Indonesia Lubricants Market Outlook to 2035
By Product Type, By Base Oil, By End-Use Sector, By Distribution Channel, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0458
- Region: Asia
- Published on: January 2026
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Indonesia Lubricants Market Outlook to 2035 – By Product Type, By Base Oil, By End-Use Sector, By Distribution Channel, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the lubricants industry in Indonesia. The report covers an overview and genesis of the market, overall market size in terms of value, detailed market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory and standards landscape, buyer-level demand profiling, key issues and challenges, and competitive landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the Indonesia lubricants market. The report concludes with future market projections based on vehicle parc growth, industrialization trends, infrastructure development, energy and mining activity, regulatory evolution, regional demand drivers, cause-and-effect relationships, and case-based illustrations highlighting the major opportunities and cautions shaping the market through 2035.
Indonesia Lubricants Market Overview and Size
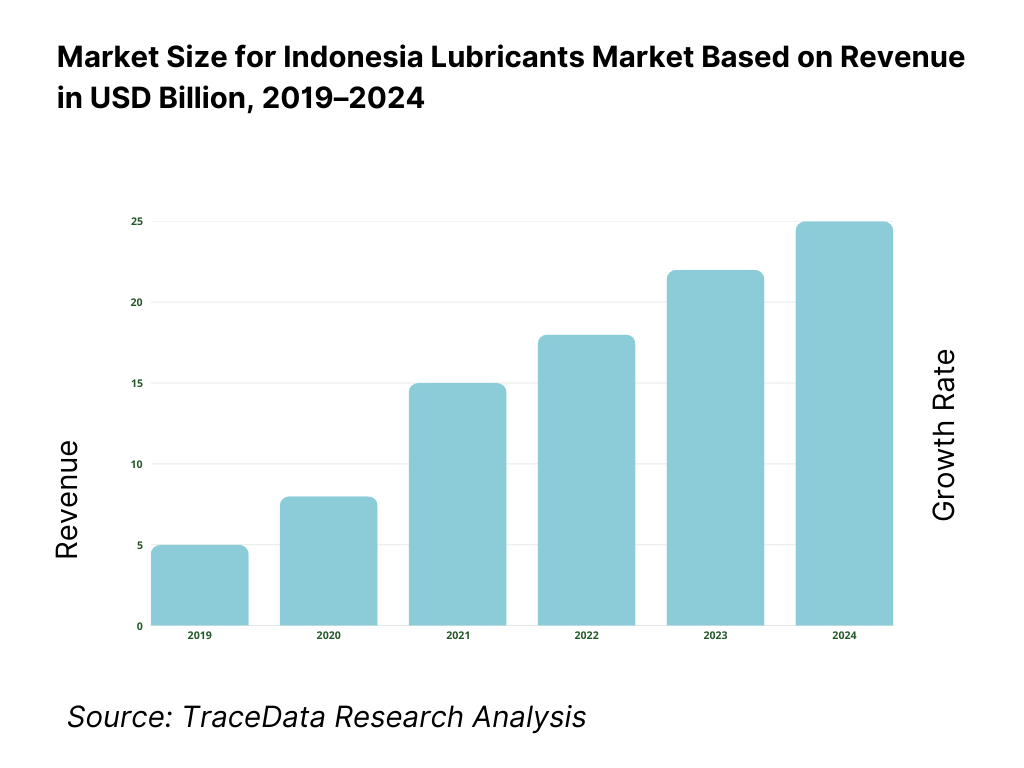
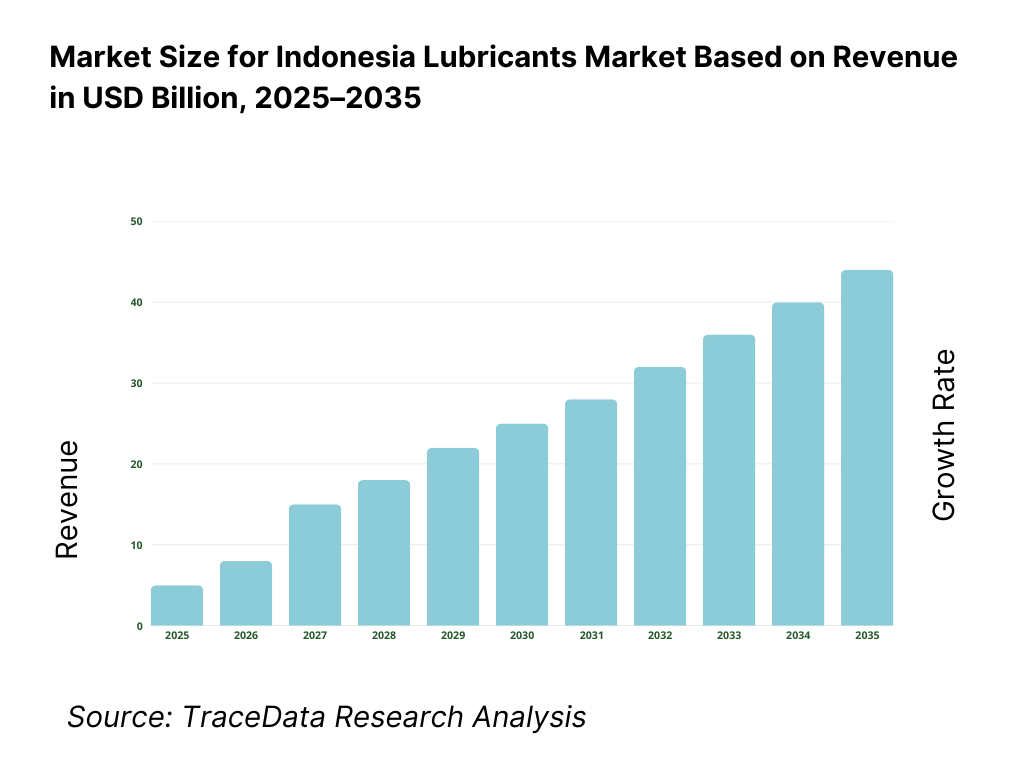
The Indonesia lubricants market is valued at approximately ~USD ~ billion, representing the supply of automotive, industrial, marine, and specialty lubricants formulated using mineral, semi-synthetic, and synthetic base oils along with additive packages designed to reduce friction, manage heat, prevent wear, and extend equipment life. Lubricants play a critical role across transportation, manufacturing, mining, power generation, agriculture, construction, and marine applications in Indonesia’s diversified and resource-intensive economy.
The market is anchored by Indonesia’s large and growing vehicle parc, high two-wheeler and passenger car penetration, expanding commercial vehicle fleet, and steady demand from industrial sectors such as cement, steel, pulp and paper, palm oil processing, mining, and power generation. Automotive lubricants account for a significant share of total consumption due to routine oil change cycles, fragmented aftermarket structure, and widespread use of motorcycles as primary transportation. Industrial lubricants form a structurally stable demand base supported by continuous-process industries and asset-heavy operations where lubrication reliability directly affects uptime and operating costs.
Java represents the largest lubricants consumption hub in Indonesia due to its concentration of population, vehicle ownership, manufacturing facilities, ports, and logistics infrastructure. Sumatra follows with strong demand from mining, palm oil plantations, heavy equipment operations, and inter-island logistics. Kalimantan and Sulawesi contribute meaningful volumes driven by coal mining, nickel processing, power plants, and marine activity, while eastern Indonesia represents a smaller but growing demand pocket linked to infrastructure development, resource extraction, and regional connectivity projects. Across regions, lubricant demand patterns are shaped by vehicle density, industrial activity mix, equipment age, and access to organized distribution networks.
