Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market Outlook to 2030
By Vehicle Type, By Powertrain Architecture, By Fuel-Use Pattern, By Engine Displacement, By Sales Channel, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0373
- Region: Central and South America
- Published on: November 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market Outlook to 2030 - By Vehicle Type, By Powertrain Architecture, By Fuel-Use Pattern, By Engine Displacement, By Sales Channel, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the flex fuel vehicle market in Brazil. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer level profiling, issues and challenges, and competitive landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the flex fuel vehicle market. The report concludes with future market projections based on vehicle production, fuel consumption trends, regional market penetration, cause-and-effect relationships, and success case studies highlighting the major opportunities and cautions.
Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market Overview and Size
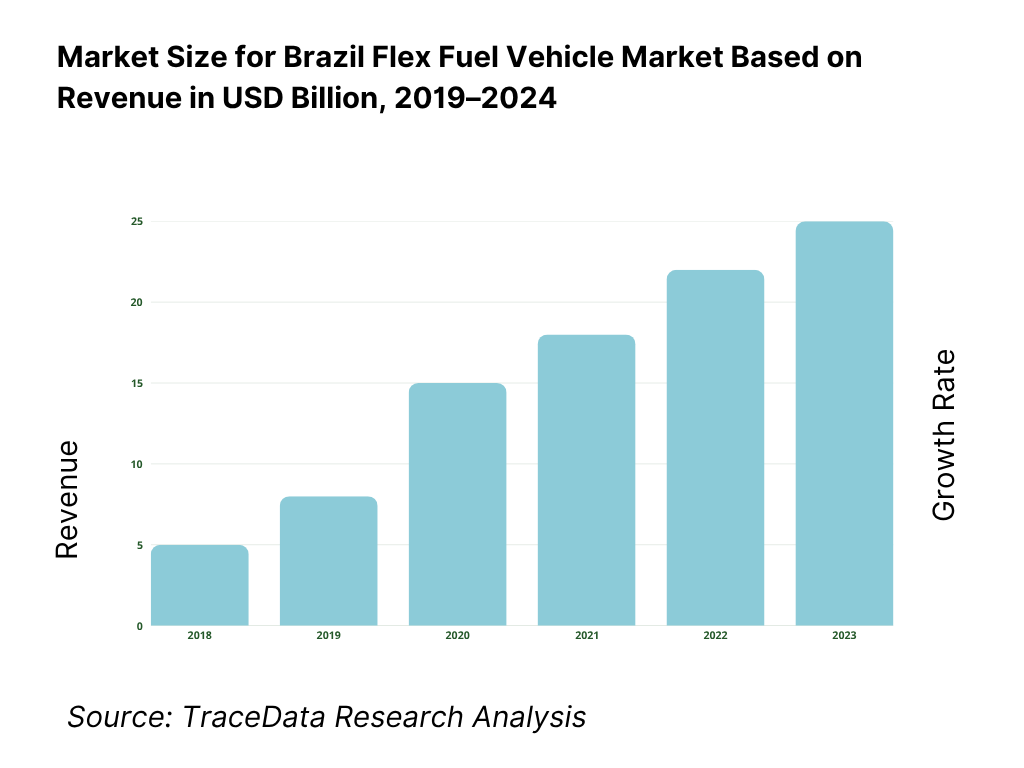
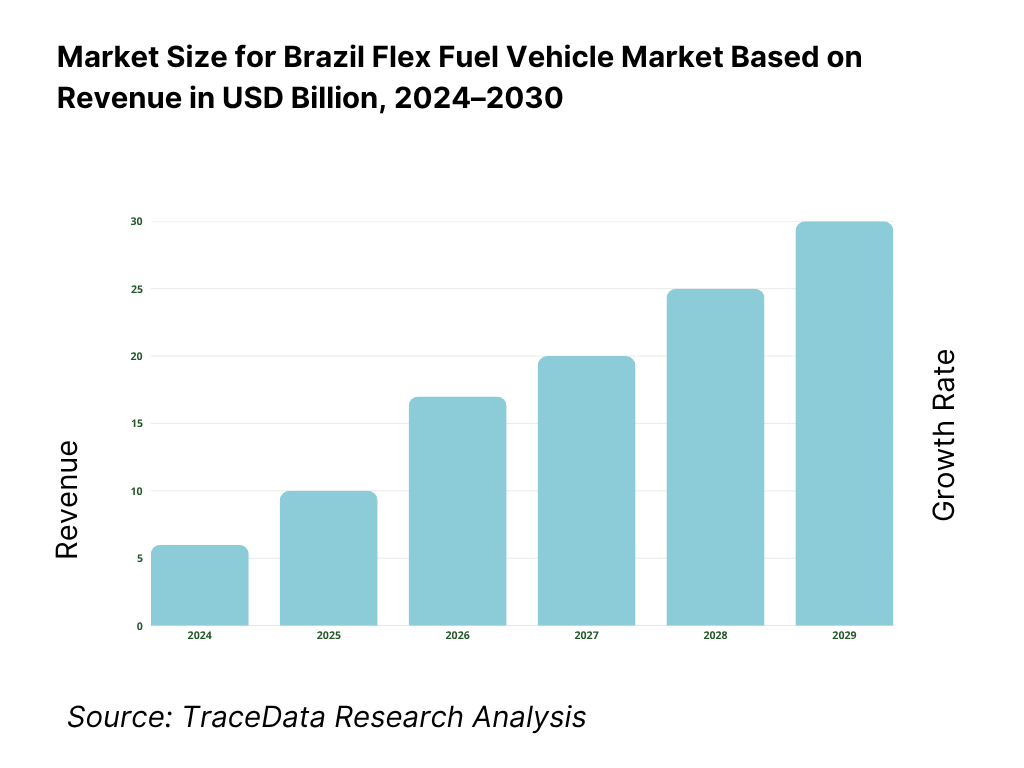
The Brazil flex fuel vehicle market is valued at USD 18.67 billion in 2024. This valuation reflects the scale of vehicles, components, and supporting infrastructure dedicated to FFVs, driven by Brazil’s deep ethanol industry, mature biofuel policies, and consumer preference for fuel cost flexibility.
