India Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Structure, By Storage and Transportation Modes, By End-User Industries, By Temperature Ranges, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0184
- Region: Asia
- Published on: May 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “India Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029 – By Market Structure, By Storage and Transportation Modes, By End-User Industries, By Temperature Ranges, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the cold chain industry in India. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation, trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer-level profiling, issues and challenges, and comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the Cold Chain Market. The report concludes with future market projections based on revenue, by service type, end-user industries, temperature ranges, and success case studies highlighting the major opportunities and cautions.
India Cold Chain Market Overview and Size
The India cold chain market reached a valuation of INR 2,100 Billion in 2023, driven by increasing demand from the pharmaceutical, dairy, seafood, and fresh produce industries. Rising urbanization, organized retail expansion, and a surge in e-commerce-based food delivery have further stimulated cold chain infrastructure development. Major players such as Snowman Logistics, Coldman Logistics, Gubba Cold Storage, and ColdEX Logistics dominate the market through their advanced storage capacities and pan-India transportation networks.
In 2023, Snowman Logistics expanded its warehouse facilities in key regions such as NCR and Bengaluru, emphasizing multi-temperature zones to serve both frozen and chilled categories. Key regional hubs for the cold chain sector include Maharashtra, Karnataka, Gujarat, and Tamil Nadu due to their strategic industrial corridors and agri-export centers.
Market Size for India Cold Chain Industry on the Basis of Revenues in USD Million, 2018-2023

What Factors are Leading to the Growth of India Cold Chain Market:
Food & Agriculture Exports: India’s position as a major exporter of seafood, meat, dairy, and fruits & vegetables necessitates robust cold storage infrastructure. In 2023, agri-based exports contributed 23% of demand for temperature-controlled logistics.
Pharmaceutical Industry Boom: The pandemic period amplified India’s vaccine production and distribution needs. The ongoing growth in biologics, temperature-sensitive drugs, and clinical trials is forecasted to drive pharma cold chain demand by a CAGR of 14% through 2029.
Government Initiatives: Under schemes like PM Kisan Sampada Yojana and cold chain subsidies by NHB and MoFPI, several integrated cold storage and reefer transport projects have been co-funded. In FY2023 alone, the government approved INR 800 Cr for cold chain modernization.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for India Cold Chain Market
Infrastructure Deficiency and Power Reliability: A major challenge in the Indian cold chain ecosystem is the lack of standardized and modern cold storage infrastructure, especially in Tier II and Tier III cities. As of 2023, more than 60% of existing cold storages were outdated and used for single-commodity storage (mainly potatoes). Additionally, frequent power outages and high electricity costs in several regions lead to increased operational inefficiencies and spoilage, affecting approximately 15% of perishable goods annually.
High Capital and Operational Costs: Establishing and maintaining cold storage facilities and reefer trucks involve substantial capital investment. Industry data shows that up to 35% of cold chain operators face cash flow constraints due to high energy costs, maintenance expenses, and loan repayments. This challenge is more pronounced among small and mid-sized logistics providers who lack access to low-interest financing or long-term leases.
Fragmentation and Lack of Integration: The cold chain market remains highly fragmented with multiple small players offering isolated storage or transportation services. This lack of end-to-end integration leads to poor coordination, especially in multi-modal logistics and last-mile delivery. In 2023, over 40% of temperature-sensitive goods experienced delays or temperature excursions during transit due to lack of centralized control systems.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market
National Centre for Cold Chain Development (NCCD): Established under the Ministry of Agriculture, the NCCD has developed technical standards and guidelines to promote integrated cold chain solutions. As of 2023, more than 250 projects had been supported through policy guidelines and advisory interventions, particularly focusing on perishable agri-produce.
PLI and Infrastructure Subsidy Schemes: The Indian government launched Production Linked Incentives (PLI) and Capital Investment Subsidy Schemes under MoFPI and NHB to enhance cold storage capacities and reduce post-harvest losses. In FY2023, over INR 900 Cr was disbursed in subsidies, supporting the development of 1.1 million MT of cold storage capacity across India.
FSSAI Regulations for Cold Chain Transport: The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) mandates strict temperature control guidelines for transport and storage of frozen and chilled food items. In 2023, new rules required transporters and storage providers to install temperature recording devices with data retention for at least 30 days. Compliance improved from 46% in 2021 to 68% in 2023.