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the Indonesia Lubricants Market
Growth in vehicle parc and sustained aftermarket demand supports volume stability: Indonesia continues to see long-term growth in its on-road vehicle population, particularly motorcycles and passenger cars, which together account for a large share of lubricant consumption. Regular oil change intervals, limited penetration of extended-drain synthetic oils in mass segments, and the dominance of the aftermarket over OEM-tied servicing sustain repeat demand. Motorcycles, in particular, drive high-frequency lubricant consumption due to shorter drain cycles and widespread use in daily commuting, delivery services, and informal transport. This structurally entrenched replacement demand provides resilience to the lubricants market even during periods of slower new vehicle sales.
Industrialization, mining activity, and infrastructure development strengthen non-automotive demand: Indonesia’s industrial base—including cement, metals, food processing, pulp and paper, chemicals, and energy—creates consistent demand for industrial lubricants such as hydraulic oils, gear oils, compressor oils, turbine oils, and greases. Mining operations, particularly coal and nickel, require heavy-duty lubricants for haul trucks, excavators, crushers, and processing equipment operating under harsh conditions. Ongoing investments in power generation, ports, roads, and industrial parks further expand the installed base of equipment requiring lubrication, reinforcing long-term consumption beyond the automotive segment.
Shift toward higher-performance lubricants improves value growth: While mineral oils still dominate volumes, there is a gradual shift toward semi-synthetic and synthetic lubricants driven by newer vehicle models, higher engine performance requirements, extended drain intervals, and growing awareness of total cost of ownership among fleet operators and industrial users. OEM recommendations, tighter emission norms, and the increasing presence of modern engines and machinery encourage the adoption of higher-specification lubricants. This transition supports value growth even when overall lubricant volumes grow at a moderate pace.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of the Indonesia Lubricants Market:
Price volatility of base oils and additives impacts margin stability and pricing discipline: The Indonesia lubricants market remains exposed to fluctuations in global base oil and additive pricing, which are influenced by crude oil movements, refinery operating rates, supply disruptions, and regional trade flows. Sudden increases in input costs can compress margins for lubricant blenders and marketers, particularly in price-sensitive automotive segments where frequent price revisions are difficult to implement without risking volume loss. Smaller players and independent blenders are especially vulnerable, as they often lack long-term supply contracts or hedging mechanisms. These dynamics create pricing uncertainty, reduce promotional flexibility, and can delay strategic investments in product upgrades or distribution expansion.
