Hong Kong Logistics and warehousing Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Structure, By Services (Freight Forwarding, Warehousing, Last Mile Delivery), By End-Users (Retail, Electronics, Automotive, Healthcare, Others), By Mode of Transportation, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0278
- Region: Asia
- Published on: September 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Hong Kong Logistics and Warehousing Market Outlook to 2029 – By Market Structure, By Services (Freight Forwarding, Warehousing, Last Mile Delivery), By End-Users (Retail, Electronics, Automotive, Healthcare, Others), By Mode of Transportation, and By Region” provides an in-depth analysis of the logistics and warehousing market in Hong Kong. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation, trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer-level insights, challenges, and competitive landscape including cross-comparison, opportunities, and company profiling of major players in the logistics space. The report concludes with future projections for market performance, segmented by service category, industry verticals, and key growth drivers, along with success case studies and strategic implications.
Hong Kong Logistics and Warehousing Market Overview and Size
The Hong Kong logistics and warehousing market reached a valuation of HKD 167 billion in 2023, driven by its strategic location as a regional trade hub, growing e-commerce penetration, and increasing demand for integrated logistics services. Major players in the ecosystem include Kerry Logistics, SF Express, DHL, DB Schenker, and Yusen Logistics, each with robust infrastructure and diversified service offerings.
In 2023, Kerry Logistics expanded its smart warehousing capabilities through AI and automation technologies to cater to high-growth industries such as fashion, electronics, and pharmaceuticals. Regions like Kwai Tsing, Tuen Mun, and Yuen Long are central to warehousing activities due to their proximity to the port and efficient land utilization.
%2C%202019-2024.png)
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Hong Kong Logistics and Warehousing Market:
Strategic Port and Trade Connectivity: Hong Kong is among the world’s top logistics hubs with direct sea and air links to global markets. In 2023, over 18 million TEUs were processed through the Hong Kong port, making it a vital transshipment center for China and Southeast Asia.
E-commerce Growth: With online retail sales exceeding HKD 45 billion in 2023, logistics firms have ramped up investment in last-mile delivery solutions. Companies are increasingly offering same-day and next-day delivery services, especially in dense urban zones such as Kowloon and Causeway Bay.
Smart Warehousing Adoption: By 2023, over 35% of warehouses in Hong Kong integrated smart technologies including warehouse management systems (WMS), automated storage/retrieval systems (AS/RS), and RFID. This has improved operational efficiency and reduced lead times.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for Hong Kong Logistics and Warehousing Market
Land Scarcity and High Rental Costs: The availability of suitable land for warehousing has become increasingly limited in Hong Kong, driving rental prices to among the highest in Asia. As of 2023, prime logistics space in areas such as Kwai Chung and Tsing Yi recorded average monthly rents of HKD 16–20 per sq. ft., nearly 40% higher than regional averages. This significantly increases operational costs for logistics providers, especially SMEs, and limits capacity expansion.
Labour Shortages and Talent Retention: The logistics sector faces a persistent shortage of skilled labour, particularly for warehousing and last-mile delivery roles. In 2023, industry surveys indicated that over 45% of logistics firms in Hong Kong reported difficulties in hiring or retaining qualified staff, especially for night shifts and physically intensive work. High turnover rates and ageing workforce trends are compounding operational inefficiencies.
Cross-Border Disruptions and Regulatory Complexities: Despite proximity to Mainland China, logistical integration remains challenged by customs clearance delays, regulatory mismatches, and frequent procedural updates. In 2023, cross-border trucking delays averaged 16–24 hours, particularly affecting deliveries via the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macau Bridge, thus hampering service-level agreements with end customers.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market
Smart Logistics Development Blueprint (2022–2030): The Hong Kong Government launched this blueprint to promote automation, AI-based logistics coordination, and digital supply chain visibility. By end-2023, over 120 logistics firms had applied for smart logistics subsidies, enabling investments in robotics, warehouse sensors, and predictive analytics. This initiative is expected to reduce warehouse operation costs by 15–20% over the next five years.
Green Logistics Initiatives and Carbon Compliance: As part of Hong Kong’s Climate Action Plan 2050, logistics operators are required to comply with stricter emissions norms. This includes incentivizing the transition to electric delivery vehicles and eco-certified warehouses. In 2023, the government introduced a rebate scheme covering up to 30% of the cost of switching to EV logistics fleets, aimed at reducing carbon emissions from freight transport.
Free Trade and Cross-Border Facilitation Measures: Hong Kong continues to leverage its position under the Greater Bay Area Framework to streamline cross-border logistics. In 2023, customs digitalization measures allowed pre-clearance documentation for over 70% of outbound shipments, reducing average dwell time at ports by nearly 12%. Pilot programs are being expanded in collaboration with Shenzhen and Zhuhai to achieve end-to-end paperless logistics corridors.
