India Flex Fuel Vehicle Market Outlook to 2035
By Fuel Compatibility, By Vehicle Type, By Powertrain Architecture, By Sales & Adoption Model, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0490
- Region: Asia
- Published on: January 2026
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “India Flex Fuel Vehicle Market Outlook to 2035 – By Fuel Compatibility, By Vehicle Type, By Powertrain Architecture, By Sales & Adoption Model, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the flex fuel vehicle (FFV) ecosystem in India. The report covers an overview and genesis of the market, overall market size in terms of value and volume, detailed market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory and policy landscape, buyer-level demand profiling, key issues and challenges, and competitive landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major participants in the India flex fuel vehicle market.
The report concludes with future market projections based on India’s biofuel blending roadmap, ethanol availability and pricing dynamics, OEM powertrain localization strategies, infrastructure readiness, consumer acceptance patterns, regional policy execution differences, cause-and-effect relationships, and case-based illustrations highlighting the major opportunities and cautions shaping the market through 2035.
India Flex Fuel Vehicle Market Overview and Size
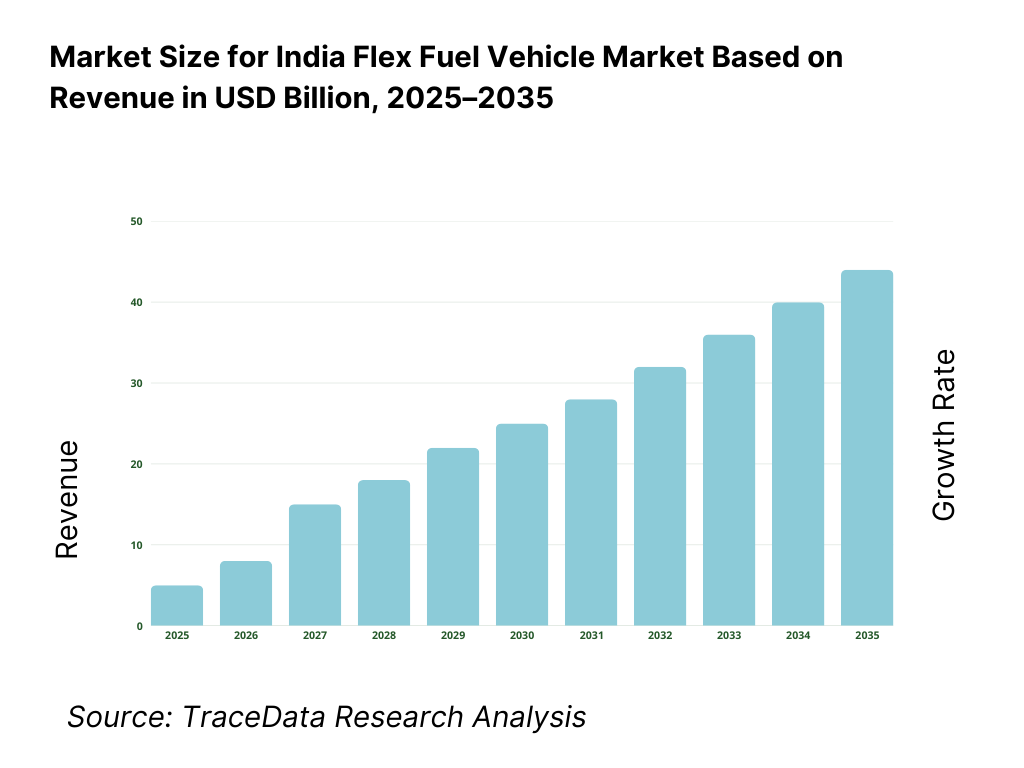
The India flex fuel vehicle market is valued at approximately ~USD ~ billion, representing the production and sale of passenger vehicles and commercial vehicles designed to operate on gasoline–ethanol blended fuels, typically ranging from E20 to E85, through compatible engine calibration, fuel systems, and materials. Flex fuel vehicles are positioned as a transitional mobility solution that enables higher ethanol adoption without requiring a full shift away from internal combustion engine (ICE) platforms.
The market is anchored by India’s aggressive biofuel blending targets, growing domestic ethanol production capacity, and the government’s push to reduce crude oil import dependence while supporting the agricultural economy. Flex fuel vehicles offer a pathway for automakers to align with decarbonization objectives while continuing to leverage existing ICE manufacturing ecosystems, supplier bases, and dealer networks. Their relevance is particularly strong in price-sensitive segments where full electrification faces cost, infrastructure, and range-related adoption barriers.
Passenger vehicles account for the majority of current and near-term flex fuel vehicle adoption, supported by pilot programs, concept launches, and gradual OEM portfolio expansion. Two-wheelers and three-wheelers form an adjacent opportunity pool as higher ethanol blends are progressively approved for smaller engines. Commercial vehicle adoption remains limited but presents long-term potential in fleet and government procurement segments where fuel cost economics and sustainability mandates intersect.
