Japan Car Detailing Services Market Outlook to 2030
By Market Structure, By Service Provider, By Service Type, By Protection Technology, By Vehicle Class, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0319
- Region: Asia
- Published on: September 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Japan Car Detailing Services Market Outlook to 2030 – By Market Structure, By Service Provider, By Service Type, By Protection Technology, By Vehicle Class, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of Japan’s car beautification and protection ecosystem. The study covers the overview and genesis of the detailing industry, overall market size in revenue terms, and granular market segmentation. The report details trends and developments, the regulatory landscape, customer-level profiling, and issues & challenges. The competitive landscape evaluates competition intensity and differentiation levers, including competition scenario, cross-comparison of leading operators on eight KPIs, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players. The report concludes with future market projections segmented by service type, provider channel, technology, vehicle class, and region, underpinned by a cause-and-effect framework that links vehicle flows, dealer attach-rates, installer capacity, and regulatory shifts to revenue outcomes. It also includes success case studies—dealer bundle programs, LABO/PROSHOP subscription models, PPF full-front vs full-body economics, and SS express-to-studio conversion—highlighting key opportunities and cautions to guide market entry, expansion, and investment decisions.
Japan Car Detailing Market Overview and Size
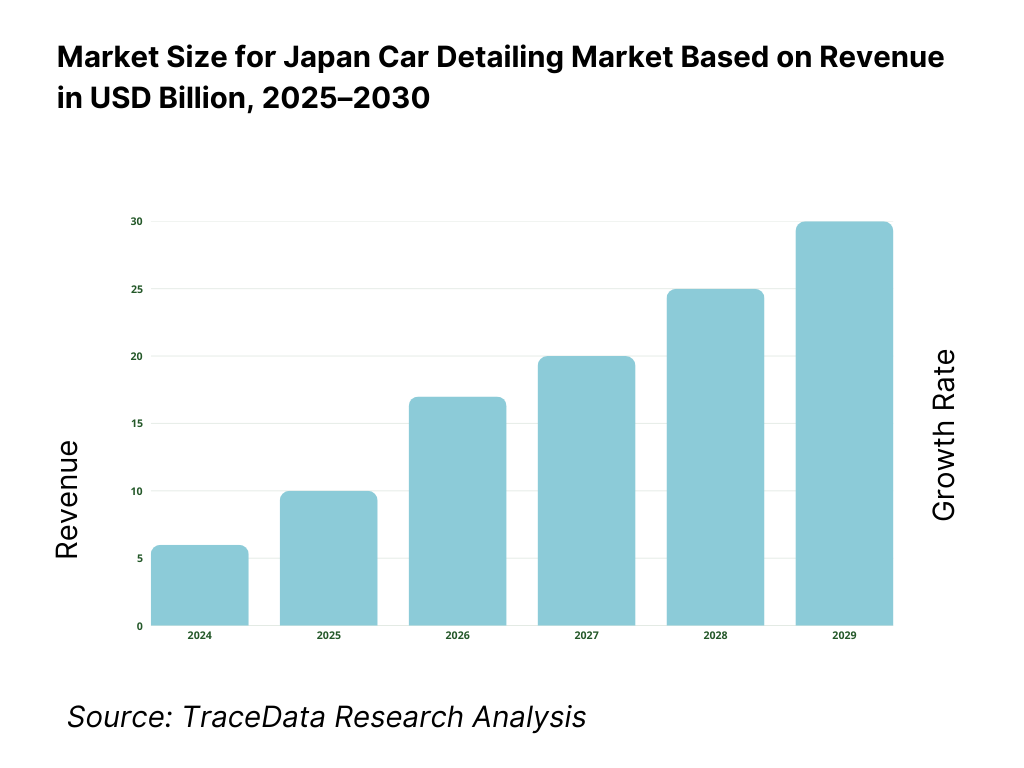
Japan’s car detailing services market is documented at US$1,319.8 million based on a country databook that compiles a five-year historical series and a current base year; the same source charts steady post-pandemic recovery driven by premium exterior services and growing attach-rates at dealer channels. In the next data point available, the market stands at US$1,319.8 million with exterior services the largest revenue stream. Parallel adjacent spend in car wash services is US$1,724.0 million, underscoring the hygiene-to-appearance continuum that funnels demand into higher-value detailing packages.
