Israel Logistics and warehousing Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Segments (Transportation, Warehousing, and Value-Added Services), By End-Users, By Domestic vs International Flow, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0283
- Region: Middle East
- Published on: September 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Israel Logistics and Warehousing Market Outlook to 2029 - By Market Segments (Transportation, Warehousing, and Value-Added Services), By End-Users, By Domestic vs International Flow, and By Region” provides an in-depth analysis of the logistics and warehousing industry in Israel. The report covers the genesis and overview of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, segmentation by key parameters; emerging trends, regulatory and infrastructure framework, customer preferences, challenges and risks, competitive landscape including market share of leading players, comparative insights, and company profiling of major logistics and warehousing service providers in Israel. The report concludes with future projections for the market segmented by services, regions, and end-use industries, backed by cause-effect relationships and success case studies.
Israel Logistics and Warehousing Market Overview and Size
The Israel logistics and warehousing market was valued at USD 6.4 Billion in 2023, driven by rising demand from e-commerce, pharmaceuticals, and hi-tech industries, coupled with Israel’s strategic geographical location as a trade gateway between Europe, Asia, and Africa. The market is supported by advanced port infrastructure in Haifa and Ashdod, a robust road and rail network, and significant investments in cold chain and automated warehousing solutions.
Leading players include DHL Israel, FedEx, ZIM Integrated Shipping, Flying Cargo, and Fridenson Group. These companies are known for their end-to-end logistics capabilities, specialized warehousing solutions, and adoption of digital technologies.
In 2023, ZIM partnered with a local warehousing provider to expand inland distribution centers near Tel Aviv and Haifa, enhancing last-mile efficiency and reducing lead times for e-commerce clients. Central Israel remains the logistics hub due to proximity to ports, industrial clusters, and major population centers.
%2C%202019-2024.png)
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the Israel Logistics and Warehousing Market
Strategic Location and Trade Connectivity: Israel’s position at the crossroads of three continents facilitates smooth trade flows. It has Free Trade Agreements with the EU and the U.S., enhancing its logistics potential. Over 90% of Israel’s imports and exports move via maritime routes, with efficient container handling at Haifa and Ashdod ports.
E-Commerce and Retail Boom: Online retail penetration in Israel crossed 75% in 2023, driving up demand for faster fulfillment and micro-warehousing in urban centers. E-commerce logistics revenue grew by 15% YoY, especially for last-mile delivery and returns management services.
Government Investments in Infrastructure: The Ministry of Transport’s “National Logistics Strategy 2030” includes expansion of rail freight corridors, smart logistics hubs, and green warehousing initiatives. In 2023, over USD 800 million was allocated for enhancing freight corridors and dry port facilities.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for Israel Logistics and Warehousing Market
Land and Infrastructure Constraints: Limited availability of industrial land, especially in central Israel, has led to soaring warehouse rental costs. In 2023, prime warehousing rents in Tel Aviv and Haifa surged by 12% YoY, making it challenging for SMEs and logistics startups to scale operations. With less than 2% vacancy in major logistics parks, space constraints are a significant bottleneck.
Geopolitical Uncertainty: Periodic regional tensions and security issues have impacted cross-border logistics operations and caused delays in supply chain continuity. According to trade bodies, disruptions in 2023 led to a 5–7% increase in insurance premiums and additional compliance requirements, affecting delivery timelines and costs.
Fragmentation of Domestic Logistics Services: The domestic logistics sector remains fragmented, with numerous small-scale operators lacking standardization and digital capabilities. Approximately 60% of local logistics providers still rely on manual processes, leading to inefficiencies in inventory management and transportation planning.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market
Port Privatization and Expansion Programs: The Israeli government has undertaken reforms to privatize and modernize the Haifa and Ashdod ports to increase operational efficiency and reduce turnaround times. In 2023, container handling time at Haifa Port was reduced by 18%, driven by private sector involvement and equipment upgrades.
