KSA Agricultural Equipment Market Outlook to 2035
KSA Agricultural Equipment Market Outlook to 2035 – By Equipment Type, By Power Source, By Farm Size, By Application, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0435
- Region: Middle East
- Published on: January 2026
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “KSA Agricultural Equipment Market Outlook to 2035 – By Equipment Type, By Power Source, By Farm Size, By Application, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the agricultural machinery and equipment ecosystem in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The report covers an overview and genesis of the market, overall market size in terms of value, detailed market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory and policy landscape, buyer-level demand profiling, key issues and challenges, and competitive landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players operating in the KSA agricultural equipment market.
The report concludes with future market projections through 2035 based on national food security priorities, water-efficiency mandates, controlled-environment agriculture expansion, mechanization of commercial farms, public-sector procurement programs, regional agricultural development strategies, and cause-and-effect relationships illustrating how policy, climate constraints, and technology adoption are reshaping equipment demand in Saudi Arabia.
KSA Agricultural Equipment Market Overview and Size
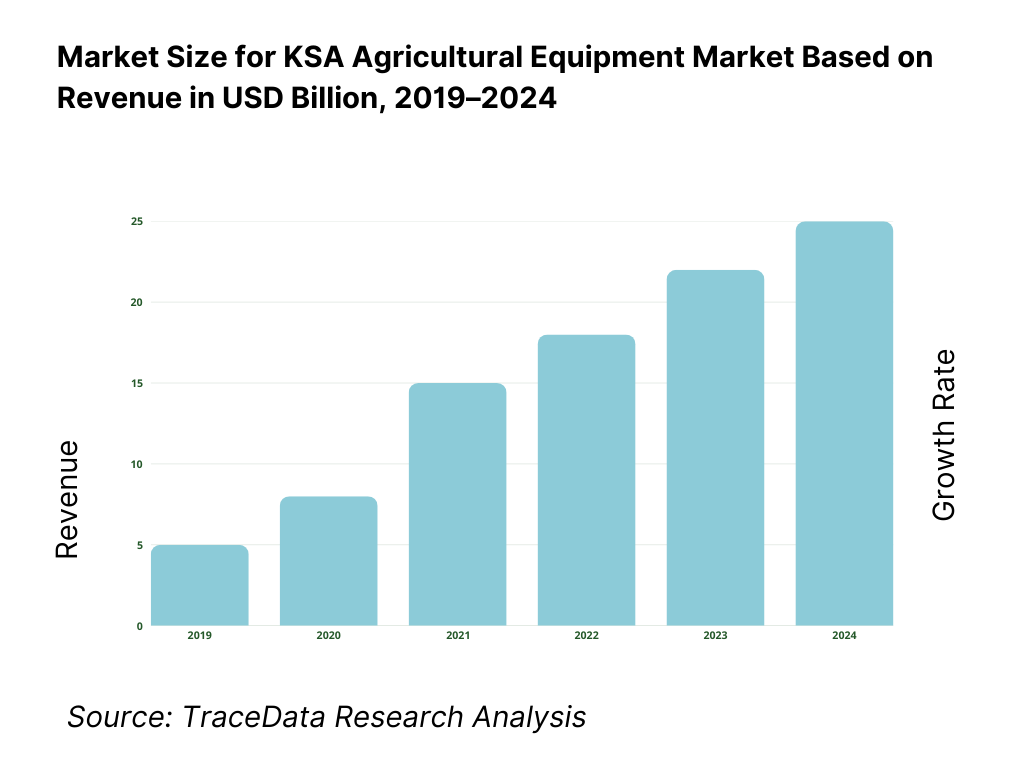
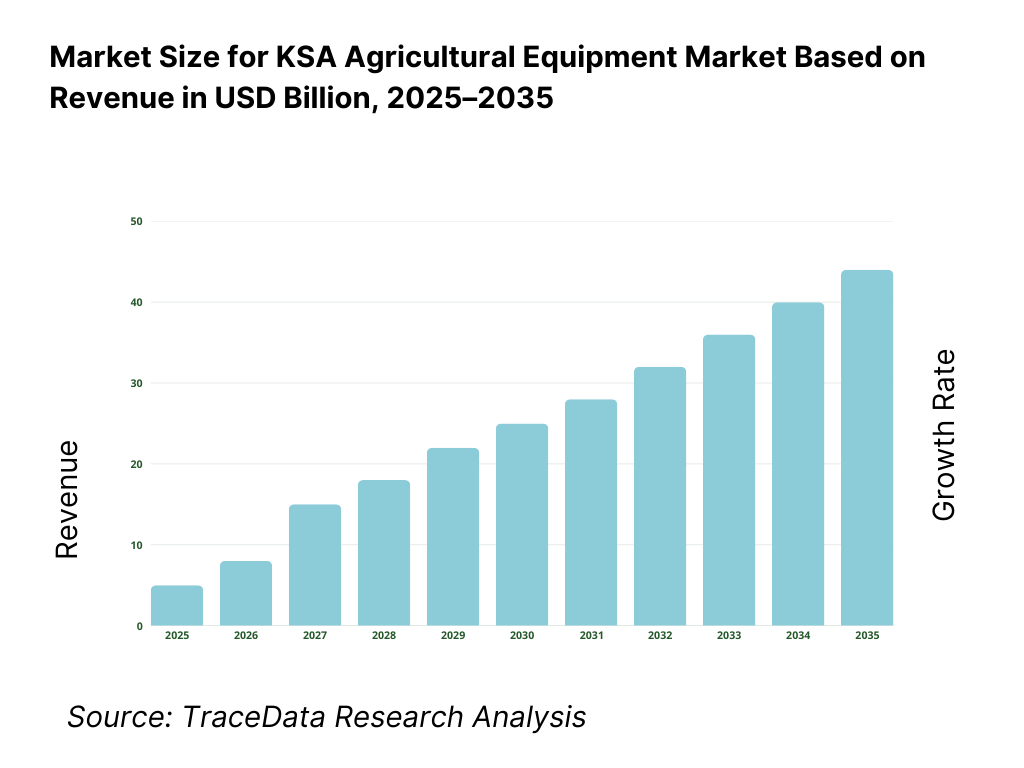
The Saudi Arabia agricultural equipment market is valued at approximately ~USD ~ billion, representing the supply of farm machinery and mechanized solutions used across land preparation, planting, irrigation, crop care, harvesting, and post-harvest handling activities. The market includes tractors, tillage equipment, planting and seeding machinery, irrigation systems, harvesting equipment, crop protection machinery, and specialized equipment designed for arid and semi-arid farming conditions.
Agricultural equipment demand in KSA is structurally different from traditional agrarian economies, as it is shaped by water scarcity, controlled farming practices, large-scale commercial operations, and state-led food security initiatives. Mechanization is not only a productivity lever but also a necessity to optimize water usage, reduce labor dependency, and enable year-round production under harsh climatic conditions.
