India Plastic Additives Market Outlook to 2035
By Additive Type, By Polymer Type, By End-Use Industry, By Application, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0465
- Region: Asia
- Published on: January 2026
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “India Plastic Additives Market Outlook to 2035 – By Additive Type, By Polymer Type, By End-Use Industry, By Application, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the plastic additives industry in India. The report covers an overview and genesis of the market, overall market size in terms of value and volume, detailed market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory and compliance landscape, buyer-level demand profiling, key issues and challenges, and the competitive landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the India plastic additives market.
The report concludes with future market projections based on polymer consumption growth, packaging and infrastructure expansion, automotive lightweighting trends, agricultural plastics penetration, regulatory shifts toward sustainability, regional manufacturing clusters, cause-and-effect relationships, and case-based illustrations highlighting the major opportunities and cautions shaping the market through 2035.
India Plastic Additives Market Overview and Size
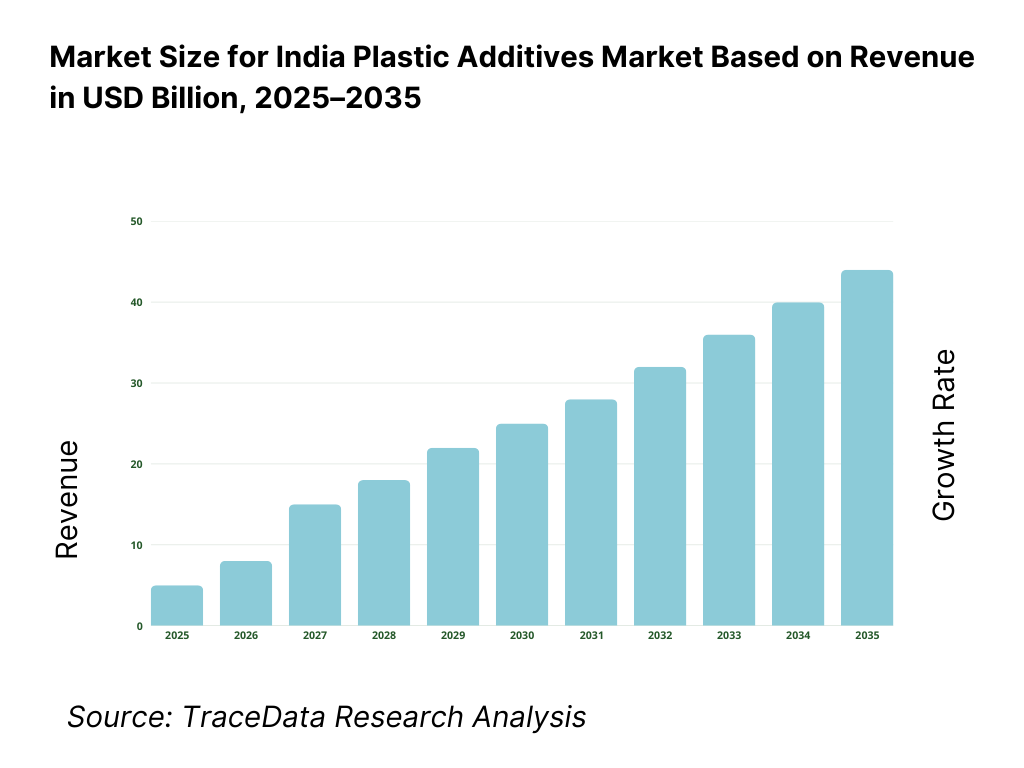
The India plastic additives market is valued at approximately ~USD ~ billion, representing the supply of functional and performance-enhancing chemical additives used in plastic formulations to improve processability, durability, appearance, safety, and end-use performance. Plastic additives typically include plasticizers, stabilizers, flame retardants, impact modifiers, lubricants, antioxidants, UV absorbers, colorants, and specialty functional additives, which are blended with base polymers such as PVC, PE, PP, PET, ABS, and engineering plastics during compounding or processing.
The market is anchored by India’s rapidly expanding polymer consumption base, driven by strong growth in packaging, construction materials, consumer goods, automotive components, electrical and electronics, agriculture films, and healthcare products. Plastic additives play a critical role in enabling plastics to meet application-specific requirements such as heat resistance, flexibility, flame retardancy, UV stability, weatherability, impact strength, and regulatory compliance.
India’s plastic additives demand is closely linked to domestic polymer production, downstream compounding activity, and the growth of organized plastics processing clusters across states such as Gujarat, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, and Karnataka. The increasing penetration of organized converters, higher adoption of specialty and performance plastics, and rising quality expectations from end-users are steadily shifting the market from commodity additive consumption toward higher-value, application-specific additive solutions.
