Chile Auto Finance Market Outlook to 2029
By Vehicle Type, By Lender Type (Banks, NBFCs, Captives), By Tenure of Loan, By Age Group of Borrowers, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0150
- Region: Central and South America
- Published on: April 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Chile Auto Finance Market Outlook to 2029 – By Vehicle Type, By Lender Type (Banks, NBFCs, Captives), By Tenure of Loan, By Age Group of Borrowers, and By Region” provides an in-depth analysis of the auto finance industry in Chile. The report includes a comprehensive overview of the sector’s genesis, current market size based on loan disbursement and outstanding credit, key market segmentation, evolving consumer behavior, regulatory framework, recent trends, digital innovation, and competitive landscape. It concludes with a future outlook, projected market size, key opportunities, potential bottlenecks, and profiling of major players within the auto finance ecosystem.
Chile Auto Finance Market Overview and Size
In 2023, the Chile Auto Finance Market was valued at CLP 6.2 Trillion in terms of loan disbursements. The market is being propelled by rising vehicle ownership, favorable interest rate policies, and strong participation from both public and private financial institutions. Major lenders such as Banco de Chile, Santander Consumer Finance, Forum Servicios Financieros, BCI Auto, and Scotiabank are actively shaping the landscape through customized financial products, partnerships with dealerships, and expanding digital loan disbursal platforms.
In 2023, Forum Servicios Financieros introduced a digital loan approval system in partnership with local dealerships, cutting average processing time by 35% and improving conversion rates. Santiago and Valparaíso are key hotspots due to urban density and high vehicle registration rates.
Market Size for Chile Auto Finance Industry Based on Loan Disbursed in USD Billion, 2018-2023 (CLP Trillion)
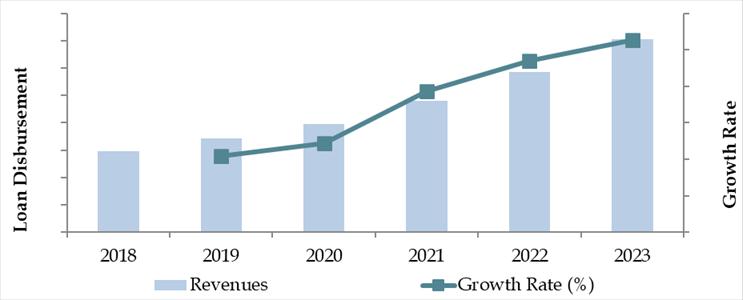
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the Chile Auto Finance Market:
Macroeconomic Recovery and Urban Mobility Demand: The post-pandemic recovery and government support schemes have stimulated consumer demand, particularly in urban centers. In 2023, new car registrations grew by 7.2% YoY, directly impacting auto loan issuance.
Increased Role of Captive Finance Arms: Automakers are strengthening their in-house financing arms. Brands like Toyota Chile and Chevrolet Servicios Financieros have aggressively expanded zero-interest and flexible EMI products, particularly for EV and hybrid models.
Digital Loan Platforms and API Integrations: Over 45% of auto loan applications in Chile are now initiated through online platforms, supported by APIs integrating dealership networks and credit scoring algorithms. This trend has reduced loan turnaround time from 4 days to under 48 hours, enhancing accessibility for younger borrowers.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for Chile Auto Finance Market
High Default Risk Among Lower-Income Borrowers: One of the most persistent challenges in Chile’s auto finance landscape is the high default rate among lower-income segments. As of 2023, approximately 28% of loan defaults in the auto finance space were traced to borrowers in the bottom two income quintiles. This trend has led many lenders to tighten credit eligibility norms, which in turn reduces access to auto finance for a large portion of the population.
High Cost of Credit and Inflation Pressure: Despite moderate interest rate levels compared to regional peers, the effective cost of credit in Chile remains elevated due to add-on insurance products, administrative fees, and inflation-indexed repayments (UF-based loans). In 2023, the average effective interest rate exceeded 13% for used vehicles, making loans unaffordable for many. The burden of inflation has further reduced household purchasing power, affecting overall auto loan demand.
