India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market Outlook to 2035
By Pump Type, By Fuel Type, By End-Use Sector, By Distribution Channel, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0467
- Region: Asia
- Published on: January 2026
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market Outlook to 2035 – By Pump Type, By Fuel Type, By End-Use Sector, By Distribution Channel, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the fuel transfer pumps industry in India. The report covers an overview and genesis of the market, overall market size in terms of value, detailed market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory and safety landscape, buyer-level demand profiling, key issues and challenges, and competitive landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players operating in the Indian fuel transfer pumps market.
The report concludes with future market projections based on industrial fuel consumption trends, expansion of fuel retail and storage infrastructure, growth in construction, mining, agriculture, and backup power systems, modernization of logistics and fleet operations, regional demand drivers, cause-and-effect relationships, and case-based illustrations highlighting the major opportunities and cautions shaping the market through 2035.
India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market Overview and Size
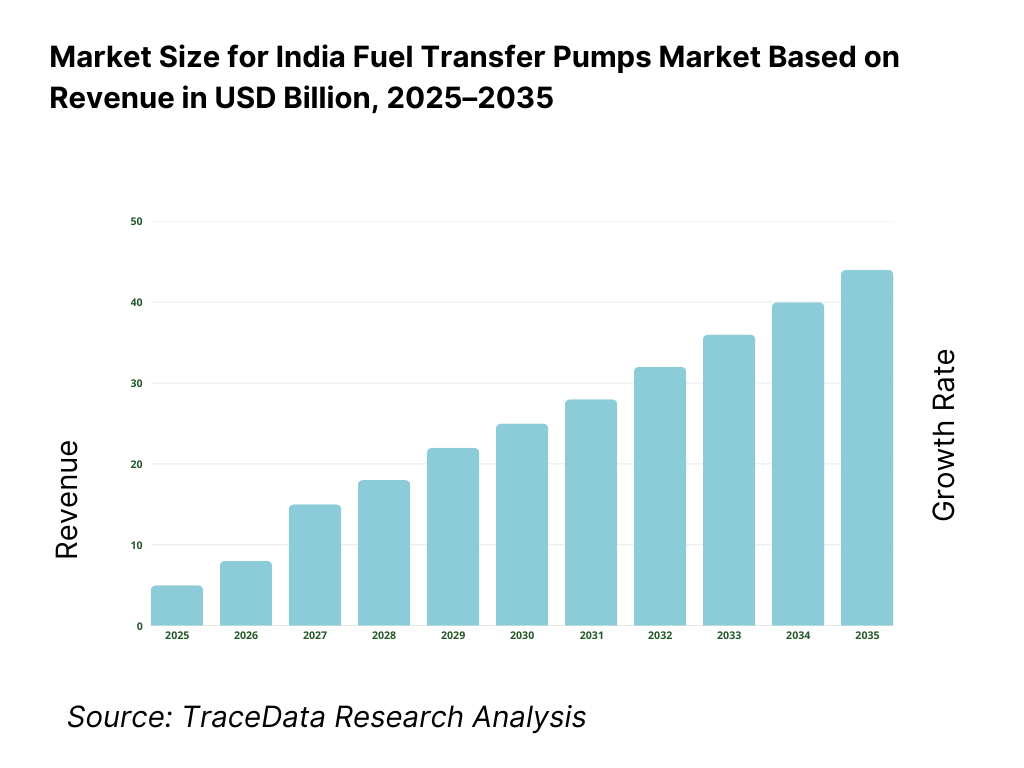
The India fuel transfer pumps market is valued at approximately ~USD ~ million, representing the supply of mechanical and electromechanical pumping solutions used for the safe and efficient transfer of liquid fuels such as diesel, petrol, kerosene, aviation turbine fuel (ATF), and biofuels from storage tanks to vehicles, machinery, generators, and intermediate containers. Fuel transfer pumps include manual, AC-powered, DC-powered, and engine-driven pumps, typically supplied as standalone units or integrated systems comprising motors, impellers, hoses, flow meters, filters, nozzles, and safety accessories.
The market is anchored by India’s large base of diesel-dependent applications, including construction equipment, agricultural machinery, mining fleets, industrial generators, telecom towers, and commercial transport vehicles. Fuel transfer pumps are critical enablers of decentralized fuel handling, particularly in locations without direct access to fuel dispensing infrastructure. The widespread use of diesel gensets for backup power, combined with fuel storage norms across industrial and commercial sites, sustains consistent baseline demand for these pumps.
Infrastructure development, industrialization, and urban expansion continue to drive fuel handling requirements across both organized and unorganized sectors. Small workshops, fleet operators, farms, and project sites often rely on portable or skid-mounted fuel transfer pumps for operational flexibility. At the same time, organized buyers such as oil marketing companies (OMCs), logistics firms, and large industrial plants demand higher-capacity, metered, and safety-compliant pumping systems.