Hong Kong Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
By Market Structure: The organized logistics segment dominates the Hong Kong market due to high service standards, compliance with regulatory requirements, and demand from multinational clients. These firms operate integrated logistics systems, use smart warehousing technologies, and maintain strong partnerships with global brands. Meanwhile, the unorganized segment, including small freight forwarders and local courier operators, continues to operate in niche pockets where cost sensitivity is high. However, rising expectations for real-time tracking and performance consistency are pushing consolidation across this space.
%2C%202023.png)
By Service Type: Freight forwarding continues to command the highest share due to Hong Kong’s role as a global trade and transshipment hub. In 2023, over 55% of logistics revenue was attributed to freight forwarding operations (air, sea, and land), serving both intra-Asia and international trade routes.
Warehousing is the second-largest segment, driven by demand for space optimization and inventory management, especially from e-commerce and electronics firms. Last-mile delivery has grown rapidly in urban districts, supported by the e-commerce boom and demand for express parcel services.
%2C%202023.png)
By End-User Industry: The retail and e-commerce sectors are leading contributors to logistics demand, accounting for a growing portion of last-mile and inventory holding costs. Rapid order fulfillment and reverse logistics are key drivers in this space. Electronics and high-tech manufacturing contribute significantly due to the high-value and time-sensitive nature of shipments.
Healthcare and pharmaceutical sectors are emerging as a strategic growth area, requiring cold-chain warehousing, compliance-driven handling, and regulatory adherence.
Competitive Landscape in Hong Kong Logistics and Warehousing Market
The Hong Kong logistics and warehousing market is moderately consolidated, with a few large players dominating air and sea freight operations, while warehousing and last-mile delivery have seen increasing competition from emerging tech-enabled startups. The entry of cross-border players and the rapid rise of e-commerce logistics specialists have diversified the market and increased service differentiation.
Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
Kerry Logistics | 1981 | Hong Kong |
SF Express | 1993 | Shenzhen, China |
DHL Express | 1969 | Bonn, Germany |
DB Schenker | 1872 | Essen, Germany |
Yusen Logistics | 1955 | Tokyo, Japan |
Zeek Logistics | 2019 | Hong Kong |
Lalamove | 2013 | Hong Kong |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
Kerry Logistics: A dominant force in Hong Kong’s logistics ecosystem, Kerry expanded its smart warehousing footprint in 2023 with an automated distribution center in Tuen Mun. The company also entered into a joint venture to enhance multimodal logistics integration under the Greater Bay Area framework.
SF Express: Leveraging its Mainland China network, SF Express strengthened its Hong Kong operations with temperature-controlled warehousing for pharmaceuticals and time-sensitive goods. In 2023, it handled over 2.5 million cross-border parcels per month, up by 18% year-on-year.
DHL Express: Focused on premium express delivery, DHL saw a 22% increase in international parcel volumes from Hong Kong in 2023, driven by growing SME and e-commerce demand. The company also upgraded its aviation fleet serving Hong Kong International Airport.
DB Schenker: Positioned as a leader in freight forwarding, DB Schenker launched a green logistics initiative in 2023, integrating electric vehicles and carbon tracking tools. Their warehouse automation solutions attracted major retail and fashion clients in Hong Kong.
Yusen Logistics: Known for its strength in contract logistics and cold chain solutions, Yusen expanded its pharmaceutical-grade storage capabilities in Hong Kong in 2023. Its compliance with international standards has made it a preferred partner for healthcare multinationals.
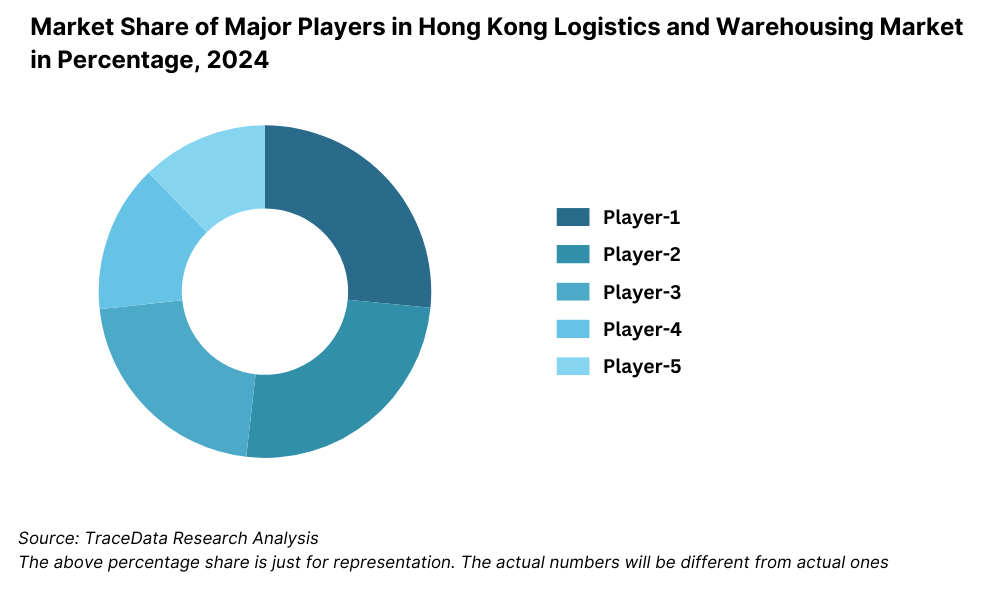
What Lies Ahead for Hong Kong Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Hong Kong logistics and warehousing market is projected to witness steady growth through 2029, supported by its strategic location in the Greater Bay Area, growing demand from cross-border e-commerce, and continued investments in smart logistics infrastructure. The industry is expected to record a moderate yet resilient CAGR over the forecast period, despite challenges related to land constraints and labour shortages.
