organized sector—comprising national-level 3PL providers, multinational logistics firms, and specialized warehousing companies—is gradually expanding, driven by rising e-commerce demand, global supply chain integration, and infrastructure improvements. Organized players are increasingly focusing on multimodal logistics, automation, and end-to-end service offerings to attract institutional and international clients.
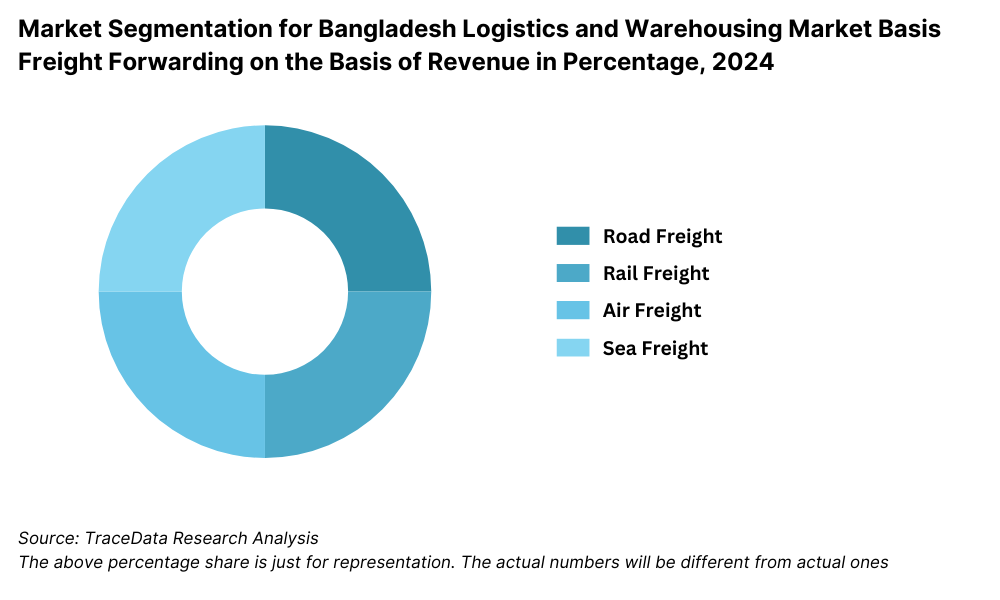
By Mode of Transport: Road transport remains the dominant mode in Bangladesh due to limited rail and inland waterway infrastructure. Over 75% of goods movement still occurs via roadways, which are more flexible and accessible across urban and rural regions. However, government initiatives such as the Padma Bridge and the Dhaka-Chattogram Expressway are expected to further streamline road logistics. Rail and waterways are underutilized but gaining attention for bulk cargo movement due to lower costs and sustainable benefits.
