Brazil Auto Finance Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Structure, By Vehicle Type, By Ownership, By Loan Tenure, By Region, and By Financier Type
- Product Code: TDR0159
- Region: Central and South America
- Published on: May 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Brazil Auto Finance Market Outlook to 2029 – By Market Structure, By Vehicle Type, By Ownership, By Loan Tenure, By Region, and By Financier Type” provides a detailed assessment of the auto finance industry in Brazil. It includes an industry overview, historical market size and growth trajectory, segmentation by key criteria, recent trends and developments, regulatory and consumer landscape, competitive benchmarking, market challenges, and profiles of leading players. The report concludes with future projections based on credit disbursed, outstanding loan values, and vehicle type, alongside success case studies, opportunities, and strategic recommendations for stakeholders.
Brazil Auto Finance Market Overview and Size
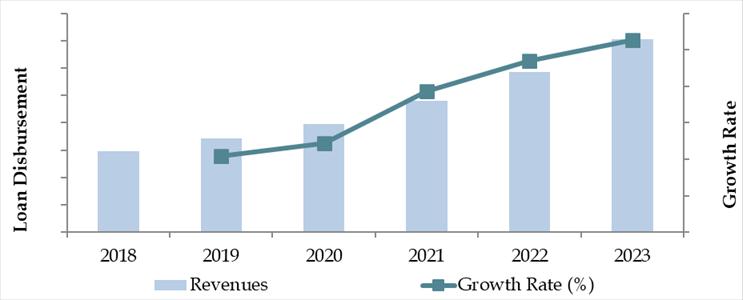
The Brazil auto finance market was valued at BRL 230 billion in 2023, driven by an increasing demand for financing across both new and used vehicles, expanding credit accessibility, and a rise in automotive sales post-COVID recovery. Major players dominating the market include Banco Itaú, BV Financeira, Santander Financiamentos, Banco PAN, and Porto Seguro Bank, supported by OEM-affiliated captives like Volkswagen Financial Services and GM Financial.
In 2023, the Brazilian Central Bank’s easing of benchmark interest rates led to improved consumer credit conditions, boosting vehicle financing. São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, and Minas Gerais emerged as major hubs due to high car ownership levels and strong financial infrastructure.
Market Size for Brazil Auto Finance Industry on the Basis of Loan Disbursed, 2018–2023
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Brazil Auto Finance Market
Economic Recovery & Monetary Policy Support: Brazil’s recovery post-pandemic, coupled with supportive interest rate policies by Banco Central do Brasil, has led to increased consumer spending power. The auto finance market benefited from lower lending rates and increasing vehicle affordability.
Rising Used Car Sales: In 2023, over 60% of vehicles financed in Brazil were used cars. This was fueled by affordability concerns and limited availability of new vehicles due to global supply chain disruptions. Financing used vehicles presents an attractive value proposition for price-sensitive buyers.
Digital Financing Models: With fintech players like Creditas Auto and Banco Inter gaining market share, the shift toward digital lending platforms is accelerating. In 2023, approximately 35% of auto loan applications originated via online channels, reflecting a growing preference for seamless, technology-enabled loan disbursal processes.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for Brazil Auto Finance Market
High Interest Rate Volatility: Brazil has historically witnessed fluctuations in its benchmark interest rates (SELIC), which directly impact auto loan affordability. In 2022, with SELIC reaching over 13.75%, loan repayments became significantly costlier, reducing the credit uptake. Approximately 28% of loan applicants in 2022 either postponed or cancelled their vehicle purchase plans due to unfavorable loan terms.
Credit Accessibility Constraints for Lower-Income Groups: A major challenge remains the limited creditworthiness of large segments of Brazil’s population. Around 42% of potential borrowers in lower-income brackets face loan rejections due to insufficient documentation or high default risk. This directly hampers market penetration outside major urban regions.