Western India represents the largest demand center for plastic additives, supported by a dense concentration of petrochemical complexes, polymer producers, compounders, and large plastic processing hubs. Northern India follows due to strong consumption in packaging, pipes, cables, consumer goods, and agricultural films. Southern India shows increasing demand driven by automotive, electrical and electronics, and appliance manufacturing clusters, while Eastern India remains relatively smaller but is witnessing gradual growth with infrastructure development and packaging capacity additions.
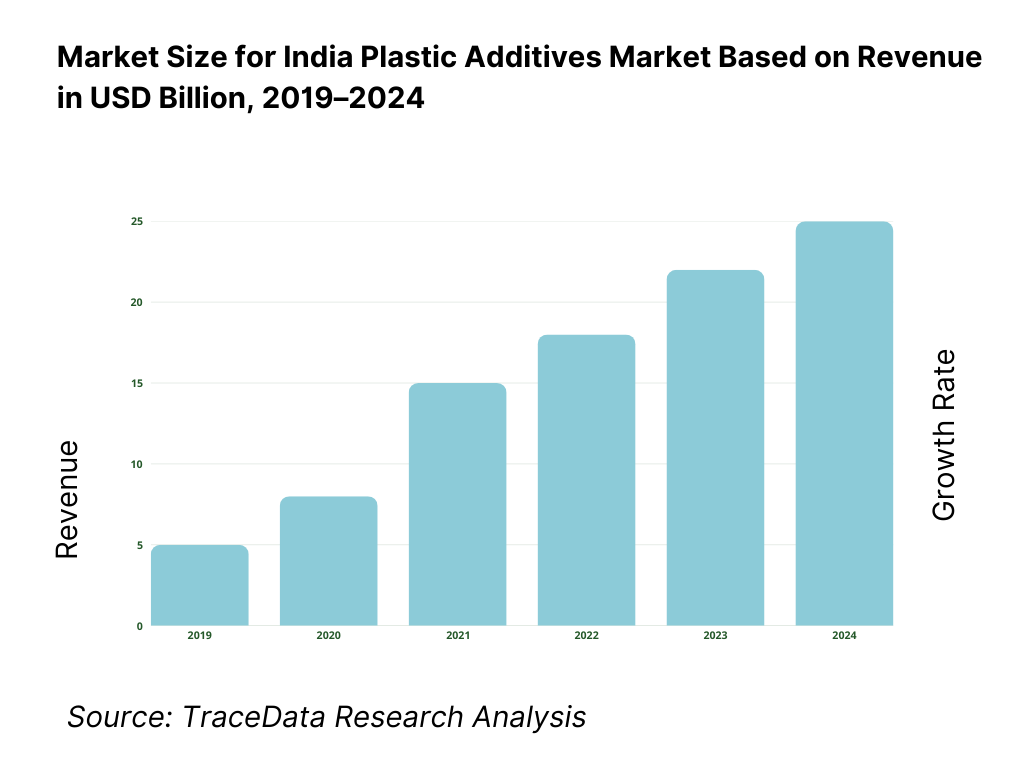
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the India Plastic Additives Market:
Expansion of packaging, consumer goods, and flexible plastics drives volume-led additive demand: India’s packaging sector continues to expand rapidly due to urbanization, rising disposable incomes, organized retail growth, and the penetration of packaged food, beverages, pharmaceuticals, and personal care products. Flexible packaging, rigid containers, films, sheets, and closures require a wide range of additives such as plasticizers, stabilizers, slip agents, antiblock additives, antioxidants, and colorants to achieve performance consistency and shelf-life requirements. As packaging converters scale operations and move toward higher-speed processing and downgauging, demand for processing aids and performance additives increases proportionally.
Infrastructure development and pipe, wire & cable consumption strengthen stabilizer and modifier demand: India’s ongoing investments in urban infrastructure, water supply, sanitation, power distribution, and housing continue to support strong demand for PVC pipes, fittings, profiles, and cable insulation. These applications rely heavily on heat stabilizers, impact modifiers, lubricants, and processing aids to ensure long service life and compliance with Indian standards. Replacement of legacy infrastructure, expansion of irrigation networks, and electrification projects further reinforce long-term demand for additives used in construction-related plastics.