Market Segmentation for Bangladesh Logistics and Warehousing Market Basis Market Segment on the Basis of Revenue in Percentage, 2024
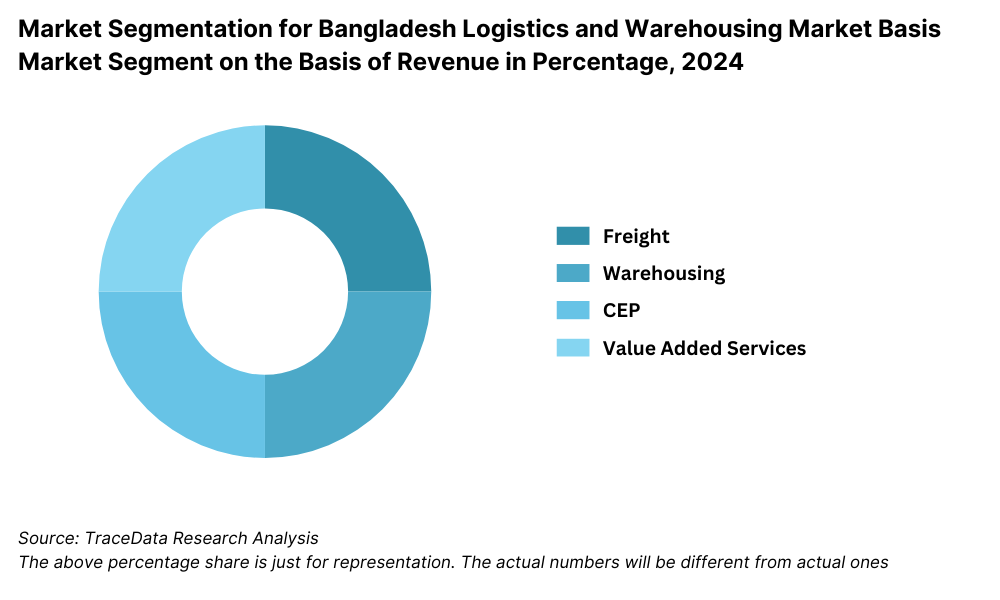
By End-User Industry: The FMCG and Retail sectors are the largest demand drivers for logistics and warehousing services, due to rising urban consumption, expansion of modern trade formats, and growth in inventory turnover. E-commerce, particularly in last-mile delivery, has seen exponential growth and is pushing demand for organized, tech-enabled warehousing and faster logistics solutions. Pharmaceuticals and Cold Chain sectors are also growing, led by regulatory compliance and increasing health infrastructure needs.
Competitive Landscape in Bangladesh Logistics and Warehousing Market
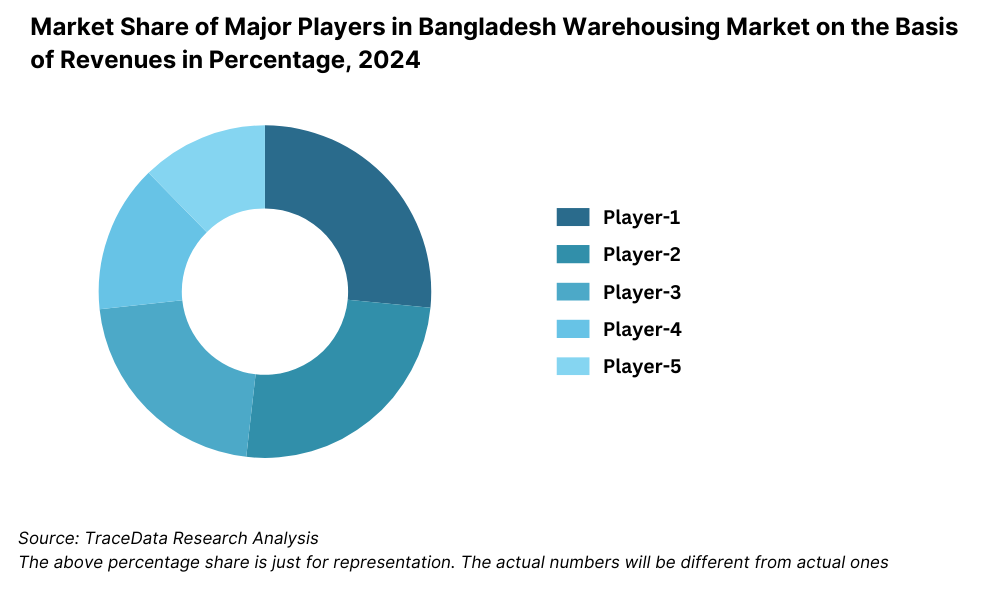
The Bangladesh logistics and warehousing market is moderately fragmented, with a mix of traditional operators and emerging organized players. The sector is seeing increasing participation from multinational 3PL providers, tech-driven logistics startups, and specialized warehousing firms. Key players include SA Paribahan, eCourier, Paperfly, Sundarban Courier, DB Schenker Bangladesh, DHL Bangladesh, PRAN-RFL Logistics, and City Express, each offering unique service capabilities across different logistics verticals such as B2B freight, cold chain, last-mile delivery, and warehousing infrastructure.
