India Auto Finance Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Structure, By Lenders, By Vehicle Type, By Loan Tenure, By Interest Rates, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0130
- Region: Asia
- Published on: April 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “India Auto Finance Market Outlook to 2029 - By Market Structure, By Lenders, By Vehicle Type, By Loan Tenure, By Interest Rates, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the auto finance market in India. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of outstanding loans, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer-level profiling, issues and challenges, and a comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the auto finance market. The report concludes with future market projections based on loan disbursements, market segments, vehicle categories, region, cause and effect relationship, and success case studies highlighting the major opportunities and risks.
India Auto Finance Market Overview and Size
The India auto finance market reached a valuation of INR 10 Trillion in 2023, driven by increasing vehicle ownership, a growing middle-class population, and the rising affordability of auto loans. The market is characterized by major players such as HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, State Bank of India (SBI), Mahindra Finance, and Bajaj Finance. These companies are recognized for their extensive financial service networks, competitive interest rates, and customer-centric loan offerings.
In 2023, leading banks and NBFCs introduced digital lending platforms to enhance the customer experience and simplify loan disbursement processes. These initiatives aim to leverage fintech solutions and tap into the growing digital ecosystem in India, providing a seamless and hassle-free auto loan experience. Key metropolitan areas like Mumbai, Delhi, Bangalore, and Chennai remain prime markets due to their high vehicle penetration and financial infrastructure.
Market Size for India Auto Finance Industry Size on the Basis of Loan Disbursement in USD Billion, 2018-2024

What Factors are Leading to the Growth of India Auto Finance Market:
Economic Growth & Rising Disposable Income: India’s expanding economy and increasing disposable income levels have fueled the demand for vehicle financing. The growing aspiration for vehicle ownership, supported by economic stability, has led to an increased uptake of auto loans. In 2023, auto loans constituted nearly 75% of total vehicle purchases in India.
Growing Middle-Class & Urbanization: The rapid expansion of the middle-class segment, along with increasing urbanization, has significantly contributed to the rise in vehicle financing. Over the past five years, the middle-income population in India has grown by 15%, driving demand for auto loans as car ownership becomes more feasible for a larger segment of the population.
Digitalization & Fintech Innovations: The rise of digital banking and fintech-driven lending solutions has revolutionized the auto finance market in India. In 2023, approximately 45% of auto loan applications were processed online, reflecting a major shift towards digital platforms. These platforms offer instant approvals, simplified documentation, and enhanced transparency, boosting market growth.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for India Auto Finance Market
Credit Accessibility Issues: Many consumers, especially those with low credit scores or informal employment, face difficulties in securing auto loans. In 2023, approximately 40% of potential buyers struggled with loan approvals due to stringent eligibility criteria. Many customers in rural and semi-urban areas also lack proper credit histories, making it even more challenging to access financing options. The lack of alternative credit evaluation methods further restricts loan approval rates in the market.
Rising Interest Rates: Fluctuations in interest rates impact loan affordability, deterring some consumers from financing vehicle purchases. In 2023, the average auto loan interest rate in India rose by 1.5%, leading to a decline in loan uptake. With inflationary pressures and the Reserve Bank of India’s monetary tightening, interest rates are expected to remain volatile, affecting both consumers and lenders.
Regulatory Compliance: The Indian auto finance industry is subject to evolving financial regulations, including stricter lending norms and mandatory credit checks. These regulations can increase operational costs for lenders and limit loan availability for high-risk borrowers. Additionally, regulatory changes regarding NBFCs and new compliance requirements for digital lenders have increased the administrative burden for auto finance providers, resulting in slower loan processing times.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market
Vehicle Loan Interest Rate Policies: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) regulates interest rates for auto loans through monetary policies. In recent years, efforts have been made to ensure fair lending rates and prevent predatory loan practices. The RBI’s periodic revisions to repo rates directly influence auto loan affordability, impacting both lenders and consumers.
Digital Loan Disbursement Guidelines: The Indian government has encouraged the adoption of digital lending frameworks to enhance transparency and efficiency. As of 2023, over 50% of auto loan applications were processed through digital platforms. The integration of AI-driven risk assessment tools has improved credit evaluations, reducing processing times and enhancing loan accessibility for tech-savvy consumers.
Incentives for Electric Vehicles (EVs): The government has introduced subsidies and lower interest rates for electric vehicle financing to promote sustainable transportation. In 2023, EV auto loans grew by 25% due to these incentives. The Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME) initiative continues to drive demand for EV financing, making green mobility more affordable for Indian consumers.
