Indonesia Express Delivery Market Outlook to 2029
By Delivery Types (Same-Day, Next-Day, 2 Days, More than 2 Days), By Industry (E-commerce, Healthcare, FMCG, Retail, Manufacturing, Others) and By Provinces
- Product Code: TDR0016
- Region: Asia
- Published on: September 2024
- Total Pages: 80-100
Report Summary
The report titled "Indonesia Express Delivery Market Outlook to 2029 - By Domestic and International Express, By Delivery Types (Same-Day, Next-Day, 2 Days, More than 2 Days), By Industry (E-commerce, Healthcare, FMCG, Retail, Manufacturing, Others) and By Provinces" provides a comprehensive analysis of the express delivery market in Indonesia. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer level profiling, issues and challenges, and comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the Express Delivery Market. The report concludes with future market projections based on revenue, by market, product types, region, and case studies highlighting the major opportunities and risks.
Indonesia Express Delivery Market Overview and Size
In 2023, Indonesia's express delivery market was worth US$ 3.86 billion due to the aggressive development of e-commerce platforms, increase in urbanization, and also a sharp rising demand for solutions that support shipping speed. Its key players dominate this lucrative business for having broad-scale logistics, multipronged offerings concerning varieties, and focusing more on the perspective of customers through better services, including JNE Express, J&T Express, SiCepat, Ninja Van, and Pos Indonesia.
In 2023, J&T Express introduced a next-day delivery service across Indonesia's key cities to meet demand for quicker deliveries-particularly from e-commerce platforms-a move meant to increase consumer experience and tap into the highly digitized economy of Indonesia. Jakarta and Surabaya remain critical to high population densities, robust infrastructure, and large e-commerce customer bases.
Market Size for Indonesia Express Delivery Industry on the Basis of Revenues in USD Million, 2018-2024

What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the Indonesia Express Delivery Market:
Growth of E-commerce: With the rapid development of e-commerce platforms in Indonesia, the demand for express delivery services is increasing at an incredible rate. In 2023, it was estimated that about 70% of all express deliveries were linked to online shopping as consumers increasingly expect quicker shipping times for their purchases. This has also been highly contributed by the convenience and time-saving benefits associated with express delivery.
Urbanization: The population in Indonesia's urban setting is continuously growing; people in urban areas need to have easy and quick access to goods. Growth has increased demand for express delivery service packages, especially in large metropolitan cities such as Jakarta, Surabaya, and Bandung. In addition, urbanization created modern infrastructure that has eased the logistics of express delivery.
Rising Middle-Class Income: The income growth of the rising middle class fuels demand for high-value services that charge a premium. Therefore, increasingly, Indonesian middle-class consumers who value convenience and time will continue to drive demand for same-day and next-day delivery options.
Digitalization: Adding digital channels to the express delivery industry helped rationalize operations, improve customer experiences, and change the way work is done within the industry. In 2023, nearly 80% of orders in express delivery were already being processed through the digital channels: real-time tracking, online payment, and accelerated communication.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of the Indonesia Express Delivery Market
Logistic and Infrastructure Limitations: Indonesia is immensely spread out, meaning rural and remote areas do not enjoy decent road networks or avenues. In 2023, approximately 30% of deliveries to rural areas experienced delays due to poor road conditions and limited transportation options. This infrastructure gap hampers the ability to provide reliable and timely delivery services across the entire country.
High Operational Costs: Incrementing fuel prices and labor costs, rising competition, have inflated operation costs for express delivery companies. Operational costs were up 15% in 2023 and have brutally squeezed profit margins, particularly for the smaller and newest market entrants. These costs are not allowing companies to maintain competitive pricing while ensuring service quality.
Regulatory Compliance: The government of Indonesia is setting up much more stringent guidelines with regard to vehicle emissions and delivery safety, which necessitates heavy investment in upgrading its fleet and bringing in compliance measures. A total of almost 25% of the road delivery vehicles did not meet the new emission standards last year, thereby causing disruption to operations and thus adding to company costs in upgrading to meet these regulations.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives Governing the Indonesia Express Delivery Market:
Emission Standards for Delivery Fleets: The Indonesian government has tightened emission standards for delivery vehicles amidst growing air pollution, especially in urban areas. In 2022, it set a target that all the fleets of delivery vehicles are at the euro 4 emission standard, which is environmentally friendly. As of 2023, it is estimated that about 70% of delivery vehicles attained this standard while failure of compliance to the standard resulted in an operational set back to several small companies that were involved in delivery services.
