Germany Logistics and warehousing Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Structure, By Service Mix, By End-User Industries, By Type of Cargo, By Region and By Mode of Transport
- Product Code: TDR0275
- Region: Europe
- Published on: September 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market Outlook to 2029 - By Market Structure, By Service Mix, By End-User Industries, By Type of Cargo, By Region and By Mode of Transport” provides a comprehensive analysis of the logistics and warehousing market in Germany. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation, trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer level profiling, issues and challenges, and comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the Logistics and Warehousing Market. The report concludes with future market projections based on revenue, by market, service types, region, cause and effect relationship, and success case studies highlighting the major opportunities and cautions.
Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market Overview and Size
The Germany logistics and warehousing market reached a valuation of EUR 310 Billion in 2023, driven by the country’s strategic location in Europe, growing industrial output, and increasing demand for integrated logistics services. The market is characterized by major players such as DHL, DB Schenker, Kühne + Nagel, Dachser, and Hellmann Worldwide Logistics. These companies are recognized for their extensive distribution networks, advanced warehousing systems, and integrated supply chain solutions.
In 2023, DHL inaugurated a new automated logistics hub in Lower Saxony to improve delivery speed and operational efficiency. Cities like Hamburg, Frankfurt, and Munich are key logistics clusters due to their multimodal connectivity and industrial concentration.
%2C%202019-2024.png)
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market:
Strategic Location and Infrastructure: Germany’s central location in Europe and its robust road, rail, and air infrastructure have made it a preferred logistics hub. In 2023, nearly 70% of EU freight transport had Germany as a key transit or destination node, enhancing the demand for warehousing and freight forwarding services.
Manufacturing and Export Base: Germany is a manufacturing and export powerhouse. With exports making up around 47% of GDP in 2023, the need for efficient and timely logistics solutions continues to surge. Industries such as automotive, chemicals, and engineering heavily rely on warehousing and international freight services.
Rise in E-commerce Fulfillment: The growing penetration of online retail, especially post-pandemic, has accelerated the need for last-mile delivery and fulfillment centers. In 2023, Germany’s e-commerce logistics segment witnessed a 15% YoY growth, accounting for EUR 42 Billion, driven by high consumer demand for quick delivery and real-time tracking.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market
Rising Labor and Operational Costs: The German logistics sector is facing rising wage costs and shortages of skilled labor. According to a 2023 industry report, over 30% of logistics companies cited workforce availability as a key bottleneck, leading to increased delivery times and higher operating expenses. This is particularly evident in last-mile delivery and warehousing segments, where manual labor remains essential.
Infrastructure Bottlenecks: Despite having a strong transport network, parts of Germany’s road and rail infrastructure suffer from congestion and underinvestment. In 2023, nearly 18% of logistics providers reported delays due to road traffic congestion, particularly around urban centers such as Berlin and Hamburg. These issues have negatively affected service reliability and increased transit time for freight shipments.
Energy Costs and Carbon Regulations: The push towards carbon-neutral operations has led to increased compliance costs for logistics providers. Rising electricity and fuel prices—especially post-2022—have added significant financial strain. Over 40% of logistics firms in Germany indicated that sustainability-related upgrades (e.g., electric vehicles, green warehouses) have impacted their short-term profitability despite long-term benefits.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market
Carbon Emission Reduction Mandates: Under the EU Green Deal, Germany enforces stringent CO₂ emission regulations for freight and logistics providers. By 2025, logistics companies must reduce carbon emissions by 15% compared to 2020 levels. This has accelerated investment in green technologies such as rail freight and electric trucks, but has also increased capital expenditure for small and mid-sized operators.
Truck Tolling System (MAUT): Germany imposes distance-based tolls on trucks operating on federal highways, with charges dependent on weight class and emission standards. In 2023, the MAUT was extended to vehicles above 3.5 tons, increasing operational costs for many SME logistics firms and reshaping route and pricing strategies.