The market is anchored by commercial-scale farms, corporate agribusinesses, government-backed agricultural projects, and integrated food producers focusing on cereals, fodder crops, vegetables, fruits, and animal feed. Equipment demand is further supported by the expansion of greenhouses, net houses, hydroponic farms, and desert agriculture projects, where precision machinery and automation-friendly equipment are critical.
Regionally, Riyadh Province represents the largest agricultural equipment demand hub due to its concentration of commercial farms, agribusiness headquarters, and government-supported agricultural initiatives. Al-Qassim remains a structurally important region driven by cereal, date, and fodder cultivation, while Eastern Province shows steady demand linked to large landholdings and integrated agri-industrial operations. Asir and Jazan contribute niche demand for smaller equipment suited to horticulture and terrace farming, though mechanization penetration remains relatively lower in these regions.
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the KSA Agricultural Equipment Market
National food security strategy drives sustained investment in farm mechanization: Saudi Arabia’s long-term food security agenda emphasizes domestic production of select crops, reduction of import dependency for strategic food categories, and development of resilient agricultural supply chains. To achieve these goals under water and climate constraints, farm operators increasingly rely on mechanized and technology-enabled equipment to improve yield consistency, optimize input usage, and scale production efficiently. Government-backed programs, subsidies, and financing support accelerate equipment adoption, particularly among medium and large farms.
Shift toward water-efficient and controlled-environment agriculture increases demand for specialized equipment: Water scarcity has fundamentally reshaped agricultural practices in KSA. The gradual transition away from water-intensive open-field farming toward drip irrigation, precision sprinklers, greenhouses, and hydroponic systems has created strong demand for specialized equipment. Irrigation controllers, precision planters, climate-controlled greenhouse machinery, and automated fertigation systems are becoming core equipment categories rather than optional upgrades, structurally expanding the addressable market.
