Italy Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Structure, By Products Handled, By Temperature Range, By End-User Industry, By Type of Storage & Transportation, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0284
- Region: Europe
- Published on: September 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Italy Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029 – By Market Structure, By Products Handled, By Temperature Range, By End-User Industry, By Type of Storage & Transportation, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the cold chain logistics industry in Italy. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer level profiling, issues and challenges, and comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the cold chain industry. The report concludes with future market projections based on revenue, market segments, regions, cause and effect relationship, and success case studies highlighting the major opportunities and cautions.
Italy Cold Chain Market Overview and Size
The Italy cold chain market reached a valuation of EUR 4.8 Billion in 2023, driven by rising demand for temperature-sensitive goods, growth in pharmaceutical exports, and expanding e-commerce-based grocery delivery. Major players such as Stef Italia, DHL Supply Chain, Kuehne + Nagel, Lanzi Trasporti, and Number1 Logistics Group are recognized for their integrated cold logistics solutions, temperature-controlled warehousing, and distribution capabilities.
In 2023, DHL expanded its pharma-dedicated cold chain capacity near Milan to serve the growing biopharmaceutical segment. Lombardy, Emilia-Romagna, and Lazio emerged as key logistics hubs due to their advanced infrastructure, high volume of food and pharma activity, and proximity to urban consumption centers.
%2C%202019-2024.png)
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Italy Cold Chain Market:
Pharma & Healthcare Boom: The growth in Italy’s biopharma exports, particularly vaccines and biologics, has boosted the need for ultra-low temperature storage and validated transport protocols. In 2023, over 35% of cold chain logistics revenue was derived from pharmaceutical handling.
Rising Fresh Food Demand: Increasing consumption of fresh and organic food, alongside changing dietary habits, has raised demand for cold storage and refrigerated distribution. The Italian organic food sector grew by 11.2% in 2023, directly supporting cold chain expansion.
Retail & E-Commerce Integration: With online grocery orders growing over 17% YoY in 2023, especially in urban centers, the need for last-mile refrigerated transport has intensified. Major supermarket chains are investing in cold chain automation and micro-fulfillment centers to ensure quality and safety of perishables.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for Italy Cold Chain Market
Fragmented Infrastructure: Despite growth in cold chain demand, Italy still suffers from fragmented logistics infrastructure. A 2023 industry assessment revealed that nearly 42% of small-to-mid-sized food exporters face challenges in accessing end-to-end cold chain services, especially in Southern regions. This fragmentation results in inconsistent temperature control and increased spoilage risk, limiting market efficiency.
Energy and Operational Costs: High electricity prices and fuel costs continue to strain profitability across cold storage and refrigerated transport segments. Energy expenses account for up to 30–35% of operational costs in cold warehouses. In 2023, spikes in utility rates led to a 12% YoY increase in cold chain service prices, impacting affordability for SMEs and reducing service uptake among cost-sensitive users.
Talent and Technical Skill Gaps: The cold chain industry in Italy faces a shortage of trained professionals skilled in refrigeration technology, GDP compliance, and cold chain monitoring. A recent logistics sector report indicated that over 25% of cold storage operators cite difficulty in hiring skilled technicians, impacting their ability to maintain regulatory standards and service reliability.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market
Good Distribution Practice (GDP) Compliance: Italy mandates strict adherence to EU GDP guidelines for the storage and transport of pharmaceutical and biological products. Regulatory authorities conduct routine audits of cold chain providers. In 2023, over 80% of inspected pharma logistics facilities were found to be GDP compliant, a significant rise from 68% in 2019, indicating improving regulatory maturity.
EU Food Safety Standards (HACCP, ISO 22000): Italian food-grade cold storage and transport must comply with HACCP protocols and EU hygiene standards. The Italian Ministry of Health has increased enforcement in recent years. In 2023, around 15% of regional facilities were issued improvement notices after inspections, highlighting the need for tighter quality controls in rural zones.