Automotive lightweighting and appliance manufacturing increase usage of performance and specialty additives: The automotive and consumer appliance sectors are increasingly adopting plastics and polymer composites to reduce weight, improve fuel efficiency, and enhance design flexibility. This trend drives demand for impact modifiers, flame retardants, UV stabilizers, heat stabilizers, and color masterbatches in interior, exterior, and under-the-hood applications. As OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers raise quality and durability standards, additive formulations are becoming more specialized, favoring suppliers with strong technical support and application development capabilities.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of the India Plastic Additives Market:
Volatility in raw material pricing and feedstock availability impacts margin stability and contract pricing: The India plastic additives market remains highly sensitive to fluctuations in upstream petrochemical feedstocks and specialty chemical intermediates, many of which are linked to crude oil prices and global chemical supply cycles. Sudden changes in input costs for plasticizers, stabilizers, antioxidants, and specialty additives can compress margins for domestic manufacturers and disrupt long-term supply contracts with polymer processors and compounders. This volatility often limits the ability of additive suppliers to offer fixed-price agreements, creating pricing uncertainty for converters—particularly small and mid-sized processors operating on thin margins. Periodic supply disruptions due to plant shutdowns, import dependency, or logistics constraints further add to procurement risk.
High dependence on imports for specialty additives constrains supply reliability and increases cost exposure: While India has a strong base in commodity additives, a significant portion of specialty additives—such as advanced UV stabilizers, high-performance flame retardants, impact modifiers, and application-specific functional additives—continues to be imported. This import dependence exposes the market to currency fluctuations, extended lead times, and geopolitical or trade-related disruptions. For downstream processors serving regulated or export-oriented markets, delays or inconsistencies in additive supply can disrupt production planning and customer commitments. These dynamics create uneven access to advanced additive technologies across different tiers of the plastics processing ecosystem.
Fragmentation among plastic processors limits adoption of high-value and customized additive solutions: India’s plastics processing industry is highly fragmented, with a large number of small-scale and unorganized converters operating alongside a limited pool of large, integrated players. Smaller processors often prioritize cost over performance optimization, limiting the uptake of premium or customized additive formulations. This fragmentation reduces standardization in additive usage, complicates technical support and application development efforts, and slows the transition toward higher-value additive consumption. As a result, suppliers must balance volume-driven commodity sales with more resource-intensive technical engagement for advanced applications.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
Chemical safety standards and application-specific regulations governing additive usage in plastics: Plastic additives used in India must comply with a range of safety and application-specific standards, particularly for food contact materials, medical products, toys, and consumer goods. Regulations and standards issued by Indian authorities, along with alignment to international norms, influence permissible additive chemistries, migration limits, and labeling requirements. These rules directly shape additive selection, formulation design, and quality assurance processes across the value chain. Compliance requirements often necessitate close coordination between additive suppliers, compounders, and end-use manufacturers.
Plastic waste management rules and sustainability initiatives influencing additive formulation choices: India’s plastic waste management framework increasingly emphasizes recyclability, material recovery, and reduction of environmental impact. These initiatives indirectly affect additive demand by encouraging the use of additives compatible with recycling streams, reprocessing stability, and circular economy objectives. Additives that improve recyclate quality, enhance multiple processing cycles, or enable downgauging are gaining relevance, while certain legacy additives face gradual phase-down pressure. This shift is reshaping R&D priorities and portfolio strategies among additive suppliers.
Standards for construction, electrical, automotive, and packaging applications shaping performance requirements: Sector-specific standards governing pipes, cables, automotive components, packaging materials, and agricultural plastics define minimum performance thresholds for durability, heat resistance, flame retardancy, and weatherability. These standards drive consistent demand for stabilizers, modifiers, flame retardants, and processing aids tailored to each application. Compliance with these norms often determines supplier qualification and long-term sourcing relationships, particularly for organized and export-oriented manufacturers. As enforcement and quality expectations strengthen, additive performance consistency and documentation become increasingly critical in procurement decisions.