India Cold Chain Market Segmentation
By Market Structure: The Indian cold chain market is primarily led by unorganized players that manage single-commodity cold storages or operate regionally with limited infrastructure. These operators dominate due to low-cost models and proximity to farms or local mandis. However, the organized segment is growing rapidly with the entry of third-party logistics (3PL) providers and integrated cold chain players offering end-to-end services. Organized players such as Snowman Logistics and ColdEX are gaining share through their adherence to global standards, real-time monitoring systems, and multi-temperature warehousing solutions.

By Temperature Range: The cold chain industry is segmented by temperature needs – Controlled Ambient (15–25°C), Chilled (2–8°C), and Frozen (-18°C and below). The Frozen segment holds the largest share in 2023, primarily driven by seafood, meat, and ice-cream logistics. The Chilled category is gaining momentum with the rise in dairy, fresh fruits, vegetables, and vaccines. Controlled ambient storage is used for food additives, bakery items, and certain pharma products, and is projected to grow steadily as FMCG players expand their portfolios.
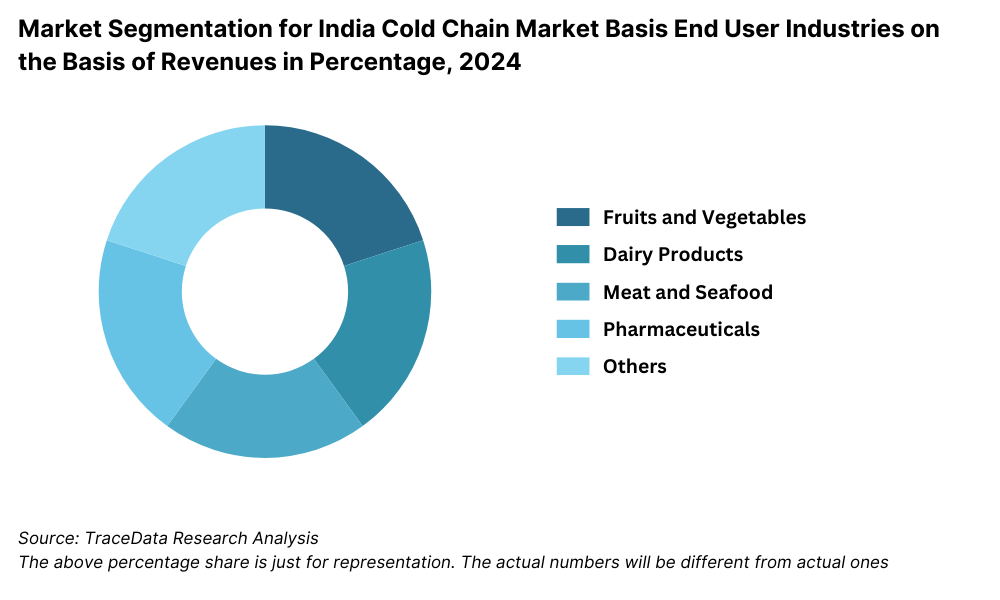
By End-User Industry: The food & agriculture sector remains the largest consumer of cold chain services in India, accounting for over half of the market’s revenue share in 2023. Dairy, meat, seafood, and fresh produce form the bulk of this demand. The pharmaceutical segment has shown the fastest growth, driven by temperature-sensitive drugs, vaccine exports, and clinical trial logistics. Other segments include quick service restaurants (QSR), organized retail, and e-commerce grocery, which are rapidly expanding in metro and Tier I cities.
Competitive Landscape in India Cold Chain Market
The India cold chain market is moderately fragmented, with both national logistics companies and regional players operating across various cold storage and transportation segments. However, increasing demand for integrated and tech-enabled solutions has led to rapid scaling by organized players. Major players in the market include Snowman Logistics, Coldman Logistics, Gubba Cold Storage, ColdEX Logistics, Dev Bhumi Cold Chain, and MJ Logistics.