Regionally, flex fuel vehicle adoption potential is highest in states with strong ethanol production bases and blending infrastructure, such as Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Karnataka, and parts of the northern and western regions. These regions benefit from proximity to sugarcane feedstock, ethanol distilleries, and relatively higher readiness of fuel distribution networks. Southern and eastern markets are expected to see phased adoption as infrastructure alignment improves and OEM offerings broaden. Urban centers will act as early demonstration markets, while semi-urban and rural regions are expected to drive volume-led adoption over the medium to long term.
.png)
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the India Flex Fuel Vehicle Market
Government-led ethanol blending mandates create structural demand for flex fuel-compatible vehicles: India’s national biofuel policy and ethanol blending roadmap have set progressively higher blending targets, positioning ethanol as a strategic fuel for energy security, emissions reduction, and agricultural income stabilization. As fuel blends move beyond E20 toward higher ethanol concentrations over time, conventional ICE vehicles face compatibility limitations. Flex fuel vehicles address this challenge by allowing consumers to use a wide range of ethanol–petrol blends without operational or durability risks. This policy-driven transition creates a structural pull for FFV development and commercialization, particularly as regulatory timelines become more explicit and enforcement mechanisms strengthen.
Rising domestic ethanol production improves long-term fuel availability confidence: Significant investments in ethanol distillation capacity, supported by public-sector oil marketing companies and private players, are improving India’s ability to supply blended fuels at scale. Expanded use of sugarcane, surplus grains, and second-generation feedstocks strengthens supply resilience and reduces volatility risks. As ethanol availability becomes more predictable across regions, OEMs gain confidence to scale flex fuel vehicle platforms, and consumers perceive lower risk in adopting ethanol-compatible vehicles. This supply-side stabilization is a critical enabler for sustained FFV market growth.
Flex fuel vehicles offer a cost-effective decarbonization pathway versus full electrification: For both manufacturers and consumers, flex fuel vehicles present a lower incremental cost route to emissions reduction compared to electric vehicles. OEMs can adapt existing ICE platforms with relatively modest changes to engines, fuel systems, and calibration, avoiding large capital investments in new architectures. For consumers, FFVs eliminate range anxiety and charging infrastructure dependence while potentially offering fuel cost savings when ethanol pricing is favorable. This economic logic makes flex fuel vehicles particularly attractive in mass-market passenger segments and in regions where EV infrastructure rollout remains uneven.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of the India Flex Fuel Vehicle Market:
Uncertainty around ethanol availability, pricing stability, and regional supply consistency affects OEM scale-up decisions: While India has made significant progress in expanding ethanol blending, the availability of ethanol at higher blend levels remains uneven across regions and seasons. Ethanol supply is closely linked to agricultural output, feedstock diversion policies, and distillery operating economics, which can result in periodic volatility in pricing and distribution. For automakers, this uncertainty complicates long-term product planning and nationwide rollouts of flex fuel vehicles, as consumer value propositions depend on reliable access to compatible fuel. In regions where ethanol supply confidence is weak, buyers may be hesitant to pay a premium for flex fuel capability, limiting early adoption and slowing volume ramp-up.
Incremental vehicle cost and limited consumer awareness reduce near-term demand traction: Flex fuel vehicles require upgraded fuel systems, corrosion-resistant materials, revised engine calibration, and additional validation, all of which increase vehicle cost compared to standard petrol variants. In a highly price-sensitive market such as India, even modest cost premiums can influence purchase decisions, particularly in mass-market passenger segments. At the same time, consumer awareness of flex fuel technology, its benefits, and its operational differences remains limited. Many buyers do not clearly understand ethanol compatibility, fuel economy trade-offs, or long-term cost implications, which reduces perceived value and delays mainstream acceptance.
Fuel efficiency variability at higher ethanol blends creates perception challenges for consumers: Ethanol has lower energy density than petrol, which can lead to reduced fuel economy when vehicles operate on higher ethanol blends. Although flex fuel vehicles are designed to adapt to varying blends, real-world mileage outcomes can differ based on driving patterns, blend availability, and calibration strategies. In a market where fuel efficiency is a primary purchase criterion, even marginal reductions in kilometers per liter can negatively influence consumer perception. This creates a communication and expectation-management challenge for OEMs, especially in the absence of standardized consumer guidance on blend-specific performance.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
National biofuel policy and ethanol blending targets shaping long-term flex fuel vehicle relevance: India’s biofuel policy framework, including defined ethanol blending targets, forms the structural backbone of the flex fuel vehicle market. These targets are designed to reduce crude oil imports, lower tailpipe emissions, and support domestic agricultural value chains. As blending mandates progressively increase, regulatory pressure mounts on conventional petrol-only vehicles, creating a favorable environment for flex fuel platforms. While timelines may evolve, the long-term policy direction provides a clear signal to OEMs to invest in ethanol-compatible powertrains as part of compliance and transition strategies.