Regionally, North and West India represent the largest demand centers, supported by concentration of construction activity, manufacturing clusters, logistics hubs, and large agricultural belts. Western states benefit from strong industrialization, port-linked fuel movement, and refinery-adjacent storage infrastructure. South India shows steady demand driven by industrial parks, commercial real estate, and telecom infrastructure, while East and Central India are emerging growth regions supported by mining activity, road construction, irrigation projects, and expanding diesel-based power applications in semi-urban and rural areas.
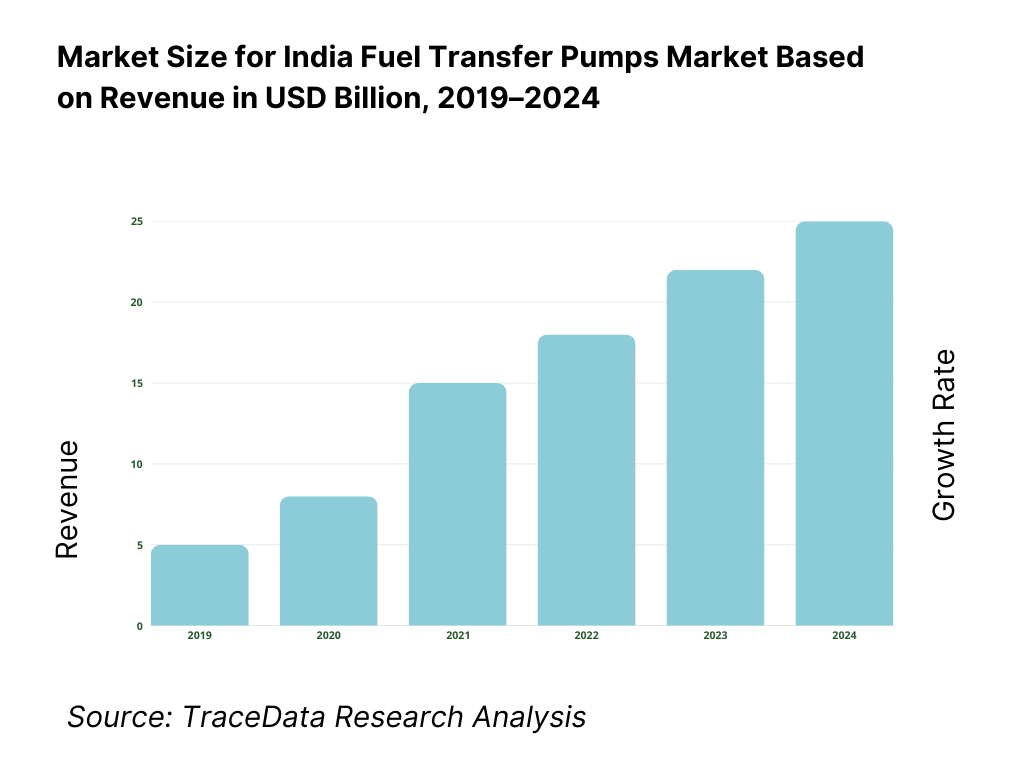
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market
Expansion of construction, infrastructure, and mining activity sustains diesel handling demand: India’s ongoing investments in highways, metro rail, airports, irrigation, and mining projects require extensive use of diesel-powered equipment such as excavators, loaders, cranes, and generators. Fuel transfer pumps enable on-site refueling, reducing downtime and improving equipment utilization. Portable and high-flow diesel transfer pumps are particularly favored at project sites where centralized fuel dispensing is not feasible. As infrastructure execution timelines tighten, reliable fuel handling solutions become essential operational tools.
High dependence on diesel generators across commercial and industrial facilities supports recurring replacement demand: Despite grid expansion, diesel generators remain a critical backup power source for hospitals, data centers, telecom towers, manufacturing units, commercial buildings, and residential complexes. These facilities typically store diesel in bulk tanks and require fuel transfer pumps for refilling gensets, maintaining fuel circulation, and managing stock. Regular wear, safety upgrades, and compliance needs drive replacement and upgrade demand, particularly for electrically driven and metered pump systems.
Growth of agriculture mechanization and rural fuel handling increases penetration of small and portable pumps: Indian agriculture continues to rely heavily on diesel-powered tractors, irrigation pumps, harvesters, and allied equipment, especially in regions with limited electric power availability. Farmers, cooperatives, and agri-service providers increasingly use compact and affordable fuel transfer pumps to manage diesel storage and refueling at farms and rural depots. Seasonal usage patterns and price sensitivity shape demand toward simple, durable, and easy-to-maintain pump designs.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of the India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market:
Price sensitivity and fragmentation across unorganized suppliers impact margin stability and quality consistency: The India fuel transfer pumps market is characterized by a large number of small, regional, and unorganized manufacturers offering low-cost pumps, particularly for diesel applications. While this improves affordability for small users, it creates intense price competition and compresses margins for organized and branded players. In many cases, buyers prioritize upfront cost over durability, safety certifications, or lifecycle performance, leading to inconsistent product quality in the market. This fragmentation also makes it difficult for organized suppliers to enforce standard pricing, invest in product innovation, or scale premium offerings.