Green Logistics and Emission Norms: To curb emissions, Israel has introduced environmental regulations mandating lower-emission transport fleets and energy-efficient warehouse construction. New logistics facilities must comply with Israel’s Green Building Standard (IS 5281), and over 25% of new warehouses in 2023 were certified green.
Digitization Incentives: The Ministry of Economy has launched subsidies and grants to encourage digital transformation in logistics. In 2023, over 150 logistics SMEs received grants to adopt technologies like transport management systems (TMS), automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS), and IoT tracking. This initiative aims to reduce logistics lead times and improve operational visibility.
Israel Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
By Market Structure: The Israeli logistics market is primarily driven by organized players that offer integrated logistics solutions, including transportation, warehousing, and value-added services. These companies, such as DHL, Flying Cargo, and Fridenson Group, dominate due to their established infrastructure, technology adoption, and service reliability. However, unorganized players—mostly small-scale transporters and independent warehouse operators—still play a significant role in domestic and last-mile logistics. They are especially prominent in secondary cities and offer lower-cost solutions for small and medium-sized businesses.
%2C%202023%20(1).png)
By End-User Industry: Retail and e-commerce are among the top users of logistics and warehousing services, driven by rising consumer demand and rapid fulfillment expectations. In 2023, e-commerce logistics accounted for a significant share, especially in urban areas like Tel Aviv and Jerusalem. Pharmaceuticals and high-tech electronics also contribute significantly due to their requirement for specialized, often temperature-controlled, and secure logistics environments. Additionally, agriculture and food processing industries rely on cold chain logistics and regional warehousing for export-oriented supply chains.
%2C%202023.png)
By Type of Services: Transportation services continue to command the largest share of the logistics sector, covering road freight, sea freight, and air cargo. Road transportation is the most dominant due to its extensive use for domestic delivery. Warehousing services, including cold storage and automated facilities, are gaining traction with the rise in inventory holding needs. Meanwhile, value-added services—such as packaging, labeling, and cross-docking—are increasingly offered as bundled solutions by third-party logistics providers to enhance efficiency and customer satisfaction.
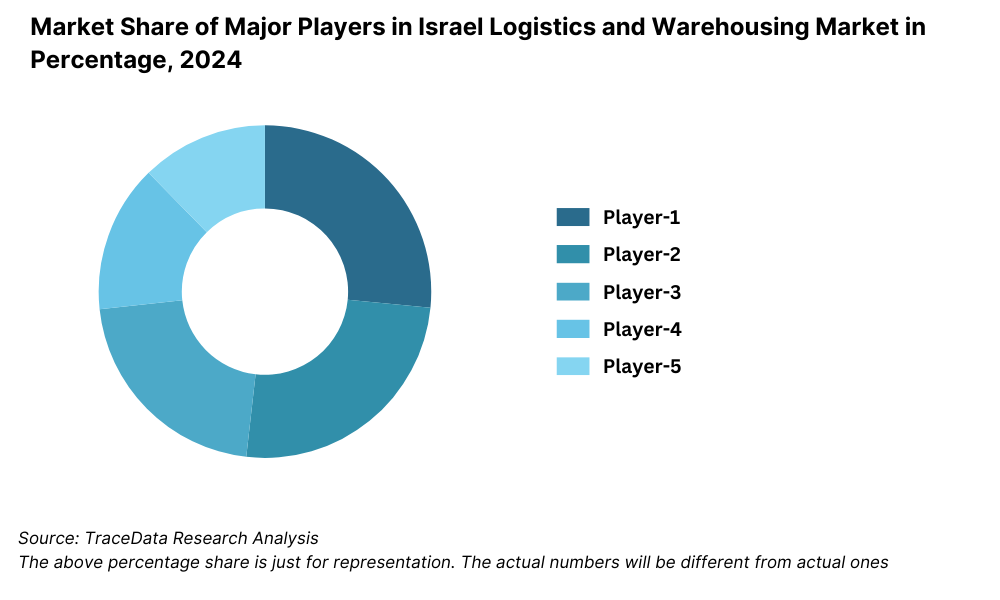
Competitive Landscape in Israel Logistics and Warehousing Market
The Israel logistics and warehousing market is moderately consolidated, with a few major domestic and international players offering end-to-end logistics services. However, the rise of specialized and tech-driven firms has added new dynamics to the market, especially in last-mile delivery, cold chain logistics, and smart warehousing. Key players include DHL Israel, Flying Cargo, Fridenson Group, ZIM Integrated Shipping, and Orian.
Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
DHL Israel | 1969 | Tel Aviv, Israel |
Flying Cargo | 1982 | Lod, Israel |
Fridenson Group | 1975 | Rishon LeZion, Israel |
ZIM Integrated Shipping | 1945 | Haifa, Israel |
Orian | 1953 | Airport City, Israel |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
DHL Israel: One of the most established international logistics players in Israel, DHL has strengthened its B2B and B2C logistics capabilities. In 2023, DHL expanded its warehousing footprint in Central Israel by 15% to meet rising demand from the pharmaceutical and electronics sectors. It also introduced electric delivery vans to support sustainability goals.
Flying Cargo: A major player in freight and express delivery, Flying Cargo reported a 12% increase in third-party logistics (3PL) contracts in 2023, driven by growing demand from e-commerce and retail sectors. The company continues to invest in automation technologies and cold storage capacity.
Fridenson Group: Known for its strong presence in warehousing, sea freight, and customs brokerage, Fridenson launched a 20,000 sq. m automated distribution center in 2023 in the Modi’in region. The move is part of its strategy to enhance fulfillment efficiency and support omni-channel retail logistics.
ZIM Integrated Shipping: ZIM, a global container shipping company headquartered in Haifa, is expanding its inland logistics solutions. In 2023, ZIM launched “ZIM Logistics Israel,” aiming to provide integrated services from port to warehouse for large importers and exporters.
Orian: A logistics solutions provider focused on customs, freight forwarding, and contract logistics, Orian achieved 18% revenue growth in 2023. It is leveraging data analytics and WMS (Warehouse Management Systems) to enhance inventory accuracy and reduce fulfillment time for its clients.
What Lies Ahead for Israel Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Israel logistics and warehousing market is projected to grow steadily through 2029, supported by robust trade dynamics, technological innovation, and increasing investments in infrastructure. The industry is expected to register a healthy CAGR during the forecast period, driven by demand across sectors like e-commerce, pharma, agriculture, and electronics.
Rise of Smart Warehousing and Automation: The future of logistics in Israel will be shaped by the adoption of AI, IoT, and robotics in warehouse operations. Automated inventory management, predictive maintenance, and real-time tracking will become industry norms, reducing operational costs and improving efficiency. By 2029, it is estimated that nearly 40% of warehousing operations will be partially or fully automated.
Expansion of Cold Chain Logistics: With Israel increasing exports of high-value agricultural and pharmaceutical products, demand for cold chain infrastructure will accelerate. Investments in temperature-controlled storage and real-time monitoring systems are expected to drive this segment. Cold chain is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 9% through 2029.
Sustainability and Green Logistics Initiatives: Environmental concerns are prompting logistics firms to adopt cleaner technologies. Electric delivery fleets, solar-powered warehouses, and carbon offset programs will play a central role in the industry’s evolution. The government’s green logistics policies will further push companies toward eco-friendly operations, especially in urban logistics zones.
Regional Logistics Hubs Development: To reduce dependence on Tel Aviv and Haifa, the government plans to develop regional logistics corridors, particularly in the Negev and Northern regions. This includes dry ports, multimodal logistics parks, and enhanced rail freight connectivity. These initiatives are aimed at decentralizing logistics capacity and improving nationwide distribution efficiency.