India Plastic Additives Market Segmentation
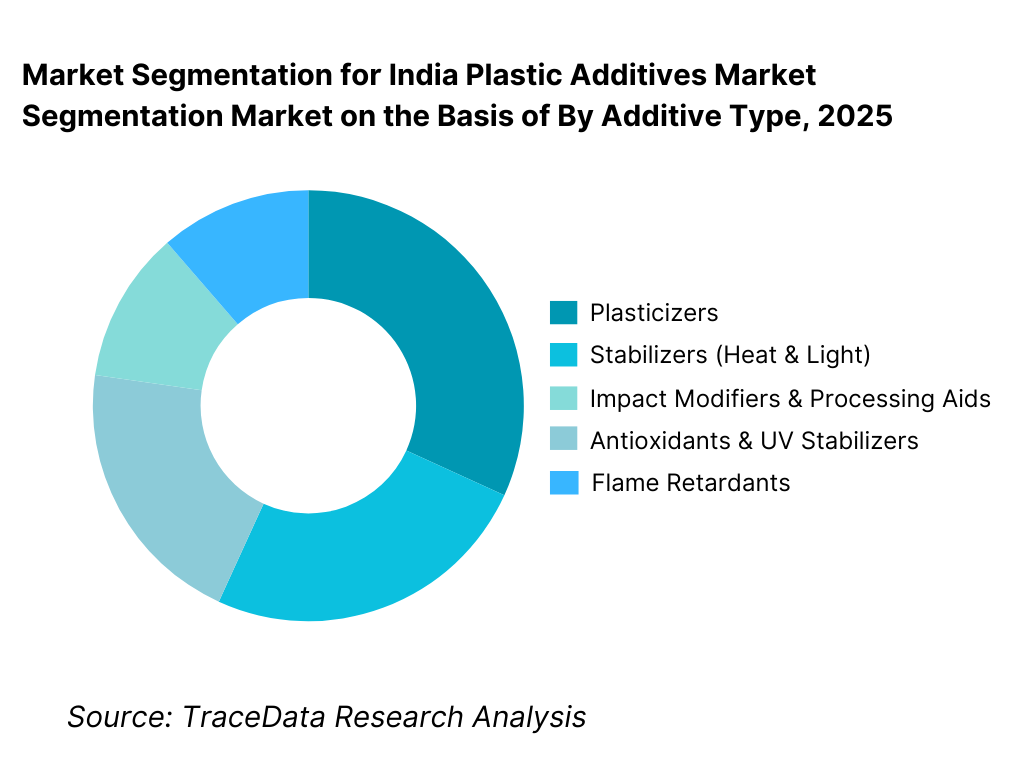
By Additive Type: Plasticizers and stabilizers hold dominance. This is because flexible PVC and commodity plastics continue to account for a large share of India’s polymer consumption, particularly in pipes, cables, films, sheets, footwear, synthetic leather, and packaging applications. Plasticizers are critical for imparting flexibility and workability, while stabilizers are essential for thermal stability during processing and long-term performance in end-use environments. Although specialty additives such as impact modifiers, flame retardants, and UV stabilizers are gaining traction, volume-led demand remains concentrated in plasticizers and stabilizers due to their widespread use and repeat consumption across mass-market applications.
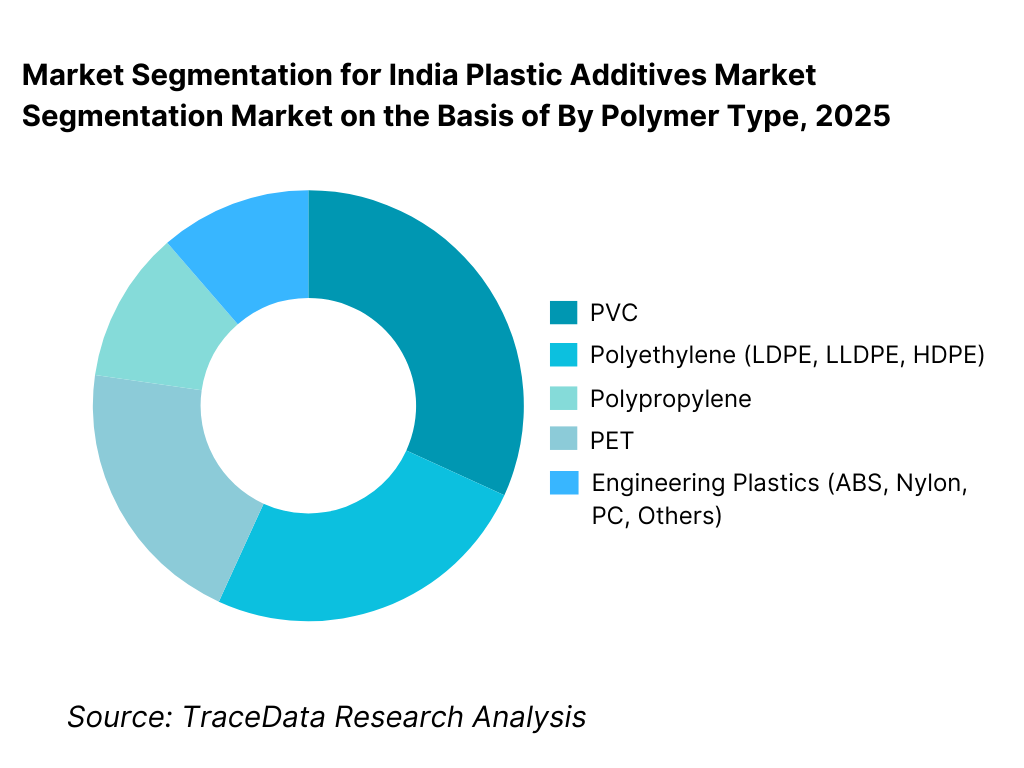
By Polymer Type: PVC remains the largest additive-consuming polymer. PVC dominates additive consumption in India because of its inherently high additive loading compared to other polymers. Applications such as pipes, fittings, profiles, cables, flooring, and synthetic leather require multiple additives to achieve processing stability, flexibility, durability, and compliance. Polyolefins such as PE and PP follow, driven by packaging films, rigid containers, consumer goods, and automotive components. Engineering plastics represent a smaller but higher-value segment, where additive usage is more specialized and performance-driven.