The dominance of certain regions underpins the Brazilian FFV market. The state of São Paulo (and the Southeast region broadly) leads adoption because it is a major hub for sugarcane ethanol production, has dense fueling infrastructure (many E100/ethanol pumps), favorable state tax regimes, and strong OEM presence. In addition, cities like Brasília, Rio de Janeiro, and Minas Gerais benefit from proximity to biofuel logistic corridors, enabling more competitive ethanol availability.
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market:
Bioethanol supply depth and agribase scale: Brazil’s bioethanol ecosystem anchors the global flex-fuel model with unmatched feedstock depth. National cane production reached 713.2 million tonnes in the 2023/24 harvest, while ethanol output totaled 37 billion liters in 2024—both record highs. This abundant supply is underpinned by a population of 211,998,573, including 177.5 million urban residents whose mobility needs sustain domestic demand. The synergy between large-scale agricultural productivity, mature refining infrastructure, and an urbanized, motorized population directly supports stable fuel availability and continued flex-fuel vehicle adoption across Brazil’s transportation network.
High liquid-fuel throughput sustaining FFV usage: Brazil’s downstream fuel infrastructure remains ethanol-intensive and resilient. National consumption in 2024 surpassed 133 billion liters of automotive fuels, including 21.66 billion liters of hydrous ethanol. The country’s extensive fuel retail network, hosting over 42,000 active stations, ensures that both E100 and gasoline C are readily available in all major corridors. These high transaction volumes validate OEM investments in flex-calibrated engines and hybrid-flex innovations while ensuring that the ethanol value chain—from sugarcane mills to distributors—operates at efficient, large-scale utilization levels.