E-commerce Support Initiatives: Tax incentives were given to support e-commerce for businesses that invested in the integral structure of delivery services, such as warehouses and digital platforms. This increased investments in logistics infrastructure by 15% due to the tax incentives given in 2023. This investment was more glaringly seen in areas like Jakarta and Surabaya, which have large hubs for e-commerce.
Vehicle Safety Regulations: The Indonesian government requires periodic safety checks for delivery vehicles to ensure their roadworthiness. These checks are supposed to be performed for critical safety features like brakes, tires, and lighting systems. In 2023, about 85% of the vehicles passed these checks in the first attempt, which is a pretty good compliance rate among the major logistics companies.
Indonesia Express Delivery Market Segmentation
By Mode of Transportation: Road freight is the most prominent mode of express delivery in Indonesia, as the country has extensive road networks connecting urban centers. Road delivery is preferred for its speed, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness in densely populated areas such as Jakarta and Surabaya. Air freight is also significant, especially for time-sensitive deliveries across the archipelago's more remote islands, while maritime and rail freight play smaller roles, mainly in bulk shipments.

- By Shipment Category: B2C shipments have the leading market share, contributed by exponential growth in Indonesian e-commerce. Consumers increasingly rely on fast, reliable delivery for their online purchases. The second most in demand is B2B shipments, which cater to the manufacturing, retail, and healthcare sectors where timely delivery of supplies and equipment is critical.

By Speed of Delivery: The market is dominated by next-day delivery services, which are appealing to both consumers and businesses when speed is an issue. Besides, same-day delivery is gaining momentum and, in most cases, occurs within metropolitan cities where consumers have a huge demand for quicker shipment methods. Standard delivery takes 2-5 days and is still applied for shipments that are less sensitive and meant for customers on a budget.
Competitive Landscape in Indonesia Express Delivery Market
With a number of key players holding major shares, the structure of the Indonesia express delivery market is relatively centralized. Yet, with the entry of new players into the market and the extension of online platforms like JNE Express, J&T Express, SiCepat, Ninja Van, and Pos Indonesia, the competition has broadened, offering more choices and improving the services for consumers.
| Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
| Pos Indonesia | 1746 | Bandung, Indonesia |
| JNE (Jalur Nugraha Ekakurir) | 1990 | Jakarta, Indonesia |
| TIKI (Titipan Kilat) | 1970 | Jakarta, Indonesia |
| J&T Express | 2015 | Jakarta, Indonesia |
| Ninja Van Indonesia | 2014 | Singapore |
| SiCepat Express | 2014 | Jakarta, Indonesia |
| Lalamove | 2013 | Hong Kong |
| DHL Express Indonesia | 1969 | Bonn, Germany |
| FedEx Indonesia | 1971 | Memphis, USA |
| Lion Parcel | 2013 | Jakarta, Indonesia |
Recent Competitor Trends and Key Information
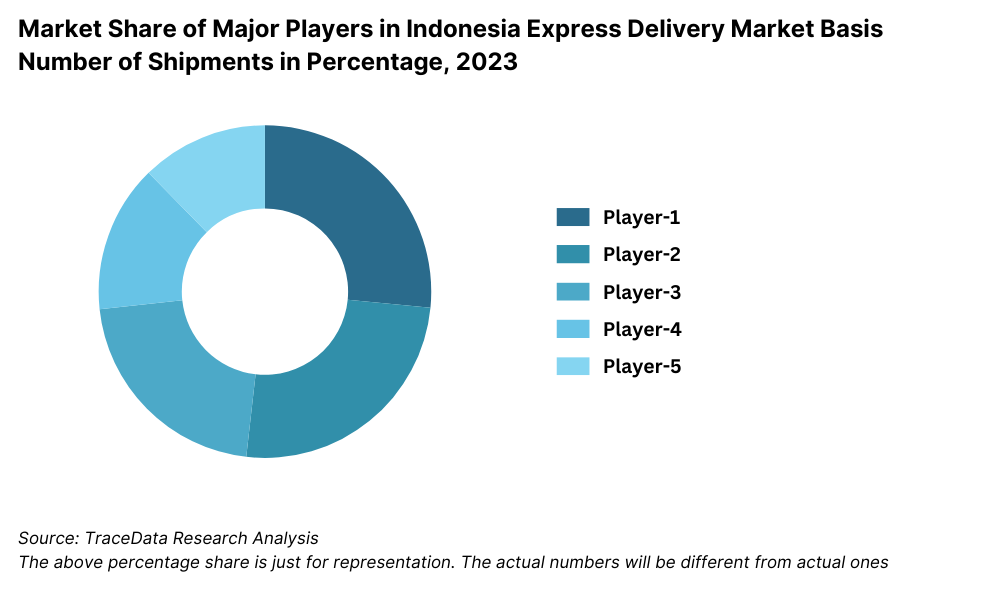