Vehicle emission norms and certification requirements governing engine calibration and durability standards: Flex fuel vehicles must comply with prevailing emission regulations while operating across a wide range of ethanol–petrol blends. This requires rigorous certification, durability testing, and calibration validation to ensure emissions compliance under different operating conditions. Regulatory oversight ensures that higher ethanol usage does not lead to uncontrolled emissions or reliability risks, but it also increases development timelines and validation costs for manufacturers. These technical and regulatory requirements shape the pace at which flex fuel models can be introduced and localized.
Fuel quality standards and material compatibility guidelines influencing OEM engineering choices: Fuel standards governing ethanol purity, water content, and blend consistency directly influence flex fuel vehicle design. Engines, fuel lines, seals, injectors, and tanks must be engineered to withstand ethanol’s corrosive and hygroscopic properties over the vehicle’s lifecycle. Regulatory clarity on fuel specifications helps OEMs standardize designs and reduce risk, but variability in real-world fuel quality can still pose challenges. As standards tighten and enforcement improves, confidence in flex fuel vehicle durability and performance is expected to strengthen.
India Flex Fuel Vehicle Market Segmentation
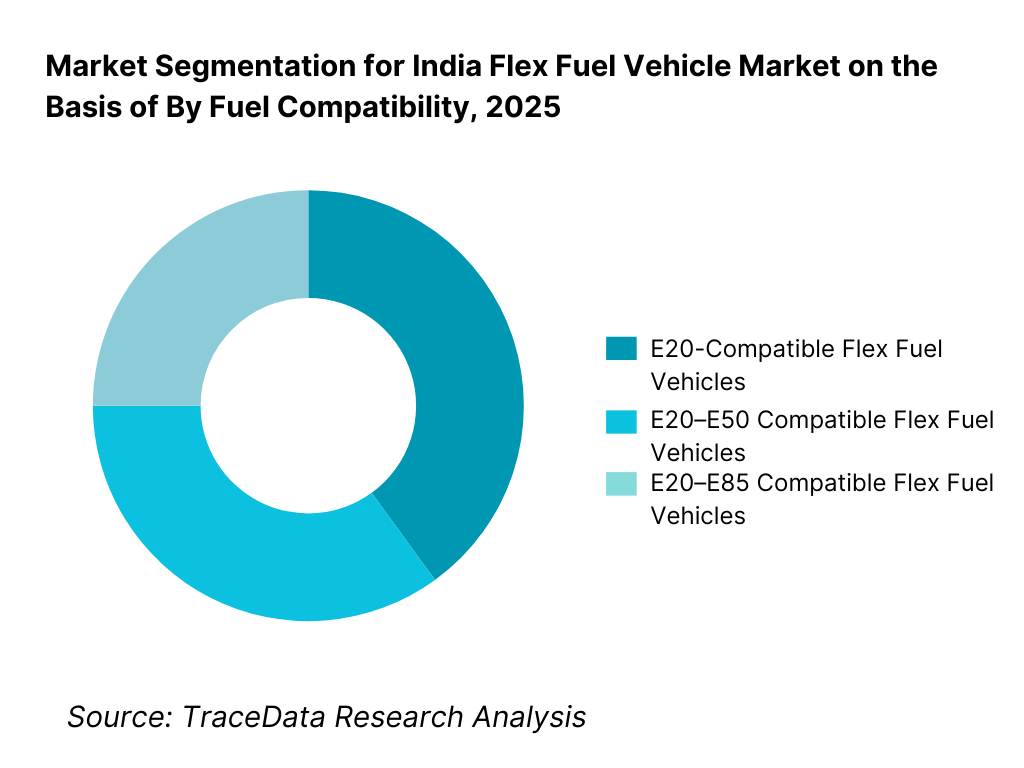
By Fuel Compatibility: The E20–E85 compatible vehicle segment holds long-term strategic dominance in the India flex fuel vehicle market. While current nationwide fuel availability is largely centered around E20, OEMs and policymakers view higher ethanol blend capability as essential for future-proofing vehicle platforms against evolving blending mandates. Vehicles designed for broader blend tolerance allow manufacturers to align with long-term biofuel targets while offering consumers operational flexibility across regions and fuel availability conditions. In the near term, E20-compatible vehicles account for the majority of deployed volumes, but E85-capable architectures are expected to gain share as infrastructure and supply mature.