Large, urbanized user base and motorization context: With a total population exceeding 211.9 million and 177.5 million living in cities, Brazil maintains one of the world’s densest automotive user bases. The Southeast region—including São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, and Minas Gerais—hosts over 60 % of national light-vehicle registrations and a dense network of ethanol fueling points. This spatial concentration of vehicles, retail outlets, and logistics infrastructure drives consistent FFV refueling cycles and reinforces automakers’ continuous focus on optimizing E100 and E27/E30 calibrations for the domestic fleet.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of the Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market:
Feedstock and production variability: Despite record cane output of 713.2 million tonnes in 2023/24, production dropped to 676.96 million tonnes in 2024/25 due to climate and crop-cycle variations. These fluctuations affect ethanol yield and create downstream supply-demand imbalances that influence fuel pricing and consumer parity choices. Variability in agricultural throughput requires sugarcane mills to hedge against seasonal shocks, while automakers and distributors must adapt operations to unpredictable ethanol availability and changing regional inventories.
Emissions-compliance tightening for light vehicles: Brazil’s automotive sector is undergoing stricter environmental oversight under the PROCONVE L-7 and L-8 phases, which mandate advanced OBD systems and tighter emission limits for vehicles operating on both E100 and gasoline C. The implementation of these standards from 2025 onward compels automakers to upgrade catalysts, recalibrate engines, and perform additional durability testing, extending development timelines and costs. This intensifies the engineering workload for FFV and hybrid-flex platforms already balancing ethanol’s combustion characteristics with efficiency and performance targets.
Demand sensitivity across fuel cycles: ANP data show pronounced intra-year shifts between ethanol and gasoline sales, with hydrous ethanol contributing 21.66 billion liters out of 133 billion liters total fuel sold in 2024. These shifts follow regional parity fluctuations that can change rapidly with cane harvests and refinery output. Such volatility complicates production forecasting and dealership inventory planning, while also stressing distribution logistics across Brazil’s five macro-regions. For OEMs, managing FFV model mix and maintaining profitability amid these short-term consumption swings remains a critical challenge.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
PROCONVE L-7/L-8 for light-duty vehicles (IBAMA/CONAMA): Brazil’s PROCONVE L-7/L-8 framework enforces stricter emission and OBD compliance for light-duty vehicles, covering both pure ethanol (E100) and gasoline C operation. These standards introduce new laboratory certification requirements, long-term durability testing, and conformity-of-production audits managed by IBAMA. The regulation anchors future technology roadmaps for OEMs, ensuring that new flex-engine and hybrid-flex systems align with decarbonization and air-quality objectives while preserving ethanol’s strategic role in transport.
Ethanol blend in gasoline (ANP Res. 19/2015 / CNPE policy): Brazil’s gasoline C is blended with 27 % anhydrous ethanol, with federal authorization now expanding the cap to 30 %. This regulatory evolution ensures consistent demand for ethanol producers while guiding automakers’ calibration maps for ignition timing, fuel economy, and cold-start systems. The policy not only sustains ethanol integration but also strengthens Brazil’s leadership in renewable liquid fuels, reducing petroleum dependence and supporting national emissions-reduction goals.
RenovaBio — CBIO issuance and retirement mechanics (ANP/CNPE): RenovaBio structures a credit-based decarbonization system through Carbon Intensity Credits (CBIOs), directly tied to biofuel production and lifecycle emissions. Distributors and producers generate, trade, and retire CBIOs to meet annual carbon-reduction targets, incentivizing efficiency improvements and sustainability certification among ethanol mills. For the flex-fuel vehicle ecosystem, this mechanism ensures steady capital flow into cleaner ethanol production, reinforcing the financial and policy foundation sustaining Brazil’s FFV market.
Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market Segmentation
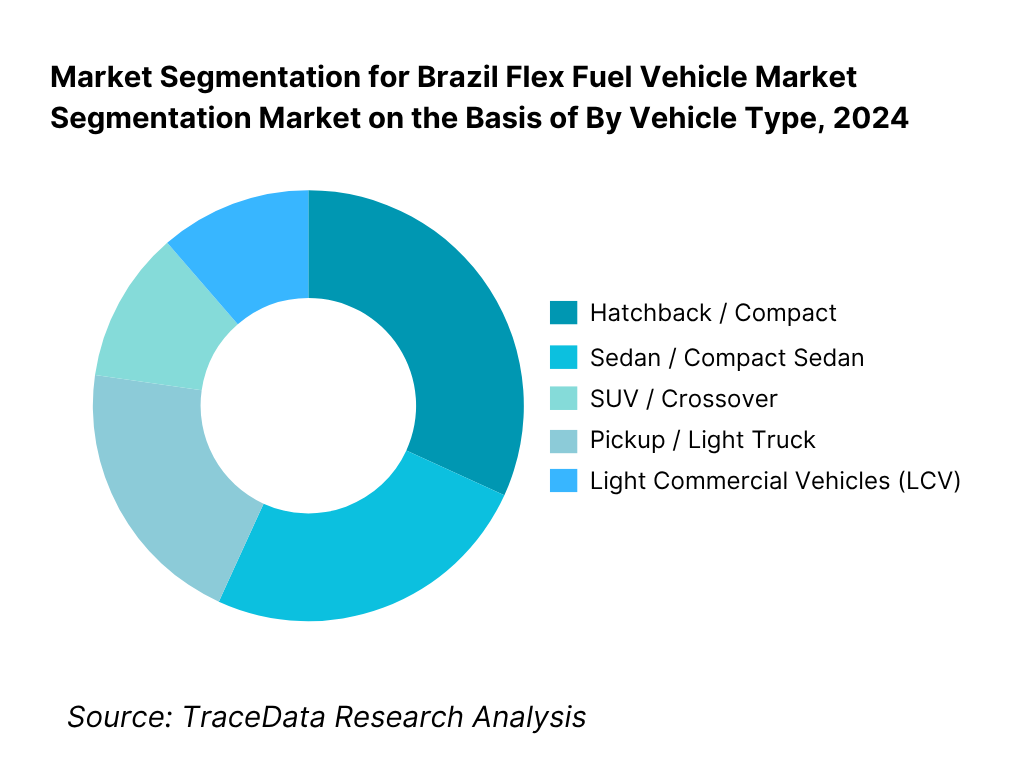
By Vehicle Type: SUV / Crossover sub-segment has emerged as dominant. This dominance is driven by rising consumer preference for SUVs (due to perceived safety, road clearance, and family utility) combined with OEMs rolling out more flex versions of their crossover lines. The SUV form factor often commands premium pricing, allowing brands to afford more advanced flex fuel calibration, hybrid-flex variants, and better features. Moreover, as infrastructure improves in periphery zones, buyers in semi-urban and suburban regions favor SUVs, elevating their penetration. Compact cars (hatchbacks) continue to hold significant share because low operating costs make flex fuel appeal for economy buyers, but the growth momentum is skewed toward crossover models.
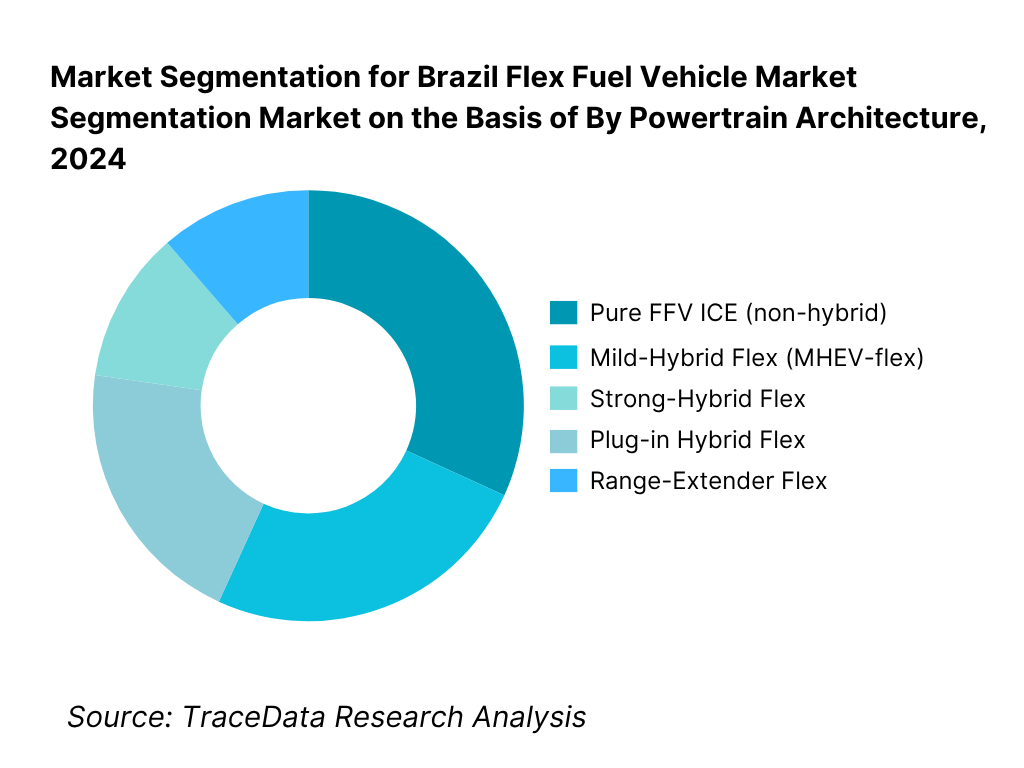
By Powertrain Architecture: The Pure FFV ICE (non-hybrid) sub-segment continues to dominate the market. The dominance stems from decades of refinement in Brazil’s flex ICE technology—automakers have optimized calibration, cold-start systems, durability, and broad fuel-blend resilience, making pure FFV powertrains cost-effective and high volume. The cost premium of adding hybrid systems (battery, control electronics) still restrains hybrid-flex share, particularly in volume segments. However, mild-hybrid flex is gaining traction especially in premium trims or environmentally conscious buyers looking for slightly better efficiency without fully shifting to electrification. The plug-in hybrid flex and range-extender flex remain niche, reserved for experimental or flagship models, because of higher cost and complexity relative to the pure ICE baseline.
Competitive Landscape in Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market