Digitization Incentives for Supply Chain Automation: The German government, in collaboration with the EU, offers grants and subsidies to logistics firms adopting digital solutions like warehouse automation, AI-based route optimization, and blockchain for supply chain transparency. In 2023, over EUR 700 million was allocated under the “Digital Now” initiative, benefiting over 12,000 logistics SMEs across Germany.
Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
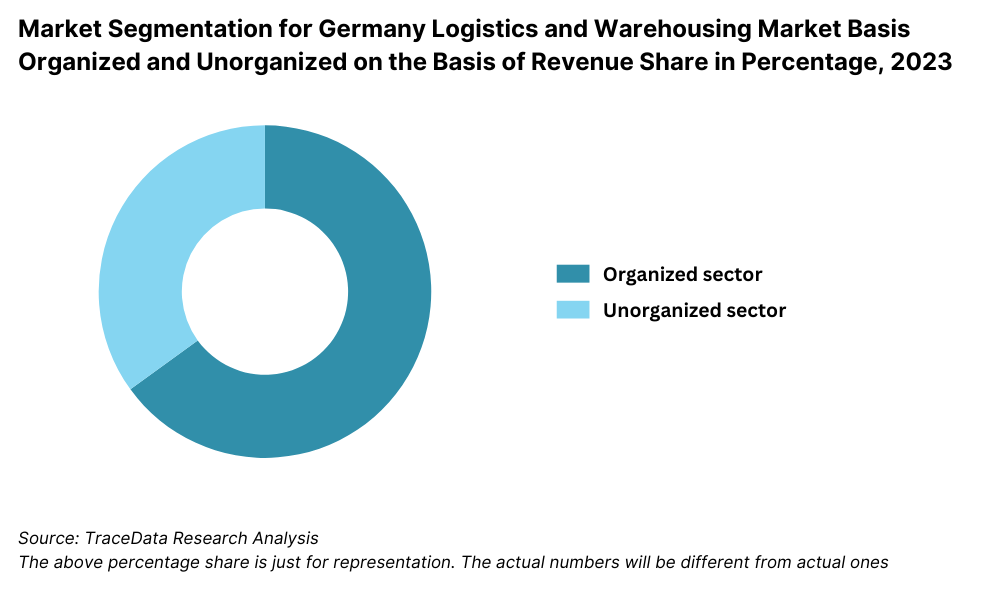
By Market Structure: Organized players dominate the market due to their established infrastructure, compliance with regulatory standards, digital integration, and international networks. These firms provide end-to-end logistics solutions and cater to industries such as automotive, retail, and pharma. Unorganized players still serve regional and niche markets, but their share is declining due to increasing compliance demands and competition from large providers.
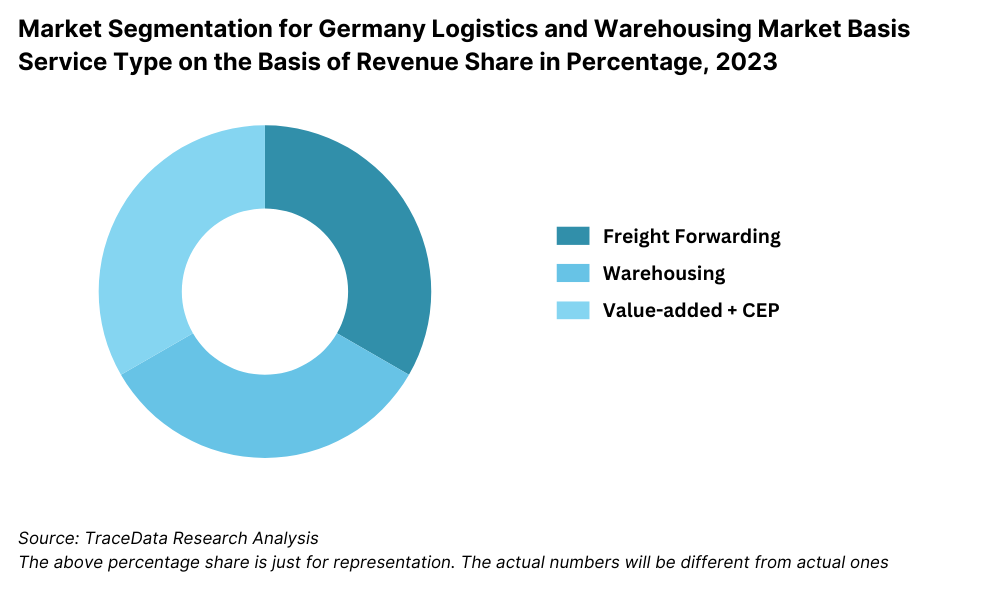
By Service Type: Freight forwarding remains the dominant service due to Germany’s central role in European and global trade. This includes air, sea, and land freight. Warehousing contributes significantly as e-commerce and manufacturing sectors demand scalable storage and fulfillment solutions. Value-added services such as packaging, labeling, and reverse logistics are increasingly being adopted to support supply chain efficiency.