Greater Tokyo, Nagoya (Aichi), and Osaka-Kansai dominate Japan’s car beautification spend owing to the concentration of dealerships, luxury and near-luxury car parc, and density of certified PROSHOP/LABO outlets that upsell glass/ceramic coatings and interior reconditioning. These metros anchor OEM production and retail networks, sustain high vehicle usage, and exhibit faster adoption of paid maintenance subscriptions—all conditions that lift average ticket sizes and repeat purchase of coatings and paint-protection film. The clustering of large dealer groups and service plazas further channels traffic into organized detailing formats.
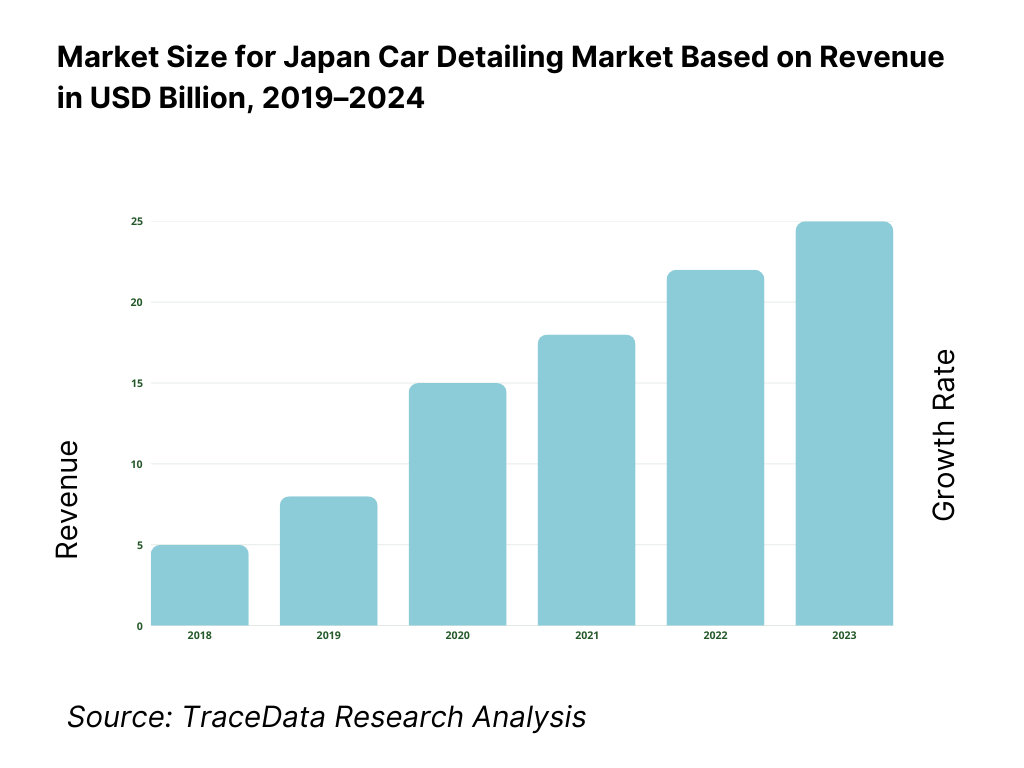
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the Japan Car Detailing Market:
Dense vehicle parc, vigorous sales & reconditioning throughput (market funnel into detailing): Japan’s auto ecosystem guarantees a large flow of vehicles needing paint protection, interior care, and periodic reconditioning. New vehicle registrations total 4,780,000 units, with used‐vehicle transactions adding 6,430,000 units, creating continuous intake for pre-delivery detailing, resale prep, and refresh jobs. On the supply side, the domestic production base delivered 8,998,538 vehicles, sustaining dealer networks that routinely bundle coatings, films, and appearance care. Auto-related employment stands at 5,580,000 people, anchoring a nationwide service footprint (dealers, specialty studios, SS operators) capable of standardized detailing SOPs and warranty programs—key preconditions for high-value glass/ceramic coatings and paint-protection film (PPF) penetration.
Urban and demographic scale that concentrates premium demand (metro pull for coatings & PPF): Japan’s older, affluent urban core keeps vehicles longer and prioritizes cosmetic preservation. The population aged 65+ is 36,243,000 while the 15–64 working cohort is 73,728,000, a mix that sustains routine maintenance yet values warranty-backed appearance protection. Motorcycle parc alone totals 10,300,000 units, expanding the base for glass, trim and plastics care beyond passenger cars. Imported new vehicles add 311,000 premium-leaning units at the showroom, where dealer delivery-day coating attach-rates are highest. These metropolitan clusters concentrate high-ticket exterior coatings and growing PPF jobs, supported by dense dealer and certified-installer networks.