JNE Express: JNE Express has been considered as one of the major firms within the industry for express delivery services in Indonesia. Having dealt with 1.2 billion packages by the year 2023, there is significantly higher growth recorded in customer scale for the firm at an astonishing growth rate. Around 15%, especially from places like Jakarta and Surabaya with improved last-mile delivery services. Their forays into the digitization of their delivery platform have boosted operational efficiency and made it easier for both retailers and customers to access the tracking capabilities.
J&T Express: J&T Express has a guarantee of fast delivery. It reported 20% revenue growth in 2023. Its focus on next-day delivery, particularly in major cities, and its adoption of AI-driven logistics solutions have put the company in one of the leading positions in the market.
SiCepat: SiCepat reported a 25% shipment volume increase in 2023, given its concentration on same-day delivery services within Jakarta and its surrounding areas. Major partnerships with key e-commerce players such as Tokopedia and Shopee also contributed to the growth of this company.
Ninja Van: The firm has transformed into a regional powerhouse across Southeast Asia and consequently increased market share in Indonesia to 10% in 2023. A strong focus on cross-border e-commerce logistics allows Ninja Van to leverage increasing demands for international shipment services.
Pos Indonesia: Pos Indonesia became the oldest player in the market, yet it still managed to retain its prominent presence, especially in rural areas. In 2023, this company handled more than 800 million packages while improving its digital capability to be relevant in the digitally driven market.
What Lies Ahead for Indonesia Express Delivery Market?
The Indonesia express delivery market is expected to witness significant growth by 2029, with a strong CAGR during the forecast period. Some of the factors that will support this growth include ongoing expansion in e-commerce, improvement of infrastructure, and increasing demand for faster and better delivery services.
- Switch to Sustainable Delivery Solution: The Indonesian government is still promoting green logistics initiatives, and with that, more electric delivery vehicles and eco-friendly packaging solutions will also likely be adopted. It is supported by the available government incentives and increasing consumer awareness regarding environmental sustainability.
Integration of Advanced Technologies: There will be implementation of AI, machine learning, and big data analytics into logistics operations that are set to optimize route planning, improving the speed of delivery and reducing costs. Such improved efficiency in delivering services will result in accurate real-time tracking by customers, therefore increasing customer satisfaction.
Increase in Same-Day and Next-Day Deliveries: This involves an increasing desire, initiated for ultra-fast deliveries such as the same-day or next-day options. Such desires especially are to be considered for city areas and will definitely prove to increase investments by e-commerce companies into their delivery infrastructures; such trends have gained significant attention with an aim to ensure successful consumer satisfaction that would add toward growing demand.
Focusing on Cross-border E-commerce Logistics: With the rising demand for international posting and cross-border e-commerce transactions, growth can be seen in express delivery services focusing on cross-border and international regions. Firms chalking out seamless international logistics solutions would find a number of opportunities as trade across Southeast Asia increases.