Market Segmentation of India Auto Finance Market
By Lenders: Banks are the leading players in the auto finance industry, accounting for the highest share in loan disbursements due to their competitive interest rates and strong customer base. NBFCs have also gained substantial traction by offering customized loan solutions with flexible repayment terms. Digital lenders and fintech firms are emerging as new competitors, leveraging technology to streamline loan approvals and offer faster processing times.

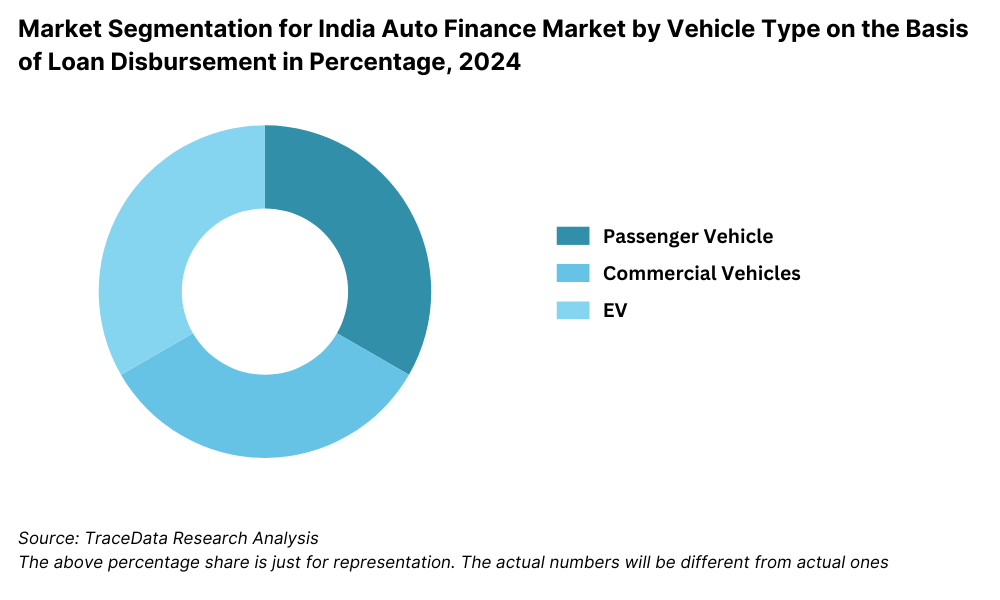
By Vehicle Type: The auto finance market is segmented based on vehicle types, including new vehicles and used vehicles. New vehicle financing dominates the market, as banks and financial institutions prioritize funding new car purchases due to lower risk factors. Used vehicle financing, though growing steadily, faces challenges such as higher interest rates, limited loan tenure, and vehicle depreciation concerns.
Competitive Landscape in India Auto Finance Market
The India auto finance market is highly competitive, with several established players and new entrants shaping the landscape. The market includes traditional banks, non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), and digital lenders, all vying for a share in the growing auto loan segment.
Major Players in the India Auto Finance Market
| Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
| HDFC Bank Auto Loan | 1994 | Mumbai, India |
| ICICI Bank Auto Finance | 1994 | Mumbai, India |
| State Bank of India (SBI) Car Loan | 1955 | Mumbai, India |
| Axis Bank Auto Loan | 1993 | Mumbai, India |
| Kotak Mahindra Prime Ltd. | 1996 | Mumbai, India |
| Bajaj Finance Ltd. (Auto Finance) | 1987 | Pune, India |
| Mahindra Finance (Mahindra & Mahindra Financial Services) | 1991 | Mumbai, India |
| Tata Capital Auto Loan | 2007 | Mumbai, India |
| Cholamandalam Investment & Finance Co. Ltd. | 1978 | Chennai, India |
| Shriram Transport Finance Company | 1979 | Chennai, India |
| L&T Finance Auto Loan | 1994 | Mumbai, India |
| IndusInd Bank Auto Finance | 1994 | Mumbai, India |
| Muthoot Capital Services Ltd. | 1994 | Kochi, India |
| Sundaram Finance Ltd. | 1954 | Chennai, India |
| Hero FinCorp (Hero MotoCorp Group) | 1991 | New Delhi, India |