Sustainability and Emission Norms: Italy is aligning with EU Green Deal objectives by introducing energy efficiency benchmarks for cold storage and incentivizing the use of low-emission refrigerated vehicles. In 2023, the Italian government launched a EUR 60 million fund to co-finance fleet upgrades and energy retrofits, aiming to reduce the cold chain sector’s carbon footprint by 20% by 2027.
Italy Cold Chain Market Segmentation
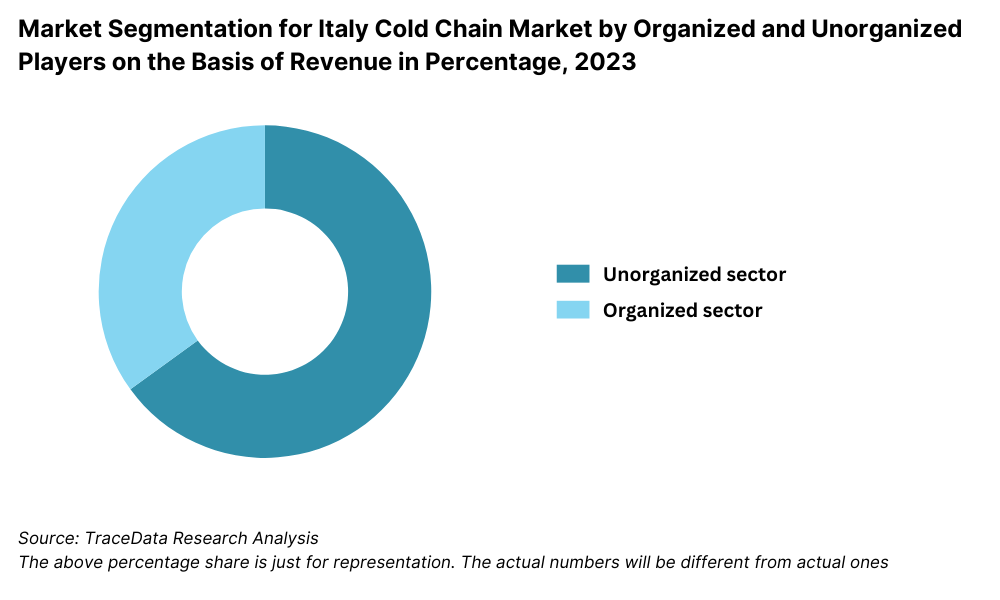
By Market Structure: The Italian cold chain market is primarily driven by organized players, particularly in the pharmaceutical and large-scale food retail segments, due to regulatory compliance and demand for traceability. These players offer integrated end-to-end cold logistics, validated temperature control systems, and high service reliability. However, unorganized players still maintain a presence in smaller cities and traditional food distribution networks, often operating with limited compliance to EU GDP or HACCP standards. Their cost-competitive nature appeals to local SMEs and niche food producers.
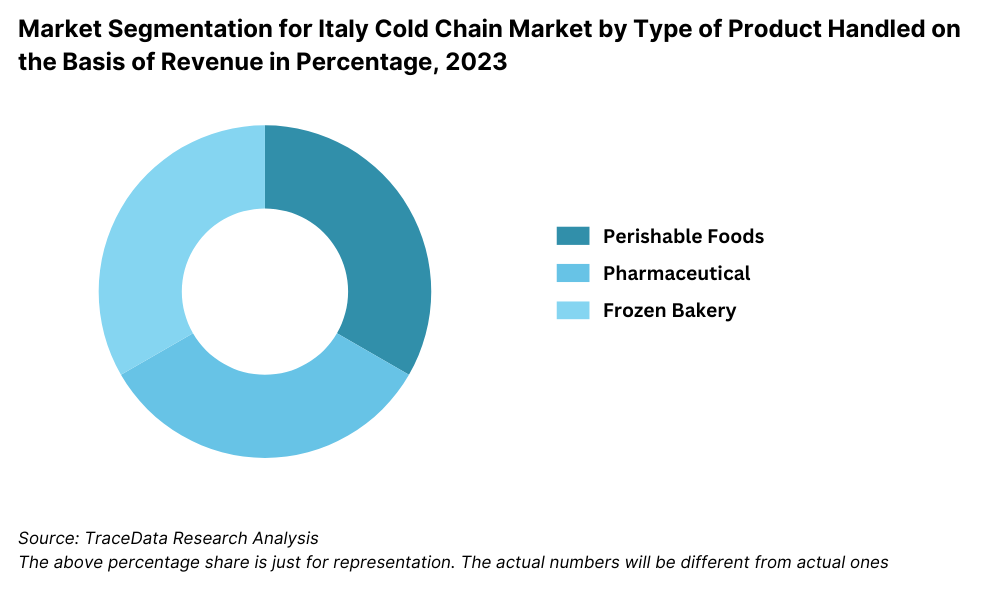
By Product Handled: Perishable food items, including dairy, fruits, vegetables, meat, and seafood, represent the largest share due to Italy's large agri-food export industry and high domestic consumption of fresh products. The pharmaceutical segment has witnessed rapid growth owing to expanding vaccine distribution, clinical trial logistics, and export-oriented biologics. Additionally, frozen bakery, gelato, and artisanal cheese logistics form an important niche within Italy’s premium cold chain offerings.