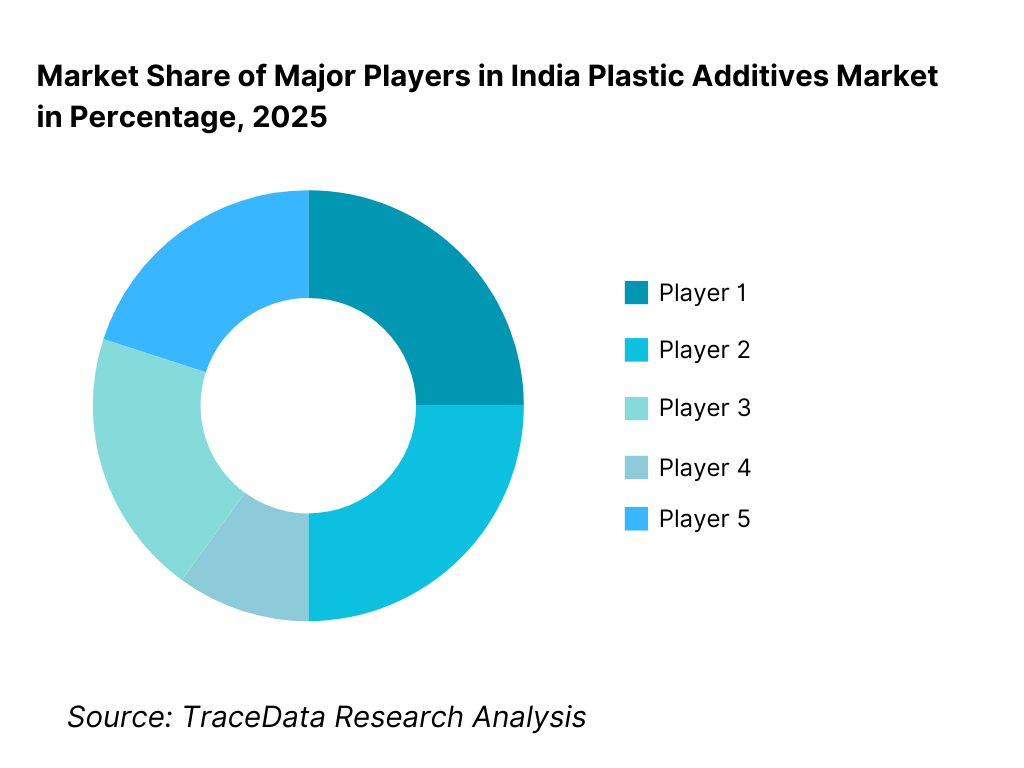
Competitive Landscape in India Plastic Additives Market
The India plastic additives market exhibits moderate fragmentation, characterized by a mix of large multinational chemical companies, established domestic manufacturers, and a long tail of regional and niche additive suppliers. Competitive positioning is driven by product portfolio breadth, cost competitiveness, regulatory compliance, application development capability, supply reliability, and technical support to downstream processors. Multinational players dominate higher-value and specialty additive segments, while domestic manufacturers maintain strong positions in commodity additives through pricing advantage, localized supply, and relationships with small and mid-sized processors.
Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
BASF | 1865 | Ludwigshafen, Germany |
Clariant | 1995 | Muttenz, Switzerland |
Songwon Industrial | 1965 | Ulsan, South Korea |
Adeka Corporation | 1917 | Tokyo, Japan |
Baerlocher | 1823 | Munich, Germany |
PMC Group | 1970 | Mumbai, India |
Fine Organics | 1970 | Mumbai, India |
Galaxy Surfactants | 1980 | Mumbai, India |
A. Schulman | 1928 | Akron, Ohio, USA |
Evonik | 2007 | Essen, Germany |
Some of the Recent Competitor Trends and Key Information About Competitors Include:
BASF: BASF continues to strengthen its position in India by focusing on high-performance additives aligned with regulatory compliance, sustainability, and advanced polymer applications. The company’s competitive advantage lies in its deep R&D capabilities, broad global product portfolio, and ability to support large processors and OEMs with application-specific solutions rather than commodity formulations.
Clariant: Clariant remains a strong player in specialty additives, masterbatches, and performance solutions, particularly for packaging, consumer goods, and industrial plastics. Its market positioning is reinforced by a focus on compliant additives, color and functional masterbatches, and close technical collaboration with converters targeting export and premium domestic markets.