High fragmentation and prevalence of unorganized products undermine brand-led value growth: Indonesia’s lubricant aftermarket remains highly fragmented, with a significant presence of unbranded, counterfeit, or low-quality products sold through informal channels. These products compete primarily on price and often fail to meet OEM or international performance standards, but continue to attract cost-conscious consumers, especially in two-wheeler and rural markets. This environment limits the ability of organized brands to fully pass on cost increases, slows premiumization, and creates uneven quality perception across the market. For end users, inconsistent product quality can lead to equipment wear and reliability issues, while for established players, it increases the cost of brand building, channel monitoring, and enforcement.
Distribution inefficiencies and geographic complexity increase go-to-market challenges: Indonesia’s archipelagic geography presents logistical challenges for lubricant distribution, particularly beyond Java and major urban centers. Inter-island transportation costs, port congestion, storage constraints, and uneven distributor capability can affect product availability and service levels in remote regions. These challenges increase working capital requirements, complicate inventory planning, and reduce responsiveness to demand fluctuations. For industrial and mining customers operating in remote locations, inconsistent supply can impact maintenance schedules and equipment uptime, making logistics reliability a critical differentiator but also a structural challenge for suppliers.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
National standards and quality regulations governing lubricant formulation and performance: Lubricants sold in Indonesia are subject to national standards and technical requirements covering product classification, viscosity grades, labeling, and performance characteristics. Compliance with Indonesian National Standards (SNI) and alignment with internationally recognized specifications such as API and OEM standards influence formulation choices and product positioning. Regulatory oversight aims to improve product quality, reduce circulation of substandard lubricants, and protect consumers and industrial users from performance-related risks. However, enforcement effectiveness can vary across regions and channels, affecting the pace at which quality standards translate into market-wide improvements.