| Company Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
| Snowman Logistics Ltd. | 1993 | Bengaluru, Karnataka, India |
| ColdEX Logistics Pvt. Ltd. | 2007 | Indore, Madhya Pradesh, India |
| Gati Kausar India Ltd. | 1984 | Hyderabad, Telangana, India |
| Cold Star Logistics Pvt. Ltd. | 2012 | Ludhiana, Punjab, India |
| Future Supply Chain Solutions Ltd. | 2006 | Mumbai, Maharashtra, India |
| TCI Cold Chain Solutions Ltd. | 2009 | Gurugram, Haryana, India |
| Kool-Ex Cold Chain Ltd. | 2007 | Mumbai, Maharashtra, India |
| IRC Cold Chain Solutions | 2012 | New Delhi, Delhi, India |
| LEAP India Pvt. Ltd. | 2013 | Mumbai, Maharashtra, India |
| Crystal Group (Cold Chain Division) | 1994 | Indore, Madhya Pradesh, India |
| Siddhivinayak Cold Storage Pvt. Ltd. | 1985 | Mumbai, Maharashtra, India |
| Rivigo (Cold Chain Services) | 2014 | Gurugram, Haryana, India |
| Adani Logistics Ltd. (Cold chain via acquisitions) | 2005 | Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India |
| DP World India (via Cold Chain Expansion) | 1972 (Global) | Dubai, UAE |
| Maersk India (Cold Chain Logistics) | 1904 (India: ~1990s) | Copenhagen, Denmark |
| Lineage Logistics (via acquisition of Cold Star) | 2008 (India: ~2020s) | Novi, Michigan, USA |
| SnowLink Cold Chain Logistics | 2017 | Mumbai, Maharashtra, India |
| Samsara Group (Cold Chain Services) | 1996 | Mumbai, Maharashtra, India |
| Blue Cold Refrigeration Pvt. Ltd. | 2002 | Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India |
| Coldman Logistics |
| India |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
Snowman Logistics: A leading integrated cold chain company, Snowman expanded its warehousing capacity by 20% in 2023, focusing on multi-temperature storage in Bengaluru, Coimbatore, and Mumbai. The company also invested in GPS-enabled reefer fleet expansion, targeting QSR and pharma clients.
Coldman Logistics: Known for end-to-end cold chain services, Coldman added 1.2 lakh sq. ft. of storage space in western India in 2023. It also partnered with global pharma companies to meet compliance with WHO-GDP standards, boosting its pharma logistics business.
Gubba Cold Storage: Specializing in seed and life sciences cold storage, Gubba added new bulk storage facilities in Hyderabad. The company reported a 25% rise in pharma and agri-client onboarding in 2023, attributed to its temperature calibration technologies and long-term storage capabilities.
ColdEX Logistics: With a strong presence in frozen foods and QSR logistics, ColdEX reported a 30% YoY increase in reefer deliveries in 2023. It invested in AI-based route optimization tools to enhance last-mile efficiency in metro markets like Delhi NCR and Mumbai.
Dev Bhumi Cold Chain: Focused on Himalayan states, the company scaled up its fruit and vegetable cold transport networks. In 2023, it secured contracts for apple and cherry logistics in Himachal and J&K, improving cold linkages from farm to city markets.
MJ Logistics: A multi-modal logistics company, MJ launched a cold chain division in 2021 and by 2023 had established regional cold hubs in NCR and Gujarat. It is now targeting pharmaceutical and food exports, leveraging its dry logistics expertise.

What Lies Ahead for India Cold Chain Market?
The India cold chain market is projected to grow robustly by 2029, exhibiting a strong CAGR driven by rising demand from organized retail, pharmaceuticals, and agritech sectors. The sector will benefit from policy support, infrastructure modernization, and rising private sector investments. Market players are expected to expand capacity, enhance last-mile delivery capabilities, and adopt smart technologies to ensure quality preservation and operational efficiency.
Expansion of End-to-End Cold Chain Solutions: As more businesses seek integrated logistics, there will be a surge in end-to-end cold chain service offerings that cover farm gate procurement, storage, long-haul transport, and last-mile delivery. Companies offering bundled services will gain a competitive edge by reducing wastage and improving turnaround times.
Digitization and IoT-Driven Monitoring: The adoption of IoT, cloud-based warehouse management systems, and real-time temperature tracking solutions will accelerate. These technologies will enhance traceability, compliance, and asset utilization. By 2029, over 60% of organized cold chain operators are expected to be using tech-enabled monitoring systems for their fleets and warehouses.
Rising Role of Pharmaceuticals and Biologics: The pharmaceutical sector, especially biologics, vaccines, and clinical trial samples, will become a dominant demand driver for the cold chain market. With India expanding its position in global drug manufacturing and exports, the need for GDP-compliant cold chain infrastructure will see double-digit growth.
Focus on Multi-Temperature Warehousing: Market players will increasingly invest in multi-temperature warehousing facilities that can cater to frozen, chilled, and ambient goods under a single roof. This will enable efficient utilization of real estate, reduce energy costs, and improve turnaround for 3PL and 4PL providers.