| Company Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
| Karnaphuli Group (Logistics Division) | 1954 | Dhaka, Bangladesh |
| MGH Group | 1992 | Dhaka, Bangladesh |
| Summit Alliance Port Limited (SAPL) | 2003 | Dhaka, Bangladesh |
| Container Movers (Bangladesh) Ltd. | 1991 | Dhaka, Bangladesh |
| QC Logistics Ltd. | 2003 | Dhaka, Bangladesh |
| Haque Logistics Ltd. | 2005 | Chattogram, Bangladesh |
| Tropical Shipping & Logistics | 2004 | Dhaka, Bangladesh |
| DHL Global Forwarding Bangladesh | 1969 (BD: ~1980s) | Bonn, Germany |
| DB Schenker Bangladesh | 1872 (BD: ~2000s) | Essen, Germany |
| Kuehne + Nagel Bangladesh Ltd. | 1890 (BD: ~2000s) | Schindellegi, Switzerland |
| Agility Logistics Bangladesh | 1979 (BD: ~2006) | Kuwait City, Kuwait |
| CEVA Logistics Bangladesh | 2006 (BD: ~2010) | Marseille, France |
| UPS Bangladesh (via local agents) | 1907 (BD: ~1997) | Atlanta, USA |
| FedEx Bangladesh (via Homebound) | 1971 (BD: ~1989) | Memphis, USA |
| Nippon Express Bangladesh | 1937 (BD: ~1990s) | Tokyo, Japan |
| Maersk Logistics Bangladesh | 1904 (BD: ~2000s) | Copenhagen, Denmark |
| TNT Express Bangladesh | 1946 (BD: ~1990s) | Hoofddorp, Netherlands |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
SA Paribahan: A leading player in intercity cargo transport, SA Paribahan operates over 200 hubs nationwide. In 2023, the company expanded its warehousing space by 300,000 sq. ft., focusing on FMCG and pharma clients in the Chattogram-Dhaka corridor.
Sundarban Courier: Specializing in B2C and parcel delivery services, Sundarban saw a 20% rise in last-mile shipments in 2023, driven by the growing e-commerce boom. The company also launched GPS-based parcel tracking services to improve delivery transparency.
eCourier: One of the top e-commerce logistics providers, eCourier reported a 35% YoY growth in order volumes in 2023. The company has also invested in AI-based routing and delivery management tools to optimize its delivery network in Dhaka and nearby districts.
Paperfly: Known for its hybrid distribution and smart delivery models, Paperfly expanded to over 100 delivery hubs in 2023 and introduced a dedicated “Fulfillment as a Service” offering targeting SME e-retailers.
PRAN-RFL Logistics: The logistics arm of PRAN-RFL Group handles integrated warehousing and distribution for over 500 SKUs. In 2023, it deployed automated racking systems and expanded its cold storage chain to support its growing agro-processing exports.
DHL Bangladesh: A global 3PL leader, DHL invested in temperature-controlled logistics and customs clearance support tailored to Bangladesh’s pharma and textile export sectors. DHL’s cross-border trade facilitation hubs handled over 50,000 consignments in 2023.
DB Schenker Bangladesh: Focused on multimodal logistics, DB Schenker recently launched dedicated supply chain solutions for automotive and electronics clients. Their 2023 investments included expansion into ICD (Inland Container Depot) support services.