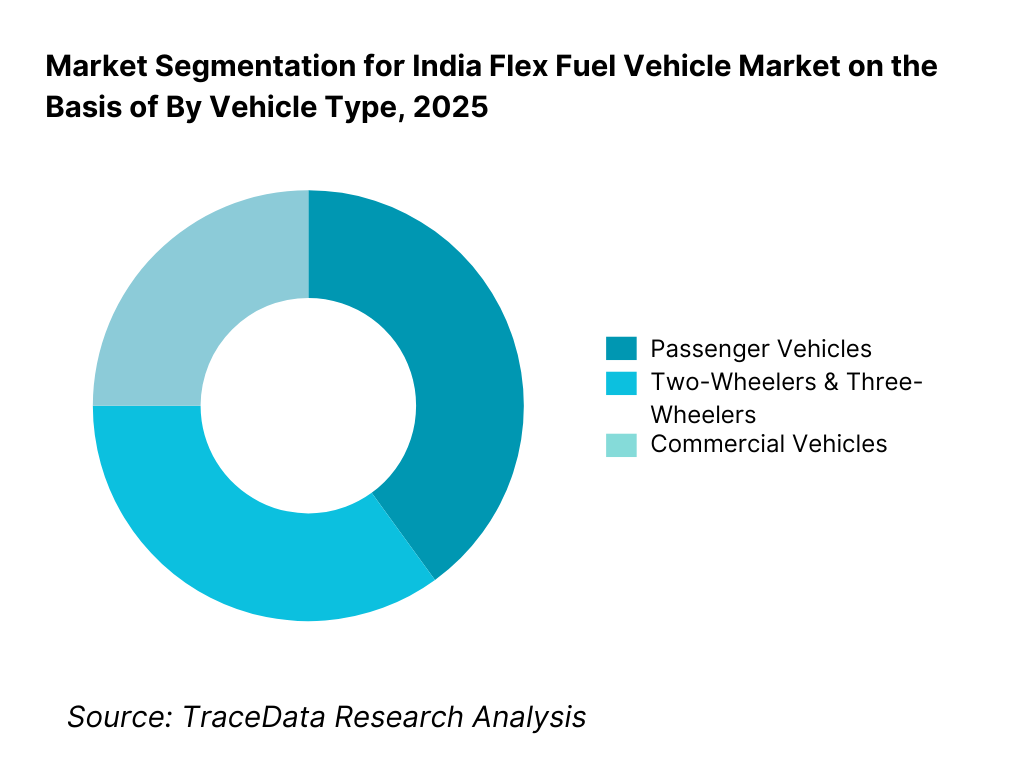
By Vehicle Type: Passenger vehicles dominate the India flex fuel vehicle market, driven by OEM pilot launches, concept introductions, and gradual portfolio expansion in mass and mid-sized segments. Passenger cars represent the most commercially viable pathway for flex fuel adoption due to higher production volumes, faster consumer visibility, and alignment with national emission and fuel transition strategies. Two-wheelers and three-wheelers form an emerging secondary segment, supported by regulatory approvals for higher ethanol blends and their importance in India’s mobility ecosystem. Commercial vehicle adoption remains limited but is expected to develop over the long term, particularly in government fleets and cost-sensitive logistics applications.
Competitive Landscape in India Flex Fuel Vehicle Market
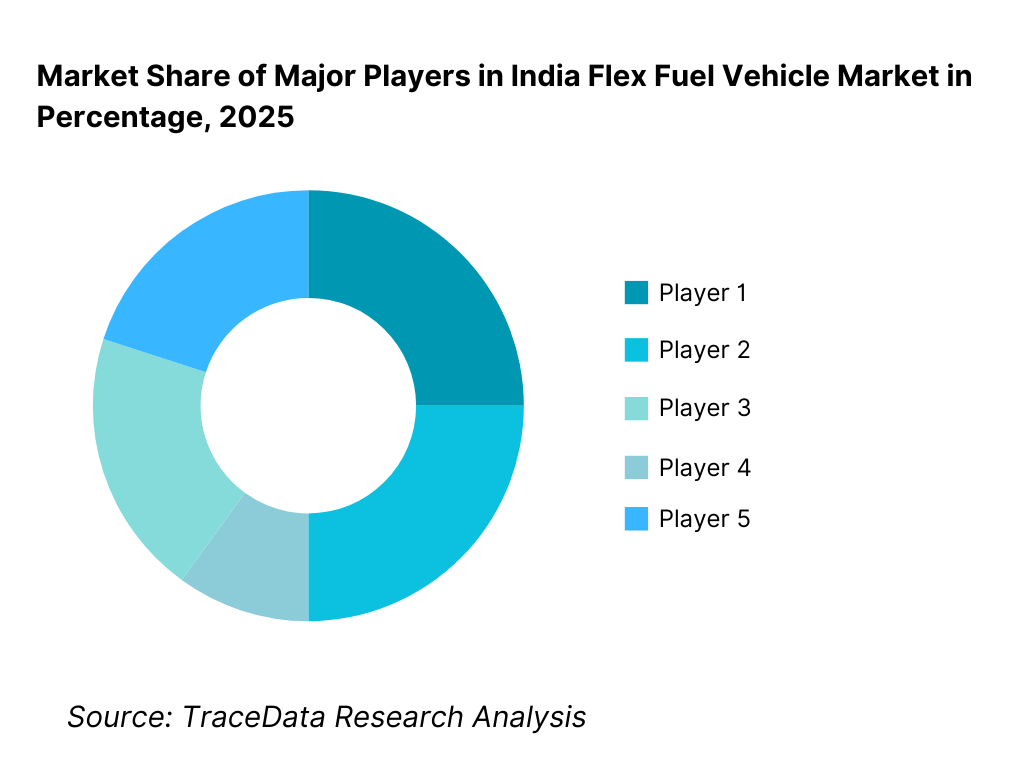
The India flex fuel vehicle market is in an early development stage and exhibits low to moderate concentration, characterized by a small number of domestic OEMs with the engineering scale, regulatory alignment, and manufacturing footprint required to introduce ethanol-compatible platforms. Competitive positioning is shaped less by current sales volumes and more by technology readiness, regulatory engagement, pilot participation, localization capability, and alignment with national biofuel policy direction. Early movers benefit from policy visibility and brand association with sustainability initiatives, while broader competition is expected to intensify as ethanol availability stabilizes and consumer awareness improves.
Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
Tata Motors | 1945 | Mumbai, India |
Maruti Suzuki India | 1981 | New Delhi, India |
Toyota Kirloskar Motor | 1997 | Bengaluru, India |
Mahindra & Mahindra | 1945 | Mumbai, India |
Hyundai Motor India | 1996 | Gurugram, India |
Hero MotoCorp | 1984 | New Delhi, India |
Bajaj Auto | 1945 | Pune, India |
Some of the Recent Competitor Trends and Key Information About Competitors Include:
Tata Motors: Tata Motors has positioned flex fuel technology as part of its broader multi-powertrain transition strategy, alongside electric, CNG, and conventional petrol offerings. The company’s focus lies in developing ethanol-compatible platforms that can be localized efficiently and deployed across mass-market segments, leveraging its strong domestic manufacturing base and policy engagement.