Labor constraints and rising operating costs push farms toward mechanization and automation: Agriculture in Saudi Arabia faces persistent labor availability challenges and rising operational costs linked to workforce localization policies and wage inflation. Agricultural equipment helps reduce reliance on manual labor across land preparation, planting, crop care, and harvesting stages. For commercial farms, the payback period on mechanized equipment is increasingly justified by improved operational predictability, reduced labor intensity, and higher output consistency, reinforcing long-term demand.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of the KSA Agricultural Equipment Market:
High capital cost of advanced agricultural machinery constrains adoption among small and mid-sized farms: While mechanization is critical for improving productivity and water efficiency in Saudi agriculture, many categories of modern agricultural equipment—such as high-horsepower tractors, precision irrigation systems, greenhouse automation tools, and harvesting machinery—require significant upfront capital investment. Smaller and family-operated farms often face budget constraints and longer payback periods, making them hesitant to invest despite long-term efficiency benefits. Although subsidy and financing programs exist, access can vary by region, crop type, and farm registration status, resulting in uneven mechanization penetration across the sector.
Dependence on imported equipment exposes the market to supply chain delays and cost volatility: The KSA agricultural equipment market remains heavily reliant on imported machinery and components, particularly for tractors, harvesters, and advanced irrigation systems. Global supply chain disruptions, shipping delays, currency fluctuations, and changes in international manufacturing lead times can directly affect equipment availability and pricing in the Saudi market. During peak agricultural seasons or periods of accelerated government-led farm development, these constraints can delay procurement decisions, disrupt planting or harvesting schedules, and increase total project costs for farm operators.
Limited availability of skilled operators and maintenance technicians affects equipment utilization efficiency: Advanced agricultural equipment requires trained operators and specialized maintenance capabilities to deliver optimal performance and lifespan. In many agricultural regions of Saudi Arabia, shortages of skilled machine operators and service technicians limit effective equipment usage. Improper operation, delayed servicing, or lack of access to spare parts can reduce productivity gains and increase downtime, discouraging some buyers from upgrading to more sophisticated machinery. These challenges are particularly pronounced in remote farming clusters where dealer service networks are less dense.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