The Brazil FFV market is concentrated around a few major OEMs and biofuel-ecosystem players. Legacy automakers such as Fiat (Stellantis), Volkswagen, GM do Brasil, Toyota, Honda, and Renault dominate by virtue of long-standing local manufacturing, flex engine technology, and integrated distribution networks. Their dominance reinforces barriers for newcomers and ensures that new entrants must invest heavily in local adaptation, calibration, and fueling partnerships.
Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
Fiat (Stellantis) | 1899 | Turin, Italy |
Volkswagen do Brasil | 1953 | São Paulo, Brazil |
GM do Brasil (Chevrolet) | 1925 | Detroit, USA |
Toyota do Brasil | 1937 | Aichi, Japan |
Honda Automóveis do Brasil | 1948 | Tokyo, Japan |
Renault do Brasil | 1899 | Boulogne-Billancourt, France |
Nissan do Brasil | 1933 | Yokohama, Japan |
Jeep (Stellantis) | 1941 | Toledo, USA |
Peugeot (Stellantis) | 1810 | Paris, France |
Citroën (Stellantis) | 1919 | Paris, France |
Caoa Chery | 1997 | Wuhu, China |
Mitsubishi Motors do Brasil | 1970 | Tokyo, Japan |
GWM Brasil (Great Wall Motors) | 1984 | Baoding, China |
Ford Brasil | 1919 | Dearborn, USA |
BMW Brasil | 1916 | Munich, Germany |
Some of the Recent Competitor Trends and Key Information About Competitors Include:
Toyota do Brasil: Toyota strengthened its hybrid-flex portfolio, with the Corolla and Corolla Cross hybrid-flex consolidating leadership in this segment. In 2024, Toyota invested in expanding Sorocaba production lines to increase hybrid-flex capacity and prepare for higher demand from fleet buyers and environmentally conscious consumers.
Honda Automóveis do Brasil: Honda renewed its Civic and HR-V flex models, improving cold-start reliability and offering more efficient ethanol calibration. In 2024, Honda announced testing of hybrid-flex prototypes to align with PROCONVE emissions standards and meet Brazil’s evolving regulatory environment.
Renault do Brasil: Renault expanded its Kwid and Logan flex models, emphasizing affordability and efficiency for retail buyers. In 2024, Renault announced development of a biofuel-ready hybrid powertrain, aiming to strengthen competitiveness in Brazil’s economy segment.