Maruti Suzuki India: As India’s largest passenger vehicle manufacturer, Maruti Suzuki plays a pivotal role in shaping flex fuel adoption trajectories. The company’s approach emphasizes scalability, cost control, and fuel efficiency optimization, with flex fuel compatibility viewed as a compliance-aligned extension of its dominant petrol portfolio rather than a standalone premium offering.
Toyota Kirloskar Motor: Toyota brings global flex fuel experience into the Indian context, focusing on technology validation, long-term durability, and alignment with alternative fuel strategies. The company’s emphasis remains on hybridization and ethanol compatibility as complementary pathways, particularly for mid-sized and premium vehicle segments.
Mahindra & Mahindra: Mahindra’s flex fuel strategy is closely tied to its strength in utility vehicles and rural mobility segments, where ethanol availability and agricultural linkages are structurally stronger. The company’s positioning benefits from alignment with farmer-focused narratives and utility-driven use cases.
Hyundai Motor India: Hyundai’s engagement with flex fuel technology is primarily exploratory, focused on regulatory readiness and portfolio optionality. The company continues to balance investments across petrol, CNG, and electric platforms while monitoring ethanol infrastructure evolution before large-scale flex fuel commercialization.
Hero MotoCorp and Bajaj Auto: In the two-wheeler and three-wheeler segments, Hero and Bajaj are actively evaluating higher ethanol blend compatibility as part of future compliance strategies. Their participation is critical for volume-led ethanol adoption, given the scale of India’s two-wheeler parc and its fuel consumption impact.
What Lies Ahead for India Flex Fuel Vehicle Market?
The India flex fuel vehicle market is expected to expand gradually but structurally through 2035, supported by the country’s long-term biofuel blending roadmap, rising domestic ethanol production capacity, and the need for pragmatic decarbonization pathways within the internal combustion engine ecosystem. Flex fuel vehicles are positioned as a transition technology that enables higher ethanol utilization without requiring a disruptive shift in manufacturing infrastructure or consumer behavior. Growth momentum will be shaped by policy continuity, fuel availability alignment, OEM localization strategies, and consumer acceptance across mass and mid-sized vehicle segments. As India balances energy security, emission reduction, and affordability objectives, flex fuel vehicles are expected to play a complementary role alongside CNG, hybrid, and electric powertrains.