Resilient fuel/retail service station and chain retail infrastructure (capture for entry-level services & upsell): Despite long-term consolidation, Japan still runs a very large fuel/service network that channels drivers into express exterior services and entry-level coatings. The national SS (service station) stock at the end of the latest reported fiscal year is 27,009 sites, following 27,963 at the end of a prior fiscal year. These thousands of bays remain powerful acquisition funnels into higher-value studio jobs or dealer-grade packages. At the same time, Japan’s energy system—documented by METI and the energy white papers—maintains reliable liquid-fuel logistics and retail outlets that co-locate wash bays and appearance menus, keeping traffic and frequency high for basic detailing add-ons. 1,140,000,000 tonnes-CO₂ also frames ongoing environmental compliance investments that modernize SS water/chemical handling relevant to detailing operations.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of the Japan Car Detailing Market:
Shrinking SS footprint & operator consolidation (pressure on low-ticket volumes and access): The fuel-station base—historically the main gateway for entry-level exterior services—continues to contract, reducing convenient wash/quick-detail access and funnel size in rural prefectures. Stations fell to 27,009 sites at the end of the latest fiscal year, from 27,963 the previous fiscal year, less than half of a historical peak of 60,421. Fewer independent operators—12,113—tighten local competition and can curtail on-site wash bay investments, limiting feeder volumes into studio-grade coatings/PPF and raising customer travel time, especially outside megacity belts.
Demographic headwinds for labor & miles driven (aging workforce, fewer young entrants): Japan’s age structure is skewing older: 36,243,000 people are 65+, while the core working population is 73,728,000. MLIT analysis highlights accelerating aging within transportation-adjacent workforces, foreshadowing technician scarcity in car-care roles and slower studio expansion. Policy deck evidence shows rising shares of older workers in transport and related fields. Tight labor pools increase training loads and make it harder to scale certified installer capacity—a prerequisite for multi-layer coatings and PPF—while potentially lowering annual driving exposure in older cohorts, trimming incidental wash/detail frequency.
Compliance cost & operational rigor: water/chemical handling thresholds (SDS/PRTR & effluent rules): Detailers using solvents, cleaners and coatings operate under numeric thresholds that trigger reporting and facility standards. The PRTR/SDS framework covers 462 Class-I substances and 100 Class-II substances; reporting applies from 1 tonne annually (or 0.5 tonne for 15 specific Class-I carcinogens) and typically to businesses with 21+ employees. Wastewater discharges must meet national effluent standards such as BOD 160 mg/L (daily average 120 mg/L), SS 200 mg/L, and n-hexane extracts (mineral oil) 5 mg/L. These numeric limits compel equipment and SOP upgrades, raising fixed costs and requiring technician training.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
Water Pollution Control Act — National Effluent Standards (numeric discharge limits & daily-average caps): Detailing facilities that discharge 50 m³/day or more fall under uniform national standards for living-environment protection. Key limits include BOD 160 mg/L (daily average 120 mg/L), COD 160 mg/L (daily average 120 mg/L), suspended solids 200 mg/L (daily average 150 mg/L), and n-hexane extracts for mineral oil 5 mg/L. Protection-of-health items also set numeric caps—e.g., lead 0.1 mg/L and hexavalent chromium 0.5 mg/L—relevant when handling certain cleaners/primers. Prefectures may impose stricter local values, requiring site-specific wastewater treatment planning.
PRTR & SDS obligations — substance counts, employee triggers, and handling thresholds: Under the PRTR Act and SDS system, Japan specifies 462 Class-I designated chemical substances and 100 Class-II substances for SDS provision. Reporting applies to targeted business operators with 21+ employees that handle 1 tonne or more annually (or 0.5 tonne for 15 “Specific Class I” carcinogens such as benzene and formaldehyde). For detailers, these numeric thresholds determine whether coating chemicals and solvents require PRTR reporting and formal SDS hand-offs to business customers, shaping procurement, storage, and record-keeping.
Fire Service Act — storage/handling permits for flammable liquids used in coatings & cleaning: The Fire Service Act regulates designated quantities of hazardous materials at shops and studios; crossing these volumes requires compliant storage/permits under Article 10. Local governments publish numeric thresholds used by inspectors: gasoline 200 liters, ethanol/methanol 400 liters, and kerosene/light oil 1,000 liters are representative designated quantities for on-site storage. Detailers using solvent-borne degreasers, panel-wipe products, or adhesive removers must engineer storage rooms, spill control, and fire-prevention measures to these values, and coordinate with local fire authorities for inspections and approvals.