Future Outlook and Projections for India Cold Chain Market on the Basis of Revenues in USD Million, 2024-2029


India Cold Chain Market Segmentation
- By Market Structure:
o Standalone Cold Storage Units
o Integrated Cold Chain Providers
o Reefer Transport Operators
o Cold Warehousing Services
o 3PL/4PL Logistics Firms
o Government-Aided Cold Storages
o Private Commercial Cold Chains - By Temperature Range:
o Controlled Ambient (15°C–25°C)
o Chilled (2°C–8°C)
o Frozen (-18°C and below) - By End-User Industry:
o Fruits & Vegetables
o Dairy Products
o Meat & Seafood
o Pharmaceuticals & Vaccines
o Bakery & Confectionery
o Quick Service Restaurants (QSR)
o E-Commerce Grocery - By Storage Type:
o Bulk Cold Storage
o Hub & Spoke Warehousing
o Dedicated Pharma Storage
o Ripening Chambers - By Transportation Mode:
o Reefer Trucks
o Cold Rail Cargo
o Air Freight (Pharma & Exports)
o Multi-Modal Logistics - By Region:
o Northern India
o Western India
o Southern India
o Eastern India
o Central India
o North-Eastern States
Players Mentioned in the Report:
- Snowman Logistics
- ColdEx Logistics
- Gati Kausar
- Stellar Value Chain Solutions
- Future Supply Chain Solutions
- TCI Express
- Coldman Logistics
- AWL India
- Reefer Express
- Coldrush Logistics
- Gubba Cold Storage
- Indicold Logistics
- Arihant Cold Storage
- Celcius Logistics
- Cold Star Logistics
- Crystal Group
- Fresh and Healthy Services
- R.K. Foodland
- Stockarea
- Ark Supply Chain
Key Target Audience:
- Cold Chain Logistics Providers
- Refrigerated Transport Companies
- Food & Agro Exporters
- Pharma Manufacturers and Distributors
- Cold Storage Equipment Manufacturers
- Government Bodies (MoFPI, NCCD, NHB)
- Institutional Investors and Infrastructure Funds
- Technology Providers (IoT, WMS, Fleet Management)
- Industry Associations (CII, FICCI Cold Chain Taskforce)
Time Period:
- Historical Period: 2018–2023
- Base Year: 2024
- Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
6.1. Revenues, 2018-2024P
7.1. By Cold Storage and Cold Transport, 2023-2024P
7.2. By End-User Application (Dairy Products, Meat and Seafood, Pharmaceuticals, Fruits and Vegetables and Others), 2023-2024P
7.3. By Ownership (Owned and 3PL Cold Chain Facilities), 2023-2024P
10.1. India Cold Storage Market Size
10.1.1. By Revenue, 2018-2024P
10.1.2. By Number of Pallets, 2018-2024P
10.2. India Cold Storage Market Segmentation
10.2.1. By Temperature Range (Ambient, Chilled and Frozen), 2023-2024P
10.2.2. By End-User Application (Dairy Products, Meat and Seafood, Pharmaceuticals, Fruits and Vegetables and Others), 2023-2024P
10.2.3. By Major Cities (Manila, Quezon, Cebu and others), 2023-2024P
10.3. India Cold Storage Market Future Outlook and Projections, 2025-2029
10.3.1. By Temperature Range (Ambient, Chilled and Frozen), 2025-2029
10.3.2. By Major Cities, 2025-2029
11.1. India Cold Transport Market Size (By Revenue and Number of Reefer Trucks), 2018-2024P
11.2. India Cold Transport Market Segmentation
11.2.1. By Mode of Transportation (Land, Sea and Air), 2023-2024P
11.2.2. By Location (Domestic and International), 2023-2024P
11.3. India Cold Transport Market Future Outlook and Projections, 2025-2029
11.3.1. By Mode of Transport (Land, Sea and Air), 2025-2029
11.3.2. By Location (Domestic and International), 2025-2029
12.1. Trends and Developments in India Cold Chain Market
12.2. Issues and Challenges in India Cold Chain Market
12.3. Decision Making Parameters for End Users in India Cold Chain Market
12.4. SWOT Analysis of India Cold Chain Industry
12.5. Government Regulations and Associations in India Cold Chain Market
12.6. Macroeconomic Factors Impacting India Cold Chain Market
13.1. Parameters to be covered for Each End Users to Determine Business Potential:
13.1.1. Production Clusters
13.1.2. Market Demand, Major Products Stored, Cold Storage Companies in Guwahati catering to End Users
13.1.3. Location Preference for Each End User and their Production Plants, Preferences for Outsourcing and Captive Facility, Services Required, Facility Preferences, Decision Making Parameters
13.1.4. Cross comparison of leading end users/companies based on Headquarters, Manufacturing Plants, Products Stored, Major Products, Total Production, Cold Chain Partner, Facility Outsourced/Captive, Pallets Owned/Hired, Contact Person, Address and others
16.1. Competitive Landscape in India Cold Chain Market
16.2. Competition Scenario in India Cold Chain Market (Competition Stage, Major Players, Competing Parameters)
16.3. Key Metrics (Temperature Range, Pallet Position, Prices Charged, Occupancy Rate, Revenue (2023) and Employee Base) for Major Players in India Cold Chain Market
16.4. Company Profiles of Major Companies in India Cold Chain Market (Year of Establishment, Company Overview, Service Offered, USP, Warehousing Facilities, Warehousing Price, Cold Storage by location, Occupancy Rate, Major Clientele, Industries Catered, Employee Base, Temperature Range, Topline OPEX*, Revenue, Recent Developments, Future Strategies)