Vehicle Depreciation and Insurance Costs: Brazil's high depreciation rates—averaging 15–20% annually—combined with mandatory comprehensive insurance for financed vehicles, raise the total cost of ownership. Many consumers perceive auto loans as financially burdensome over time, deterring demand.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives Which Have Governed the Market
Regulatory Oversight by Banco Central do Brasil: The Central Bank regulates interest rate caps, non-performing asset norms, and disclosure requirements. In 2023, new guidelines were introduced mandating greater transparency in vehicle financing agreements, including pre-closure fees and insurance bundling disclosures, increasing consumer trust.
Government Subsidies for Low-Emission Vehicles: The Brazilian government introduced tax credits and financing incentives for hybrid and electric vehicles (EVs) under the Rota 2030 program. Captive financiers and NBFCs are now offering up to 1.5% lower interest rates on EV loans, with EV loan volumes increasing by 18% YoY in 2023.
Digital KYC and Open Banking Adoption: As part of the broader fintech regulation wave, Brazil’s Open Finance initiative enables auto financiers to access verified consumer credit histories and financial profiles across institutions. This has reduced loan processing times by 30–40%, especially for tech-first lenders and digital banks, streamlining consumer onboarding.
Brazil Auto Finance Market Segmentation
By Market Structure: Banks dominate Brazil’s auto finance market due to their wide branch networks, long-standing consumer trust, and competitive interest rates. Major players like Banco Itaú and Santander Financiamentos continue to lead, especially for new vehicle financing. However, NBFCs and Digital Lenders are gaining ground rapidly by offering faster disbursal, lower documentation, and tech-enabled customer journeys. Captive finance arms (e.g., Volkswagen Financial Services, Toyota Financial Services) are strong in Tier 1 cities, promoting bundled financing schemes directly through dealerships.

By Vehicle Type: Used car financing now accounts for a growing share of the market, driven by affordability and increased availability of certified pre-owned vehicles. In 2023, used cars made up an estimated 62% of all vehicles financed. New car loans remain important in metro markets but face headwinds due to inflation and price hikes. Two-wheeler and commercial vehicle financing are niche but growing, especially in logistics-driven southern states.

By Ownership Type: Individual vehicle loans remain dominant, comprising over 80% of disbursals, especially among first-time car buyers and salaried individuals. Fleet and commercial vehicle financing is steadily expanding, led by ride-hailing, rental, and logistics firms leveraging favorable fleet financing schemes.
Competitive Landscape in Brazil Auto Finance Market
The Brazil auto finance market is moderately consolidated, with a strong presence of traditional banks and increasing competition from captives and digital lending platforms. Major incumbents include Banco Itaú, Santander Financiamentos, BV Financeira, Banco PAN, and Volkswagen Financial Services, while fintechs such as Creditas Auto, Banco Inter, and Nubank are driving innovation and digital access to financing.
| Company Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
| Banco do Brasil | 1808 | Brasília, Brazil |
| Caixa Econômica Federal | 1861 | Brasília, Brazil |
| Banco Bradesco | 1943 | Osasco, Brazil |
| Itaú Unibanco | 2008 | São Paulo, Brazil |
| Banco Santander Brasil | 1982 | São Paulo, Brazil |
| Banco Safra | 1955 | São Paulo, Brazil |
| Banco BV (Votorantim) | 1988 | São Paulo, Brazil |
| Banco Pan | 1969 | São Paulo, Brazil |
| Banco Daycoval | 1968 | São Paulo, Brazil |
| Creditas | 2012 | São Paulo, Brazil |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
Banco Itaú: Brazil’s largest private bank remains the leader in new car financing. In 2023, it financed over 1.4 million vehicles, backed by robust dealer partnerships and end-to-end loan lifecycle management through its digital platform.
Santander Financiamentos: Known for its aggressive retail strategy, Santander grew its auto loan portfolio by 17% in 2023, with special focus on used vehicle financing in partnership with large dealerships and multi-brand networks.