Adoption of Drones and Autonomous Delivery Solution: Continuing technological development could see resurgence in the experimentation of drones and autonomous vehicles for last-mile delivery in the market. These could be networking prospects that, while making further reductions to delivery times and operational costs, offer new frontiers for market expansion.
Future Outlook and Projections for Indonesia Express Delivery Market on the Basis of Revenues in USD Million, 2024-2029


Indonesia Express Delivery Market Segmentation
- By Market Structure:
- Domestic
- International
- By Delivery Type:
- Same-Day Delivery
- Next-Day Delivery
- 2 Days Delivery
- More than 2 Days Delivery
- By Industry:
- E-commerce
- Retail
- FMCG
- Healthcare
- Manufacturing
- Automotive
- By Delivery Mode:
- Road Transport
- Air Freight
- By Customer Type:
- B2B (Business to Business)
- B2C (Business to Consumer)
- C2C (Consumer to Consumer)
- By Region:
- Java
- Sumatra
- Kalimantan
- Sulawesi
- Bali and Nusa Tenggara
- Papua
Players Mentioned in the Report:
- Pos Indonesia
- JNE (Jalur Nugraha Ekakurir)
- TIKI (Titipan Kilat)
- J&T Express
- Ninja Van Indonesia
- SiCepat Express
- Lalamove
- DHL Express Indonesia
- FedEx Indonesia
- Lion Parcel
Key Target Audience:
- E-commerce Platforms
- Logistics and Delivery Companies
- Postal Service Providers
- Government Bodies (e.g., Ministry of Transportation)
- Research and Development Institutions
Time Period:
- Historical Period: 2018-2023
- Base Year: 2024
- Forecast Period: 2024-2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
5.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Margins Involved, Stakeholders, and Challenges They Face
5.2. Seasonality Trends Involved
5.3. Delivery Model Involved in Indonesia Express Delivery Market
5.4. Business Model Canvas for Indonesia Express Delivery Market
6.1. Growth of E-commerce Impact on Express Delivery, 2018-2024
6.2. Spend on Logistics and Delivery Services in Indonesia, 2024
6.3. Number of Express Delivery Companies in Indonesia
9.1. Revenues, 2018-2024
9.2. Number of Shipments, 2018-2024
10.1. By Domestic and International Express Delivery, 2023-2024P
10.2. By Delivery Type (Same-Day, Next-Day, 2 Days, more than 2 Days), 2023-2024P
10.3. By Industry (E-commerce, Healthcare, FMCG, Retail, Manufacturing, Others), 2023-2024P
10.4. By Weight of Shipments, 2023-2024P
10.5. By Region, 2023-2024P
10.6. By Customer Type (B2B, B2C, C2C), 2023-2024P
10.7. By Delivery Mode (Ground and Air), 2023-2024P
10.8. Key Lanes for Domestic and International Express Delivery
11.1. Customer Landscape and Cohort Analysis
11.2. Customer Journey and Decision-Making Process
11.3. Need, Desire, and Pain Point Analysis
11.4. Gap Analysis Framework
12.1. Trends and Developments for Indonesia Express Delivery Market
12.2. Growth Drivers for Indonesia Express Delivery Market
12.3. SWOT Analysis for Indonesia Express Delivery Market
12.4. Issues and Challenges for Indonesia Express Delivery Market
12.5. Government Regulations for Indonesia Express Delivery Market
15.1. Market Share of Key Players in Indonesia Domestic Express Delivery Market, 2023
15.2. Market Share of Key Players in Indonesia International Express Delivery Market, 2023
15.3. Benchmark of Key Competitors in Indonesia Express Delivery Market Including Variables Such as Year of Inception, Ownership/Funding, Geographies Covered (Emirates and International), Services Offered, USP, Annual Shipments Delivered, Number of Employees, Fleet Size, Client Portfolio, Latest News, and Value-Added Services
15.4. Strength and Weakness
15.5. Operating Model Analysis Framework
15.6. Gartner Magic Quadrant
15.7. Bowmans Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
16.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
16.2. Number of Shipments, 2025-2029
17.1. By Domestic and International Express Delivery, 2025-2029
17.2. By Delivery Type (Same-Day, Next-Day, 2 Days, More than 2 Days), 2025-2029
17.3. By Industry (E-commerce, Healthcare, FMCG, Retail, Manufacturing, Others), 2025-2029
17.4. By Weight of Shipments, 2025-2029
17.5. By Region, 2025-2029
17.6. By Customer Type (B2B, B2C, C2C), 2025-2029
17.7. By Delivery Mode (Ground and Air), 2025-2029
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Ecosystem Mapping: Identify all demand-side and supply-side entities involved in the Indonesia Express Delivery Market. This includes courier service providers, e-commerce platforms, logistics infrastructure providers, and end-users. We will shortlist the top 5-6 leading players based on their financial performance, delivery volumes, and market penetration.