Japan Car Detailing Market Segmentation
By Service Type: Japan’s car detailing market is segmented into exterior and interior services. Recently, exterior detailing holds the dominant share in Japan, driven by the country’s strong aesthetic culture, the maturity of glass/ceramic coating technologies, and well-known brands such as KeePer LABO and G’ZOX (SOFT99) that have standardized processes and warranties. Organized chains anchor dealer-installed coatings on new deliveries, while urban consumers refresh coatings periodically, lifting spend on premium SKUs and PPF. These formats are supported by certified technician networks and robust after-care programs that sustain repeat revenue.
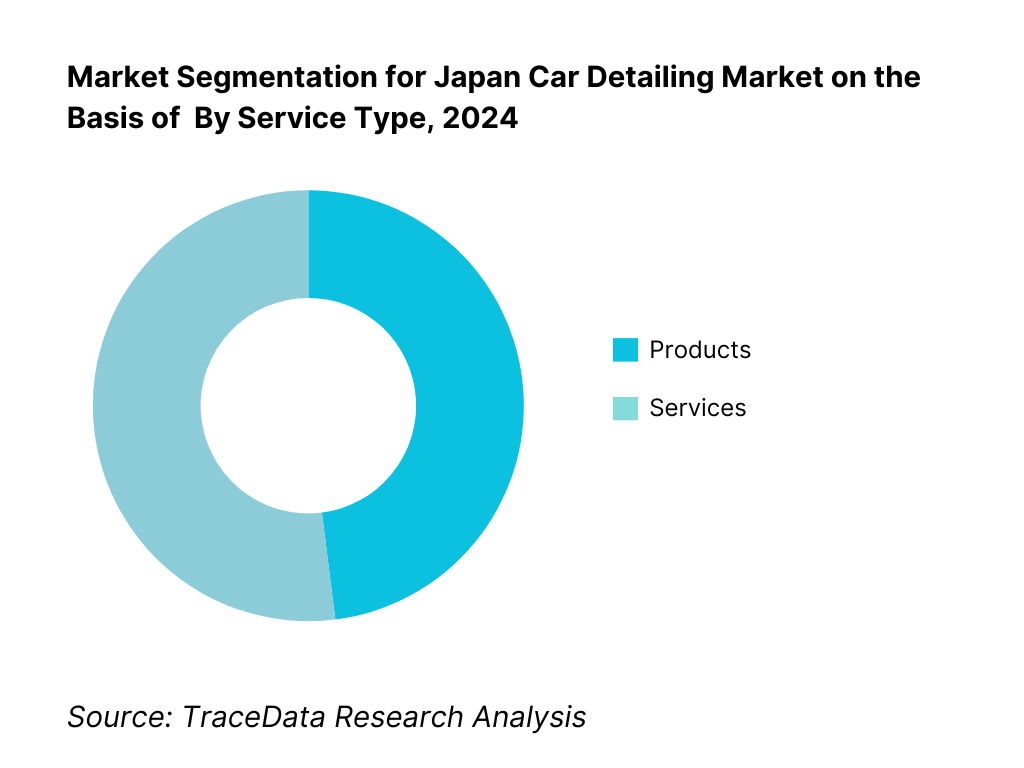
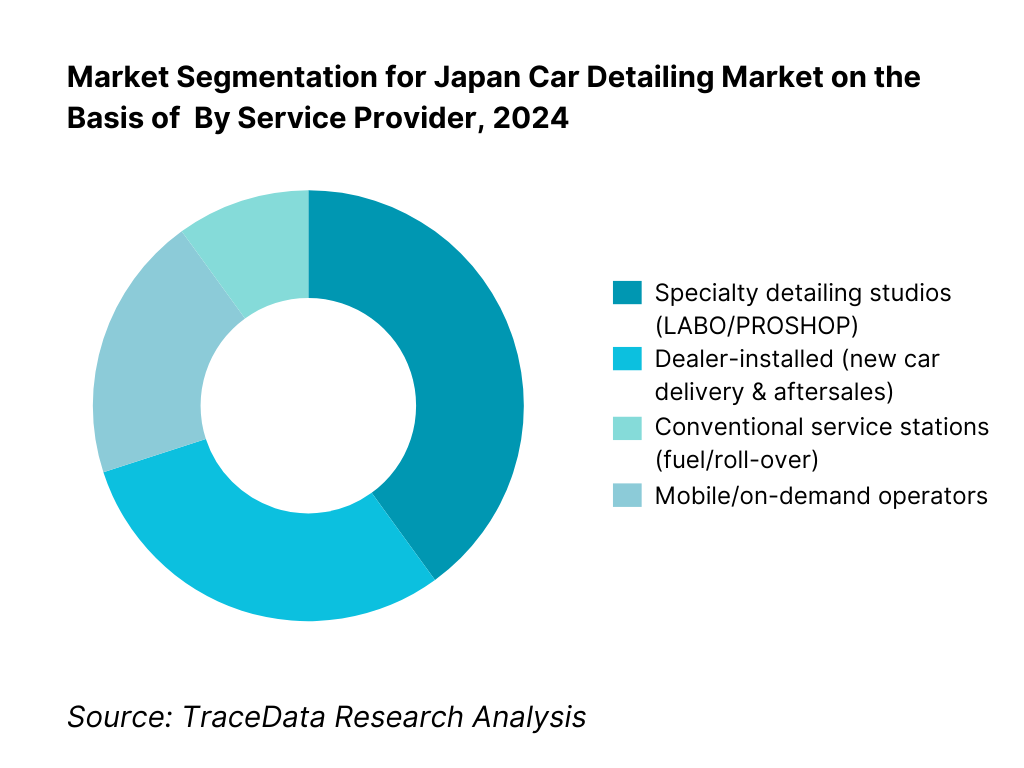
By Service Provider: Japan’s market is served by specialty studios (LABO/PROSHOP), dealer-installed programs, conventional service stations, and mobile operators. Specialty studios are currently dominant, as they concentrate high-margin coating and PPF jobs, standardized SOPs, and nationwide branding that builds trust and willingness to pay. Dealer-installed packages scale through OEM retail networks and raise attach rates at delivery. Fuel-station formats capture volume with basic exterior refresh, whereas mobile providers grow in corporate parks and gated communities but remain ticket-size constrained. The mix benefits from Japan’s preference for certified workmanship and warranty-backed services.
Competitive Landscape in Japan Car Detailing Market