Dependence on imported components exposes manufacturers to supply chain volatility and currency risk: Many fuel transfer pumps—especially electrically driven and higher-capacity variants—rely on imported motors, seals, bearings, electrical components, and metering systems. Fluctuations in global commodity prices, freight costs, and foreign exchange rates can impact manufacturing costs and delivery timelines. During periods of import disruption or currency depreciation, suppliers face challenges in maintaining price commitments to customers, which can delay procurement decisions and reduce competitiveness in tender-driven or project-based demand.
Limited awareness of safety standards and improper fuel handling practices restrict adoption of compliant systems: In several end-use segments, particularly small construction sites, farms, workshops, and rural operations, fuel transfer pumps are often selected without adequate consideration of fire safety, grounding, spill prevention, or motor protection requirements. Improper installation and usage increase operational risk and can lead to pump failures, accidents, or regulatory non-compliance. The lack of widespread awareness and enforcement limits demand for certified, explosion-protected, or safety-enhanced fuel transfer systems, slowing the transition toward higher-value products.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
Fire safety norms, petroleum storage guidelines, and local authority approvals influencing equipment selection: Fuel transfer pumps used in bulk storage, commercial premises, and industrial facilities are governed by fire safety regulations and petroleum storage guidelines issued by local fire departments and regulatory bodies. Requirements related to safe electrical fittings, earthing, flameproof motors (in specific applications), and controlled dispensing influence pump specifications, especially for organized buyers. Compliance with these norms is critical for approvals, insurance coverage, and operational licensing, shaping demand toward safer and more standardized pump systems.
Electrical standards and motor efficiency regulations affecting design and component choices: Electrically operated fuel transfer pumps must comply with applicable electrical safety standards related to insulation, overload protection, and motor performance. Increasing emphasis on energy efficiency and standardized motor ratings influences the selection of AC and DC motors used in pump assemblies. While these requirements improve safety and efficiency, they can increase manufacturing costs and create challenges for smaller suppliers transitioning to compliant designs.
Environmental and spill-prevention considerations shaping handling practices at industrial and commercial sites: Growing attention to environmental protection and pollution control has increased scrutiny of fuel handling practices, particularly in industrial plants, logistics hubs, and large infrastructure projects. Measures related to spill containment, controlled dispensing, and leak prevention indirectly influence the adoption of better-quality fuel transfer pumps with integrated hoses, nozzles, filters, and flow control features. Although enforcement varies by region, these considerations are gradually raising expectations around equipment reliability and operational discipline.
India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market Segmentation
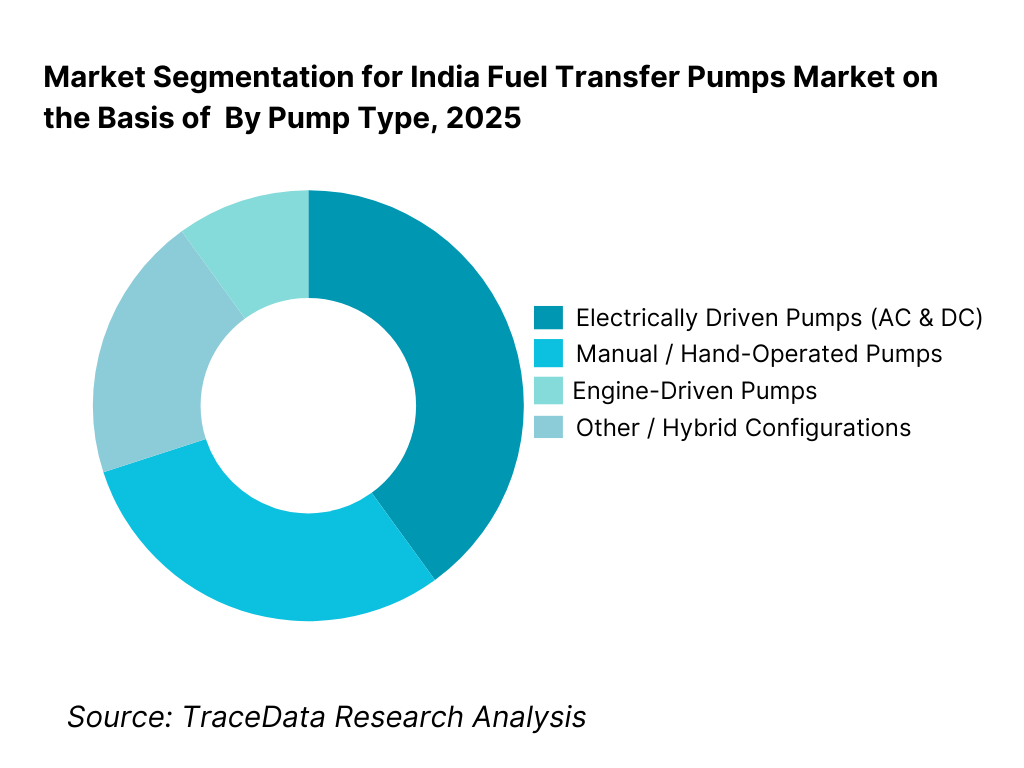
By Pump Type: Electrically driven pumps dominate the India fuel transfer pumps market, driven by their ease of operation, higher flow rates, and suitability for continuous-duty applications in industrial, commercial, and fleet environments. AC-powered pumps are widely used in factories, warehouses, fuel depots, and commercial buildings where grid power is available, while DC-powered pumps are preferred in mobile and off-grid applications such as construction sites, mining areas, and fleet refueling yards. Manual and engine-driven pumps continue to serve price-sensitive and remote-use segments but are gradually losing share in organized procurement.