%2C%202024-2030.png)
Israel Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
• By Market Structure:
o Organized Sector
o Unorganized Sector
o 3PL (Third-Party Logistics Providers)
o In-House Logistics
o Freight Forwarders
o Warehousing Operators
o Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Services
o Cold Chain Operators
• By End-User Industry:
o E-commerce
o Retail and FMCG
o Pharmaceuticals
o Agriculture and Food Processing
o Hi-Tech and Electronics
o Automotive
o Industrial Goods
• By Type of Services:
o Transportation (Road, Rail, Sea, Air)
o Warehousing (Dry, Cold, Automated)
o Value-Added Services (Packaging, Labelling, Kitting)
o Last-Mile Delivery
o Cross-Docking
o Inventory Management
• By Type of Transport Mode:
o Road Freight
o Sea Freight
o Air Freight
o Rail Freight
• By Cold Chain Logistics:
o Pharmaceuticals
o Dairy Products
o Fruits and Vegetables
o Meat and Seafood
o Frozen Food
• By Region:
o Central Israel (Tel Aviv, Petah Tikva)
o Northern Israel (Haifa, Acre)
o Southern Israel (Be’er Sheva, Negev)
o Jerusalem Area
o Coastal Corridor
Players Mentioned in the Report
• DHL Israel
• Flying Cargo
• Fridenson Group
• ZIM Integrated Shipping
• Orian
• UPS Israel
• Israel Post
• FedEx Israel
Key Target Audience
• Logistics Companies
• Warehousing Operators
• Cold Chain Logistics Providers
• E-commerce and Retail Chains
• Industrial and Pharmaceutical Manufacturers
• Transportation and Freight Companies
• Investment and Infrastructure Firms
• Government and Regulatory Authorities
• Market Research and Consulting Firms
Time Period
• Historical Period: 2018–2023
• Base Year: 2024
• Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and Challenges Faced
4.2. Revenue Streams for Israel Logistics and Warehousing Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Israel Logistics and Warehousing Market
4.4. Client Logistics Decision-Making Process
4.5. Supply-Side Decision-Making Process
5.1. Israel Trade Volume and Logistics Infrastructure, 2018-2024
5.2. Road vs Rail vs Sea Freight Usage Share, 2018-2024
5.3. Logistics Spend as % of GDP in Israel, 2024
5.4. Number of Logistics Operators and Warehouses by Region
8.1. Revenues, 2018-2024
8.2. Freight Volume and Warehouse Capacity, 2018-2024
9.1. By Market Structure (Organized vs Unorganized), 2023-2024P
9.2. By End-Use Industry (E-commerce, Pharma, Agriculture, Electronics), 2023-2024P
9.3. By Type of Service (Transportation, Warehousing, Value-Added Services), 2023-2024P
9.4. By Transport Mode (Road, Rail, Air, Sea), 2023-2024P
9.5. By Cold Chain Segments (Food, Dairy, Pharma), 2023-2024P
9.6. By Region (Central, Northern, Southern, Jerusalem, Coastal), 2023-2024P
10.1. Industry-Wise Logistics Spend Behavior
10.2. Buyer Journey and Selection Criteria
10.3. Need-Pain Point Mapping Across Segments
10.4. Demand-Supply Gap Analysis Model
11.1. Trends and Developments for Israel Logistics and Warehousing Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Israel Logistics and Warehousing Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Israel Logistics and Warehousing Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges for Israel Logistics and Warehousing Market
11.5. Government Regulations for Israel Logistics and Warehousing Market
12.1. Market Size and Growth Potential for E-commerce Fulfillment, 2018-2029
12.2. Business Models and Revenue Streams
12.3. Comparison of Leading Last-Mile Delivery Players on Key Variables
13.1. Penetration and Growth of Cold Chain Services, 2018-2029
13.2. Regulatory Framework for Pharma and Food Logistics
13.3. Cold Storage Capacity Split by Region and Sector
13.4. Key Cold Chain Logistics Providers and Innovations
16.1. Benchmarking of Key Logistics Players: Overview, Services, Revenue, Coverage, Warehousing, Technology Adoption
16.2. Strength and Weakness Mapping
16.3. Operating Model Analysis Framework
16.4. Gartner Magic Quadrant
16.5. Bowmans Strategic Clock for Competitive Positioning
17.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
17.2. Freight Volume and Warehouse Demand, 2025-2029
18.1. By Market Structure (Organized vs Unorganized), 2025-2029
18.2. By End-Use Industry, 2025-2029
18.3. By Type of Service, 2025-2029
18.4. By Transport Mode, 2025-2029
18.5. By Cold Chain Segments, 2025-2029
18.6. By Region, 2025-2029
18.7. Recommendation
18.8. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the logistics ecosystem in Israel, identifying all demand-side (e.g., e-commerce firms, pharma exporters, industrial manufacturers) and supply-side entities (e.g., 3PL providers, warehousing operators, cold chain firms, transport companies). Based on this mapping, we shortlist leading 6–8 logistics providers in the country, using parameters like operational scale, infrastructure capacity, client base, and financial performance.