Japan’s detailing arena is led by organized chains and heritage chemical brands with dealer alliances. Flagships like KeePer Technical Laboratory (LABO & PROSHOP formats) and SOFT99 (G’ZOX) set the coating standard, while Autobacs Seven and Yellow Hat monetize retail-to-service funnels. International marques (3M/Meguiar’s, SONAX) operate via distributors and certification networks. This consolidation around brands, training, and warranties raises switching costs and concentrates share in top operators.
Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
KeePer Technical Laboratory | 1985 | Ōbu, Aichi, Japan |
SOFT99 Corporation (G’ZOX) | 1954 | Osaka, Japan |
Autobacs Seven Co., Ltd. | 1948 | Tokyo, Japan |
Yellow Hat Ltd. | 1978 | Tokyo, Japan |
SurLuster Co., Ltd. | 1950s | Tokyo, Japan |
Prostaff Co., Ltd. | 1919 | Osaka, Japan |
Wako Chemical Co., Ltd. (WAKO’S) | 1972 | Kanagawa, Japan |
Willson Co., Ltd. | 1953 | Tokyo, Japan |
Car Beauty Pro (Franchise Network) | 1985 | Tokyo, Japan |
Modesta (Kōgen Co., Ltd.) | 1990s | Hiroshima, Japan |
KISHO Corporation | 1960s | Hiroshima, Japan |
3M Japan Ltd. | 1960 | Tokyo, Japan |
SONAX Japan | 1950 | Tokyo, Japan |
XPEL Japan | 1997 | Tokyo, Japan |
ENEOS Corporation | 1888 | Tokyo, Japan |
Some of the Recent Competitor Trends and Key Information About Competitors Include:
Autobacs Seven Co., Ltd.: Autobacs leveraged its nationwide retail and service chain to upsell detailing and coating services alongside accessories. In 2024, the company rolled out new ceramic coating packages in urban stores, supported by bundled promotions with wheels and tire protection products, boosting average ticket size.
Yellow Hat Ltd.: Yellow Hat enhanced its detailing offerings by integrating express coating services into its car care menu in 2024. The company also strengthened its loyalty programs to retain repeat customers, while experimenting with PPF partnerships in premium outlets to capture higher-end demand.