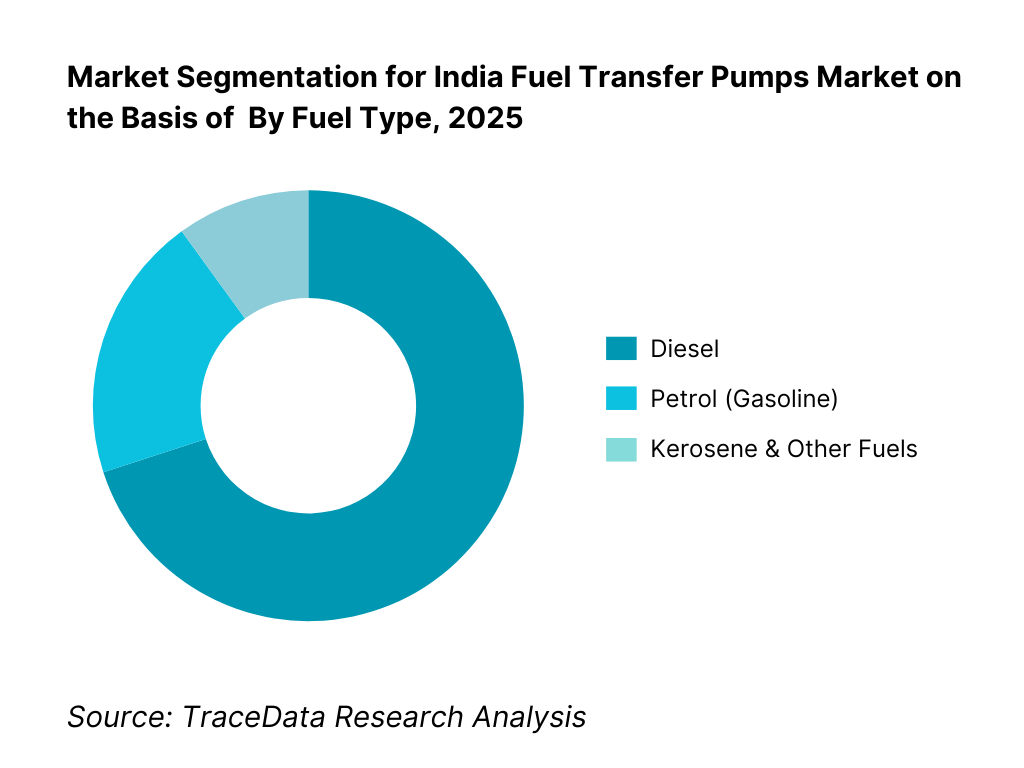
By Fuel Type: Diesel accounts for the overwhelming share of demand due to its dominant use across construction equipment, generators, agricultural machinery, transport fleets, and industrial backup power systems. Petrol transfer pumps are used mainly in workshops, small depots, and service applications, while kerosene and other fuels represent niche demand. Emerging interest in biofuels and blended fuels is present but remains limited in volume terms.