Environmental regulations influencing formulation, disposal, and sustainability practices: Environmental policies related to waste oil management, hazardous materials handling, and emissions control increasingly affect lubricant producers and users. Regulations governing used oil collection, recycling, and disposal place compliance responsibilities on industrial operators, workshops, and service centers. These requirements encourage the adoption of longer-drain lubricants, improved maintenance practices, and, in some cases, re-refined base oils. While sustainability considerations are gaining prominence, cost and infrastructure limitations continue to influence the speed of adoption across different customer segments.
Import regulations and trade policies shaping base oil and additive supply: Indonesia relies significantly on imported base oils and additives to support domestic lubricant blending. Import duties, licensing requirements, and trade policies directly influence input costs, supply continuity, and sourcing strategies. Changes in regional trade agreements or customs procedures can affect lead times and working capital cycles for lubricant manufacturers. At the same time, government initiatives aimed at strengthening domestic refining capacity and downstream petrochemical industries have the potential to gradually reduce import dependence, though such impacts are expected to materialize over the longer term.
Indonesia Lubricants Market Segmentation
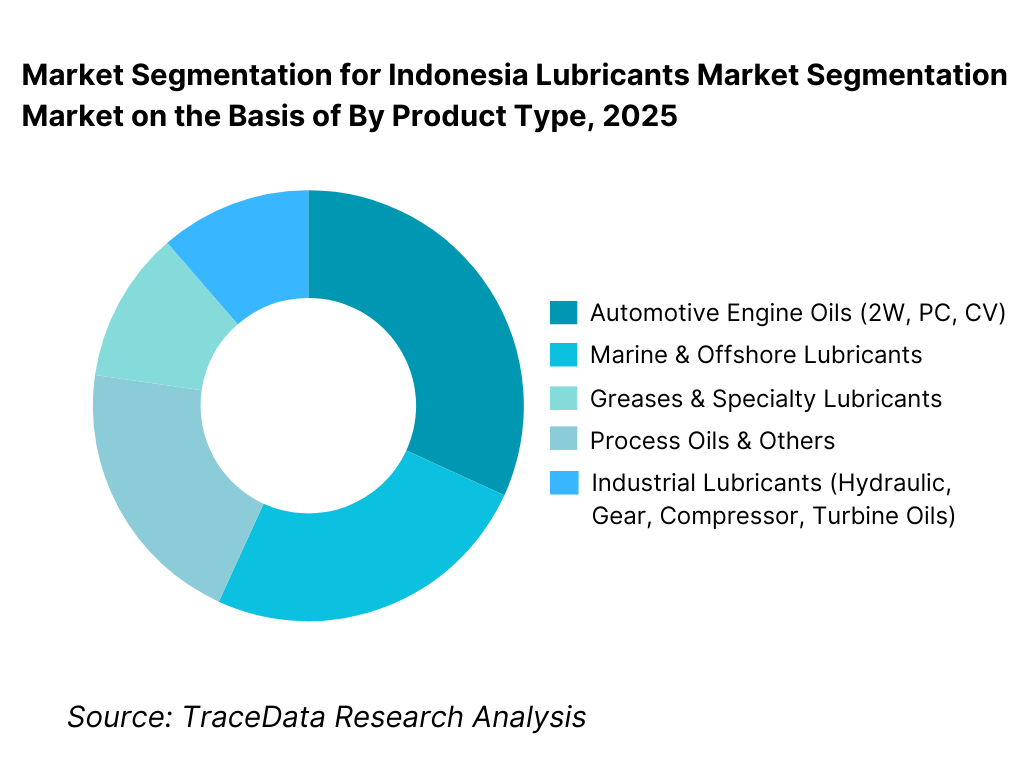
By Product Type: The automotive lubricants segment holds dominance in the Indonesia lubricants market. This is because Indonesia has one of the largest two-wheeler and passenger car populations in Southeast Asia, with motorcycles serving as the primary mode of daily transportation. Frequent oil change intervals, a large aftermarket-driven service ecosystem, and strong penetration of entry- and mid-grade engine oils sustain high volume consumption. While industrial, marine, and specialty lubricants contribute steadily, automotive lubricants continue to benefit from recurring replacement demand and widespread retail availability.
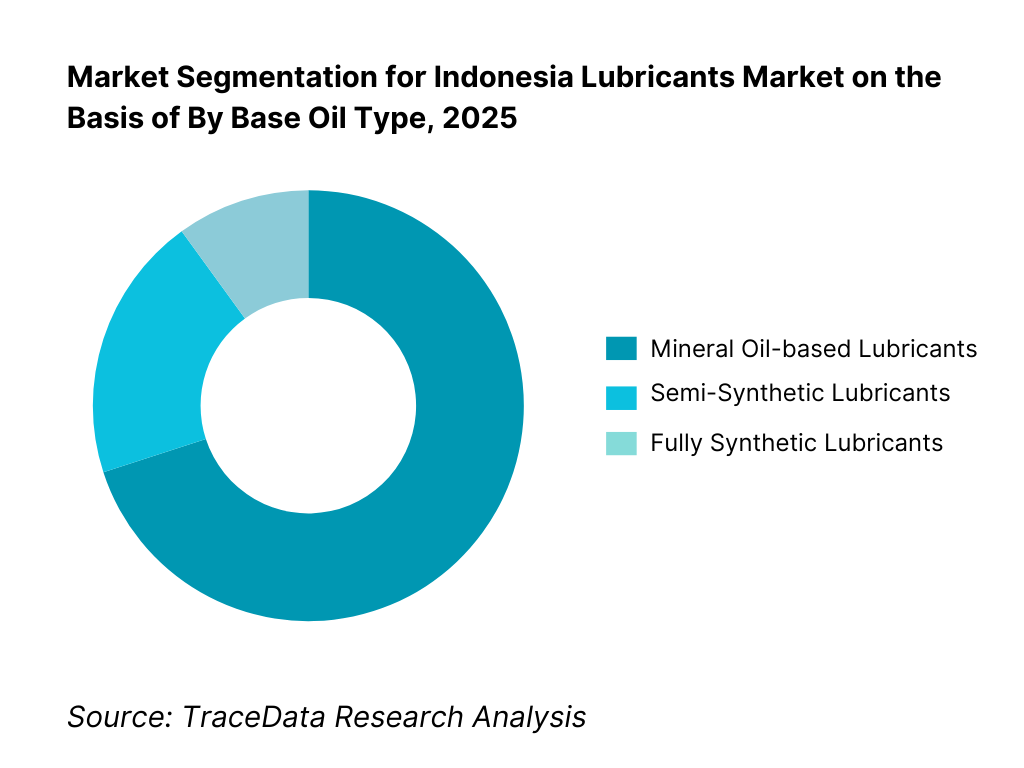
By Base Oil Type: Mineral oils continue to dominate lubricant volumes in Indonesia due to their affordability and suitability for older vehicles and legacy industrial equipment. However, semi-synthetic and synthetic lubricants are gradually increasing their share as newer vehicle models, OEM recommendations, and fleet operators prioritize performance, fuel efficiency, and extended drain intervals. Value growth is increasingly driven by higher-spec formulations even as mineral oils retain volume leadership.