Shift Toward Higher Ethanol Compatibility and Future-Ready Engine Platforms: The future of the India flex fuel vehicle market will see a steady transition from E20-only compatibility toward broader E20–E85 capable platforms. OEMs are increasingly designing engines and fuel systems with higher blend tolerance to future-proof portfolios against evolving blending mandates. This shift allows manufacturers to amortize development investments over longer product cycles while maintaining regulatory flexibility. As ethanol supply stabilizes and fuel retail infrastructure matures, higher-blend-compatible vehicles will gain relevance, particularly in regions with strong biofuel ecosystems.
Integration of Flex Fuel Capability into Mass-Market and High-Volume Segments: Rather than remaining a niche or premium offering, flex fuel capability is expected to be progressively embedded into high-volume passenger vehicle platforms. OEM strategies will prioritize cost optimization, platform sharing, and minimal price premiums to enable broader adoption. The mass-market integration of flex fuel technology will be critical for achieving meaningful ethanol displacement at a national level, given the scale of India’s passenger vehicle parc and annual sales volumes.
Role of Two-Wheelers and Three-Wheelers in Volume-Led Ethanol Adoption: Two-wheelers and three-wheelers will emerge as an important lever for ethanol adoption over the medium to long term due to their dominant share in India’s mobility mix. As regulatory approvals for higher ethanol blends expand and engine durability validation progresses, flex fuel-compatible two- and three-wheelers can deliver significant aggregate fuel substitution benefits. OEMs active in these segments will influence the pace and depth of flex fuel penetration more than any single passenger vehicle program.
Gradual Expansion of Fleet and Institutional Adoption Driven by Fuel Economics: Fleet operators, government agencies, and institutional buyers are expected to adopt flex fuel vehicles selectively where ethanol pricing offers operating cost advantages or where sustainability reporting requirements justify adoption. While fleet penetration will remain smaller than private retail demand, these buyers play an important signaling role by validating commercial viability and supporting early utilization in controlled environments.
India Flex Fuel Vehicle Market Segmentation
By Fuel Compatibility
• E20-Compatible Flex Fuel Vehicles
• E20–E50 Compatible Flex Fuel Vehicles
• E20–E85 Compatible Flex Fuel Vehicles
By Vehicle Type
• Passenger Vehicles
• Two-Wheelers & Three-Wheelers
• Commercial Vehicles
By Powertrain Architecture
• Naturally Aspirated Flex Fuel Engines
• Turbocharged Flex Fuel Engines
• Hybrid-Flex Fuel Architectures
By Sales & Adoption Model
• Private Retail Buyers
• Fleet & Institutional Buyers
• Government & Pilot Programs
By Region
• North & West India
• South India
• East & North-East India
• Central India
Players Mentioned in the Report:
• Tata Motors
• Maruti Suzuki India
• Toyota Kirloskar Motor
• Mahindra & Mahindra
• Hyundai Motor India
• Hero MotoCorp
• Bajaj Auto
• Domestic powertrain suppliers, fuel system manufacturers, and ethanol ecosystem participants
Key Target Audience
• Passenger vehicle, two-wheeler, and commercial vehicle OEMs
• Automotive powertrain and fuel system suppliers
• Ethanol producers and biofuel ecosystem stakeholders
• Oil marketing companies and fuel retail operators
• Fleet operators and institutional vehicle buyers
• Government agencies and transport policy bodies
• Automotive dealers and distribution networks
• Investors tracking alternative fuel and transition mobility opportunities
Time Period:
Historical Period: 2019–2024
Base Year: 2025
Forecast Period: 2025–2035
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4. 1 Vehicle Powertrain and Fuel Compatibility including E20, E20-E50, E20-E85, engine types, fuel system adaptations, and OEM-dealer margins, preferences, strengths, and weaknesses
4. 2 Revenue Streams for Flex Fuel Vehicle Market including vehicle sales, fleet leasing, government procurement, fuel efficiency incentives, and after-sales service
4. 3 Business Model Canvas for Flex Fuel Vehicle Market covering OEMs, component suppliers, dealers, fleet operators, fuel distributors, ethanol producers, and government bodies
5. 1 Global Automotive OEMs vs Regional and Local Players including Tata Motors, Maruti Suzuki, Mahindra & Mahindra, Hyundai, Toyota Kirloskar, Hero MotoCorp, Bajaj Auto, and other domestic or regional manufacturers
5. 2 Investment Model in Flex Fuel Vehicle Market including platform adaptation investments, engine R&D, localization strategies, and pilot programs
5. 3 Comparative Analysis of Vehicle Distribution by Direct-to-Consumer, Dealer Networks, and Fleet Procurement including OEM-dealer linkages and fleet integration strategies
5. 4 Consumer Vehicle Budget Allocation comparing flex fuel vehicle purchase versus conventional petrol, hybrid, and electric vehicles with average spend per household or fleet operator
8. 1 Revenues from historical to present period
8. 2 Growth Analysis by vehicle type, powertrain architecture, and fuel compatibility