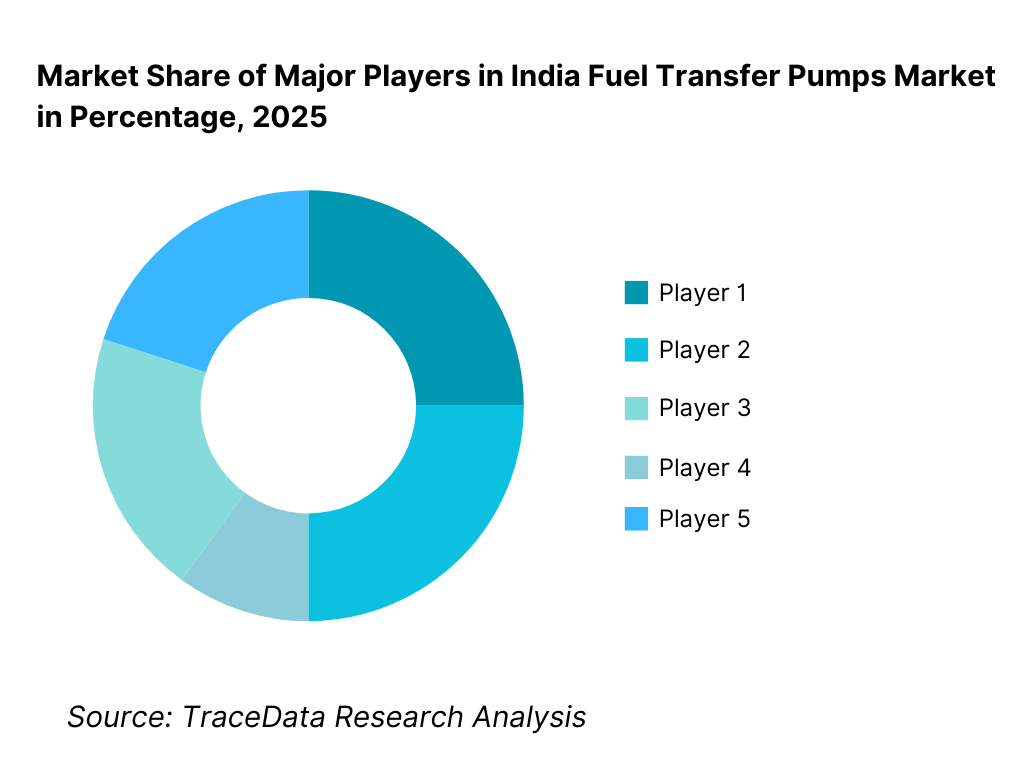
Competitive Landscape in India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market
The India fuel transfer pumps market exhibits high fragmentation, with a mix of organized manufacturers, regional engineering firms, and a large unorganized segment supplying low-cost pumps. Competition is primarily driven by pricing, availability, flow rate specifications, and basic reliability, particularly in diesel-focused applications. Organized players differentiate through product range depth, motor quality, safety compliance, warranties, and after-sales support, while unorganized suppliers compete aggressively on upfront price and customization for local needs.
Market leadership in the organized segment is shaped by manufacturing capability, breadth of pump configurations (manual, AC, DC), distribution reach across industrial clusters and rural markets, and the ability to supply bundled systems including hoses, meters, and dispensing accessories. Import dependence for motors and components remains a key factor influencing cost structures and competitive positioning.
Key Players Operating in the India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market:
Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
Kirloskar Brothers Limited | 1888 | Pune, Maharashtra, India |
CRI Pumps | 1961 | Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India |
Texmo Industries (Texmo / Aquagroup) | 1956 | Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India |
Crompton Greaves Consumer Electricals (Industrial Pumps) | 1937 | Mumbai, Maharashtra, India |
Shakti Pumps | 1982 | Pithampur, Madhya Pradesh, India |
KSB Limited (India operations) | 1960 | Pune, Maharashtra, India |
Regional & Unorganized Manufacturers | — | Various locations across India |
Some of the Recent Competitor Trends and Key Information About Competitors Include:
Kirloskar Brothers Limited: Kirloskar remains a reference brand in industrial pumping solutions, with fuel transfer pumps benefiting from strong motor integration, reliability perception, and established relationships with industrial and institutional buyers. The company’s focus on engineered solutions and service coverage supports demand from infrastructure, manufacturing, and utility-linked projects.
CRI Pumps: CRI has built competitiveness through a wide portfolio of electrical pump systems and strong penetration in both urban and semi-urban markets. Its strength lies in scalable manufacturing, cost competitiveness, and extensive dealer networks, making it well-positioned for diesel transfer applications in agriculture, construction, and small industries.
Texmo Industries: Texmo competes effectively in price-sensitive segments by offering robust and simple pump designs suited for rural, agricultural, and small commercial use. The company benefits from deep reach into tier-2 and tier-3 markets where affordability and ease of maintenance are primary buying criteria.
KSB Limited: KSB’s presence in the fuel transfer pump space is linked to its broader industrial pumping portfolio. The company is typically specified in higher-capacity, safety-critical, or industrial-grade applications where compliance, engineering support, and lifecycle performance outweigh upfront cost considerations.
Unorganized and Regional Players: A large number of small manufacturers supply locally assembled fuel transfer pumps, often customized to customer specifications. While these players dominate volumes in certain regions, inconsistent quality, limited warranties, and weak after-sales capability constrain their participation in large institutional and regulated projects.
What Lies Ahead for India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market?