Jeep (Stellantis): Jeep reinforced its SUV portfolio by updating Compass and Renegade with new turbo-flex engines. In 2024, Jeep highlighted record flex SUV sales in the premium category and began work on ethanol-hybrid projects at its Pernambuco plant.
Caoa Chery: The brand has expanded aggressively with SUV flex models, offering competitive warranties to capture market share. In 2024, Caoa Chery announced plans to localize more flex engine production in Anápolis, aligning with Brazil’s local-content requirements.
What Lies Ahead for Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market?
The Brazil flex fuel vehicle market is expected to continue expanding through the end of the decade, supported by the country’s unparalleled ethanol production scale, supportive regulatory frameworks like RenovaBio, and strong consumer preference for flexible fueling. Rising biofuel supply and new hybrid-flex launches from major automakers will help the segment strengthen its role as a transition pathway between internal combustion and electrified mobility in Brazil.
Rise of Hybrid-Flex Models: The next phase of FFV development in Brazil is the rise of hybrid-flex models, combining electric assistance with ethanol engines. Automakers such as Toyota and Stellantis are investing in hybrid-flex production lines, responding to national goals for emissions reduction and efficiency. This trend is set to reshape the market as consumers gain access to vehicles that blend affordability of ethanol with improved mileage and lower carbon footprints.
Expansion of Ethanol Integration: Higher ethanol blending mandates, including the approved increase of anhydrous ethanol in gasoline from 27% to 30%, will reinforce the foundation of the FFV market. This shift ensures steady demand for flex-ready vehicles and encourages OEMs to fine-tune calibration for higher ethanol ratios. The greater use of E100 and E30 strengthens the role of sugarcane and corn ethanol as sustainable fuels and provides the policy backing for automakers to scale up their flex portfolios.
Emphasis on Sustainable Transport Transition: Brazil’s commitment to carbon reduction under RenovaBio and broader energy transition strategies is creating room for FFVs to remain central in the transport system even as battery-electric vehicle adoption rises. The ability of flex cars to deliver lower lifecycle emissions when run on ethanol provides Brazil with a unique advantage. Policymakers view FFVs as a bridge solution that can coexist with EVs while ensuring affordability and infrastructure compatibility across diverse regions.
Leveraging Connected Tech and Fuel Optimization: Connected technologies that monitor ethanol-gasoline price parity and recommend cost-optimal fueling are expected to become standard in FFVs. Automakers are embedding telematics and app-based solutions that help consumers decide whether to use E100 or gasoline, improving cost efficiency and building stronger value propositions. These tools will also feed real-time data into OEM strategies for calibration improvements and consumer loyalty.
Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market Segmentation
By Vehicle Type (In Value %)
Hatchback / Compact Cars
Sedan / Compact Sedan
SUV / Crossover
Pickup / Light Truck
Light Commercial Vehicles (LCV)
By Powertrain Architecture (In Value %)
Pure FFV ICE (Non-Hybrid)
Mild-Hybrid Flex (MHEV-Flex)
Strong-Hybrid Flex (HEV-Flex)
Plug-in Hybrid Flex (PHEV-Flex)
Range-Extender Flex
By Fuel-Use Pattern (In Value %)
E100-Dominant Users
Gasoline-C (E27/E30 blend) Dominant Users
Mixed/Seasonal Users (switching based on parity and supply)
By Engine Displacement (In Value %)
≤ 1.0L
1.1 – 1.6L
1.7 – 2.0L
2.0L
By Sales Channel (In Value %)
Retail (Individual Buyers)
Corporate Fleets
Rental & Ride-Hailing Operators
Government & Public Sector Procurement
Rural / Agricultural Buyers
Players Mentioned in the Report:
Fiat (Stellantis)
Volkswagen do Brasil
GM do Brasil (Chevrolet)
Toyota do Brasil
Honda Automóveis do Brasil
Renault do Brasil
Nissan do Brasil
Jeep (Stellantis)
Peugeot (Stellantis)
Citroën (Stellantis)
Caoa Chery
Mitsubishi Motors do Brasil
GWM Brasil
Ford Brasil
BMW Brazil (for flex or hybrid-flex models)
Key Target Audience