16.5. Strength and Weakness
16.6. Operating Model Analysis Framework
16.7. Gartner Magic Quadrant
16.8. Bowmans Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
17.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
18.1. By Cold Storage and Cold Transport, 2025-2029
18.2. By End-User Application (Dairy Products, Meat and Seafood, Pharmaceuticals, Fruits and Vegetables and Others), 2025-2029
18.3. By Ownership (Owned and 3PL Cold Chain Facilities), 2025-2029
18.4. Recommendation
18.5. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand side and supply side entities for India Cold Chain Market. Basis this ecosystem, we will shortlist leading 5-6 service providers in the country based upon their financial information, warehousing capacity, reefer fleet size, and geographical presence.
Sourcing is made through industry articles, multiple secondary, and proprietary databases to perform desk research around the market to collate industry-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
Subsequently, we engage in an exhaustive desk research process by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This approach enables us to conduct a thorough analysis of the market, aggregating industry-level insights. We delve into aspects like the market revenues, number of active cold storage units, capacity utilization, demand by commodity, and service gaps. We supplement this with detailed examinations of company-level data, relying on sources like press releases, annual reports, financial statements, and similar documents. This process aims to construct a foundational understanding of both the market and the entities operating within it.
Step 3: Primary Research
We initiate a series of in-depth interviews with C-level executives and other stakeholders representing various India Cold Chain Market companies and end-users. This interview process serves a multi-faceted purpose: to validate market hypotheses, authenticate statistical data, and extract valuable operational and financial insights from these industry representatives. Bottom to top approach is undertaken to evaluate installed capacities and service revenues for each player thereby aggregating to the overall market.
As part of our validation strategy, our team executes disguised interviews wherein we approach each company under the guise of potential customers. This approach enables us to validate the operational and financial information shared by company executives, corroborating this data against what is available in secondary databases. These interactions also provide us with a comprehensive understanding of storage types, reefer vehicle rates, pricing, and other factors.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- Bottom to top and top to bottom analysis along with market size modeling exercises is undertaken to assess sanity check process.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the India Cold Chain Market?
The India cold chain market holds significant growth potential, reaching a valuation of INR 2,100 Billion in 2023. This growth is driven by rising demand from the pharmaceutical, dairy, fruits & vegetables, and seafood sectors, as well as the increasing penetration of organized retail and e-commerce. The market's potential is further supported by government initiatives like the Pradhan Mantri Kisan SAMPADA Yojana (PMKSY), which encourages infrastructure investment across cold storage and transportation segments.
2. Who are the Key Players in the India Cold Chain Market?
The India Cold Chain Market is dominated by key players such as Coldman Logistics, Snowman Logistics, Gati Kausar, Future Supply Chain, and ColdStar Logistics. These companies are recognized for their widespread storage infrastructure, temperature-controlled transportation capabilities, and industry-specific solutions. New entrants and regional players are also expanding aggressively with niche offerings in Tier II and Tier III cities.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the India Cold Chain Market?
The key growth drivers include increasing urbanization and changing food consumption patterns, which have heightened the need for temperature-sensitive logistics. The surge in pharmaceutical exports, expansion of QSR chains, and growing awareness around food safety also contribute to cold chain demand. Moreover, government subsidies and FDI inflow in the logistics sector are accelerating infrastructure development, boosting market growth.
4. What are the Challenges in the India Cold Chain Market?
The India Cold Chain Market faces several challenges, including high capital expenditure, inadequate rural connectivity, and frequent power supply issues that affect cold storage reliability. Fragmented market structures, inconsistent temperature compliance, and lack of skilled personnel also hinder operational efficiency. Moreover, low awareness among small and medium farmers about cold chain benefits limits full market utilization.