Competitive Landscape in Indonesia Lubricants Market
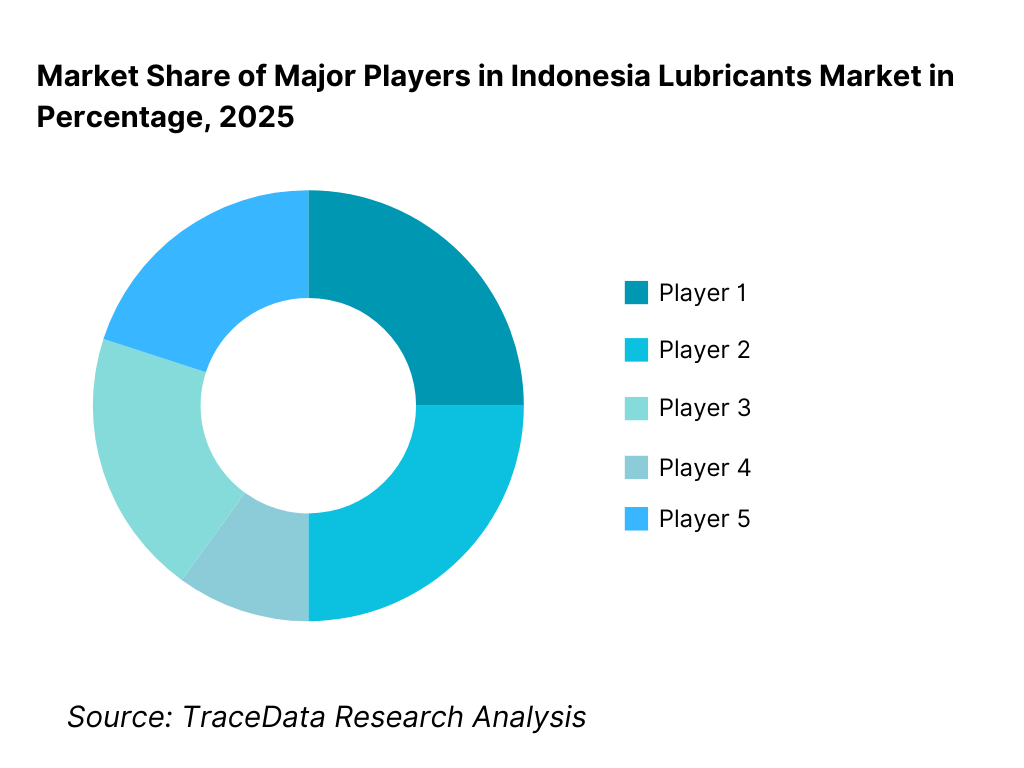
The Indonesia lubricants market exhibits moderate-to-high fragmentation, characterized by the presence of global oil majors, strong regional brands, state-owned players, and a large number of local blenders. Market competition is driven by brand recognition, distribution reach, pricing discipline, OEM approvals, and the ability to serve both mass-market and industrial customers. While multinational brands dominate premium and OEM-aligned segments, local and regional players compete aggressively in volume-driven motorcycle and industrial markets through pricing, localized distribution, and channel relationships.
Key Companies Operating in the Indonesia Lubricants Market
Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
Pertamina Lubricants | 1957 | Jakarta, Indonesia |
Shell Lubricants | 1907 | The Hague, Netherlands |
ExxonMobil Lubricants | 1870 | Irving, Texas, USA |
Castrol | 1899 | London, United Kingdom |
TotalEnergies Lubricants | 1924 | Paris, France |
Chevron Lubricants | 1879 | San Ramon, California, USA |
Idemitsu Lubricants | 1911 | Tokyo, Japan |
ENEOS | 1888 | Tokyo, Japan |
Fuchs Lubricants | 1931 | Mannheim, Germany |
Some of the Recent Competitor Trends and Key Information About Competitors Include:
Pertamina Lubricants: As Indonesia’s national oil company lubricant arm, Pertamina Lubricants maintains strong market leadership through extensive retail penetration, competitive pricing, and alignment with domestic fuel distribution infrastructure. The company benefits from widespread brand recognition and continues to strengthen its position in both automotive and industrial segments through localized product formulations and government-linked contracts.
Shell Lubricants: Shell maintains a strong premium positioning in Indonesia, particularly in passenger car, commercial vehicle, and industrial lubricants. Its competitive advantage is supported by OEM partnerships, advanced additive technology, and branded service programs that emphasize engine protection and efficiency. Shell is especially strong in urban markets and organized service networks.
ExxonMobil Lubricants: Mobil-branded lubricants are widely recognized for performance and durability, with strong traction in commercial vehicles, mining, and industrial applications. ExxonMobil’s positioning is reinforced by global technical credentials and its ability to serve fleet and industrial customers seeking extended drain intervals and lifecycle cost optimization.
Castrol (bp): Castrol continues to leverage strong brand equity in motorcycle and passenger car segments, supported by aggressive marketing, motorsports associations, and mechanic loyalty programs. The brand’s strength lies in premium and semi-premium offerings, particularly in urban and semi-urban markets.