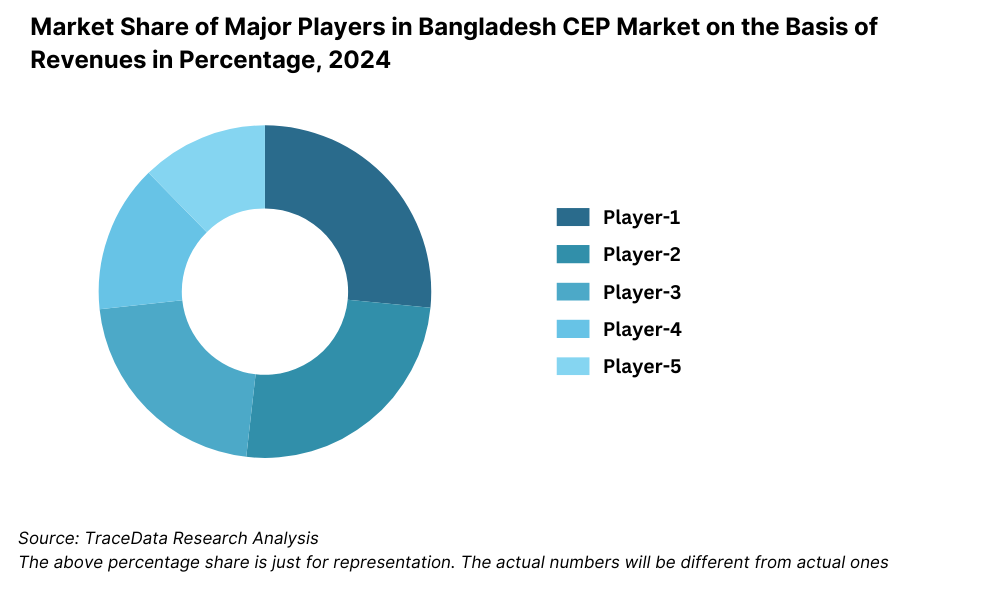
What Lies Ahead for Bangladesh Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Bangladesh logistics and warehousing market is projected to witness steady growth through 2029, supported by government infrastructure investments, rising manufacturing output, and rapid e-commerce penetration. The sector is expected to expand at a healthy CAGR, driven by structural reforms, improved connectivity, and a shift towards organized logistics solutions.
Emergence of Smart Warehousing: The future of warehousing in Bangladesh will see increasing adoption of smart technologies such as RFID, IoT-based inventory management, automated sorting, and real-time visibility tools. These innovations will enhance operational efficiency, reduce shrinkage, and provide better tracking across the supply chain.
E-commerce and Last-Mile Acceleration: With online retail growing at double-digit rates annually, the demand for last-mile logistics and hyperlocal warehousing will surge. Logistics firms are expected to expand fulfillment centers closer to urban clusters, and same-day/next-day delivery models will become standard practice in major cities.
Development of Integrated Logistics Parks (ILPs): Government and private sector investments into ILPs, especially along key trade corridors (e.g., Dhaka–Chattogram, Khulna–Mongla), will play a key role in reducing logistics costs and enabling multimodal connectivity. These parks will provide warehousing, cold storage, container terminals, and value-added services under one ecosystem.
Policy-Driven Reforms and Public-Private Partnerships (PPP): The long-awaited National Logistics Policy is likely to be finalized by 2025, which will bring greater clarity on regulations, single-window clearances, and incentives for infrastructure development. PPP models will become more common, especially for port modernization, inland depots, and dry ports.
Future Outlook and Projections for Bangladesh Logistics and Warehousing Market on the Basis of Revenues in USD Billion, 2024-2029

Bangladesh Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
- By Market Structure:
o Organized Logistics Providers
o Unorganized/Traditional Transporters
o Freight Forwarding Companies
o Courier and Parcel Service Providers
o Cold Chain Logistics Operators
o Warehousing Providers
o E-commerce Fulfillment Service Providers - By Mode of Transport:
o Road Transport
o Rail Transport
o Inland Waterways
o Air Freight
o Maritime Shipping - By End-User Industry:
o FMCG
o Retail and E-commerce
o Pharmaceuticals and Healthcare
o Manufacturing and Industrial Goods
o Apparel and Textiles
o Agriculture and Food Processing
o Electronics and Consumer Durables - By Type of Warehousing:
o General Warehouses
o Cold Storage Warehouses
o Bonded Warehouses
o E-commerce Fulfillment Centers
o ICDs (Inland Container Depots) - By Region:
o Dhaka Division
o Chattogram Division
o Khulna Division
o Rajshahi Division
o Sylhet Division
o Barisal Division
o Rangpur Division
o Mymensingh Division
Players Mentioned in the Report:
Freight Forwarding Companies
- 3i Logistics Group
- A.H. Khan & Co.