Songwon Industrial: Songwon has built a strong presence in antioxidants and stabilizers, benefiting from cost-competitive manufacturing and reliable supply capabilities. The company is increasingly favored by processors seeking alternatives to traditional Western suppliers while maintaining consistent quality and performance across large-volume applications.
Fine Organics: Fine Organics is a leading domestic supplier of specialty additives such as lubricants, processing aids, and performance enhancers. The company benefits from strong relationships with Indian processors, a focus on application-driven product development, and the ability to serve both organized and mid-scale converters efficiently.
PMC Group: PMC Group has established itself as a key Indian player in plasticizers and stabilizers, leveraging localized manufacturing, cost competitiveness, and deep understanding of domestic processing conditions. The company’s strength lies in serving high-volume PVC applications across construction, cables, and flexible products.
What Lies Ahead for India Plastic Additives Market?
The India plastic additives market is expected to expand steadily by 2035, supported by sustained growth in polymer consumption, expansion of packaging and construction activities, rising automotive and consumer goods production, and gradual upgrading of quality and compliance standards across the plastics processing ecosystem. Growth momentum is further reinforced by infrastructure development, increasing penetration of organized plastics converters, and the growing role of additives in improving performance, durability, and sustainability of plastic products. As end-users increasingly demand consistency, regulatory compliance, and application-specific performance, plastic additives will remain a critical enabler of downstream plastics growth in India.
Transition Toward Higher-Performance and Application-Specific Additive Formulations: The future of the India plastic additives market will see a gradual shift from commodity-driven additive consumption toward higher-performance and application-specific formulations. Demand is increasing for additives that enhance recyclability, thermal stability, UV resistance, flame retardancy, and long-term durability in demanding environments. Packaging, automotive, electrical, and construction applications are increasingly specifying additives based on end-use performance rather than price alone. Suppliers with formulation expertise, application development capabilities, and technical service support will be better positioned to capture higher-value demand and build long-term customer relationships.
Growing Emphasis on Regulatory Compliance, Safety, and Sustainability Alignment: Regulatory oversight related to food contact safety, consumer product standards, and environmental impact will continue to shape additive selection and formulation strategies. Additives with low migration, non-toxic profiles, and compatibility with recycling streams will gain prominence. Sustainability narratives—such as extended product life, downgauging, improved reprocessability, and reduced material wastage—will increasingly influence procurement decisions, particularly among organized processors and export-oriented manufacturers. This trend is expected to favor suppliers offering compliant and future-ready additive portfolios.
Rising Importance of Packaging and Construction as Structural Demand Anchors: Packaging and building & construction will remain the primary demand anchors for plastic additives through 2035. Flexible packaging films, rigid containers, pipes, fittings, cables, and profiles will continue to consume large volumes of plasticizers, stabilizers, lubricants, and processing aids. Growth in infrastructure investment, housing development, water management, and electrification will sustain long-term additive demand in PVC- and polyolefin-based applications. These segments benefit from repeat consumption patterns and predictable volume growth tied to macroeconomic and demographic trends.
Increased Role of Domestic Manufacturing and Import Substitution in Specialty Additives: India is expected to gradually expand domestic manufacturing capacity for select specialty additives to reduce import dependence and improve supply reliability. While complete substitution is unlikely in the near term, localized production of antioxidants, stabilizers, and functional additives will increase, supported by cost competitiveness and proximity to downstream processors. This shift may improve availability, shorten lead times, and reduce currency-related cost exposure for Indian converters.