Recent Competitor Trends and Key Developments
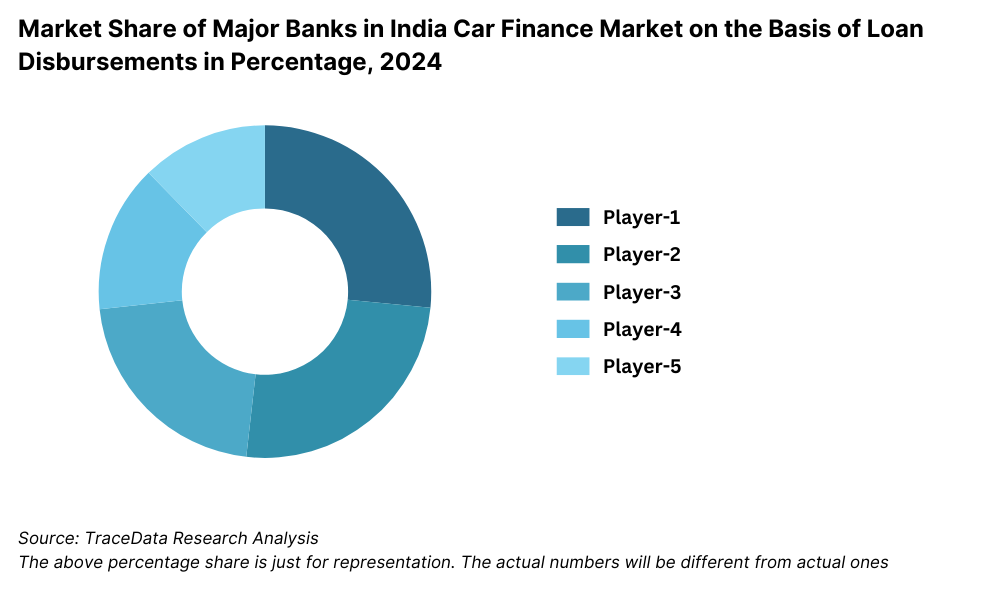
HDFC Bank: One of the leading auto finance providers in India, HDFC Bank saw a 15% increase in auto loan disbursements in 2023, driven by expanding digital lending initiatives and competitive interest rates.
ICICI Bank: ICICI Bank has focused on fintech collaborations, enabling faster loan approvals through AI-driven credit assessments, leading to a 12% growth in auto loan financing.
State Bank of India (SBI): The largest public sector bank, SBI introduced flexible repayment plans for auto loans, boosting customer acquisition, and reported a 10% increase in auto loan volumes.
Mahindra Finance: Specializing in vehicle financing for rural and semi-urban customers, Mahindra Finance reported a 20% growth in loan disbursements, particularly for commercial and utility vehicles.
Bajaj Finance: Known for its quick loan approval process, Bajaj Finance expanded its auto loan portfolio, recording a 17% rise in financed vehicles, particularly in Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities.

What Lies Ahead for India Auto Finance Market?
The India auto finance market is expected to grow steadily by 2029, exhibiting a strong CAGR during the forecast period. Several key trends will shape the future of the industry:
Shift Towards Electric Vehicles (EVs): With government incentives and increased awareness of environmental sustainability, the demand for electric vehicle financing is expected to rise significantly. Financial institutions are expected to introduce specialized loan products for EVs with lower interest rates and longer repayment periods.
Integration of Digital Technology: AI-driven risk assessment models, blockchain-based loan contracts, and automated loan disbursement systems will enhance transparency, reduce fraud, and improve customer experience. Digital lending platforms will continue to gain market share.
Growth of Used Vehicle Financing: As the demand for affordable transportation rises, used vehicle financing is expected to witness substantial growth. Lenders will introduce more structured financing options with lower interest rates and flexible repayment terms to tap into this segment.