Automotive OEM strategy and product planning departments
Biofuel producers / ethanol mills & associations
Tier-1/ Tier-2 fuel system component suppliers
Vehicle fleet operators and logistic companies
Energy & petroleum companies (e.g. Petrobras)
Investments and venture capital firms (interested in mobility / biofuel tech)
Government and regulatory bodies (ANP, MME, MAPA)
Financial institutions / banks evaluating auto & sustainability financing
Time Period:
Historical Period: 2019-2024
Base Year: 2025
Forecast Period: 2025-2030
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Delivery Model Analysis for Flex Fuel Vehicles-OEM Production, Dealer Sales, Financing, After-Sales & Service (Margins, Preference, Strengths, Weaknesses)
4.2. Revenue Streams for Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market
5.1. Freelance Mechanics & Aftermarket Workshops vs. OEM Authorized Service Centers
5.2. Investment Model in Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market
5.3. Comparative Analysis of Vehicle Distribution Process by Private vs. Government Procurement
5.4. Vehicle Purchase & Ownership Cost Allocation by Consumer Segments (Retail Buyers, Corporate Fleets, Government, Ride-Hailing/Rental Operators)
8.1. Revenues, Historical-Present
9.1. By Market Structure (In-House vs. Outsourced Fleets)
9.2. By Vehicle Type (Hatchback, Sedan, SUV/Crossover, Pickup, LCV)
9.3. By Powertrain Architecture (FFV ICE, Mild-Hybrid Flex, Strong Hybrid Flex, Plug-In Hybrid Flex)
9.4. By Fuel-Use Pattern (E100-Dominant, Gasoline-C Dominant, Mixed Users)
9.5. By Engine Displacement (≤1.0L, 1.1-1.6L, 1.7-2.0L, >2.0L)
9.6. By Region (Southeast, South, Center-West, Northeast, North)
10.1. Consumer and Fleet Buyer Landscape and Cohort Analysis
10.2. Vehicle Purchase Decision-Making Process
10.3. Performance & ROI Analysis (Cost-per-Kilometer, TCO with E100 vs. Gasoline-C)
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11.1. Trends and Developments for Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges for Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market
11.5. Government Regulations for Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market
12.1. Market Size and Future Potential for Hybrid-Flex Industry in Brazil
12.2. Business Model and Revenue Streams
12.3. Technology Models and Types of Hybrid-Flex Vehicles Offered
15.1. Market Share of Key Players in Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market Basis Revenues
15.2. Benchmark of Key Competitors (Company Overview, USP, Business Strategies, Vehicle Portfolio, Number of Models, Revenues, Pricing, Technology Used, Best-Selling Models, Fleet Clients, Strategic Tie-Ups, Marketing Strategy, Recent Developments)
15.3. Operating Model Analysis Framework
15.4. Gartner Magic Quadrant
15.5. Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
16.1. Revenues, Future Outlook
17.1. By Market Structure (In-House vs. Outsourced Fleets)
17.2. By Vehicle Type (Hatchback, Sedan, SUV/Crossover, Pickup, LCV)
17.3. By Powertrain Architecture (FFV ICE, Mild-Hybrid Flex, Strong Hybrid Flex, Plug-In Hybrid Flex)
17.4. By Fuel-Use Pattern (E100-Dominant, Gasoline-C Dominant, Mixed Users)
17.5. By Engine Displacement (≤1.0L, 1.1-1.6L, 1.7-2.0L, >2.0L)
17.6. By Region (Southeast, South, Center-West, Northeast, North)
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
We begin by mapping the ecosystem and identifying all demand-side and supply-side entities influencing the Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market. On the demand side, this includes individual vehicle buyers, fleet operators, rental companies, and government procurement agencies. On the supply side, we examine automotive OEMs, ethanol producers, component suppliers (ECU, injectors, hybrid systems), fuel distributors, and dealerships. Based on this mapped ecosystem, we shortlist 5–6 leading automakers operating in Brazil by analyzing their financial disclosures, production capacity, model portfolios, and regional market reach. Sourcing for this stage is conducted through industry articles, ANP/IBGE/CONAB publications, government databases, and proprietary datasets to collate industry-level information and ecosystem linkages.