Limited Penetration in Rural and Low-Density Regions: While urban centers like Santiago and Valparaíso are saturated with lender coverage, auto finance penetration remains below 25% in rural regions such as Araucanía and Maule. This urban-rural divide is due to limited branch presence, weak dealership networks, and lack of digital literacy, resulting in missed opportunities for financial inclusion.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
Financial Consumer Protection Law (Ley N° 20.555): This law ensures transparency in loan terms, including interest rates, total cost of credit, and repayment schedules. Lenders are mandated to provide clear disclosures in loan contracts. In 2023, over 92% of complaints received by SERNAC related to auto loans were resolved in favor of the consumer, reflecting growing enforcement of these protections.
Central Bank Interest Rate Guidelines and UF-Linked Loans: The Central Bank of Chile regulates benchmark rates that influence auto loan offerings. Many auto loans are structured in Unidad de Fomento (UF), a CPI-indexed unit that helps lenders mitigate inflation risk but increases repayment volatility for borrowers. This structure, though stable for lenders, creates affordability challenges when inflation spikes.
EV Financing Support and Green Credit Programs: In line with Chile’s National Electromobility Strategy, the government, in partnership with multilateral banks, has initiated green auto loan subsidies. These include interest rate subventions and partial guarantees for EV financing through institutions like BancoEstado. As of 2023, electric vehicles accounted for 2.4% of all financed vehicles, a figure projected to grow with increasing fiscal support.
Chile Auto Finance Market Segmentation
By Market Structure: Banks dominate Chile’s auto finance sector due to their well-established trust, widespread branch presence, and ability to offer competitive interest rates, especially for prime borrowers. Banks like Banco de Chile and Santander have strong partnerships with leading auto dealerships, offering bundled insurance and flexible tenures. Captive finance companies (such as Forum Servicios Financieros and Chevrolet Servicios Financieros) are gaining traction, particularly for new vehicles, due to preferential financing schemes, zero down-payment options, and brand-backed loyalty programs. Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) or multiservice lenders cater mainly to subprime borrowers and used vehicle segments, offering higher approval rates but at elevated interest costs.

By Vehicle Type: New vehicles account for a larger share of auto financing in Chile, driven by better loan terms, lower interest rates, and availability of manufacturer incentives. However, the used vehicle finance segment is witnessing growth due to affordability and rising used vehicle imports from Asia and the U.S.
Used vehicle loans typically have shorter tenures and higher interest rates but offer flexibility for middle-income and younger borrowers.

By Loan Tenure: Auto loans with 48–60 months tenure dominate the Chilean market as they strike a balance between manageable EMIs and overall interest burden. Shorter tenures (24–36 months) are more popular for used vehicles and among affluent borrowers aiming to minimize interest payments.
Competitive Landscape in Chile Auto Finance Market
The Chile auto finance market is moderately concentrated, with a mix of large commercial banks, captive financing arms of OEMs, and a few non-banking financial entities shaping the industry. In recent years, the sector has seen increased competition through the introduction of digital loan origination platforms, integration with automotive marketplaces, and expansion of EV-focused financing schemes. Leading players include Banco de Chile, Santander Consumer Chile, Forum Servicios Financieros, BCI Auto, Scotiabank, and emerging fintech-based lenders.
| Company Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
| Banco Santander Chile | 1978 | Santiago, Chile |
| Banco de Chile | 1893 | Santiago, Chile |
| Banco BCI | 1937 | Santiago, Chile |
| Banco Estado | 1953 | Santiago, Chile |
| Santander Consumer Finance Chile | 2019 | Santiago, Chile |
| Tanner Servicios Financieros S.A. | 1993 | Santiago, Chile |
| Autofin (Chile) | 2013 | Las Condes, Chile |
| Mitsui Auto Finance Chile Ltda. | 1986 | Santiago, Chile |
| Marubeni Auto Finance Ltda. | 2004 | Santiago, Chile |
| BMW Financial Services Chile | 2011 | Santiago, Chile |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
Banco de Chile: A market leader in auto loans, Banco de Chile disbursed over CLP 1.5 trillion in vehicle financing in 2023. The bank has expanded its digital auto loan pre-approval service, resulting in a 12% increase in loan conversion rates year-on-year.