8. 3 Key Market Developments and Milestones including government blending mandates, OEM flex fuel launches, component supplier expansions, and pilot fleet programs
9. 1 By Market Structure including global OEMs, regional OEMs, and local manufacturers
9. 2 By Vehicle Type including passenger vehicles, two-wheelers, three-wheelers, and commercial vehicles
9. 3 By Fuel Compatibility including E20, E20-E50, and E20-E85
9. 4 By User Segment including private buyers, fleet operators, and government or institutional buyers
9. 5 By Consumer Demographics including age groups, income levels, and urban versus semi-urban users
9. 6 By Vehicle Type including engine architecture, naturally aspirated, turbocharged, and hybrid-flex fuel platforms
9. 7 By Sales & Adoption Model including retail, fleet, and pilot/government programs
9. 8 By Region including North, South, East, West, and Central India
10. 1 Consumer Landscape and Cohort Analysis highlighting early adopters, urban dominance, and fleet concentration
10. 2 Vehicle Selection and Purchase Decision Making influenced by fuel availability, pricing, performance, and incentives
10. 3 Engagement and ROI Analysis measuring fuel savings, total cost of ownership, and utilization rates
10. 4 Gap Analysis Framework addressing infrastructure gaps, pricing affordability, and OEM-dealer coverage
11. 1 Trends and Developments including rising ethanol blending mandates, flex fuel pilot launches, and OEM platform adaptations
11. 2 Growth Drivers including government incentives, domestic ethanol capacity growth, and regulatory alignment
11. 3 SWOT Analysis comparing global OEM scale versus local content and regional fuel infrastructure
11. 4 Issues and Challenges including fuel availability variability, incremental vehicle cost, consumer awareness, and infrastructure readiness
11. 5 Government Regulations covering biofuel blending mandates, vehicle certification requirements, and fuel quality standards
12. 1 Market Size and Future Potential of fleet, private, and institutional flex fuel vehicle adoption
12. 2 Business Models including outright purchase, leasing, and government fleet programs
12. 3 Distribution Models and Type of Solutions including OEM-dealer networks, direct sales, and fleet partnerships
15. 1 Market Share of Key Players by revenues and vehicle volumes
15. 2 Benchmark of 15 Key Competitors including Tata Motors, Maruti Suzuki, Mahindra & Mahindra, Hyundai, Toyota Kirloskar, Hero MotoCorp, Bajaj Auto, and regional or niche manufacturers
15. 3 Operating Model Analysis Framework comparing global OEM models, regional platform strategies, and fleet-integrated models
15. 4 Gartner Magic Quadrant positioning global leaders and regional challengers in flex fuel vehicle adoption
15. 5 Bowman’s Strategic Clock analyzing competitive advantage through differentiation via technology, price, and fuel compatibility
16. 1 Revenues with projections
17. 1 By Market Structure including global OEMs, regional OEMs, and local manufacturers
17. 2 By Vehicle Type including passenger vehicles, two-wheelers, three-wheelers, and commercial vehicles
17. 3 By Fuel Compatibility including E20, E20-E50, and E20-E85
17. 4 By User Segment including private buyers, fleet operators, and government or institutional users
17. 5 By Consumer Demographics including age and income groups
17. 6 By Vehicle Type including engine architecture, naturally aspirated, turbocharged, and hybrid-flex fuel platforms
17. 7 By Sales & Adoption Model including retail, fleet, and pilot/government programs
17. 8 By Region including North, South, East, West, and Central India
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
We begin by mapping the complete ecosystem of the India Flex Fuel Vehicle Market across demand-side and supply-side entities. On the demand side, entities include private retail vehicle buyers, fleet operators, government and public-sector agencies, ride-hailing and mobility service providers, and institutional buyers adopting vehicles for operational or pilot use. Demand is further segmented by vehicle type (passenger vehicles, two-wheelers, three-wheelers, commercial vehicles), fuel compatibility level (E20, E20–E50, E20–E85), usage profile (urban commuting, intercity travel, fleet operations), and adoption model (private ownership, fleet purchase, government pilots).
On the supply side, the ecosystem includes passenger vehicle OEMs, two- and three-wheeler manufacturers, engine and powertrain developers, fuel system suppliers, ethanol-compatible material and component manufacturers, testing and certification agencies, oil marketing companies, ethanol producers and distilleries, fuel retail infrastructure operators, regulatory bodies, and policy institutions governing fuel standards and vehicle compliance. From this mapped ecosystem, we shortlist leading OEMs and representative component suppliers based on production scale, powertrain capability, regulatory engagement, pilot participation, and readiness for higher ethanol blends. This step establishes how value is created and captured across vehicle development, manufacturing, fuel compatibility, distribution, and end-user adoption.