India Plastic Additives Market Segmentation
By Additive Type
• Plasticizers
• Stabilizers (Heat & Light)
• Impact Modifiers & Processing Aids
• Antioxidants & UV Stabilizers
• Flame Retardants
• Colorants & Other Specialty Additives
By Polymer Type
• PVC
• Polyethylene (LDPE, LLDPE, HDPE)
• Polypropylene
• PET
• Engineering Plastics (ABS, Nylon, PC, Others)
By End-Use Industry
• Packaging
• Building & Construction
• Automotive
• Consumer Goods & Appliances
• Agriculture
• Electrical & Electronics
By Application
• Flexible Packaging Films
• Rigid Packaging & Containers
• Pipes, Fittings & Profiles
• Wires & Cables
• Automotive Components
• Consumer & Industrial Products
By Region
• West India
• North India
• South India
• East India
Players Mentioned in the Report:
• BASF
• Clariant
• Songwon Industrial
• Adeka Corporation
• Baerlocher
• Fine Organics
• PMC Group
• Galaxy Surfactants
• Global and regional plastic additive manufacturers, compounders, and specialty chemical suppliers
Key Target Audience
• Plastic additive manufacturers and formulators
• Polymer producers and compounders
• Plastic processors and converters
• Packaging, construction, and automotive OEMs
• Electrical and electronics manufacturers
• Regulatory and compliance-focused product developers
• Distributors and specialty chemical traders
• Private equity and strategic investors in chemicals and materials
Time Period:
Historical Period: 2019–2024
Base Year: 2025
Forecast Period: 2025–2035
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4. 1 Delivery Model Analysis for Plastic Additives-Commodity Additives, Specialty Additives, Customized Formulations [Margins, Preference, Strength & Weakness]
4. 2 Revenue Streams for India Plastic Additives Market [Bulk Additives Sales, Specialty Additives, Customized Formulations, Technical Services, Contract Manufacturing]
4. 3 Business Model Canvas for India Plastic Additives Market [Key Partners, Key Activities, Value Propositions, Customer Segments, Cost Structure, Revenue Streams]
5. 1 Local Players vs Global Vendors [Indian Manufacturers vs Multinational Chemical Companies]
5. 2 Investment Model in India Plastic Additives Market [Capacity Expansion, R&D Investment, Joint Ventures, Import Substitution]
5. 3 Comparative Analysis of Additive Adoption in Organized vs Unorganized Plastic Processing Sector [Procurement Models, Use Cases, Cost-Performance Trade-offs]
5. 4 Additives Budget Allocation by Processor Size [Large Processors, Medium Processors, Small & Unorganized Units]
8. 1 Revenues (Historical Trend)
9. 1 By Market Structure (In-House Compounding vs Merchant Additive Procurement)
9. 2 By Additive Type (Plasticizers, Stabilizers, Impact Modifiers, Flame Retardants, Antioxidants, UV Stabilizers, Others)
9. 3 By Polymer Type (PVC, PE, PP, PET, Engineering Plastics)
9. 4 By End-Use Industry (Packaging, Construction, Automotive, Consumer Goods, Agriculture, Electrical & Electronics)
9. 5 By Application (Films, Pipes & Fittings, Cables, Automotive Components, Rigid Containers, Consumer Products)
9. 6 By Additive Form (Solid, Liquid)
9. 7 By Commodity vs Specialty Additives
9. 8 By Region (North India, West India, South India, East India)
10. 1 Plastic Processor & Converter Landscape and Cohort Analysis
10. 2 Additive Selection Drivers & Decision-Making Process
10. 3 Performance, Cost Impact & ROI Analysis of Additives
10. 4 Gap Analysis Framework
11. 1 Trends & Developments in India Plastic Additives Market
11. 2 Growth Drivers for India Plastic Additives Market
11. 3 SWOT Analysis for India Plastic Additives Market
11. 4 Issues & Challenges for India Plastic Additives Market
11. 5 Government Regulations for India Plastic Additives Market
12. 1 Market Size and Future Potential for Specialty Plastic Additives in India
12. 2 Business Models & Revenue Streams [Specialty Additives, Customized Blends, Technical Support Services]
12. 3 Delivery Models & Additive Solutions Offered [Standard Additives, Application-Specific Formulations, Compounding Support]
15. 1 Market Share of Key Players in India Plastic Additives Market (By Revenues)
15. 2 Benchmark of Key Competitors [Company Overview, USP, Business Strategies, Business Model, Manufacturing Capacity, Revenues, Pricing Strategy, Product Portfolio, Key Customers, Strategic Alliances, Recent Developments]
15. 3 Operating Model Analysis Framework
15. 4 Competitive Positioning Matrix for Plastic Additives Suppliers
15. 5 Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
16. 1 Revenues (Projections)
17. 1 By Market Structure (In-House Compounding and Merchant Additives)
17. 2 By Additive Type (Plasticizers, Stabilizers, Modifiers, Flame Retardants, Antioxidants, UV Additives)
17. 3 By End-Use Industry (Packaging, Construction, Automotive, Consumer Goods, Agriculture, Electrical)
17. 4 By Processor Size (Large, Medium, Small & Unorganized)
17. 5 By Application (Films, Pipes, Cables, Automotive Parts, Rigid Packaging)
17. 6 By Additive Form (Solid, Liquid)
17. 7 By Commodity vs Specialty Additives
17. 8 By Region (North, West, South, East India)
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
We begin by mapping the complete ecosystem of the India Plastic Additives Market across demand-side and supply-side entities. On the demand side, entities include plastic processors and converters, polymer compounders, packaging manufacturers, pipe and cable producers, automotive component suppliers, consumer goods manufacturers, agricultural film producers, electrical and electronics manufacturers, and export-oriented plastics manufacturers. Demand is further segmented by end-use application (packaging, construction, automotive, consumer goods, agriculture, electrical), polymer type (PVC, PE, PP, PET, engineering plastics), and additive usage intensity (commodity vs specialty formulations).