By Temperature Range: Chilled (0–8°C) dominates the market due to its wide applicability in food and pharma logistics. Frozen segment (-18°C and below) holds a significant share in processed food, frozen seafood, and bakery goods. Ultra-cold logistics (-20°C to -80°C), though smaller in share, is growing steadily due to the rise in biologics and specialty pharmaceutical products that require stringent temperature protocols.
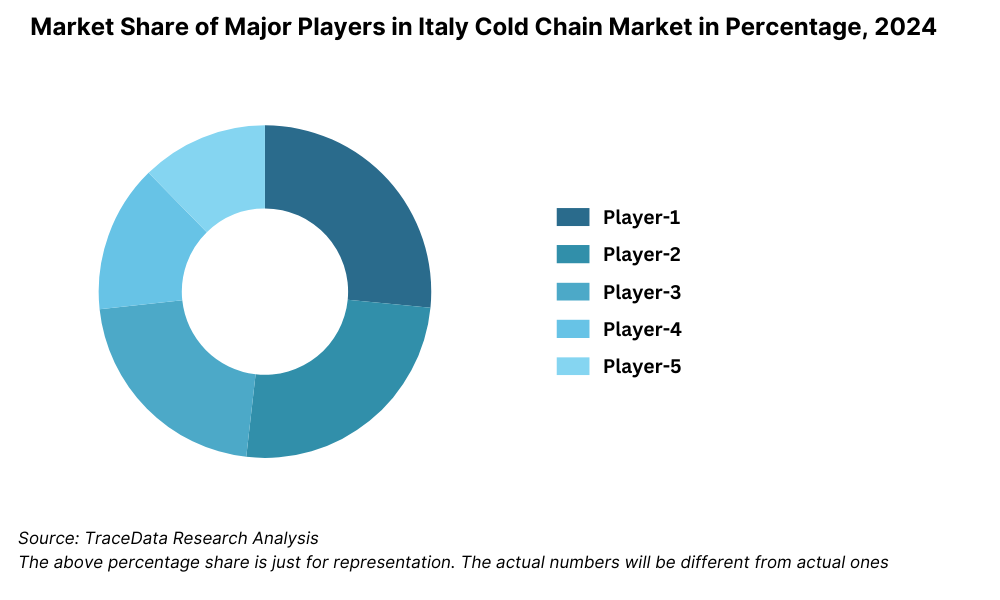
Competitive Landscape in Italy Cold Chain Market
The Italy cold chain market is moderately concentrated, with a mix of global logistics leaders and domestic players offering cold storage, refrigerated transport, and end-to-end supply chain solutions. The market has witnessed increasing investment from international firms aiming to serve the pharmaceutical and fresh food sectors, while regional players continue to dominate local distribution networks. Key companies include Stef Italia, DHL Supply Chain Italy, Kuehne + Nagel, Lanzi Trasporti, Number1 Logistics Group, and Gruppo Gruber Logistics.
Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
Stef Italia | 1997 | Parma, Italy |
DHL Supply Chain Italy | 2005 (Italy operations) | Milan, Italy |
Kuehne + Nagel Italy | 1970 (Italy operations) | Verona, Italy |
Lanzi Trasporti | 1963 | Piacenza, Italy |
Number1 Logistics Group | 1997 | Parma, Italy |
Gruppo Gruber Logistics | 1936 | Ora (BZ), Italy |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
Stef Italia: One of the largest cold logistics operators in Italy, Stef has over 30 cold storage hubs across the country. In 2023, the company expanded its Parma facility by 18,000 pallet positions to serve increasing demand from the dairy and meat export sectors.
DHL Supply Chain Italy: DHL enhanced its pharmaceutical cold chain operations in Milan and Rome in 2023 by introducing real-time temperature tracking and increasing refrigerated fleet size by 12%. The company is also leading sustainability initiatives with solar-powered cold warehouses.
Kuehne + Nagel Italy: The company reported a 14% increase in cold chain revenues in 2023, primarily driven by vaccine logistics and high-value food exports. It operates several GDP-compliant pharma hubs and has invested in IoT-enabled tracking for frozen transport.
Lanzi Trasporti: Known for its strong presence in the Emilia-Romagna region, Lanzi provides cold logistics for artisanal food producers and retail chains. In 2023, it launched a new cross-docking facility near Bologna to optimize its frozen delivery network.
Number1 Logistics Group: Focused on retail and large-scale food distribution, Number1 handled over 55 million chilled parcels in 2023. The company has been expanding its footprint in last-mile refrigerated delivery and micro-fulfillment solutions for grocery clients.
Gruppo Gruber Logistics: With a strong base in Northern Italy and cross-border operations in Austria and Germany, Gruber is increasingly focusing on cold chain for industrial food and pharma. In 2023, the company entered a strategic partnership with a leading biotech firm to provide dedicated ultra-low temperature logistics.
What Lies Ahead for Italy Cold Chain Market?
The Italy cold chain market is projected to experience steady growth through 2029, with a healthy CAGR driven by rising demand for temperature-controlled logistics in the pharmaceutical, food, and retail sectors. The convergence of regulatory compliance, e-commerce penetration, and export-led opportunities is expected to reshape the competitive landscape and drive modernization across the value chain.
Expansion of Pharma Cold Chain Logistics: With Italy’s growing pharmaceutical exports and continued investments in biotechnology, the demand for GDP-compliant, ultra-cold logistics solutions is expected to increase. By 2029, over 40% of pharma shipments may require specialized temperature protocols, prompting a rise in purpose-built cold warehouses and validated transport systems.
Adoption of Smart Cold Chain Technologies: The integration of IoT, blockchain, and real-time temperature monitoring systems is set to transform cold chain operations. These technologies will enhance traceability, reduce spoilage rates, and improve compliance, especially in cross-border logistics. Automation in cold warehouses and AI-based route optimization are expected to be key enablers.
Rise of Urban Micro-Fulfillment Hubs: With the continued growth of online grocery and quick commerce services, urban cold storage hubs will gain prominence. By 2029, Italy’s top 10 metro cities are expected to see a threefold increase in refrigerated last-mile delivery nodes to meet consumer demand for fresh, on-demand food delivery.
Sustainability and Green Logistics: Environmental sustainability will become a cornerstone of growth. Stakeholders will invest in solar-powered cold storage units, electric refrigerated trucks, and energy-efficient cooling systems. Italy’s alignment with EU carbon reduction targets will incentivize companies to adopt cleaner technologies and sustainable packaging materials.