- Agility Logistics
- Bolloré Logistics
- DHL International GmbH
- FedEx
- Schenker Logistics (Bangladesh) Ltd
- Tower Freight Logistics Ltd
- MOL Logistics Co Ltd
- Nippon Express Bangladesh Ltd
- CEVA Logistics
- Blue Ocean Freight System Ltd
- Shams Group of Companies
- Asia Pacific Logistics
- GEODIS Bangladesh
- Newport Express (BD) Ltd
- Rajpat Shipping Bangladesh
- ABC Freight Forwarding & Shipping Ltd
- CDZ Global Logistics Ltd
- Time Logistic Ltd
- NMC Bangladesh Ltd
- STO BD International Express Logistics
Warehousing Companies
- A.H. Khan & Co.
- Nippon Express Bangladesh Ltd
- Yusen Logistics Bangladesh Ltd
- WAC Logistics
- Khan Logistics Ltd
- IPort Logistics Ltd
- Omni Logistics
- Summit Alliance Port Limited
- One Union Solutions
- SEKO Logistics Bangladesh
E-Commerce Logistics Companies
- eCourier
- Paperfly
- RedX
- Pathao Courier
- Chaldal Logistics
- Ajkerdeal.com
- Shohoz
- Gluons Shop Limited
- BeshiDeshi
- Daraz Bangladesh
- Pathao Inc
- Hillsbazar
Express Logistics Companies
DHL Express Bangladesh
FedEx Bangladesh
Aramex Bangladesh
UPS Bangladesh
Bangladesh Express Co (BANEX)
BD Express Cargo
Sonar Courier
J&T Express Bangladesh
STO BD International Express Logistics
United Express
Key Target Audience:
- Logistics and Freight Companies
- Warehousing and Cold Chain Operators
- E-commerce and Retail Businesses
- Industrial Manufacturers and Exporters
- Government Authorities (e.g., Bangladesh Economic Zones Authority, BEPZA)
- Infrastructure Developers
- Transportation and Supply Chain Investors
- Technology Solution Providers (WMS, TMS)
Time Period:
- Historical Period: 2018–2023
- Base Year: 2024
- Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1 Macroeconomic framework for Bangladesh including GDP, GDP growth and GDP contribution by sector (Bangladesh macro indicators)
4.2 Logistics sector contribution to GDP and how the contribution has been changing in the historical assessment (Bangladesh logistics share in GDP)
4.3 Ease of Doing Business in Bangladesh (Regulatory and business environment)
4.4 LPI index of Bangladesh and improvements in the last decade
4.5 Customs procedure and customs charges in Bangladesh logistics market
5.1 Landscape of economic zones, investment parks and export processing zones in Bangladesh (EPZ and industrial cluster mapping)
5.2 Current scenario for logistics infrastructure in Bangladesh
5.3 Road infrastructure in Bangladesh including road network, toll charges and toll network, major goods traded through road, major flow corridors for road
5.4 Air infrastructure in Bangladesh including total volume handled, FTK for air freight, major inbound and outbound flow corridors, major goods traded through air, number of commercial and passenger airports, air freight volume by airports and other parameters
5.5 Sea infrastructure in Bangladesh including total volume handled, FTK for sea freight, major inbound and outbound flow corridors, major goods traded through sea, number of ports for coastal and ocean freight, number of vessels, sea freight volume by ports and other parameters
5.6 Rail infrastructure in Bangladesh including total volume handled, FTK for rail freight, major inbound and outbound flow corridors, major goods traded through rail and others (Rail freight infrastructure and utilization)
6.1 Basis revenues (Historical period)
7.1 By segment-freight forwarding, warehousing, CEP and value-added services
7.2 By end user industries
8.1 Market overview and genesis (Evolution of freight forwarding in Bangladesh)
8.2 Bangladesh freight forwarding market size by revenues (Historical period)
8.3 Bangladesh 3PL freight forwarding market segmentation
8.3.1 By mode of freight transport-road, sea, air and rail
8.3.1.1 Price per FTK for road, air, sea and rail in Bangladesh
8.3.1.2 Road freight-domestic and international volume, FTK and revenue; number of registered commercial vehicles (Road freight throughput and asset base)
8.3.1.3 Road freight domestic and international corridors
8.3.1.4 Ocean freight-domestic and international volume, FTK and revenue; volume by commodity; sea ports key statistics