XPEL Japan: XPEL expanded its paint protection film (PPF) installer network in metropolitan regions in 2024, including Tokyo and Nagoya, where luxury car density is high. The brand also promoted satin/matte PPF aesthetics, aligning with consumer demand for vehicle customization and protection.
SurLuster Co., Ltd.: SurLuster launched new consumer-grade DIY coatings in 2024, complementing its professional studio network. The brand’s hybrid model of retail + professional detailing support has helped it strengthen customer engagement across both enthusiast and mainstream car owners.
WAKO’S (Wako Chemical Co., Ltd.): WAKO’S increased focus on professional fluids and detailing lines in 2024, particularly targeting interior antibacterial treatments and eco-compliant chemicals in response to tightening environmental standards. Its reputation in motorsports also supported adoption among performance-car enthusiasts.
What Lies Ahead for Japan Car Detailing Market?
The Japan car detailing market is expected to continue expanding steadily toward the end of the decade, driven by strong vehicle ownership trends, premiumization in coatings and paint protection films, and the enduring consumer focus on vehicle longevity and aesthetics. Growth will also be shaped by technological upgrades in detailing products, partnerships between dealerships and detailing brands, and evolving environmental regulations that encourage eco-friendly chemicals and wastewater solutions.
Rise of Subscription and Maintenance Plans: The future of Japan’s detailing market will see greater adoption of subscription-based detailing packages, where customers pay for recurring maintenance of glass coatings, PPF touch-ups, and seasonal services. This model appeals to urban consumers seeking convenience and predictable vehicle upkeep, while offering operators a steady revenue stream.
Dealer-Driven Detailing Expansion: Automobile dealerships are expected to play an even greater role in the detailing ecosystem by bundling protective coatings and PPF with new car sales. With over 4.7 million new registrations annually (Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association), dealerships are poised to act as a major distribution channel for certified coating and protection services.
Growth of PPF and High-End Exterior Protection: Paint Protection Film (PPF) adoption is set to increase significantly, especially in metropolitan areas such as Tokyo, Nagoya, and Osaka, where luxury and imported vehicles are concentrated. Demand will be reinforced by the 311,000 imported new cars sold in the market (JAMA), many of which require advanced aesthetic preservation solutions to maintain value.
Eco-Friendly Detailing Solutions: Environmental compliance pressures, including national effluent standards and PRTR chemical handling thresholds, are pushing detailing operators to adopt water-reclaim systems, biodegradable cleaners, and low-VOC coatings. This trend is expected to intensify, with operators investing in sustainability measures not just for compliance, but also as a differentiating factor to attract eco-conscious customers.
Integration of Digital Booking & Analytics: Digital platforms for online scheduling, customer retention analytics, and warranty tracking will gain traction across both franchise studios and independent operators. This will enhance customer experience, reduce idle bay time, and enable operators to better forecast demand cycles, particularly in seasonal peaks such as pollen or winter salt exposure periods.
Japan Car Detailing Market Segmentation
By Service Type
Exterior Detailing (paint polishing, coatings, PPF, glass protection)
Interior Detailing (upholstery cleaning, leather care, odor removal, antimicrobial treatment)
Engine Bay Detailing (engine degreasing, dressing, protective coatings)
Paint Protection Film (PPF) & Wraps (gloss, matte, satin, custom finishes)
Subscription/Annual Maintenance Plans (recurring coating refresh, inspection packages)
By Service Provider/Channel
Specialty Detailing Studios (LABO/PROSHOP)
Dealer-Installed/Dealer-Affiliated Services
Fuel/Service Station Operators (ENEOS, Idemitsu, Cosmo Oil)
Automotive Retail Chains (Autobacs Seven, Yellow Hat)
Mobile/On-Demand Operators
By Vehicle Type
Kei Cars (Mini Vehicles)
Passenger Cars (Compact, Sedan, Hatchback)
SUVs & MPVs
Luxury & Imported Cars
Commercial Fleets (Taxis, Leasing, Ride-Hail, Delivery Vans)
By Protection Technology
Glass Coatings (SiO₂-based)
Ceramic/Nano Coatings (SiC-based)
Polymer Sealants & Traditional Waxes
Paint Protection Films (PPF)
Hybrid Multi-Layer Systems (Ceramic + PPF combos)
By Region
Kantō (Tokyo, Yokohama, Saitama, Chiba)
Kansai (Osaka, Kyoto, Kobe)
Chūbu (Nagoya, Aichi Prefecture)
Kyūshū (Fukuoka, Kumamoto)
Hokkaidō & Tōhoku (Sapporo, Sendai)
Players Mentioned in the Report:
KeePer Technical Laboratory
SOFT99 (G’ZOX)
Autobacs Seven
Yellow Hat
3M/Meguiar’s (Japan)
SONAX Japan
SurLuster; Prostaff
Willson; Wako’s (Eikosha)
ENEOS service station networks
Idemitsu Kosan service stations
Koch-Chemie Japan; RUPES (tools & training, Japan channel)
XPEL/LLumar (Japan PPF installer networks).