TotalEnergies Lubricants: TotalEnergies focuses on balanced growth across automotive and industrial lubricants, with increasing emphasis on fleet, mining, and energy customers. Its strategy centers on technical support, OEM approvals, and long-term supply agreements rather than purely retail-driven volume competition.
What Lies Ahead for Indonesia Lubricants Market?
The Indonesia lubricants market is expected to expand steadily through 2035, supported by long-term growth in vehicle population, sustained aftermarket consumption, industrial expansion, and ongoing infrastructure and mining activity. Demand momentum will be reinforced by the replacement-driven nature of automotive lubricants, increasing mechanization across industrial and agricultural sectors, and gradual upgrading of lubricant specifications as equipment performance requirements rise. As Indonesia continues to urbanize and modernize its transportation and industrial base, lubricants will remain a critical consumable underpinning mobility, productivity, and asset longevity across the economy.
Gradual Transition Toward Higher-Performance and Application-Specific Lubricants: The future of the Indonesia lubricants market will see a measured shift from basic mineral oils toward semi-synthetic and synthetic formulations, particularly in passenger vehicles, commercial fleets, and critical industrial applications. Newer engine technologies, OEM recommendations, tighter emission norms, and higher operating temperatures will drive demand for lubricants with better oxidation stability, wear protection, and extended drain capabilities. In industrial segments, demand will increasingly favor application-specific lubricants designed for harsh operating environments, heavy loads, and continuous-duty equipment. Suppliers that align product portfolios with evolving equipment specifications and offer technical support will capture higher-value demand.
Sustained Aftermarket Dominance Supported by Vehicle Parc Growth: Indonesia’s large and expanding vehicle parc—especially motorcycles—will continue to anchor lubricant consumption through frequent oil change cycles and a fragmented, service-oriented aftermarket. Ride-hailing, last-mile delivery, and small commercial fleets will further reinforce repeat demand. While OEM-authorized service channels will grow in importance for newer vehicles, independent workshops and retailers will remain the primary point of sale for lubricants. Brands that maintain strong mechanic engagement, retail visibility, and price-tiered offerings will be best positioned to defend volume leadership.
Industrial, Mining, and Energy Sectors Drive Stable Non-Automotive Demand: Beyond automotive usage, steady growth is expected from industrial manufacturing, mining, power generation, and resource-processing sectors. Expansion of nickel processing, coal mining, cement production, and palm oil processing will increase demand for hydraulic oils, gear oils, greases, and specialty industrial lubricants. Infrastructure development and power capacity additions will further expand the installed base of lubricated equipment. These segments value reliability, supply continuity, and lifecycle cost optimization, favoring suppliers with strong technical capabilities and direct customer engagement.
Increasing Focus on Distribution Efficiency and Regional Penetration: Through 2035, lubricant suppliers will increasingly focus on improving distribution efficiency across Indonesia’s geographically dispersed markets. Investments in regional depots, distributor capability, digital ordering platforms, and fleet-oriented supply models will be critical to maintaining service levels outside Java. Companies that can balance cost-effective logistics with reliable availability in remote and industrial regions will gain competitive advantage, particularly in mining, construction, and energy-linked demand pockets.
Indonesia Lubricants Market Segmentation
By Product Type
• Automotive Engine Oils (2W, Passenger Car, Commercial Vehicle)
• Industrial Lubricants (Hydraulic, Gear, Compressor, Turbine Oils)
• Marine & Offshore Lubricants
• Greases & Specialty Lubricants
• Process Oils & Others
By Base Oil Type
• Mineral Oil-based Lubricants
• Semi-Synthetic Lubricants
• Fully Synthetic Lubricants
By End-Use Sector
• Automotive & Transportation
• Industrial Manufacturing & Processing
• Mining, Construction & Heavy Equipment
• Marine & Others
By Distribution Channel
• Aftermarket (Retailers, Workshops, Distributors)
• OEM & Authorized Service Networks
• Direct Industrial & Fleet Supply
By Region
• Java
• Sumatra
• Kalimantan
• Sulawesi
• Eastern Indonesia
Players Mentioned in the Report:
• Pertamina Lubricants
• Shell Lubricants
• ExxonMobil Lubricants
• Castrol (bp)
• TotalEnergies Lubricants
• Chevron Lubricants
• Idemitsu Lubricants
• ENEOS
• Fuchs Lubricants
• Regional lubricant blenders, distributors, and independent brands
Key Target Audience
• Lubricant manufacturers and base oil suppliers
• Automotive lubricant marketers and brand owners
• Industrial lubricant suppliers and technical service providers
• Vehicle fleet operators and logistics companies
• Mining, construction, and energy companies
• Automotive workshops and service center networks
• Distributors and channel partners
• Private equity firms and investors tracking automotive and industrial consumables
• Government and regulatory bodies involved in standards and environmental compliance
Time Period
Historical Period: 2019–2024
Base Year: 2025
Forecast Period: 2025–2035
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4. 1 Delivery Model Analysis for Lubricants-OEM Supply, Aftermarket Distribution, Direct Industrial Supply [Margins, Preference, Strength & Weakness]
4. 2 Revenue Streams for Indonesia Lubricants Market [Automotive Lubricants, Industrial Lubricants, Marine Lubricants, Greases & Specialty Oils]
4. 3 Business Model Canvas for Indonesia Lubricants Market [Key Partners, Key Activities, Value Propositions, Customer Segments, Cost Structure, Revenue Streams]
5. 1 Local Players vs Global Brands [Pertamina vs Shell / ExxonMobil etc.]