8.3.1.5 Air freight-domestic and international volume, FTK and revenue
8.3.1.6 Rail freight-domestic and international volume, FTK and revenue; volume by commodity and region
8.3.1.7 Export-import scenario-value by mode of transport, commodity and country; volume by principal commodities
8.3.2 By intercity road freight corridors
8.3.3 By international road freight corridors
8.3.4 By end user-industrial, FMCG, F&B, retail and others
8.4 Snapshot of freight truck aggregators in Bangladesh including company overview, USP, business strategies, future plans, business model, number of fleets, margins/commission, number of bookings, major clients, average booking amount, major routes and others (Digital trucking and aggregation platform landscape)
8.5 Competitive landscape in Bangladesh freight forwarding market
8.5.1 Heat map of major players in Bangladesh freight forwarding on the basis of service offering (Service breadth and specialization)
8.5.2 Market share of major players in Bangladesh freight forwarding market
8.5.3 Cross comparison of major players in freight forwarding companies on the basis of parameters including volume of road freight, inception period, number of fleets (owned and subcontracted), fleets by type, occupancy rate, number of employees, major route network, major clients, revenues, volume of sea freight, volume of air freight, USP, business strategy, technology
8.5.4 Profiles of key freight forwarding and 3PL companies in Bangladesh
8.5.5 Cross comparison parameters for Bangladesh logistics and warehousing companies-network coverage (domestic and cross-border), TEU/tonnage handled, warehousing space under management, bonded warehouse capacity, fleet size by vehicle type, technology integration level (TMS/WMS/track & trace), key end user industry focus, annual revenue band
8.6 Bangladesh freight forwarding future market size by revenues (Forecast period)
8.7 Bangladesh freight forwarding market future segmentation (Forecast structural shifts)
8.7.1 Future market segmentation by mode of freight transport-road, sea, air and rail
8.7.2 Future market segmentation by international road freight corridors-India, Nepal and Bhutan (Future cross-border corridor potential)
8.7.3 Future market segmentation by end user-industrial, FMCG, F&B, retail and others
9.1 Market overview and genesis (Evolution of warehousing in Bangladesh)
9.2 Value chain analysis in Bangladesh warehousing market including entities, margins, role of each entity, process flow, challenges and other aspects
9.3 Bangladesh warehousing market size on the basis of revenues and warehousing space (Historical period) (Warehousing revenue and stock assessment)
9.4 Bangladesh warehousing market segmentation
9.4.1 Bangladesh warehousing revenue by business model-industrial/retail, ICD/CFS and cold storage (Business model-wise contribution)
9.4.2 Bangladesh warehousing by type of warehouse-general, open yard, freezer/chiller, ambient and bonded warehouses
9.4.3 Bangladesh warehousing revenue by end user-industrial & construction, FMCG, retail, food & beverage and others (End user-wise warehousing revenues)
9.4.4 3PL warehousing space by region-Dhaka, Gazipur, Narayanganj, Chattogram, Khulna and others (Regional warehousing footprint and vacancy)
9.5 Competitive landscape in Bangladesh warehousing market
9.5.1 Market share of top companies in Bangladesh warehousing market
9.5.2 Cross comparison of top warehousing companies on the basis of parameters including company overview, USP, business strategy, future plans, technology, revenues from warehousing, number of warehouses, warehousing space, location of warehouses, type of warehouses, occupancy rate, rental rates, clients and others
9.6 Bangladesh warehousing future market size on the basis of revenues
9.7 Bangladesh warehousing market future segmentation (Future warehouse mix)
9.7.1 Bangladesh warehousing revenue by business model-industrial/retail, ICD/CFS and cold storage (Future business model mix)
9.7.2 Bangladesh warehousing revenue by type of warehouse-general, open yard, freezer/chiller, ambient and bonded warehouses (Future warehouse type mix)