Future Outlook and Projections for India Car Finance Market Size on the Basis of Loan Disbursements in USD Billion, 2024-2029

India Auto Finance Market Segmentation
- By Market Structure:
- Banks
- Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)
- Digital Lenders
- Public Sector Banks
- Private Sector Banks
- Microfinance Institutions
- Captive Finance Companies
- By Vehicle Type:
- New Vehicles
- Used Vehicles
- Passenger Vehicles
- Commercial Vehicles
- Two-Wheelers
- Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- By Loan Tenure:
- <3 Years
- 3-5 Years
- 5-7 Years
- More than 7 Years
- By Interest Rates:
- Below 7%
- 7%-9%
- 9%-12%
- Above 12%
- By Region:
- North India
- South India
- East India
- West India
- Central India
- North-East India
Players Mentioned in the Report (Banks):
- State Bank of India (SBI)
- ICICI Bank
- HDFC Bank
- Axis Bank
- Bank of Baroda
- Punjab National Bank (PNB)
- Union Bank of India
- Canara Bank
- Kotak Mahindra Bank
- IDBI Bank
Players Mentioned in the Report (NBFCs):
- Bajaj Finance Limited
- Mahindra & Mahindra Financial Services Limited
- Sundaram Finance Limited
- Cholamandalam Investment and Finance Company Limited
- Tata Motors Finance Limited
- L&T Finance Holdings Limited
- Muthoot Finance Limited
- Shriram Transport Finance Company Limited
- HDB Financial Services Limited
- Manappuram Finance Limited
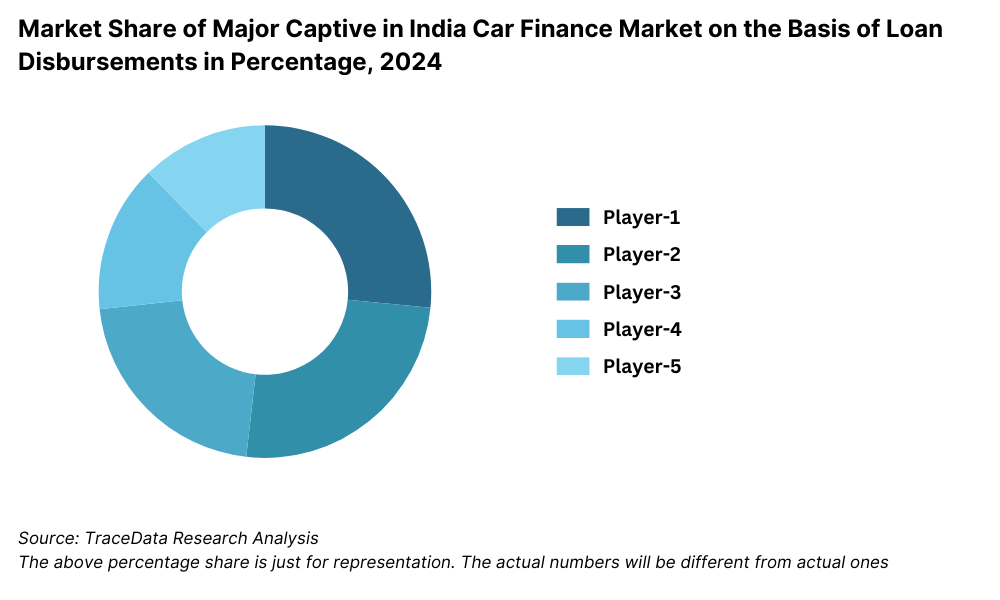
Players Mentioned in the Report (Captive):
- Toyota Financial Services India Limited
- Volkswagen Finance Private Limited
- BMW India Financial Services Private Limited
- Mercedes-Benz Financial Services India Private Limited
- Honda Financial Services India Limited
- Hyundai Motor India Finance
- Ford Credit India Private Limited
- Nissan Renault Financial Services India Private Limited
- Maruti Suzuki Smart Finance
- Tata Motors Finance Limited
Key Target Audience:
- Banks and Financial Institutions
- Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)
- Digital Lending Platforms
- Vehicle Dealerships
- Automotive Manufacturers
- Government Regulatory Bodies (e.g., Reserve Bank of India, SEBI)
- Research and Development Institutions
Time Period:
- Historical Period: 2018-2023
- Base Year: 2024
- Forecast Period: 2024-2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and challenges they face.