5. 2 Investment Model in Indonesia Lubricants Market [Capacity Expansion, Brand Investments, Distribution Partnerships, M&A]
5. 3 Comparative Analysis of Lubricant Consumption in Automotive vs Industrial Sectors [Procurement Models, Use Cases, Cost Benchmarks]
5. 4 Lubricant Budget Allocation by End-User Type [Individual Consumers, Fleets, Industrial Users]
8. 1 Revenues (Historical Trend)
9. 1 By Market Structure (OEM Supply vs Aftermarket Sales)
9. 2 By Product Type (Engine Oils, Industrial Oils, Marine Oils, Greases, Specialty Lubricants)
9. 3 By End-Use Industry (Automotive, Manufacturing, Mining, Energy, Marine, Agriculture)
9. 4 By Vehicle & Equipment Type (Two-Wheelers, Passenger Cars, Commercial Vehicles, Industrial Machinery)
9. 5 By Application (Engine, Transmission, Hydraulic Systems, Gear Systems, Compressor & Turbine)
9. 6 By Base Oil Type (Mineral, Semi-Synthetic, Fully Synthetic)
9. 7 By Branded vs Unbranded Lubricants
9. 8 By Region (Java, Sumatra, Kalimantan, Sulawesi, Eastern Indonesia)
10. 1 Customer Segmentation & Consumption Pattern Analysis
10. 2 Lubricant Purchase Drivers & Decision-Making Process
10. 3 Performance, Cost & Drain Interval Effectiveness Analysis
10. 4 Gap Analysis Framework
11. 1 Trends & Developments in Indonesia Lubricants Market
11. 2 Growth Drivers for Indonesia Lubricants Market
11. 3 SWOT Analysis for Indonesia Lubricants Market
11. 4 Issues & Challenges for Indonesia Lubricants Market
11. 5 Government Regulations for Indonesia Lubricants Market
12. 1 Market Size and Future Potential for Automotive & Industrial Lubricants in Indonesia
12. 2 Business Models & Revenue Streams [Retail Sales, Fleet Contracts, Industrial Supply Agreements]
12. 3 Distribution Models & Lubricant Applications Offered [Retail Packs, Bulk Supply, OEM-Fill Products]
15. 1 Market Share of Key Players in Indonesia Lubricants Market (By Revenues)
15. 2 Benchmark of Key Competitors [Company Overview, USP, Business Strategies, Business Model, Manufacturing Capacity, Revenues, Pricing Strategy, Product Portfolio, Key Customers, Strategic Alliances, Marketing Strategy, Recent Developments]
15. 3 Operating Model Analysis Framework
15. 4 Competitive Positioning Matrix for Lubricant Brands
15. 5 Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
16. 1 Revenues (Projections)
17. 1 By Market Structure (OEM and Aftermarket)
17. 2 By Product Type (Engine Oils, Industrial Oils, Marine Oils, Greases, Specialty Lubricants)
17. 3 By End-Use Industry (Automotive, Manufacturing, Mining, Energy, Marine, Agriculture)
17. 4 By Vehicle & Equipment Type (Two-Wheelers, Passenger Cars, Commercial Vehicles, Industrial Machinery)
17. 5 By Application (Engine, Transmission, Hydraulic, Gear, Compressor & Turbine)
17. 6 By Base Oil Type (Mineral, Semi-Synthetic, Fully Synthetic)
17. 7 By Branded vs Unbranded Lubricants
17. 8 By Region (Java, Sumatra, Kalimantan, Sulawesi, Eastern Indonesia)
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
We begin by mapping the complete ecosystem of the Indonesia Lubricants Market across demand-side and supply-side entities. On the demand side, entities include private vehicle owners (two-wheelers, passenger cars), commercial fleet operators, ride-hailing and last-mile delivery platforms, industrial manufacturers, mining companies, construction contractors, power generation operators, marine and port operators, agricultural plantations, and public-sector utilities. Demand is further segmented by application type (automotive vs industrial), equipment category (light vehicles, heavy commercial vehicles, stationary machinery), lubricant performance requirement (mineral vs semi-synthetic vs synthetic), and procurement channel (retail aftermarket, OEM-authorized service, direct industrial supply).