Key Target Audience
Automotive dealer groups & dealer-owned service companies (Toyota, Nissan, Honda retail networks)
Fuel & C-store operators (ENEOS, Idemitsu Kosan, Cosmo Oil)
Aftermarket retail chains & service franchises (Autobacs Seven, Yellow Hat)
Detailing studio chains & PROSHOP networks (LABO/independent certified installers)
Leasing & fleet management companies (ORIX Auto, Sumitomo Mitsui Auto Service)
Insurance carriers with appearance protection add-ons (Sompo, Tokio Marine)
Investments & venture capitalist firms (consumer services roll-ups, aftermarket platforms)
Government & regulatory bodies ([Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT); Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI)])
Time Period:
Historical Period: 2019-2024
Base Year: 2025
Forecast Period: 2025-2030
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Delivery Model Analysis for Car Detailing-Service Station (SS), Standalone Studio, Dealer-Installed, Mobile/On-Demand, and DIY Products [discuss margins, customer preferences, strengths & weaknesses]
4.2. Revenue Streams for Japan Car Detailing Market [one-off detailing tickets, coating/PPF packages, subscriptions, dealer bundle upsell, fleet contracts, DIY product sales]
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Japan Car Detailing Market [value propositions, key partners, cost structures, customer segments, channels, revenue streams]
5.1. Franchise Studios vs Independent Detailers [penetration, economics, branding power]
5.2. Investment Model in Japan Car Detailing Market [capex per bay, payback period, ROI across SS/studio/mobile]
5.3. Comparative Analysis of Funnelling Process by Dealer Networks and Independent Service Stations [customer acquisition, upsell rates, conversion]
5.4. Car Detailing Spend Allocation by Vehicle Class (Kei, Compact, SUV, Luxury)
8.1. Revenues (historical to present)
9.1. By Market Structure [service stations, standalone studios, dealer-installed, mobile/on-demand, DIY retail]
9.2. By Service Type [hand wash/detailing, exterior coatings, PPF/window films, interior detailing, subscription/maintenance plans]
9.3. By Industry Verticals [retail/private cars, used-car auctions, dealer prep, fleet & corporate, motorsport/exotics]
9.4. By Company Size [franchise chains, regional operators, single-site independents]
9.5. By Technician Role [certified installer, freelance/detailing helper, mobile operator]
9.6. By Mode of Delivery [in-shop detailing, mobile vans, e-commerce DIY]
9.7. By Open vs Customized Programs [standard coating/PPF packages, tailored packages by vehicle class]
9.8. By Region [Kantō, Kansai, Chūbu, Kyūshū, Hokkaidō/Tohoku]
10.1. Consumer Cohorts and Segmentation [kei owners, luxury buyers, resale-prep customers, fleet managers]
10.2. Detailing Needs and Decision-Making Process [aesthetic vs protection, warranty length sensitivity]
10.3. ROI and Satisfaction Analysis of Detailing Programs [impact on resale value, NPS]
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework [service expectations vs actual delivery]
11.1. Trends and Developments [ceramic/glass coat multi-layers, PPF matte aesthetics, digital booking, eco-chem adoption]
11.2. Growth Drivers [aging car parc, dealer bundling, metro premiumization, ride-hail fleets]
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Japan Car Detailing Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges [labor shortages, seasonality, environmental compliance, warranty claims]
11.5. Government Regulations [VOC handling, wastewater standards, worker safety certifications]
12.1. Market Size and Future Potential for Digital/DIY Channels in Japan
12.2. Business Model and Revenue Streams [apps, subscription kits, e-commerce]
12.3. Delivery Models and Product Categories Offered [DIY kits, consumer-grade coatings, on-demand platforms]
15.1. Market Share of Key Players (Basis Revenues & Job Counts)
15.2. Benchmark of 15 Competitors on [company overview, USP, strategies, store count, revenues, pricing basis service type, warranty tenor, technology used, partnerships, marketing strategy, recent developments]
15.3. Operating Model Analysis Framework [franchise vs corporate vs dealer-authorized]
15.4. Gartner Magic Quadrant [positioning of key coating & PPF brands in Japan]
15.5. Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage [pricing/quality matrix of studios & SS operators]
16.1. Revenues (future projections)
17.1. By Market Structure
17.2. By Service Type
17.3. By Industry Verticals
17.4. By Company Size
17.5. By Technician Role
17.6. By Mode of Delivery
17.7. By Open vs Customized Programs
17.8. By Region
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand-side and supply-side entities for the Japan Car Detailing Market. Based on this ecosystem, we will shortlist leading 5–6 detailing providers in the country based on their financial information, market reach, and client base. Sourcing is conducted through industry articles, multiple secondary, and proprietary databases to perform desk research around the market to collate industry-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
Subsequently, we engage in an exhaustive desk research process by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This approach enables us to conduct a thorough analysis of the market, aggregating industry-level insights. We delve into aspects like market revenues, number of detailing providers, service types, demand funnels, and other variables. We supplement this with detailed examinations of company-level data, relying on sources like press releases, annual reports, financial statements, and similar documents. This process aims to construct a foundational understanding of both the market and the entities operating within it.