The India fuel transfer pumps market is expected to expand steadily by 2035, supported by rising fuel handling needs across construction and infrastructure execution, growth in diesel-dependent industrial and commercial backup power systems, increasing fleet and logistics formalization, and the ongoing expansion of bulk fuel storage and decentralized refueling practices across Tier-2/Tier-3 India. Growth momentum is further strengthened by a gradual shift from low-cost, basic pumps toward more reliable, safer, and metered dispensing systems as institutional procurement standards tighten and buyers prioritize control, accountability, and reduced operational risk. As fuel logistics becomes more structured across industrial sites, fleet depots, and large project locations, fuel transfer pumps will remain a core enabling solution for day-to-day operations across multiple end-use sectors.
Transition Toward Metered, Controlled Dispensing and Higher Reliability Systems: The future of the India fuel transfer pumps market will see increasing movement from basic transfer pumps toward controlled dispensing solutions that include flow meters, auto shut-off nozzles, filters, and improved hose and coupling systems. Fleet owners, construction contractors, and industrial facilities are expected to prioritize fuel accountability and pilferage reduction, creating demand for higher-quality systems with calibration-friendly metering and better lifecycle performance. Suppliers offering robust metered packages, safety-compliant electrical protection, and standardized accessories will be positioned to capture higher-value demand.
Growing Role of Construction, Mining, and Infrastructure Projects in Driving Portable and High-Flow Requirements: Large infrastructure projects and expanding mining activities will increase demand for portable DC pumps and high-flow transfer systems used for on-site refueling of equipment and generators. Buyers in these segments will increasingly value rugged designs that can operate in dusty, high-temperature, and remote environments with minimal downtime. Through 2035, project-based demand will continue to create opportunities for suppliers that can deliver dependable performance, fast availability, and reliable after-sales support across key project corridors.
Expansion of Fleet Refueling Yards and Depot-Level Fuel Management Practices: As transport fleets, logistics operators, and depot-based vehicle management scale up, in-house refueling infrastructure is expected to expand, particularly for commercial trucks, buses, and multi-vehicle fleets. This will strengthen demand for fixed and semi-fixed installations, including AC pump systems, skid-mounted dispensing units, and metered solutions integrated with basic monitoring. The economic logic will be driven by reduced retail fueling dependency, improved turnaround times, and greater control over fuel consumption and losses.
Increasing Adoption of Safety-Compliant and Application-Specific Configurations in Organized Procurement: Organized buyers—industrial plants, large contractors, PSUs, utilities, and institutional facilities—are expected to increasingly specify safety-oriented configurations such as enclosed motors, better grounding provisions, improved sealing, and application-specific compatibility (diesel vs petrol vs kerosene). In select use cases such as bulk storage, sensitive industrial zones, and controlled premises, demand for flameproof/explosion-protected configurations may rise. Suppliers aligned with compliance documentation, consistent specifications, and service support will gain share in formal procurement channels.
India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market Segmentation
By Pump Type
• Electrically Driven Pumps (AC)
• Electrically Driven Pumps (DC)
• Manual / Hand-Operated Pumps
• Engine-Driven Pumps
• Other / Hybrid Configurations
By Fuel Type
• Diesel
• Petrol (Gasoline)
• Kerosene
• ATF / Aviation Applications (Niche)
• Other Fuels (including biofuel blends, niche industrial liquids)
By End-Use Sector
• Construction, Infrastructure & Industrial
• Transport & Logistics Fleets
• Agriculture
• Oil & Gas / Fuel Storage & Handling (depots, bulk storage, contractors)
• Commercial / Residential & Others
By Distribution Channel
• Distributors & Dealers
• Direct Institutional / Project Sales
• Retail & Online Channels
• OEM / Bundled Sales (with tanks, dispensing skids, genset fueling kits)
By Region
• North India
• West India
• South India
• East & Central India
Players Mentioned in the Report:
• Kirloskar Brothers Limited
• CRI Pumps
• Texmo Industries
• Crompton (Industrial Pumps)
• Shakti Pumps
• KSB Limited
• Regional fuel transfer pump assemblers, industrial equipment distributors, and unorganized manufacturers
Key Target Audience
• Fuel transfer pump manufacturers and component suppliers (motors, seals, hoses, meters)
• Industrial equipment distributors and dealer networks
• Construction contractors, EPC companies, and infrastructure project operators
• Mining operators and equipment fleet managers
• Transport and logistics fleet owners, bus depots, and fleet management companies
• Industrial plants, warehouses, and commercial facilities using bulk diesel storage and gensets
• Oil marketing ecosystem participants (storage contractors, depot operators, fuel handling integrators)
• Government/PSU procurement bodies and institutional buyers
• Investors and strategic buyers evaluating industrial equipment categories in India
Time Period:
Historical Period: 2019–2024
Base Year: 2025
Forecast Period: 2025–2035
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4. 1 Delivery Model Analysis for Fuel Transfer Pumps-Manual, AC-Powered, DC-Powered, Engine-Driven [Margins, Preference, Strength & Weakness]