Santander Consumer Chile: Known for competitive EMI options and exclusive tie-ups with auto dealerships, Santander reported a 15% rise in new vehicle loan originations in 2023. Its digital loan calculator and instant approval model have improved its customer acquisition among millennials.
Forum Servicios Financieros: As the captive finance arm of the Indumotora Group, Forum has a strong presence in dealership financing, especially for brands like Hyundai and Subaru. In 2023, Forum launched a partnership with online car marketplaces for instant financing approvals, capturing over 20% share in the new car financing segment.
BCI Auto: BCI’s auto loan division has grown rapidly by offering flexible credit structures for both salaried and self-employed buyers. The firm reported 8.5% YoY growth in used vehicle financing in 2023 and has invested in a new AI-based risk profiling system.
Scotiabank Chile: A key player in the premium car financing segment, Scotiabank has seen increasing traction through its bundled insurance products and EV-specific green loans. The bank financed over 4,200 EVs and hybrids in 2023, making it a leading financer in the sustainable vehicle space.



What Lies Ahead for Chile Auto Finance Market?
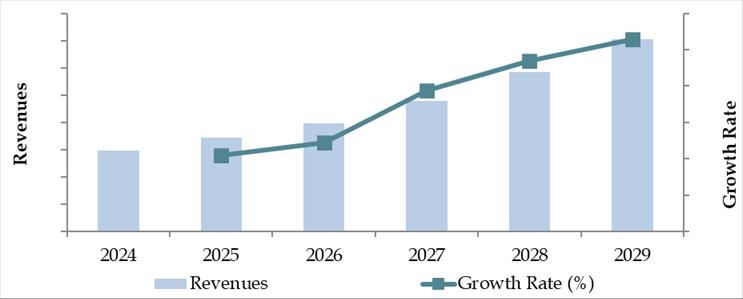
The Chile auto finance market is projected to experience steady growth through 2029, driven by urban population expansion, recovery in household income levels, increased digital adoption in financial services, and ongoing electrification in the automotive sector. The market is expected to grow at a moderate CAGR, with notable shifts in consumer preferences, financing models, and lender strategies.
Acceleration in Electric Vehicle Financing: As part of Chile’s National Electromobility Strategy, the availability of EVs is set to rise significantly, supported by public-private partnerships. This will result in a growing demand for EV-specific financing products, including low-interest green loans and longer tenures tailored for high-ticket electric vehicles. By 2029, EVs are expected to account for over 8–10% of new vehicle finance volume.
Digital Lending Ecosystem Expansion: The integration of AI-based credit scoring, open banking APIs, and dealership-fintech tie-ups will further digitize and accelerate the lending value chain. Over 70% of auto loan applications are projected to be processed digitally by 2029, reducing processing time and enhancing access, especially for younger and tech-savvy borrowers.
Customized and Flexible Loan Products: Financial institutions are expected to increasingly shift toward personalized credit products, such as income-linked EMIs, usage-based repayment schemes, and hybrid balloon payments. These innovations will allow greater inclusion of gig economy workers and self-employed borrowers into the auto finance fold.
Partnership-Driven Dealership Finance: OEMs and captive finance arms are likely to invest more in dealer engagement, offering integrated digital platforms that link vehicle selection, financing, and insurance. The emphasis will be on end-to-end digital onboarding and faster disbursal models, improving both customer experience and dealer conversion rates.