4.2. Relationship and Engagement Model between Banks-Dealers, NBFCs-Dealers and Captive-Dealers-Commission Sharing Model, Flat Fee Model and Revenue streams
5.1. New Car and Used Car Sales in India by type of vehicle, 2018-2024
8.1. Credit Disbursed, 2018-2024
8.2. Outstanding Loan, 2018-2024
9.1. By Market Structure (Bank-Owned, Multi-Finance, and Captive Companies), 2023-2024
9.2. By Vehicle Type (Passenger, Commercial and EV), 2023-2024
9.3. By Region, 2023-2024
9.4. By Type of Vehicle (New and Used), 2023-2024
9.5. By Average Loan Tenure (0-2 years, 3-5 years, 6-8 years, above 8 years), 2023-2024
10.1. Customer Landscape and Cohort Analysis
10.2. Customer Journey and Decision-Making
10.3. Need, Desire, and Pain Point Analysis
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11.1. Trends and Developments for India Car Finance Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for India Car Finance Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for India Car Finance Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges for India Car Finance Market
11.5. Government Regulations for India Car Finance Market
12.1. Market Size and Future Potential for Online Car Financing Aggregators, 2018-2029
12.2. Business Model and Revenue Streams
12.3. Cross Comparison of Leading Digital Car Finance Companies Based on Company Overview, Revenue Streams, Loan Disbursements/Number of Leads Generated, Operating Cities, Number of Branches, and Other Variables
13.1. Finance Penetration Rate and Average Down Payment for New and Used Cars, 2018-2029
13.2. How Finance Penetration Rates are Changing Over the Years with Reasons
13.3. Type of Car Segment for which Finance Penetration is Higher
17.1. Market Share of Key Banks in India Car Finance Market, 2024
17.2. Market Share of Key NBFCs in India Car Finance Market, 2024
17.3. Market Share of Key Captive in India Car Finance Market, 2024
17.4. Benchmark of Key Competitors in India Car Finance Market, including Variables such as Company Overview, USP, Business Strategies, Strengths, Weaknesses, Business Model, Number of Branches, Product Features, Interest Rate, NPA, Loan Disbursed, Outstanding Loans, Tie-Ups and others
17.5. Strengths and Weaknesses
17.6. Operating Model Analysis Framework
17.7. Gartner Magic Quadrant
17.8. Bowmans Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
18.1. Credit Disbursed, 2025-2029
18.2. Outstanding Loan, 2025-2029
19.1. By Market Structure (Bank-Owned, Multi-Finance, and Captive Companies), 2025-2029
19.2. By Vehicle Type (Passenger, Commercial and EV), 2025-2029
19.3. By Region, 2025-2029
19.4. By Type of Vehicle (New and Used), 2025-2029
19.5. By Average Loan Tenure (0-2 years, 3-5 years, 6-8 years, above 8 years), 2025-2029
19.6. Recommendations
19.7. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand-side and supply-side entities for the India Auto Finance Market. Based on this ecosystem, we will shortlist leading financial institutions and NBFCs in the country based on their financial performance, loan disbursement capacity, and market penetration.
Sourcing is conducted through industry reports, regulatory filings, secondary sources, and proprietary databases to perform desk research and collate market-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
We engage in exhaustive desk research by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This approach enables a thorough analysis of the market, aggregating insights related to loan volumes, interest rate trends, regulatory impact, and competition.
We examine company-level data, relying on sources such as press releases, annual reports, financial statements, and regulatory filings to develop a foundational understanding of the market and its key players.
Step 3: Primary Research
A series of in-depth interviews are conducted with C-level executives, industry experts, and key stakeholders representing major banks, NBFCs, digital lenders, and regulatory authorities. This process helps validate market hypotheses, authenticate statistical data, and extract valuable insights regarding operational and financial aspects of the industry.
A bottom-up approach is undertaken to assess the total loan disbursement by segment, followed by a top-down validation to ensure data consistency.
Disguised interviews are conducted with lending institutions and financial service providers to validate their reported figures and gain insights into their strategies, customer preferences, and risk management measures.
Step 4: Sanity Check
Both bottom-up and top-down analyses, along with market size modeling exercises, are performed to validate findings and ensure data accuracy.
- Cross-verification with external reports, industry benchmarks, and government data sources is conducted to refine final estimates and projections.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the India Auto Finance Market?
The India auto finance market is poised for significant growth, reaching a valuation of INR 10 Trillion in 2023. This expansion is driven by rising vehicle ownership, increased disposable income, and the digitalization of financial services, making loan processing more seamless and accessible.
2. Who are the Key Players in the India Auto Finance Market?
The key players in the India Auto Finance Market include HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, State Bank of India (SBI), Mahindra Finance, Bajaj Finance, and Axis Bank. These institutions dominate due to their extensive financial service networks, competitive interest rates, and consumer-friendly loan products.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the India Auto Finance Market?
Growth is fueled by economic expansion, increasing demand for vehicle financing, and the government’s push for financial inclusion. The rising adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and digital lending platforms also contribute to market growth.
4. What are the Challenges in the India Auto Finance Market?
The market faces challenges such as high-interest rates, stringent regulatory compliance, and increasing competition from fintech companies. Additionally, credit accessibility issues for low-income consumers and non-performing assets (NPAs) remain concerns for lenders.