By End-User Industry: Automotive and manufacturing dominate the logistics demand in Germany due to the country’s strong industrial backbone and export-driven economy. Retail and e-commerce have grown rapidly, requiring high-speed delivery and flexible warehousing. Pharmaceuticals and chemicals, which need specialized logistics such as cold chain and hazardous material handling, form a growing segment as well.
Competitive Landscape in Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market
The Germany logistics and warehousing market is relatively consolidated, with major international and national logistics providers leading the space. However, the rise of digital freight platforms and e-commerce-focused logistics startups is contributing to a gradual diversification of the market. Prominent players include DHL, DB Schenker, Kühne + Nagel, Dachser, Hellmann Worldwide Logistics, Rhenus Logistics, Fiege Logistics, and Hermes Europe.
Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
DHL | 1969 | Bonn, Germany |
DB Schenker | 1872 | Essen, Germany |
Kühne + Nagel | 1890 | Bremen, Germany |
Dachser | 1930 | Kempten, Germany |
Hellmann Worldwide | 1871 | Osnabrück, Germany |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
DHL: As one of the world’s largest logistics providers, DHL reported revenue exceeding EUR 81 billion globally in 2023. In Germany, it leads in both freight forwarding and e-commerce last-mile delivery. Its continued investment in automated sorting hubs and electric delivery fleets has reinforced its market leadership.
DB Schenker: The logistics division of Deutsche Bahn, DB Schenker reported a 10% increase in warehousing demand in 2023, particularly from the automotive and industrial machinery sectors. The company is also expanding its green logistics solutions, including intermodal rail freight offerings and CO₂-neutral supply chain options.
Kühne + Nagel: Known for its global freight forwarding operations, Kühne + Nagel strengthened its position in Germany through digital transformation. Its KN Login platform—used for real-time tracking and inventory visibility—has driven a 12% increase in customer retention in 2023.
Dachser: Focusing on integrated logistics, Dachser reported 8% revenue growth in 2023, led by demand from the FMCG and pharmaceutical sectors. Its investment in cold chain warehousing and cross-border EU logistics services continues to expand its client base.
Hellmann Worldwide Logistics: Hellmann expanded its warehousing footprint in northern Germany in 2023, targeting e-commerce and automotive parts logistics. The company’s adoption of automation and predictive analytics tools has resulted in a 20% improvement in delivery accuracy across key hubs.
.png)
What Lies Ahead for Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Germany logistics and warehousing market is projected to grow steadily by 2029, exhibiting a moderate yet consistent CAGR during the forecast period. This growth is expected to be driven by advancements in digital supply chain technologies, expansion of e-commerce, regulatory shifts towards sustainability, and increasing demand from export-oriented industries.
Expansion of Green Logistics: As environmental sustainability becomes a central theme in Europe, the German logistics industry is expected to lead the shift toward low-emission transport and warehousing solutions. The adoption of electric delivery fleets, hydrogen-powered trucks, and carbon-neutral warehouses will accelerate as companies aim to meet EU climate targets and reduce operational emissions.
Digital Supply Chain Transformation: The increasing use of AI, IoT, blockchain, and robotics in logistics operations will enhance supply chain visibility, route optimization, and predictive inventory management. This transformation is likely to reduce costs, improve lead times, and provide more responsive logistics solutions, especially in e-commerce and high-value manufacturing sectors.