Expansion of Cross-Border E-Commerce Logistics: With Mainland China continuing to drive regional manufacturing and export growth, Hong Kong’s logistics operators are expected to increasingly serve as transshipment and fulfilment hubs. Demand from platforms such as JD.com, Alibaba, and Temu will necessitate the development of high-speed, tech-enabled cross-border supply chains.
Widespread Adoption of Automation and Robotics: The integration of automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), robotic pick-and-pack, and AI-powered warehouse management systems is expected to rise significantly by 2029. This shift will address Hong Kong’s labour shortage issues and drive operational efficiencies, especially in high-density warehouse zones like Kwai Tsing and Yuen Long.
Growth of Cold Chain and Pharma Logistics: The demand for temperature-controlled storage and distribution will see robust growth, driven by rising healthcare needs, pharmaceutical imports, and vaccine distribution logistics. Companies are expected to invest in GDP-compliant (Good Distribution Practice) infrastructure to tap into this high-value segment.
Focus on Sustainability and Green Logistics: Environmental regulations and growing pressure from global partners are expected to accelerate the adoption of electric delivery vehicles, solar-powered warehouses, and carbon-neutral logistics certifications. By 2029, green logistics will not just be a compliance measure but a key differentiator for logistics providers targeting MNCs and large retail clients.
%2C%202024-2030.png)
Hong Kong Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
- By Market Structure:
o Organized Logistics Providers
o Unorganized / Local Logistics Operators
o Freight Forwarders (Air, Sea, and Land)
o Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Providers
o Fourth-Party Logistics (4PL) Integrators
o Last-Mile Delivery Companies
o Cold Chain Operators - By Service Type:
o Freight Forwarding
o Warehousing
o Distribution and Last-Mile Delivery
o Customs Clearance and Brokerage
o Contract Logistics
o Reverse Logistics
o Cold Storage - By Mode of Transportation:
o Air Freight
o Sea Freight
o Road Freight
o Rail Freight
o Intermodal Transport - By End-User Industry:
o Retail and E-commerce
o Electronics and Consumer Goods
o Automotive and Machinery
o Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
o Food and Beverage
o Fashion and Lifestyle
o Industrial Manufacturing - By Region:
o Kowloon
o Hong Kong Island
o New Territories
o Tuen Mun / Yuen Long
o Kwai Chung / Tsing Yi
Players Mentioned in the Report:
• Kerry Logistics
• SF Express
• DHL Express
• DB Schenker
• Yusen Logistics
• Zeek Logistics
• Lalamove
Key Target Audience:
• Logistics and Warehousing Companies
• E-commerce and Retail Chains
• Manufacturers and Distributors
• Government and Regulatory Authorities (e.g., Transport and Housing Bureau)
• Industrial Zone Developers
• Cold Chain & Pharma Logistics Providers
• Technology and Automation Vendors
Time Period:
• Historical Period: 2018–2023
• Base Year: 2024
• Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and Challenges They Face
4.2. Revenue Streams for Hong Kong Logistics and Warehousing Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Hong Kong Logistics and Warehousing Market
4.4. Logistics Procurement Decision-Making Process
4.5. Warehouse Location and Infrastructure Decision-Making Process
5.1. Breakdown of Logistics and Warehousing Services in Hong Kong, 2018-2024
5.2. Mode-wise Freight Volume (Air, Sea, Road), 2018-2024
5.3. Logistics Spending per Capita in Hong Kong, 2024
5.4. Number of Warehousing Units by Districts, 2023
8.1. Revenues, 2018-2024
8.2. Freight Volume and Warehouse Utilization, 2018-2024
9.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized), 2023-2024P
9.2. By Service Type (Freight Forwarding, Warehousing, Last-Mile, etc.), 2023-2024P
9.3. By Mode of Transportation (Air, Sea, Road, Rail), 2023-2024P
9.4. By End-User Industry (Retail, Pharma, Electronics, F&B, etc.), 2023-2024P
9.5. By Region (Kowloon, HK Island, NT, etc.), 2023-2024P
10.1. Client Landscape and Sector-Wise Demand Patterns
10.2. Customer Journey and Logistics Procurement Strategy
10.3. Need, Desire, and Pain Point Analysis
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11.1. Trends and Developments for Hong Kong Logistics and Warehousing Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Hong Kong Logistics and Warehousing Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis
11.4. Issues and Challenges
11.5. Government Regulations and Initiatives
12.1. Market Size and Growth in Urban Logistics, 2018-2029
12.2. Business Model and Revenue Streams of E-Commerce Logistics
12.3. Cross Comparison of Key Last-Mile Operators: Zeek, Lalamove, SF Express, etc.
13.1. Smart Warehousing Penetration and Automation Trends
13.2. IoT, AI, and Robotics Deployment, 2018-2024
13.3. Cold Chain and Pharma Logistics Infrastructure Innovation
13.4. IT Spend in Logistics Sector
16.1. Benchmark of Key Competitors in Hong Kong Logistics Market: Company Overview, Strengths, Weaknesses, Capabilities, Scale, Warehousing Assets, Technologies Used, Industry Focus, and Partnerships
16.2. Strength and Weakness Assessment
16.3. Operating Model and Value Proposition Framework
16.4. Gartner Magic Quadrant
16.5. Bowmans Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
17.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
17.2. Freight and Warehousing Volume, 2025-2029
18.1. By Market Structure, 2025-2029
18.2. By Service Type, 2025-2029
18.3. By Mode of Transportation, 2025-2029
18.4. By End-User Industry, 2025-2029
18.5. By Region, 2025-2029
18.6. Recommendation
18.7. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand side and supply side entities for Hong Kong Logistics and Warehousing Market. Basis this ecosystem, we will shortlist leading 5-6 logistics service providers in the country based upon their financial information, infrastructure capacity, and service volume.
Sourcing is made through industry articles, multiple secondary, and proprietary databases to perform desk research around the market to collate industry-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
Subsequently, we engage in an exhaustive desk research process by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This approach enables us to conduct a thorough analysis of the market, aggregating industry-level insights. We delve into aspects like the revenue segmentation, warehouse occupancy rates, freight volume, number of market players, pricing trends, and other operational variables. We supplement this with detailed examinations of company-level data, relying on sources like press releases, annual reports, financial statements, and similar documents. This process aims to construct a foundational understanding of both the market and the entities operating within it.
Step 3: Primary Research
We initiate a series of in-depth interviews with C-level executives and other stakeholders representing various Hong Kong Logistics and Warehousing companies and end-users. This interview process serves a multi-faceted purpose: to validate market hypotheses, authenticate statistical data, and extract valuable operational and financial insights from these industry representatives. Bottom to top approach is undertaken to evaluate service volumes for each player thereby aggregating to the overall market.
As part of our validation strategy, our team executes disguised interviews wherein we approach each company under the guise of potential customers. This approach enables us to validate the operational and financial information shared by company executives, corroborating this data against what is available in secondary databases. These interactions also provide us with a comprehensive understanding of revenue streams, service portfolio, value chain, pricing, and other factors.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- Bottom to top and top to bottom analysis along with market size modeling exercises is undertaken to assess sanity check process.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Hong Kong Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Hong Kong Logistics and Warehousing Market is set to grow steadily, reaching a valuation of HKD 167 billion in 2023. The market's potential is driven by Hong Kong’s strategic geographic position in Asia, robust port and airport infrastructure, and its role as a critical node in the Greater Bay Area. Growth is further supported by the expansion of cross-border e-commerce, rising demand for last-mile delivery, and increased investment in automation and smart warehousing.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Hong Kong Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Key players include Kerry Logistics, SF Express, DHL Express, DB Schenker, and Yusen Logistics. These firms lead the market with their extensive regional networks, warehousing capabilities, and value-added logistics services. Tech-driven logistics platforms such as Zeek Logistics and Lalamove are also emerging as strong players in last-mile and on-demand delivery segments.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Hong Kong Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Primary growth drivers include Hong Kong’s position as a global logistics hub, increasing e-commerce penetration, and strong demand from end-user sectors like electronics, retail, and healthcare. The adoption of smart technologies such as AI-powered warehouse systems and the push for green logistics practices are also contributing to sustained market growth.
4. What are the Challenges in the Hong Kong Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The market faces several challenges including limited land availability for new warehousing facilities, high rental costs, and labour shortages in warehousing and delivery operations. Additionally, cross-border regulatory differences and customs delays create friction in regional logistics operations, especially for time-sensitive goods. Sustainability compliance and infrastructure modernization are also critical focus areas moving forward.