%2C%202024-2030.png)
Italy Cold Chain Market Segmentation
• By Market Structure:
o Organized Cold Chain Providers
o Regional & Local Transporters
o Cold Storage Warehousing Companies
o Integrated 3PL Cold Chain Providers
o Unorganized Transport Operators
o Specialized Cold Last-Mile Delivery Firms
• By Product Handled:
o Fresh Fruits & Vegetables
o Dairy Products
o Meat & Poultry
o Seafood
o Frozen Bakery & Confectionery
o Vaccines & Biologics
o Clinical Trial Shipments
o Cosmetics & Specialty Chemicals
• By Temperature Range:
o Chilled (0–8°C)
o Frozen (-18°C and below)
o Ultra-Cold (-20°C to -80°C)
o Ambient Controlled (15–25°C)
• By Type of Storage & Transportation:
o Cold Storage Warehousing
o Reefer Trucking
o Air-Freight Cold Chain
o Rail-Based Refrigerated Cargo
o Last-Mile Refrigerated Delivery
• By End-User Industry:
o Food & Beverage Manufacturers
o Retail Chains & Supermarkets
o Pharmaceutical Companies
o Clinical Research Organizations
o HoReCa (Hotels, Restaurants, Catering)
o Cosmetic & Personal Care Brands
• By Region:
o Northern Italy (Lombardy, Veneto, Piedmont)
o Central Italy (Tuscany, Lazio)
o Southern Italy (Campania, Puglia, Calabria)
o Islands (Sicily, Sardinia)
Players Mentioned in the Report:
• Stef Italia
• DHL Supply Chain Italy
• Kuehne + Nagel Italy
• Lanzi Trasporti
• Number1 Logistics Group
• Gruppo Gruber Logistics
Key Target Audience:
• Cold Chain Logistics Companies
• Pharmaceutical & Life Sciences Firms
• Food Exporters and Retail Chains
• Industry Associations (e.g., Assologistica, IATA CEIV Pharma Italy)
• Technology Providers (IoT, Refrigeration Systems)
• Regulatory Agencies (e.g., Ministry of Health, EU GDP Oversight)
Time Period:
• Historical Period: 2018–2023
• Base Year: 2024
• Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and Challenges They Face
4.2. Revenue Streams for Italy Cold Chain Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Italy Cold Chain Market
4.4. Buying Decision-Making Process
4.5. Supply Decision-Making Process
5.1. Cold Storage Infrastructure in Italy, 2018-2024
5.2. Growth in Reefer Truck Fleet, 2018-2024
5.3. Energy Consumption in Cold Storage, 2024
5.4. Number of Cold Chain Providers in Italy by Region
8.1. Revenues, 2018-2024
8.2. Volume of Cold Chain Goods Handled, 2018-2024
9.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized), 2023-2024P
9.2. By Type of Product (Fruits, Vegetables, Meat, Pharma, Bakery, etc.), 2023-2024P
9.3. By Temperature Range (Chilled, Frozen, Ultra-Cold, Ambient Controlled), 2023-2024P
9.4. By Type of Storage & Transport (Storage, Trucking, Air Freight, Rail, Last Mile), 2023-2024P
9.5. By End-User Industry (Food, Pharma, Retail, HoReCa), 2023-2024P
9.6. By Region (North, Central, South, Islands), 2023-2024P
10.1. Customer Landscape and Cohort Analysis
10.2. Customer Journey and Decision-Making
10.3. Need, Desire, and Pain Point Analysis
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11.1. Trends and Developments for Italy Cold Chain Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Italy Cold Chain Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Italy Cold Chain Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges for Italy Cold Chain Market
11.5. Government Regulations and Sustainability Initiatives
12.1. Adoption of IoT, Blockchain, Real-Time Monitoring, 2018-2029
12.2. Business Model and Tech-Driven Innovations
12.3. Cross Comparison of Leading Cold Tech Logistics Providers
13.1. Investment Trends in Cold Infrastructure, 2018-2029
13.2. Public and Private Partnerships
13.3. EU Grants and Subsidies Utilized for Cold Chain Projects
13.4. Energy Efficiency Investments and Green Logistics Funding
16.1. Benchmark of Key Players-Company Overview, Infrastructure, USP, Strategies, Coverage, Technology Stack, Fleet Size
16.2. Strengths and Weaknesses
16.3. Operating Model Analysis Framework
16.4. Gartner Magic Quadrant Adaptation
16.5. Bowmans Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
17.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
17.2. Volume of Cold Chain Goods Handled, 2025-2029
18.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized), 2025-2029
18.2. By Type of Product (Fruits, Vegetables, Meat, Pharma, etc.), 2025-2029
18.3. By Temperature Range, 2025-2029
18.4. By Type of Storage & Transport, 2025-2029
18.5. By End-User Industry, 2025-2029
18.6. By Region, 2025-2029
18.7. Recommendation
18.8. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
We begin by mapping the entire ecosystem of the Italy Cold Chain Market, identifying all demand-side and supply-side entities. This includes cold storage providers, refrigerated transporters, pharmaceutical logistics firms, food exporters, and retail distributors. Based on this comprehensive mapping, we shortlist 5–6 leading companies across the cold storage and reefer logistics value chain, considering parameters such as revenue contribution, storage capacity, fleet size, and service offerings.