Rising Demand for Urban Warehousing: With the rise in quick-commerce and last-mile delivery expectations, the need for small-format urban warehouses near major cities like Berlin, Frankfurt, and Munich is expected to surge. These facilities will play a crucial role in meeting same-day and next-day delivery commitments, particularly in B2C logistics.
Growth of Intermodal and Rail Freight Solutions: Rail-based freight is poised to see increased adoption due to government incentives, road congestion, and environmental concerns. Germany’s strategic position in the EU will further encourage the development of multimodal hubs that integrate road, rail, and air cargo handling to improve transit efficiency and reduce carbon footprint.
%2C%202024-2030.png)
Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
• By Market Structure:
o Organized Sector
o Unorganized Sector
o Global Logistics Providers
o Regional/National Logistics Firms
o Digital Freight Platforms
o Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Providers
o Fourth-Party Logistics (4PL) Providers
• By Service Type:
o Freight Forwarding
o Warehousing and Storage
o Value-Added Services (Packaging, Labeling, Kitting)
o Inventory Management
o Last-Mile Delivery
o Customs Clearance Services
• By End-User Industry:
o Automotive
o Retail and E-commerce
o Manufacturing
o Pharmaceuticals and Healthcare
o FMCG
o Chemicals
o Food and Beverage
o Electronics and Consumer Durables
• By Type of Cargo:
o General Cargo
o Cold Chain / Temperature-Controlled Cargo
o Hazardous Materials
o Bulk Commodities
o Palletized Cargo
• By Region:
o North Rhine-Westphalia
o Bavaria
o Baden-Württemberg
o Hamburg
o Hesse
o Saxony
o Berlin
Players Mentioned in the Report:
• DHL
• DB Schenker
• Kühne + Nagel
• Dachser
• Hellmann Worldwide Logistics
• Rhenus Logistics
• Fiege Logistics
• Hermes Europe
Key Target Audience:
• Freight Forwarding Companies
• Warehousing Service Providers
• E-commerce Logistics Players
• Manufacturing and Retail Supply Chains
• Transportation Technology Providers
• Government and Regulatory Authorities (e.g., Bundesministerium für Digitales und Verkehr)
• Real Estate and Industrial Developers
• Investors and PE Firms in Infrastructure
• Research and Policy Institutions
Time Period:
• Historical Period: 2018–2023
• Base Year: 2024
• Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and Challenges They Face
4.2. Revenue Streams for Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market
4.4. Buying Decision Making Process (B2B Logistics Procurement)
4.5. Supply Decision Making Process (Warehouse/Transport Partnerships)
5.1. Freight Movement in Germany, 2018-2024
5.2. Logistics Spend as % of GDP, 2018-2024
5.3. E-commerce Penetration and Fulfillment Spend in Germany, 2024
5.4. Number of Logistics Service Providers and Warehousing Units by Region
8.1. Revenues, 2018-2024
8.2. Freight Volume (in Tonnes), 2018-2024
8.3. Warehousing Capacity (in Million Sq. Ft.), 2018-2024
9. Market Breakdown for Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market Basis
9.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized Market), 2023-2024P
9.2. By Service Type (Freight Forwarding, Warehousing, Value-Added Services), 2023-2024P
9.3. By End-User Industry (Automotive, Retail, Pharma, Manufacturing, etc.), 2023-2024P
9.4. By Cargo Type (General Cargo, Cold Chain, Hazardous, Bulk), 2023-2024P
9.5. By Region (NRW, Bavaria, Hamburg, etc.), 2023-2024P
9.6. By Mode of Transport (Road, Rail, Air, Sea), 2023-2024P
10.1. Customer Landscape and Procurement Cohorts
10.2. Logistics Vendor Selection Journey
10.3. Need, Expectation, and Pain Point Analysis
10.4. GAP Analysis Framework
11.1. Trends and Developments in Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges for Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market
11.5. Government Policies and Regulations Impacting the Market
12.1. Market Size and Future Potential for Digital Freight and Fulfillment Platforms, 2018-2029
12.2. Business Model and Revenue Streams
12.3. Cross Comparison of Leading Platforms (Service Offerings, Clients, Funding, Network Size)
13.1. Public and Private Investment Trends in Logistics Infrastructure, 2018-2029
13.2. Role of Institutional and Foreign Investors
13.3. Role of Industrial Parks and Free Trade Zones in Logistics
13.4. Trends in Warehousing Automation and Green Logistics Investment
16.1. Benchmark of Key Competitors in Germany Logistics Market Including Company Overview, Service Specialization, Revenue Streams, Strengths, Weaknesses, Network, Warehousing Footprint, and Technological Capabilities
16.2. Strength and Weakness
16.3. Operating Model Analysis Framework
16.4. Gartner Magic Quadrant Positioning