Future Outlook and Projections for Chile Car Finance Market Size on the Basis of Loan Disbursements in USD Billion, 2024-2029
Chile Auto Finance Market Segmentation
- By Vehicle Type:
o New Vehicles
o Used Vehicles - By Finance Provider:
o Banks
o Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)
o OEM Financing Companies
o Fintech and Digital Lenders - By Type of Buyer:
o Individual Buyers
o Corporate Buyers
o Fleet Owners
o Leasing Companies - By Loan Tenure:
o Less than 36 Months
o 36–60 Months
o More than 60 Months - By Vehicle Fuel Type:
o Petrol
o Diesel
o Electric
o Hybrid - By Age of Vehicle (Used Vehicle Financing):
o 0–2 Years
o 3–5 Years
o 6–10 Years
o Above 10 Years By Region:
Metropolitan Region (Santiago)
Valparaíso
Biobío
Maule
Araucanía
Antofagasta
Players Mentioned in the Report (Banks):
- Banco Santander Chile
- Banco de Chile
- Banco BICE
- Banco Estado
- Banco Ripley
- Banco Paris
- Banco Security
Players Mentioned in the Report (NBFCs):
- Santander Consumer Finance Chile
- Forum Servicios Financieros
- Tanner Servicios Financieros
- Mundo Crédito
- Global Soluciones Financieras
- Transbank
Players Mentioned in the Report (Captive):
Toyota Financial Services Chile
Volkswagen Financial Services Chile
BMW Financial Services Chile
Stellantis Financial Services Chile
Hyundai Capital Chile
Key Target Audience:
Commercial Banks and Financial Institutions
Captive Auto Finance Providers
Dealership Financing Networks
Auto Insurance Providers
Regulatory Bodies (e.g., Comisión para el Mercado Financiero - CMF)
Automotive OEMs and Importers
Digital Lending and Fintech Platforms
Research and Policy Institutions
Time Period:
Historical Period: 2018–2023
Base Year: 2024
Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and challenges they face.
4.2. Relationship and Engagement Model between Banks-Dealers, NBFCs-Dealers and Captive-Dealers-Commission Sharing Model, Flat Fee Model and Revenue streams
5.1. New Car and Used Car Sales in Chile by type of vehicle, 2018-2024
8.1. Credit Disbursed, 2018-2024
8.2. Outstanding Loan, 2018-2024
9.1. By Market Structure (Bank-Owned, Multi-Finance, and Captive Companies), 2023-2024
9.2. By Vehicle Type (Passenger, Commercial and EV), 2023-2024
9.3. By Region, 2023-2024
9.4. By Type of Vehicle (New and Used), 2023-2024
9.5. By Average Loan Tenure (0-2 years, 3-5 years, 6-8 years, above 8 years), 2023-2024
10.1. Customer Landscape and Cohort Analysis
10.2. Customer Journey and Decision-Making
10.3. Need, Desire, and Pain Point Analysis
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11.1. Trends and Developments for Chile Car Finance Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Chile Car Finance Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Chile Car Finance Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges for Chile Car Finance Market
11.5. Government Regulations for Chile Car Finance Market
12.1. Market Size and Future Potential for Online Car Financing Aggregators, 2018-2029
12.2. Business Model and Revenue Streams
12.3. Cross Comparison of Leading Digital Car Finance Companies Based on Company Overview, Revenue Streams, Loan Disbursements/Number of Leads Generated, Operating Cities, Number of Branches, and Other Variables
13.1. Finance Penetration Rate and Average Down Payment for New and Used Cars, 2018-2029
13.2. How Finance Penetration Rates are Changing Over the Years with Reasons
13.3. Type of Car Segment for which Finance Penetration is Higher
17.1. Market Share of Key Banks in Chile Car Finance Market, 2024
17.2. Market Share of Key NBFCs in Chile Car Finance Market, 2024
17.3. Market Share of Key Captive in Chile Car Finance Market, 2024
17.4. Benchmark of Key Competitors in Chile Car Finance Market, including Variables such as Company Overview, USP, Business Strategies, Strengths, Weaknesses, Business Model, Number of Branches, Product Features, Interest Rate, NPA, Loan Disbursed, Outstanding Loans, Tie-Ups and others
17.5. Strengths and Weaknesses
17.6. Operating Model Analysis Framework
17.7. Gartner Magic Quadrant
17.8. Bowmans Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
18.1. Credit Disbursed, 2025-2029
18.2. Outstanding Loan, 2025-2029
19.1. By Market Structure (Bank-Owned, Multi-Finance, and Captive Companies), 2025-2029
19.2. By Vehicle Type (Passenger, Commercial and EV), 2025-2029
19.3. By Region, 2025-2029
19.4. By Type of Vehicle (New and Used), 2025-2029
19.5. By Average Loan Tenure (0-2 years, 3-5 years, 6-8 years, above 8 years), 2025-2029
19.6. Recommendations
19.7. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all demand-side and supply-side entities relevant to the Chile Auto Finance Market. This includes commercial banks, captive finance providers, NBFCs, auto dealerships, OEMs, fintech lenders, and regulatory bodies.