9.7.3 Bangladesh warehousing revenue by end user-industrial & construction, FMCG, retail, food & beverage and others (Future end user warehousing demand)
10.1 Market overview and genesis (CEP sector evolution in Bangladesh)
10.2 Value chain analysis in Bangladesh CEP market including entities, margins, role of each entity, process flow, challenges and other aspects
10.3 Revenue composition and contribution between first mile/mid mile and last mile delivery-analysis for domestic and international shipments
10.4 Bangladesh CEP market size on the basis of revenues and shipments (Historical period) (CEP revenues and shipment volumes)
10.5 Bangladesh CEP market segmentation (Current CEP structure)
10.5.1 Segmentation by mails and documents, e-commerce shipments and express cargo (Product mix in CEP)
10.5.2 Segmentation by international and domestic express (Geographic mix in CEP)
10.5.3 Segmentation by B2B, B2C and C2C (Customer segment mix in CEP)
10.5.4 Segmentation by period of delivery
10.6 Competitive landscape in Bangladesh CEP market (Key CEP players and rivalry)
10.6.1 Overview and genesis, market nature, market stage and major competing parameters (Market structure and basis of competition)
10.6.2 Market share of companies in Bangladesh CEP market on the basis of revenues/number of shipments (Latest period) (CEP market share distribution)
10.6.3 Market share of top companies in Bangladesh e-commerce shipment market on the basis of revenues/number of shipments (Latest period)
10.6.4 Cross comparison of top CEP companies in Bangladesh on the basis of parameters including company overview, USP, business strategy, future plans, technology, number of last mile delivery shipments, revenues, major clients, number of fleets, number of employees, number of riders, number of locations served, major service offering and others (CEP operator benchmarking)
10.7 Bangladesh CEP market future size on the basis of revenues and shipments
10.8 Bangladesh CEP market future segmentation (Future CEP structural shifts)
10.8.1 Segmentation by mails and documents, e-commerce shipments and express cargo (Future product mix)
10.8.2 Segmentation by international and domestic express (Future geographic mix)
10.8.3 Segmentation by B2B, B2C and C2C (Future customer segment mix)
10.8.4 Segmentation by period of delivery (Future service-level mix)
11.1 Customer cohort analysis and end user paradigm for different industry verticals under logistics sector-telecommunications, FMCG, automotive, apparel, F&B, construction and pharmaceuticals (End user typologies and logistics criticality)
11.2 Understanding logistics spend by end user (Latest period)
11.3 End user preferences in terms of in-house or outsourcing logistics services and reasons for selection; segregated by size of company on the basis of revenues
11.4 Major logistics companies specialized in serving each type of end user-telecommunications, FMCG, apparel, F&B, construction and pharmaceuticals
11.5 Detailed landscape of each end user across parameters including major products manufactured and traded, emerging products, type of services required and type of services outsourced, major companies, contract duration, likelihood to recommend, market orientation, major clusters, type of sourcing preference, pain points, facilities/services required, future outlook; market size for end user industry vertical with growth rate (Historical period)
12.1 Basis revenues (Forecast period)
13.1 By segment-freight forwarding, warehousing, CEP and value-added services
13.2 By end user industries (Future industry-wise logistics demand distribution)
13.3 Recommendation
13.4 Opportunity analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand-side and supply-side entities for the Bangladesh Logistics and Warehousing Market. On the demand side, this includes end-user industries such as FMCG, retail, e-commerce, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing. On the supply side, it covers 3PL providers, cold chain operators, warehousing companies, transportation fleets (road, rail, air, sea), and courier/delivery service providers.