Sourcing Information: Information will be gathered through industry reports, articles, and proprietary databases. Desk research will be conducted to compile market-level data, helping us to understand the broader market landscape and key stakeholders.
Step 2: Desk Research
Data Aggregation: We engage in comprehensive desk research, referencing a wide range of secondary sources and proprietary databases. This process allows us to analyze market trends, delivery volumes, pricing, market players, and demand dynamics. We also gather data on specific companies by examining press releases, annual reports, and financial statements, allowing for a well-rounded understanding of the market.
Company Analysis: Focus on understanding individual company performance through both qualitative and quantitative data. Financial statements, pricing strategies, market expansion plans, and operational efficiencies will be closely studied to form a solid foundation for further research.
Step 3: Primary Research
In-depth Interviews: Conduct a series of interviews with C-level executives, market players, logistics managers, and key end-users in the Indonesia Express Delivery Market. These interviews are aimed at validating our market hypotheses, confirming data accuracy, and gaining insights into operational strategies and market drivers. We will also interview competitors and stakeholders to understand their views on growth opportunities and challenges.
Disguised Interviews: To validate operational and financial information, we will conduct disguised interviews by approaching market players as potential customers. This method helps us to cross-verify the data provided by company executives and identify gaps in secondary data. Through these interviews, we gain insight into the value chain, pricing models, revenue streams, and customer satisfaction levels.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- Data Validation and Modeling: A combination of bottom-up and top-down analysis is used to cross-check data and ensure accuracy in the final market size estimates. The modeling process includes building market forecasts based on historical trends, macroeconomic factors, and industry-specific variables to ensure a robust and reliable projection for the Indonesia Express Delivery Market.
FAQs
01 What is the potential for the Indonesia Express Delivery Market?
The Indonesia express delivery market is expected to witness significant growth, reaching an estimated valuation of IDR 100 trillion by 2029. This growth is fueled by factors such as the rapid expansion of e-commerce, urbanization, and increasing consumer demand for fast and reliable delivery services. Additionally, the market potential is enhanced by advancements in logistics infrastructure and digitalization, which are making delivery processes more efficient and accessible.
02 Who are the Key Players in the Indonesia Express Delivery Market?
The Indonesia express delivery market is dominated by key players such as JNE Express, J&T Express, SiCepat, and Ninja Van. These companies lead the market due to their vast logistics networks, extensive delivery services, and strong presence in both urban and rural areas. Other notable players include Paxel and Pos Indonesia, which continue to play significant roles in the market's development.
03 What are the Growth Drivers for the Indonesia Express Delivery Market?
Key growth drivers include the booming e-commerce industry, which has created an increased need for fast and reliable delivery services. Urbanization and infrastructure development across Indonesia are also critical factors, as they enable more efficient logistics operations. Furthermore, technological advancements such as AI-driven logistics management and digital payment systems are transforming the express delivery landscape, driving further market expansion.
04 What are the Challenges in the Indonesia Express Delivery Market?
The Indonesia express delivery market faces several challenges, including logistics hurdles in rural areas, where infrastructure is underdeveloped. High operational costs, driven by fuel prices and labor expenses, also pose difficulties for many companies. In addition, regulatory requirements related to emissions standards and vehicle safety can impact operational efficiency and increase costs for logistics providers. Lastly, intense competition and price sensitivity in the market create pressure on margins, particularly for smaller players.