4. 2 Revenue Streams for India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market [Pump Sales, Metering Accessories, Hoses & Nozzles, Skid-Mounted Systems, After-Sales & Spares]
4. 3 Business Model Canvas for India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market [Key Partners, Key Activities, Value Propositions, Customer Segments, Cost Structure, Revenue Streams]
5. 1 Local Players vs Global Vendors [Indian Manufacturers vs Imported Brands]
5. 2 Investment Model in India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market [Capex Manufacturing, Channel Expansion, Product Localization, Service Network Investments]
5. 3 Comparative Analysis of Fuel Transfer Pump Adoption in Organized vs Unorganized Buyers [Procurement Models, Use Cases, Cost vs Compliance Focus]
5. 4 Fuel Transfer Pump Budget Allocation by Buyer Type [Large Enterprises, MSMEs, Contractors, Fleet Operators, Agriculture Users]
8. 1 Revenues (Historical Trend)
9. 1 By Market Structure (Organized Manufacturers vs Unorganized / Regional Suppliers)
9. 2 By Pump Type (Manual, AC Electric, DC Electric, Engine-Driven)
9. 3 By Fuel Type (Diesel, Petrol, Kerosene, ATF, Others)
9. 4 By End-Use Sector (Construction & Infrastructure, Industrial & Manufacturing, Agriculture, Transport & Logistics, Commercial & Institutional)
9. 5 By Application / Use Case (On-Site Equipment Refueling, Genset Fuel Transfer, Fleet Depot Refueling, Bulk Storage Transfer, Mobile Refueling)
9. 6 By Power Source (Electric Grid, Battery, Engine-Driven)
9. 7 By Standard vs Metered Fuel Transfer Systems
9. 8 By Region (North India, West India, South India, East & Central India)
10. 1 Buyer Landscape and Cohort Analysis (Contractors, Fleet Operators, Industrial Plants, Farmers, PSUs)
10. 2 Fuel Transfer Pump Adoption Drivers & Purchase Decision-Making Process
10. 3 Operational Effectiveness & ROI Analysis (Downtime Reduction, Fuel Loss Control, Cost Savings)
10. 4 Gap Analysis Framework
11. 1 Trends & Developments in India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market
11. 2 Growth Drivers for India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market
11. 3 SWOT Analysis for India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market
11. 4 Issues & Challenges for India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market
11. 5 Government Regulations and Safety Norms for India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market
12. 1 Market Size and Future Potential for Electric Fuel Transfer Pumps in India
12. 2 Business Models & Revenue Streams [Pump Sales, Metering Systems, Integrated Fuel Handling Kits]
12. 3 Delivery Models & Applications Offered [Portable Pumps, Fixed Installations, Skid-Mounted Fuel Dispensing Systems]
15. 1 Market Share of Key Players in India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market (By Revenues)
15. 2 Benchmark of Key Competitors [Company Overview, USP, Business Strategies, Product Portfolio, Manufacturing Capacity, Revenues, Pricing Strategy, Distribution Network, Key End-Use Focus, Recent Developments]
15. 3 Operating Model Analysis Framework
15. 4 Competitive Positioning Matrix for Fuel Transfer Pump Manufacturers
15. 5 Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
16. 1 Revenues (Projections)
17. 1 By Market Structure (Organized vs Unorganized Suppliers)
17. 2 By Pump Type (Manual, Electric, Engine-Driven)
17. 3 By End-Use Sector (Construction, Industrial, Agriculture, Transport, Commercial & Institutional)
17. 4 By Buyer Type (Large Enterprises, Medium Enterprises, MSMEs, Individual Operators)
17. 5 By Application / Use Case (Equipment Refueling, Gensets, Fleet Depots, Bulk Storage)
17. 6 By Power Source (Electric, Battery, Engine-Driven)
17. 7 By Standard vs Metered Fuel Transfer Systems
17. 8 By Region (North, West, South, East & Central India)
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
We begin by mapping the complete ecosystem of the India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market across demand-side and supply-side entities. On the demand side, entities include construction and infrastructure contractors, mining operators, industrial plants, logistics and fleet operators, agricultural users (farms, cooperatives, agri-service providers), telecom tower operators, commercial facility managers (malls, hospitals, hotels), and institutional buyers such as PSUs, utilities, railways, and defense-linked establishments that require controlled fuel handling. Demand is further segmented by usage context (portable site refueling vs fixed depot dispensing), fuel storage arrangement (drums, IBCs, skid tanks, underground/above-ground tanks), duty cycle (intermittent vs continuous), and compliance expectation (basic pump vs metered/safety-compliant systems).
On the supply side, the ecosystem includes organized pump manufacturers, electrical motor and drive suppliers, metering and dispensing accessory providers (flow meters, nozzles, hoses, filters), system integrators supplying skid-mounted solutions, distributors and industrial equipment dealers, e-commerce and retail channels for small pumps, service and maintenance partners, and regulatory/inspection bodies that influence safe storage and dispensing norms at industrial and commercial sites. From this mapped ecosystem, we shortlist 6–12 organized manufacturers and key channel partners based on distribution reach, product portfolio depth (AC/DC/manual/engine-driven), presence in diesel transfer applications, service capability, and traction in institutional procurement. This step establishes how value is created and captured across manufacturing, accessory bundling, channel distribution, installation support, and after-sales service.