Step 2: Desk Research
We engage in exhaustive secondary research, referencing diverse sources including ANP energy statistics, CONAB ethanol production data, World Bank population and mobility indicators, and company-level filings. This allows us to analyze market revenues, number of registered flex vehicles, fuel sales volumes, fleet penetration, and regulatory frameworks. In addition, we examine OEM-specific data via press releases, investor presentations, and annual reports to understand production strategies, technology adoption, and investment commitments. This phase constructs a foundational understanding of the FFV market structure and competitive environment, ensuring coverage of both macroeconomic and company-level dynamics.
Step 3: Primary Research
We conduct in-depth interviews with executives, policymakers, fleet managers, and ethanol industry stakeholders. The objective is to validate hypotheses built during secondary research, authenticate numerical datasets (vehicle sales, fuel throughput), and capture qualitative insights about challenges, pricing parity, and consumer preferences. To refine accuracy, we employ a bottom-up approach, assessing model-level vehicle sales and aggregating them to total market revenues, and a top-down approach, starting with total light-vehicle registrations and isolating the flex-fuel subset. As part of validation, we also execute disguised interviews under the role of prospective buyers, allowing us to cross-check information shared by OEM representatives against secondary data.
Step 4: Sanity Check
Finally, we perform both bottom-to-top and top-to-bottom triangulation. Flex vehicle registrations from RENAVAM/ANFAVEA are cross-checked with ANP’s reported ethanol sales to confirm demand alignment. Macro indicators (urban population from IBGE, vehicle fleet statistics from World Bank) are tested against OEM production volumes. This multi-angle triangulation ensures that market size models and growth dynamics are consistent, credible, and validated before final output.
FAQs
01 What is the potential for the Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market?
The Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market holds significant growth potential, supported by the country’s robust ethanol production base and long-standing consumer preference for fuel flexibility. The market is valued at USD 18.67 billion, underpinned by annual ethanol production exceeding 37 billion liters and total vehicle fuel sales of 133 billion liters, according to the ANP. As Brazil strengthens its biofuel integration policies and hybrid-flex vehicle rollouts expand, the sector’s potential continues to grow as a cornerstone of the nation’s sustainable transportation strategy.
02 Who are the Key Players in the Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market?
The Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market features several key automotive manufacturers, including Fiat (Stellantis), Volkswagen do Brasil, GM do Brasil (Chevrolet), and Toyota do Brasil. These companies dominate due to their extensive flex engine portfolios, localized production facilities, and expansive dealership networks. Other prominent players include Honda Automóveis do Brasil, Renault do Brasil, Jeep (Stellantis), and emerging hybrid-flex entrants such as GWM Brasil and Caoa Chery, each contributing to the market’s technology and capacity expansion.
03 What are the Growth Drivers for the Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market?
Key growth drivers include Brazil’s ethanol production scale, which reached 713.2 million tonnes of sugarcane crushed and 37 billion liters of ethanol output in the 2023/24 harvest (CONAB/ANP). The country’s 211.9 million population and 177.5 million urban residents (IBGE/World Bank) ensure steady FFV demand across urbanized corridors. Regulatory momentum under RenovaBio and the government’s approval to raise ethanol content in gasoline from 27 % to 30 % further strengthen domestic biofuel use. Together, these factors position Brazil as the world’s leading FFV ecosystem, supported by scale, policy, and consumer adoption.
04 What are the Challenges in the Brazil Flex Fuel Vehicle Market?
The market faces challenges linked to feedstock volatility, with sugarcane production expected to ease from 713.2 million tonnes to 676.9 million tonnes in 2024/25 (CONAB), impacting ethanol availability. Additionally, tightening emission norms under PROCONVE L-7/L-8 raise engineering costs and certification complexities for automakers. Consumer fueling behavior fluctuates with price parity between ethanol and gasoline, creating short-term demand swings. These combined structural, regulatory, and behavioral challenges necessitate continuous innovation and policy alignment for sustainable FFV market expansion.