BV Financeira: One of the top NBFCs, BV launched AI-driven risk assessment tools in 2023, resulting in a 25% reduction in loan processing times. The firm expanded operations to smaller cities with a focus on used vehicle loans and refinancing.
Banco PAN: Specialized in used car loans, Banco PAN increased its loan disbursement by 20% YoY, leveraging its mobile-first interface and embedded financing through partner apps. Its customer base is concentrated in Tier II and Tier III regions.
Volkswagen Financial Services: As a captive finance provider, VWFS led the market in captive loan penetration, financing over 60% of Volkswagen and Audi vehicles sold in Brazil in 2023. The company rolled out customized loyalty-based refinancing offers.



What Lies Ahead for Brazil Auto Finance Market?
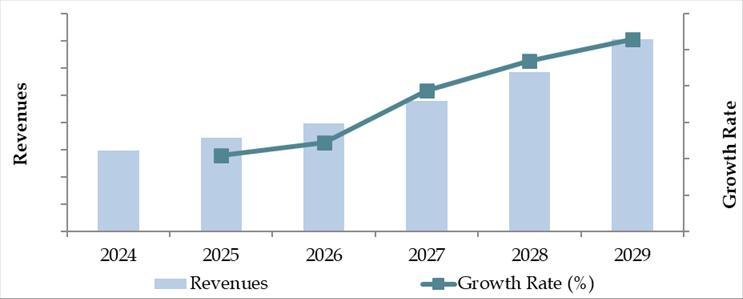
The Brazil auto finance market is expected to demonstrate consistent growth through 2029, with a projected CAGR of 6.5%–7.5% during the forecast period. This expansion will be driven by improving macroeconomic stability, technological advancements in lending, increased vehicle ownership aspirations among the middle class, and a broader push for financial inclusion.
Rising Penetration of Digital Auto Financing: As fintech adoption continues to rise, digital-first lending platforms are expected to capture a larger market share. AI-based risk profiling, instant loan approvals, and paperless disbursals will become mainstream, particularly appealing to tech-savvy millennials and first-time borrowers.
Green Financing for Electric and Hybrid Vehicles: Under Brazil’s evolving climate agenda and support via programs like Rota 2030, there will be a growing push towards financing eco-friendly vehicles. By 2029, electric and hybrid vehicle loans are projected to account for 12%–15% of total auto loans, supported by interest subsidies and tax incentives.
Expansion of Credit Access Beyond Tier-1 Cities: Financial institutions and NBFCs are expected to target underserved regions and semi-urban populations by deploying mobile-based loan origination tools, biometric verification, and rural dealership tie-ups. This expansion will drive vehicle ownership in new customer segments.
Bundled Auto Finance Ecosystems: Lenders will increasingly offer bundled services, including auto insurance, GPS tracking, vehicle servicing plans, and resale guarantees, all integrated into the loan structure. These value-added services will enhance customer retention and improve the end-to-end ownership experience.