Step 2: Desk Research
An exhaustive desk research process is undertaken to analyze the structure and evolution of the India flex fuel vehicle market. This includes reviewing national biofuel policy direction, ethanol blending targets, domestic ethanol production capacity, fuel pricing dynamics, and infrastructure rollout progress. We assess vehicle parc composition, sales trends by segment, and OEM product roadmaps related to flex fuel compatibility.
Company-level analysis includes evaluation of OEM powertrain strategies, localization efforts, pilot vehicle launches, regulatory certifications, and alignment with alternative fuel pathways such as CNG, hybrid, and electric vehicles. We also examine consumer behavior related to fuel efficiency sensitivity, price elasticity, and awareness of ethanol-blended fuels. The outcome of this stage is a robust industry foundation that defines segmentation logic and establishes baseline assumptions for market sizing and long-term outlook modeling.
Step 3: Primary Research
We conduct structured interviews with passenger vehicle OEMs, two-wheeler and three-wheeler manufacturers, powertrain engineers, fuel system suppliers, ethanol ecosystem stakeholders, oil marketing companies, dealers, and fleet operators. The objectives are threefold: (a) validate assumptions related to adoption pace, regional readiness, and OEM commitment levels, (b) authenticate segmentation splits by vehicle type, fuel compatibility, and buyer category, and (c) gather qualitative insights on incremental vehicle cost, fuel economy impact, consumer perception, infrastructure gaps, and regulatory execution challenges.
A bottom-to-top approach is applied by estimating vehicle sales volumes across segments and regions, adjusted for flex fuel penetration rates, which are aggregated to develop the overall market view. In selected cases, disguised interactions with dealers and fleet buyers are conducted to validate on-ground realities such as consumer queries, fuel availability concerns, and the practical value proposition of flex fuel vehicles versus conventional petrol alternatives.
Step 4: Sanity Check
The final stage integrates bottom-to-top and top-to-down approaches to cross-validate market estimates, segmentation splits, and forecast assumptions. Demand projections are reconciled with macro indicators such as vehicle sales growth, ethanol production expansion, crude oil import trends, and policy-driven blending timelines. Assumptions around fuel pricing, consumer acceptance, and infrastructure rollout are stress-tested to assess their impact on adoption scenarios.
Sensitivity analysis is conducted across key variables including ethanol availability consistency, incremental vehicle pricing, fuel economy differentials, and policy continuity. Market models are refined until alignment is achieved between OEM supply readiness, fuel ecosystem capacity, and realistic consumer adoption behavior, ensuring internal consistency and credible forecasting through 2035.
FAQs
01 What is the potential for the India Flex Fuel Vehicle Market?
The India Flex Fuel Vehicle Market holds medium-to-long-term structural potential, driven by national ethanol blending mandates, rising domestic ethanol production, and the need for cost-effective decarbonization pathways within the internal combustion engine ecosystem. Flex fuel vehicles are positioned as a transition solution that enables higher biofuel utilization without disrupting existing manufacturing infrastructure or consumer usage patterns. As fuel availability improves and OEM offerings expand, flex fuel vehicles are expected to play a complementary role in India’s multi-powertrain mobility transition through 2035.
02 Who are the Key Players in the India Flex Fuel Vehicle Market?
The market is shaped by leading domestic and international OEMs with strong petrol vehicle portfolios and the engineering capability to localize ethanol-compatible powertrains. Competition is currently driven by regulatory readiness, pilot participation, and alignment with national biofuel objectives rather than large-scale commercial volumes. Over time, broader OEM participation is expected as ethanol infrastructure matures and flex fuel capability becomes embedded in high-volume vehicle platforms.
03 What are the Growth Drivers for the India Flex Fuel Vehicle Market?
Key growth drivers include government-led ethanol blending targets, expansion of domestic ethanol production capacity, rising focus on energy security, and the relatively low incremental cost of flex fuel technology compared to full electrification. OEM strategies to extend the lifecycle of ICE platforms, combined with consumer preference for familiar fueling behavior, further support adoption. The large base of petrol vehicles in India provides a scalable foundation for flex fuel penetration over the long term.
04 What are the Challenges in the India Flex Fuel Vehicle Market?
Challenges include uneven ethanol availability across regions, incremental vehicle cost sensitivity in a price-driven market, limited consumer awareness of flex fuel benefits, and concerns around fuel efficiency at higher ethanol blends. Infrastructure readiness at fuel retail outlets and variability in fuel quality also influence adoption pace. Addressing these challenges through policy alignment, consumer education, and infrastructure scaling will be critical to unlocking sustained market growth.