Sourcing is done through industry articles, government policy documents, trade association reports, and multiple secondary and proprietary databases to perform desk research and build a comprehensive landscape. This helps shortlist leading 5–7 service providers in the country based on warehouse footprint, volume handled, fleet size, and revenue base.
Step 2: Desk Research
An exhaustive desk research process is conducted by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This includes reviewing industry reports, logistics performance index (LPI) scores, port throughput statistics, freight volumes, warehousing capacity, and modal share data.
Further, we evaluate company-level data from financial statements, investor presentations, public disclosures, news articles, and trade journals. The analysis covers aspects like market segmentation, pricing benchmarks, infrastructure investments, technology adoption, and customer verticals, to build a foundational understanding of the competitive environment.
Step 3: Primary Research
A series of in-depth interviews is initiated with C-level executives, logistics managers, warehousing heads, port authorities, and decision-makers from end-user industries. These interviews serve multiple purposes: validating the market hypotheses, confirming data accuracy, and gathering first-hand insights into growth drivers, operational models, challenges, and opportunities.
As part of our validation strategy, we also conduct disguised interviews with logistics operators and warehouse managers, presenting ourselves as prospective clients. This approach provides access to sensitive but essential data such as pricing, service models, capacity utilization, delivery timelines, and value-added services.
We employ a bottom-up approach to estimate throughput, storage capacity, and revenue per service line, which is aggregated to arrive at the total market size.
Step 4: Sanity Check
Both bottom-up and top-down modeling is undertaken to ensure consistency across market estimates. Cross-validation is performed using triangulation techniques and benchmark ratios (e.g., revenue/ton-km, cost/CBM, warehouse utilization %) to ensure robustness.
- Additionally, results from primary interviews are tested against the desk research findings and market assumptions to complete the sanity check and finalize the projections.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Bangladesh Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Bangladesh logistics and warehousing market holds strong growth potential, driven by rising domestic consumption, e-commerce expansion, and infrastructure development. The market is projected to grow steadily through 2029, supported by large-scale investments in roads, ports, and logistics parks. The sector is expected to contribute significantly to GDP by reducing supply chain inefficiencies and improving regional trade connectivity.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Bangladesh Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Key players in the Bangladesh logistics and warehousing market include SA Paribahan, Sundarban Courier, eCourier, Paperfly, PRAN-RFL Logistics, DHL Bangladesh, DB Schenker Bangladesh, and City Express. These companies operate across segments such as freight forwarding, last-mile delivery, cold chain, bonded warehousing, and integrated logistics solutions.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Bangladesh Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The primary growth drivers include the boom in e-commerce, government-backed infrastructure initiatives (e.g., Padma Bridge, Dhaka Bypass Expressway), rising foreign trade, and the shift towards organized logistics solutions. Additionally, increased demand for cold storage in pharma and food sectors, along with growing manufacturing investments in economic zones, are propelling logistics and warehousing expansion.
4. What are the Challenges in the Bangladesh Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The market faces several challenges, including poor road and port infrastructure, limited multimodal connectivity, fragmented regulatory oversight, and a shortage of skilled manpower. High logistics costs—estimated at nearly 15% of GDP—also hinder competitiveness. Furthermore, the slow adoption of automation and digital technologies in warehousing operations limits operational efficiency for many traditional players.