Future Outlook and Projections for Brazil Car Finance Market Size on the Basis of Loan Disbursements in USD Billion, 2024-2029
Brazil Auto Finance Market Segmentation
- By Market Structure:
o Banks
o Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)
o Captive Finance Companies (OEM-Affiliated)
o Digital Fintech Lenders
o Peer-to-Peer Lending Platforms - By Vehicle Type:
o New Passenger Vehicles
o Used Passenger Vehicles
o Commercial Vehicles (LCVs, HCVs)
o Two-Wheelers
o Electric and Hybrid Vehicles - By Ownership Type:
o Individual Financing
o Fleet and Commercial Financing - By Loan Tenure:
o Less than 24 Months
o 24–36 Months
o 36–48 Months
o More than 48 Months - By Credit Type:
o Secured Auto Loans
o Auto Refinancing Loans
o Vehicle Leasing (with Buyback Option)
o Balloon Payment/Residual Value Loans - By Region:
o Southeast (São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, Minas Gerais)
o South (Paraná, Santa Catarina, Rio Grande do Sul)
o Central-West (Goiás, Mato Grosso)
o Northeast (Bahia, Pernambuco, Ceará)
o North (Amazonas, Pará)
Players Mentioned in the Report (Banks):
- Banco do Brasil
- Caixa Econômica Federal
- Banco Bradesco
- Santander Brasil
- Itaú Unibanco
- Banco Safra
- Banco Pan
- Banco Votorantim (BV)
- Banco Daycoval
- Banco Alfa
Players Mentioned in the Report (NBFCs):
- BV Financeira
- Omni Financeira
- Crefisa
- Creditas
- BizCapital
- Solfácil
- PRAVALER
- Zippi
- Ume
- Gringo
Players Mentioned in the Report (Captive):
- Banco Volkswagen
- Banco Hyundai Capital Brasil
- Banco GMAC Brasil
- Banco Toyota do Brasil
- Banco Mercedes-Benz do Brasil
- Banco PSA Finance Brasil
- Banco CNH Industrial Capital
- Banco Honda
- Banco Renault
- Banco Stellantis
Key Target Audience
- Commercial and Retail Banks
- Captive Auto Finance Companies
- NBFCs and Digital Fintech Lenders
- Auto OEMs and Dealerships
- Vehicle Leasing and Fleet Management Companies
- Regulatory Authorities (e.g., Banco Central do Brasil, CVM)
- Investment Firms and Credit Bureaus
- Auto Insurance Providers
- Research and Strategy Consulting Firms
Time Period
- Historical Period: 2018–2023
- Base Year: 2024
- Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and challenges they face.
4.2. Relationship and Engagement Model between Banks-Dealers, NBFCs-Dealers and Captive-Dealers-Commission Sharing Model, Flat Fee Model and Revenue streams
5.1. New Car and Used Car Sales in Brazil by type of vehicle, 2018-2024
8.1. Credit Disbursed, 2018-2024
8.2. Outstanding Loan, 2018-2024
9.1. By Market Structure (Bank-Owned, Multi-Finance, and Captive Companies), 2023-2024
9.2. By Vehicle Type (Passenger, Commercial and EV), 2023-2024
9.3. By Region, 2023-2024
9.4. By Type of Vehicle (New and Used), 2023-2024
9.5. By Average Loan Tenure (0-2 years, 3-5 years, 6-8 years, above 8 years), 2023-2024
10.1. Customer Landscape and Cohort Analysis
10.2. Customer Journey and Decision-Making
10.3. Need, Desire, and Pain Point Analysis
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11.1. Trends and Developments for Brazil Car Finance Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Brazil Car Finance Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Brazil Car Finance Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges for Brazil Car Finance Market
11.5. Government Regulations for Brazil Car Finance Market
12.1. Market Size and Future Potential for Online Car Financing Aggregators, 2018-2029
12.2. Business Model and Revenue Streams
12.3. Cross Comparison of Leading Digital Car Finance Companies Based on Company Overview, Revenue Streams, Loan Disbursements/Number of Leads Generated, Operating Cities, Number of Branches, and Other Variables
13.1. Finance Penetration Rate and Average Down Payment for New and Used Cars, 2018-2029
13.2. How Finance Penetration Rates are Changing Over the Years with Reasons
13.3. Type of Car Segment for which Finance Penetration is Higher
17.1. Market Share of Key Banks in Brazil Car Finance Market, 2024
17.2. Market Share of Key NBFCs in Brazil Car Finance Market, 2024
17.3. Market Share of Key Captive in Brazil Car Finance Market, 2024
17.4. Benchmark of Key Competitors in Brazil Car Finance Market, including Variables such as Company Overview, USP, Business Strategies, Strengths, Weaknesses, Business Model, Number of Branches, Product Features, Interest Rate, NPA, Loan Disbursed, Outstanding Loans, Tie-Ups and others
17.5. Strengths and Weaknesses
17.6. Operating Model Analysis Framework
17.7. Gartner Magic Quadrant
17.8. Bowmans Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
18.1. Credit Disbursed, 2025-2029
18.2. Outstanding Loan, 2025-2029
19.1. By Market Structure (Bank-Owned, Multi-Finance, and Captive Companies), 2025-2029
19.2. By Vehicle Type (Passenger, Commercial and EV), 2025-2029
19.3. By Region, 2025-2029
19.4. By Type of Vehicle (New and Used), 2025-2029
19.5. By Average Loan Tenure (0-2 years, 3-5 years, 6-8 years, above 8 years), 2025-2029
19.6. Recommendations
19.7. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand side and supply side entities for the Brazil Auto Finance Market. Based on this ecosystem, we shortlisted leading 6–8 financiers in the country including banks, NBFCs, captives, and fintech players, based on their loan portfolio, disbursement value, customer base, and digital enablement.