On the supply side, the ecosystem includes multinational lubricant marketers, state-owned lubricant producers, regional and local blenders, base oil and additive suppliers, importers, distributor networks, independent retailers, workshops and service centers, logistics providers, and used oil collection and recycling entities. From this mapped ecosystem, we shortlist 8–12 leading lubricant brands and a representative set of regional distributors based on brand penetration, distribution reach, product portfolio breadth, OEM approvals, and exposure across automotive and industrial segments. This step establishes how value is created and captured across formulation, blending, distribution, marketing, and after-sales technical support.
Step 2: Desk Research
An exhaustive desk research process is undertaken to analyze the Indonesia lubricants market structure, demand drivers, and segment behavior. This includes reviewing vehicle parc trends, motorcycle and passenger car penetration, oil change intervals, industrial output indicators, mining and infrastructure project pipelines, and energy sector activity. We assess consumer and fleet behavior related to lubricant selection, price sensitivity, brand loyalty, and adoption of higher-spec formulations.
Company-level analysis includes review of lubricant product ranges, pricing tiers, distribution strategies, retail and workshop engagement models, and industrial customer focus. We also examine regulatory and standards dynamics shaping the market, including national quality standards, environmental guidelines related to waste oil handling, and import policies affecting base oil and additive supply. The outcome of this stage is a comprehensive industry foundation that defines segmentation logic and establishes the assumptions required for market sizing and long-term outlook modeling.
Step 3: Primary Research
We conduct structured interviews with lubricant manufacturers, base oil suppliers, distributors, automotive workshop owners, fleet operators, industrial maintenance managers, and procurement heads across mining, manufacturing, and energy sectors. The objectives are threefold:
(a) validate assumptions around demand concentration by vehicle type, industrial sector, and region,
(b) authenticate segment splits by product type, base oil category, end-use sector, and distribution channel, and
(c) gather qualitative insights on pricing behavior, margin structures, promotional intensity, supply reliability, and customer expectations around performance and drain intervals.
A bottom-to-top approach is applied by estimating lubricant consumption volumes across key vehicle categories and industrial applications, which are aggregated to develop the overall market view. In selected cases, disguised buyer-style interactions are conducted with workshops and distributors to validate field-level realities such as price dispersion, brand substitution behavior, availability issues, and the prevalence of unbranded or counterfeit products.
Step 4: Sanity Check
The final stage integrates bottom-to-top and top-to-down approaches to cross-validate market size, segmentation splits, and forecast assumptions. Demand estimates are reconciled with macro indicators such as vehicle sales trends, industrial production indices, mining output, fuel consumption, and infrastructure investment levels. Assumptions around base oil price volatility, premium lubricant adoption rates, and aftermarket dominance are stress-tested to assess their impact on volume and value growth. Sensitivity analysis is conducted across key variables including vehicle parc growth, industrial expansion intensity, distribution efficiency improvements, and regulatory enforcement. Market models are refined until alignment is achieved between lubricant supply capacity, distribution throughput, and end-user consumption behavior, ensuring internal consistency and robust directional forecasting through 2035.
FAQs
01 What is the potential for the Indonesia Lubricants Market?
The Indonesia lubricants market holds strong long-term potential, supported by a large and growing vehicle parc, high dependence on motorcycles for daily mobility, and sustained industrial, mining, and infrastructure activity. The replacement-driven nature of lubricant consumption provides structural demand stability, while gradual upgrading toward higher-performance formulations supports value growth. As industrialization deepens and equipment intensity increases, lubricants will remain a critical consumable across the Indonesian economy through 2035.
02 Who are the Key Players in the Indonesia Lubricants Market?
The market features a mix of multinational oil majors, state-owned lubricant producers, and strong regional and local brands. Competition is shaped by brand recognition, distribution reach, pricing discipline, OEM approvals, and the ability to serve both mass-market automotive demand and technically demanding industrial applications. Distributor networks and workshop relationships play a central role in market penetration and volume leadership, particularly in the automotive aftermarket.
03 What are the Growth Drivers for the Indonesia Lubricants Market?
Key growth drivers include expansion of the on-road vehicle population, frequent oil change cycles in motorcycles and commercial vehicles, growth of ride-hailing and delivery fleets, and steady demand from industrial, mining, and energy sectors. Additional momentum comes from gradual adoption of semi-synthetic and synthetic lubricants, OEM-led specification upgrades, and increasing awareness of lifecycle cost benefits among fleet and industrial users.
04 What are the Challenges in the Indonesia Lubricants Market?
Challenges include volatility in base oil and additive prices, intense price competition in the aftermarket, high market fragmentation, and the prevalence of unbranded or counterfeit products. Distribution inefficiencies across Indonesia’s archipelagic geography can affect supply reliability and working capital cycles. Slower adoption of premium lubricants in price-sensitive segments also limits near-term value uplift despite strong underlying volume demand.