Sourcing is initiated through in-depth analysis of industry articles, market intelligence platforms, port and freight reports, and proprietary databases to build a robust understanding of the logistics and warehousing landscape.
Step 2: Desk Research
Comprehensive desk research is conducted using secondary and proprietary sources to collect and synthesize macroeconomic and sector-level data. This includes analysis of import-export trends, transport infrastructure development, warehousing capacity expansion, and trade statistics.
Company-level analysis is also carried out through examination of press releases, annual reports, investor presentations, financial disclosures, and regulatory filings. This enables the estimation of market share, growth strategies, investment flows, and service segmentation.
Step 3: Primary Research
In-depth interviews are conducted with key decision-makers across logistics companies, warehousing firms, e-commerce clients, cold chain operators, and transportation service providers. These include operations heads, logistics planners, supply chain directors, and regulatory officials.
These interviews serve to validate market assumptions, confirm operational practices, and collect qualitative and quantitative insights into pricing, demand patterns, customer preferences, and operational challenges. A bottom-up approach is taken to estimate segment-wise revenue contributions which are then aggregated to size the overall market.
To cross-verify the findings, disguised interviews are performed where our researchers approach selected companies as potential clients. This ensures cross-validation of cost structures, turnaround times, service portfolios, and warehouse occupancy rates.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- Final market size estimation is performed using a triangulated methodology involving top-down, bottom-up, and peer benchmarking analysis. Internal models based on capacity utilization, demand-side consumption, and revenue generation trends are applied to validate the figures and ensure consistency across verticals and regions.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Israel Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Israel logistics and warehousing market holds significant potential, reaching an estimated value of USD 6.4 Billion in 2023. Growth is being driven by rising demand from sectors like e-commerce, pharmaceuticals, and high-tech manufacturing, as well as Israel’s strategic position as a trade gateway between Europe, Asia, and Africa. Ongoing infrastructure investments and the adoption of smart technologies are expected to accelerate growth through 2029.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Israel Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Key players in the Israel logistics and warehousing market include DHL Israel, Flying Cargo, Fridenson Group, ZIM Integrated Shipping, and Orian. These companies lead the market due to their established networks, advanced infrastructure, and comprehensive service offerings. Other important players include UPS Israel, Israel Post, and FedEx Israel, especially in the express delivery and cross-border logistics segments.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Israel Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Major growth drivers include the rapid expansion of e-commerce, increasing exports of pharmaceuticals and agricultural products, and continued government investment in logistics corridors, ports, and freight infrastructure. The adoption of automation and digitization across warehousing and transportation operations is also improving efficiency and enabling scale. Additionally, green logistics initiatives are gaining momentum, creating new opportunities in sustainable supply chain solutions.
4. What are the Challenges in the Israel Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The market faces several challenges such as limited availability of industrial land in key urban areas, high logistics costs due to fuel and toll charges, and a fragmented domestic logistics network with many small operators still relying on manual processes. Geopolitical instability in the region can also disrupt trade routes and impact freight movement. Moreover, a shortage of skilled labor in supply chain management and automation remains a barrier to scaling smart logistics solutions.