16.5. Bowmans Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
17.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
17.2. Freight Volume, 2025-2029
17.3. Warehousing Capacity, 2025-2029
18.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized Market), 2025-2029
18.2. By Service Type (Freight Forwarding, Warehousing, Value-Added Services), 2025-2029
18.3. By End-User Industry, 2025-2029
18.4. By Region, 2025-2029
18.5. By Mode of Transport, 2025-2029
18.6. By Cargo Type, 2025-2029
18.7. Recommendation
18.8. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand side and supply side entities for Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market. Basis this ecosystem, we will shortlist leading 5–6 logistics providers in the country based upon their financial information, service diversification, infrastructure scale, and operational presence.
Sourcing is made through industry articles, multiple secondary, and proprietary databases to perform desk research around the market to collate industry-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
Subsequently, we engage in an exhaustive desk research process by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This approach enables us to conduct a thorough analysis of the market, aggregating industry-level insights. We delve into aspects like service revenue, warehouse capacity, freight volumes, number of market players, pricing benchmarks, and modal split (road, rail, air, sea).
We supplement this with detailed examinations of company-level data, relying on sources like press releases, annual reports, financial statements, and similar documents. This process aims to construct a foundational understanding of both the market and the entities operating within it.
Step 3: Primary Research
We initiate a series of in-depth interviews with C-level executives, operational heads, and logistics managers representing various Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market companies and end-users. This interview process serves a multi-faceted purpose: to validate market hypotheses, authenticate statistical data, and extract valuable operational and financial insights from these industry representatives. Bottom to top approach is undertaken to evaluate service revenues and warehousing footprint for each player thereby aggregating to the overall market.
As part of our validation strategy, our team executes disguised interviews wherein we approach each company under the guise of potential customers. This approach enables us to validate the operational and financial information shared by company executives, corroborating this data against what is available in secondary databases. These interactions also provide us with a comprehensive understanding of logistics processes, warehouse utilization, service mix, pricing, and value-added services.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- Bottom to top and top to bottom analysis along with market size modeling exercises is undertaken to assess sanity check process.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Germany logistics and warehousing market is poised for sustained growth, reaching a valuation of EUR 310 Billion in 2023. This growth is driven by factors such as Germany’s central location in Europe, its strong industrial base, and increasing demand for e-commerce fulfillment and green logistics. The country’s strategic role as a logistics hub for the EU further enhances its long-term potential.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market features several key players, including DHL, DB Schenker, and Kühne + Nagel. These companies lead the market due to their integrated service offerings, extensive infrastructure, and strong digital capabilities. Other notable players include Dachser, Hellmann Worldwide Logistics, Rhenus Logistics, and Hermes Europe.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Primary growth drivers include the rise of e-commerce and the need for faster last-mile delivery, Germany’s export-oriented economy, and increasing digitalization across the logistics value chain. In addition, growing investments in sustainable logistics solutions and government incentives for digital transformation are expected to fuel market expansion in the coming years.
4. What are the Challenges in the Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Germany Logistics and Warehousing Market faces several challenges, including rising labor and energy costs, infrastructure congestion in urban areas, and strict regulatory requirements related to carbon emissions. Additionally, the shortage of skilled workforce and the need for continuous technological upgradation create operational hurdles for both large and mid-sized logistics providers.