Sourcing is performed through a mix of industry publications, Italian logistics associations (such as Assologistica), EU cold chain compliance documents, and multiple proprietary and open-access databases to collect initial market-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
We conduct thorough desk research using diverse sources including Euromonitor, Statista, company websites, sustainability reports, national logistics policy documents, and trade databases. The goal is to build a robust understanding of the Italy cold chain landscape—covering market size by revenue, end-user segmentation, service pricing benchmarks, and geographic demand.
This step also includes an in-depth review of company-level information such as financial filings, cold chain infrastructure investments, strategic partnerships, and expansion plans—using sources like Orbis, press releases, annual reports, and business news portals.
Step 3: Primary Research
We conduct structured and semi-structured interviews with C-suite executives, supply chain heads, warehouse managers, and fleet operators across Italy’s cold chain sector. These interviews help validate our secondary findings, uncover operational bottlenecks, and generate qualitative insights on pricing models, service differentiation, and regulatory challenges.
A bottom-up approach is adopted to estimate volume (e.g., storage capacity in cubic meters or pallet positions, transport volume in tons) across individual firms and regions, which are then aggregated to arrive at the overall market estimates.
As part of our triangulation process, disguised interviews are also conducted under the pretext of potential customers. This covert method allows us to cross-check claims made during formal interviews—especially related to storage fees, delivery turnaround times, GDP certification status, and technology usage.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- Both top-down (macroeconomic drivers, cold chain demand from food/pharma exports) and bottom-up (firm-level operational metrics) approaches are employed for market sizing. We also run sensitivity models to check variance ranges, perform scenario testing, and conduct peer benchmarking with comparable EU nations such as Spain and France to validate our base assumptions.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Italy Cold Chain Market?
The Italy cold chain market holds strong growth potential, reaching a valuation of EUR 4.8 Billion in 2023. This growth is driven by rising demand for temperature-controlled logistics across food, pharmaceutical, and retail sectors. The country’s strategic location in the EU, combined with increasing pharmaceutical exports and evolving consumer expectations for fresh and frozen products, positions Italy as a key market in Europe’s cold chain ecosystem.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Italy Cold Chain Market?
The Italy Cold Chain Market features several prominent players including Stef Italia, DHL Supply Chain Italy, and Kuehne + Nagel. These companies dominate the organized segment through their extensive cold storage infrastructure, validated pharma logistics capabilities, and advanced temperature-monitoring technologies. Other key players include Lanzi Trasporti, Number1 Logistics Group, and Gruppo Gruber Logistics.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Italy Cold Chain Market?
Key growth drivers include increased pharmaceutical and vaccine shipments, rising exports of Italian agri-food products, and the expansion of e-commerce-led fresh grocery delivery. Additionally, stricter EU compliance regulations (such as GDP and HACCP), growing consumer focus on food safety, and the adoption of smart logistics technologies are fueling demand for more reliable and scalable cold chain solutions.
4. What are the Challenges in the Italy Cold Chain Market?
Major challenges include fragmented infrastructure, high operational and energy costs, and shortages of skilled cold chain professionals. Smaller regional players often lack the resources to meet stringent compliance standards, especially in southern and rural areas. Additionally, inflationary pressures on fuel and utilities have led to increased service costs, making affordability a concern for SMEs and mid-sized exporters.