Sourcing was conducted through a combination of industry articles, press coverage, annual reports, and proprietary databases to perform detailed desk research around the market and consolidate industry-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
We engaged in an exhaustive desk research process utilizing a range of credible secondary and proprietary data sources. This included government publications, financial statements, investor presentations, company websites, credit bureau reports, and auto industry trade associations.
Through this, we analyzed market size, segment-wise disbursement volumes, interest rate movements, NPA levels, and emerging regulatory policies. Company-level data including borrower profiles, distribution network reach, product offerings, and digital adoption strategies were also captured in detail.
Step 3: Primary Research
In-depth interviews were conducted with senior executives from commercial banks, NBFCs, captives, and digital fintech firms. These interviews aimed to validate desk-based hypotheses, understand borrower behavior, assess competitive strategies, and gather business-level insights around underwriting, asset quality, and default rates.
End-users including individual borrowers, fleet owners, and used car dealers were also interviewed to understand loan tenure preferences, EMI sensitivity, and financing channel choices.
Our team also conducted disguised interviews posing as prospective customers to validate offerings such as interest rates, down payment flexibility, bundled services, and document processing time. This helped triangulate internal claims with market-level realities.
Step 4: Sanity Check
A comprehensive top-down and bottom-up modeling exercise was conducted to estimate the Brazil auto finance market size by loan disbursed and outstanding loan portfolio.
- Sanity checks were applied by comparing values with industry growth benchmarks, macroeconomic data (e.g., car sales, GDP trends, inflation), and past growth rates to ensure logical consistency and forecast reliability.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Brazil Auto Finance Market?
The Brazil auto finance market holds significant growth potential, reaching a valuation of BRL 230 billion in 2023. Driven by increasing vehicle ownership, expanding access to credit, and strong demand for both new and used vehicles, the market is set to grow at a steady pace through 2029. The rise of digital lenders, supportive government policies, and increased participation from Tier II and Tier III regions will further boost market expansion.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Brazil Auto Finance Market?
The Brazil auto finance landscape includes a mix of traditional banks, NBFCs, and digital lenders. Key players include Banco Itaú, Santander Financiamentos, BV Financeira, Banco PAN, and Volkswagen Financial Services. Emerging fintechs such as Creditas Auto, Banco Inter, and Nubank are disrupting the market through digital platforms and consumer-centric offerings.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Brazil Auto Finance Market?
Major growth drivers include improved macroeconomic stability, declining interest rates, and increasing demand for used vehicle financing. The shift towards online loan disbursals, expansion of vehicle financing in rural areas, and government incentives for electric and hybrid vehicles are also expected to accelerate market growth. Additionally, bundled finance-insurance-maintenance packages are gaining popularity among urban consumers.
4. What are the Challenges in the Brazil Auto Finance Market?
The market faces challenges such as interest rate volatility, limited credit access for lower-income segments, and high vehicle depreciation rates. Regulatory complexity and compliance requirements add operational pressure on smaller NBFCs and digital lenders. Trust issues in used vehicle valuations and concerns about default risks further complicate loan underwriting, especially in underserved regions.