Step 3: Primary Research
We initiate a series of in-depth interviews with C-level executives and other stakeholders representing various Japan Car Detailing Market companies and end-users. This interview process serves a multi-faceted purpose: to validate market hypotheses, authenticate statistical data, and extract valuable operational and financial insights from these industry representatives. A bottom-to-top approach is undertaken to evaluate revenue contributions for each player, thereby aggregating to the overall market. As part of our validation strategy, our team executes disguised interviews wherein we approach each company under the guise of potential clients. This approach enables us to validate the operational and financial information shared by company executives, corroborating this data against what is available in secondary databases. These interactions also provide us with a comprehensive understanding of revenue streams, value chains, processes, pricing, and other factors.
Step 4: Sanity Check
A bottom-to-top and top-to-bottom analysis along with market size modeling exercises is undertaken to assess the sanity of the process.
FAQs
01 What is the Potential for the Japan Car Detailing Market?
The Japan Car Detailing Market is poised for steady expansion, supported by strong fundamentals such as the country’s large automotive base and high consumer emphasis on vehicle longevity. With 4.78 million new vehicles registered and 6.43 million used vehicles transacted in the domestic market (JAMA), the funnel for dealer-prep detailing, resale reconditioning, and periodic refresh services is significant. The market’s potential is further strengthened by premium trends such as ceramic coatings, paint protection films, and subscription maintenance programs that enhance vehicle aesthetics and resale value.
02 Who are the Key Players in the Japan Car Detailing Market?
The Japan Car Detailing Market features several key players, including KeePer Technical Laboratory (LABO & PROSHOP), SOFT99 Corporation (G’ZOX), and Autobacs Seven Co., Ltd. These companies dominate the market due to their extensive installer networks, dealership tie-ups, and strong brand equity. Other notable players include Yellow Hat, SurLuster, Prostaff, Wako’s, and international brands such as 3M/Meguiar’s, SONAX, and XPEL that partner with certified installers for paint protection film (PPF) and premium coatings.
03 What are the Growth Drivers for the Japan Car Detailing Market?
The primary growth drivers include macroeconomic and automotive factors. Japan produced 8.99 million vehicles in its domestic plants (JAMA), ensuring continuous dealer activity that bundles detailing packages at delivery. Urban affluence supports higher spend per job, with 311,000 imported vehicles entering the market, many of them luxury or premium, where coatings and PPF are in high demand. In addition, the 36.2 million elderly consumers (65+) maintain long-term vehicle ownership, fueling demand for periodic detailing to preserve car value. Together, these dynamics drive robust opportunities across service stations, studios, and dealer channels.
04 What are the Challenges in the Japan Car Detailing Market?
The Japan Car Detailing Market faces several challenges, including a shrinking service station footprint, which dropped to 27,009 outlets nationwide (ANRE), limiting access to quick detailing services in rural regions. Labor shortages caused by an aging workforce—Japan’s population aged 65+ is 36.2 million (Statistics Bureau)—are restricting the supply of certified detailing technicians. Additionally, strict environmental regulations such as effluent discharge limits under the Water Pollution Control Act (BOD 160 mg/L, SS 200 mg/L) and PRTR chemical handling thresholds increase compliance costs for operators, particularly smaller studios and independent installers.