Step 2: Desk Research
An exhaustive desk research process is undertaken to analyze the structure of the India fuel transfer pumps market, end-use demand behavior, and segment adoption dynamics. This includes reviewing infrastructure and construction execution intensity, mining and industrial activity, diesel generator installation base growth, expansion of logistics fleets and depot refueling practices, and fuel storage trends across commercial facilities. We assess buyer preferences around portability, flow rate, power source compatibility (AC vs DC), durability in harsh environments, and the growing need for fuel accountability through metering.
Company-level analysis includes review of product catalogs, typical use-case positioning (construction vs agriculture vs fleet), channel strategies (dealer-led vs direct institutional), warranty practices, and accessory bundling approaches. We also examine safety and compliance dynamics influencing equipment choice, including fire safety norms for storage and dispensing, electrical safety expectations for motors, and procurement documentation requirements for PSU and large enterprise buying. The outcome of this stage is a comprehensive industry foundation that defines the segmentation logic and builds the assumptions required for market estimation and 2035 outlook modeling.
Step 3: Primary Research
We conduct structured interviews with fuel transfer pump manufacturers, industrial equipment distributors, system integrators, construction site managers, fleet depot operators, generator service companies, and institutional procurement stakeholders. The objectives are threefold: (a) validate assumptions around demand concentration and decision-making criteria across key end-use sectors, (b) authenticate segment splits by pump type, fuel type, end-use, and distribution channel, and (c) gather qualitative insights on pricing behavior, failure modes, service expectations, and adoption barriers for metered and safety-compliant systems.
A bottom-to-top approach is applied by estimating the installed base and replacement cycles across diesel-dependent applications (construction equipment, gensets, fleet depots, agricultural refueling), combined with average pump system values by configuration (manual vs AC/DC vs metered skids). These are aggregated to develop the overall market view. In selected cases, disguised buyer-style interactions are conducted with dealers and integrators to validate field-level realities such as common pump specifications sold, margin structures, availability constraints of motors/meters, and typical buyer concerns related to safety, pilferage, and maintenance.
Step 4: Sanity Check
The final stage integrates bottom-to-top and top-to-down approaches to cross-validate market size, segmentation splits, and forecast assumptions. Demand estimates are reconciled with macro indicators such as infrastructure execution cycles, diesel consumption patterns in key sectors, growth in commercial transport fleets, and trends in backup power usage. Assumptions around channel markup, component import sensitivity, and durability-driven replacement cycles are stress-tested to understand their impact on volume growth and value growth.
Sensitivity analysis is conducted across key variables including infrastructure acceleration, mining activity intensity, formalization of fleet fuel management, increased enforcement of safety norms, and adoption of metered dispensing solutions. Market models are refined until alignment is achieved between manufacturer throughput, channel sales capacity, and realistic buyer installation and replacement patterns, ensuring internal consistency and robust directional forecasting through 2035.
FAQs
01 What is the potential for the India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market?
The India fuel transfer pumps market holds strong potential through 2035, supported by continued infrastructure and construction activity, a large and persistent diesel generator installed base, expanding logistics and fleet operations, and widespread decentralized fuel handling needs across Tier-2/Tier-3 regions. As buyers increasingly prioritize reliability, safety, and fuel accountability, higher-value pump systems—especially metered and controlled dispensing configurations—are expected to gain share, strengthening overall market value growth over the forecast period.
02 Who are the Key Players in the India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market?
The market includes a combination of organized pump manufacturers with established dealer networks and industrial portfolios, along with a fragmented base of regional and unorganized suppliers. Competition is shaped by product durability, range breadth across AC/DC/manual options, accessory bundling capability (meters, hoses, nozzles), channel reach, and after-sales support. Institutional procurement and PSU-linked demand tends to favor suppliers with compliance documentation, consistent quality, and service readiness.
03 What are the Growth Drivers for the India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market?
Key growth drivers include increasing on-site refueling needs in construction and mining, recurring diesel handling requirements driven by backup power systems, rising fleet depot refueling and fuel control practices, and expanding bulk fuel storage usage across industrial and commercial facilities. Additional momentum comes from the shift toward metered dispensing systems for pilferage control and improved operational accountability, especially among organized fleet and industrial buyers.
04 What are the Challenges in the India Fuel Transfer Pumps Market?
Challenges include high price competition and fragmentation due to unorganized suppliers, component and currency-driven cost volatility for motor and metering parts, limited awareness and enforcement of safety practices in small and informal segments, and operational variability across harsh field conditions that increases service and warranty complexity. In value-added segments, adoption barriers persist due to higher upfront costs of metered and safety-compliant systems compared to basic pumps.