Based on this ecosystem, we shortlist the top 5–6 financial institutions and vehicle financiers in Chile by assessing their loan disbursement volumes, market share, digital capabilities, and consumer reach.
Sourcing is done via industry articles, market portals, government publications, and proprietary and public databases to initiate desk research and build foundational market intelligence.
Step 2: Desk Research
An exhaustive secondary research exercise is conducted by leveraging multiple data sources including IMF, Central Bank of Chile, Asociación Nacional Automotriz de Chile (ANAC), SERNAC, and company reports.
The objective is to collect and synthesize data points around auto loan disbursement trends, number of financed vehicles, regional splits, lender-wise market shares, product structure, and regulatory impact.
Detailed company-level benchmarking is conducted based on available annual reports, investor presentations, media releases, and filings with CMF (Comisión para el Mercado Financiero).
Step 3: Primary Research
In-depth interviews are conducted with C-level executives, regional heads, loan officers, dealership partners, and digital platform providers in Chile’s auto finance space.
These discussions are designed to validate market size hypotheses, understand growth drivers, assess the impact of interest rate policies, and capture consumer behavior trends.
A bottom-up approach is used to estimate market size by collecting disbursement data from individual players and aggregating to industry level.
To cross-verify company-level information, disguised interviews are also conducted under the pretext of being potential borrowers, which help uncover data on interest rates, approval processes, tenures, and bundled offerings.
Step 4: Sanity Check
A triangulation methodology is employed combining both top-down and bottom-up analysis to verify the accuracy of market size projections.
- Multiple validation layers are used through internal modeling exercises, external expert reviews, and historical trend alignment to ensure data robustness.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Chile Auto Finance Market?
The Chile auto finance market is set for consistent growth, with the total loan disbursement value reaching CLP 6.2 trillion in 2023. This potential is driven by an expanding vehicle parc, rising demand for mobility solutions in urban centers, supportive lending interest rates, and increased adoption of digital loan platforms. Future growth is expected to be further accelerated by EV financing schemes and the digitization of credit processing.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Chile Auto Finance Market?
The Chile Auto Finance Market is led by major players such as Banco de Chile, Santander Consumer Chile, Forum Servicios Financieros, BCI Auto, and Scotiabank Chile. These institutions have established strong networks, diversified lending portfolios, and digital offerings. Other notable players include Tanner Servicios Financieros, Autofin, and Euromotors Financia.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Chile Auto Finance Market?
Key growth drivers include the recovery in household incomes, increased vehicle ownership rates, and a growing preference for structured financing among both new and used car buyers. The push for electric vehicle adoption and green credit initiatives by the Chilean government are also expected to contribute significantly. Additionally, the rapid digitalization of loan application and approval processes is improving accessibility and turnaround time, boosting market participation.
4. What are the Challenges in the Chile Auto Finance Market?
Challenges include high credit default risk in lower-income segments, uneven credit access in rural regions, and elevated effective loan costs due to inflation-linked repayment models (UF-based). Regulatory compliance burdens and a lack of uniform data on used vehicle valuations can also create bottlenecks in loan underwriting and disbursal processes. Ensuring financial inclusion while managing risk continues to be a balancing act for lenders.