On the supply side, the ecosystem includes multinational additive manufacturers, domestic additive producers, specialty chemical companies, compounders with in-house additive formulation capability, distributors and traders, polymer producers, R&D and testing laboratories, and regulatory and certification bodies. From this mapped ecosystem, we shortlist 8–12 leading additive suppliers operating in India—covering both global and domestic players—based on product portfolio breadth, local manufacturing or sourcing presence, application coverage, technical support capability, and penetration across high-volume and specialty segments. This step establishes how value is created and captured across additive formulation, manufacturing, distribution, technical service, and downstream application support.
Step 2: Desk Research
An exhaustive desk research process is undertaken to analyze the India plastic additives market structure, demand drivers, and segment behavior. This includes reviewing polymer consumption trends, plastics processing capacity expansion, packaging and construction growth indicators, automotive and appliance production trends, and infrastructure-led demand for pipes and cables. We assess additive consumption patterns by polymer type and end-use industry, along with shifts toward higher-performance, compliant, and sustainability-aligned additives.
Company-level analysis includes review of additive portfolios, manufacturing footprints, import versus domestic supply dynamics, pricing positioning, and typical customer segments served. We also examine regulatory and compliance frameworks affecting additive usage, including food contact safety norms, plastic waste management rules, and sector-specific standards for construction, automotive, and electrical applications. The outcome of this stage is a comprehensive industry foundation that defines segmentation logic and establishes the assumptions required for market sizing and future outlook modeling.
Step 3: Primary Research
We conduct structured interviews with plastic additive manufacturers, compounders, polymer producers, plastic processors, distributors, and application specialists. The objectives are threefold: (a) validate assumptions around demand concentration, additive loading levels, and application-specific usage, (b) authenticate segment splits by additive type, polymer type, and end-use industry, and (c) gather qualitative insights on pricing behavior, sourcing preferences, import dependence, technical support requirements, and regulatory compliance challenges.
A bottom-to-top approach is applied by estimating polymer consumption volumes, average additive loading rates, and application-level additive value across key segments, which are aggregated to develop the overall market view. In selected cases, disguised buyer-style interactions are conducted with processors and distributors to validate field-level realities such as supplier switching behavior, lead times, price sensitivity, and adoption barriers for specialty additives.
Step 4: Sanity Check
The final stage integrates bottom-to-top and top-to-down approaches to cross-validate the market view, segmentation splits, and forecast assumptions. Demand estimates are reconciled with macro indicators such as polymer production growth, packaging consumption trends, infrastructure spending, and automotive output projections. Assumptions around raw material volatility, import dependence, regulatory tightening, and sustainability adoption are stress-tested to understand their impact on additive demand and formulation shifts. Sensitivity analysis is conducted across key variables including polymer growth rates, regulatory enforcement intensity, recycling penetration, and specialty additive adoption. Market models are refined until alignment is achieved between supplier capacity, downstream processing volumes, and end-use demand trajectories, ensuring internal consistency and robust directional forecasting through 2035.
FAQs
01 What is the potential for the India Plastic Additives Market?
The India Plastic Additives Market holds strong long-term potential, supported by sustained growth in polymer consumption, expansion of packaging and construction activity, rising automotive and consumer goods production, and gradual upgrading of quality and compliance standards across the plastics industry. Additives remain essential for enabling performance, durability, safety, and sustainability in plastic products. As applications become more demanding and regulated, higher-value and application-specific additives are expected to capture a growing share of market value through 2035.
02 Who are the Key Players in the India Plastic Additives Market?
The market features a mix of multinational chemical companies, established domestic additive manufacturers, and specialty chemical suppliers, supported by distributors and compounders serving diverse processor segments. Competition is shaped by product portfolio breadth, cost competitiveness, regulatory compliance, technical service capability, and reliability of supply. Global players dominate specialty and performance additives, while domestic suppliers maintain strong positions in high-volume commodity additives through localized manufacturing and customer proximity.
03 What are the Growth Drivers for the India Plastic Additives Market?]
Key growth drivers include expansion of packaging consumption, infrastructure-led demand for pipes and cables, increasing use of plastics in automotive and appliances, and rising expectations around product quality and durability. Additional momentum comes from regulatory alignment, sustainability initiatives, and the need for additives that enhance recyclability and processing efficiency. The steady shift from unorganized to organized plastics processing also supports greater adoption of standardized and performance-driven additive solutions.
04 What are the Challenges in the India Plastic Additives Market?
Challenges include raw material price volatility, dependence on imports for specialty additives, fragmented downstream processing capacity, and evolving regulatory requirements. Price sensitivity among small and mid-sized processors can limit adoption of premium additives, while compliance-driven reformulation increases development and validation costs. Managing supply reliability, technical support intensity, and regulatory transitions remains a key challenge for both suppliers and processors.