Water usage regulations and groundwater extraction controls shaping equipment selection: Agricultural activity in Saudi Arabia is governed by strict policies aimed at conserving water resources and regulating groundwater extraction. These regulations strongly influence agricultural equipment demand, particularly favoring water-efficient irrigation systems such as drip and micro-irrigation technologies over traditional flood irrigation methods. Equipment suppliers increasingly tailor offerings to meet regulatory requirements related to water usage efficiency, flow control, and monitoring, making compliance a key specification criterion for buyers.
Government subsidy programs and financing initiatives supporting mechanization adoption: Public-sector initiatives play a central role in shaping agricultural equipment demand in KSA. Subsidy schemes, low-interest financing programs, and equipment support initiatives are designed to encourage mechanization, improve productivity, and support domestic food production goals. These programs influence purchasing behavior by reducing effective capital costs and accelerating adoption among eligible farms. However, compliance documentation, eligibility conditions, and approval timelines can impact procurement cycles and favor established suppliers with experience navigating government-linked programs.
Standards, certification requirements, and import regulations governing equipment quality and safety: Agricultural equipment imported into Saudi Arabia must comply with national standards related to safety, energy efficiency, and operational reliability. Certification requirements, conformity assessments, and customs procedures influence product specifications, documentation needs, and time-to-market for suppliers. For certain equipment categories—such as powered machinery and electrical irrigation systems—additional testing and approval processes may apply. These regulatory requirements raise entry barriers for new suppliers but also enhance overall equipment quality and reliability across the market.
KSA Agricultural Equipment Market Segmentation
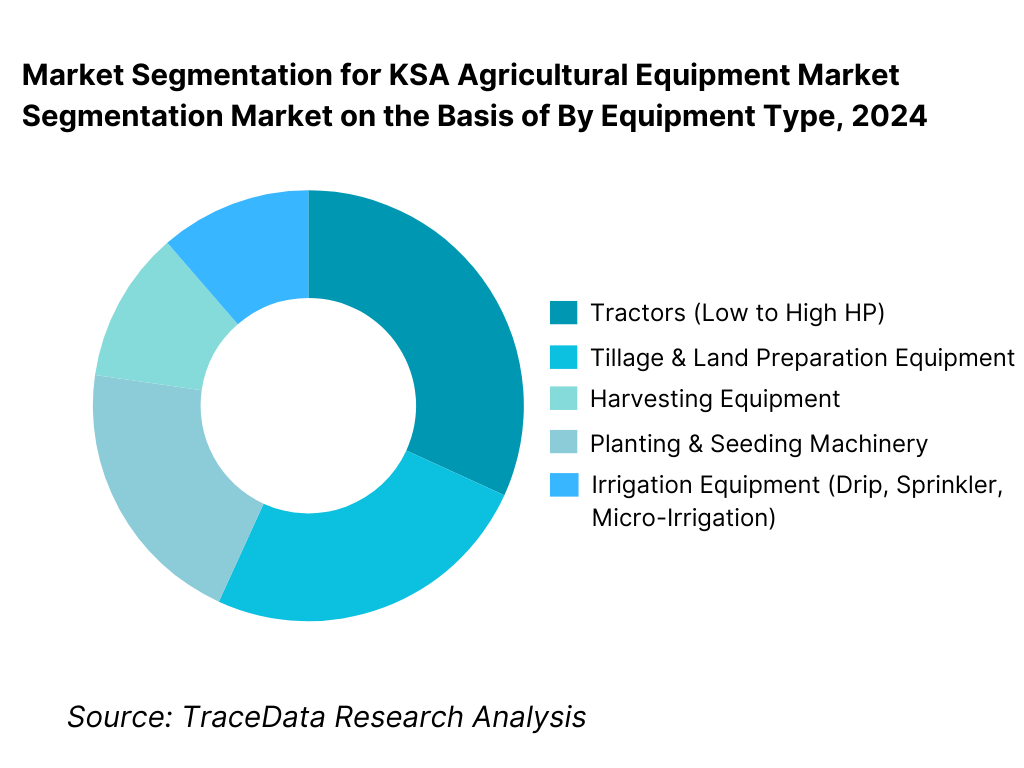
By Equipment Type: The irrigation equipment and tractors segment holds dominance in the KSA agricultural equipment market. This is because agricultural activity in Saudi Arabia is highly constrained by water availability and climatic conditions, making water-efficient irrigation systems and mechanized power equipment critical for farm viability. Tractors form the backbone of mechanized farming across land preparation, planting, and haulage activities, particularly for medium and large commercial farms. Irrigation systems—including drip, sprinkler, and automated fertigation solutions—are indispensable due to regulatory controls on groundwater usage and the need to optimize water productivity. While harvesting and crop protection equipment are gaining traction, especially in commercial-scale farms, core demand continues to be driven by tractors and irrigation systems due to their cross-crop applicability and recurring replacement cycles.
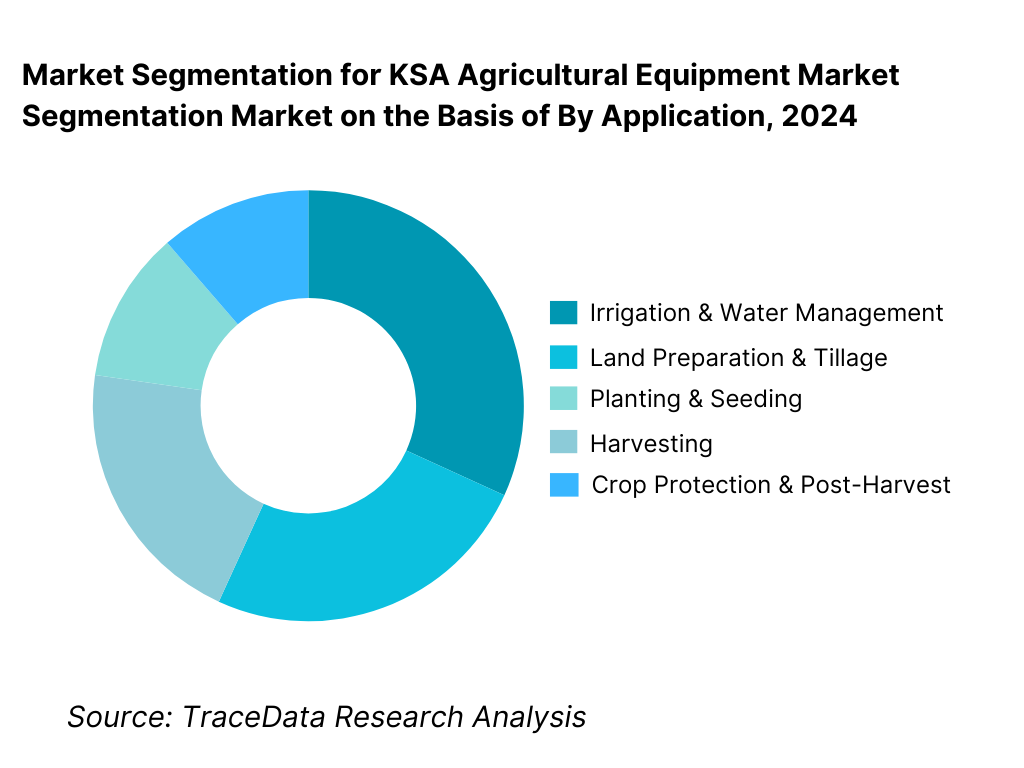
By Application: Irrigation and water management applications dominate the KSA agricultural equipment market. Given the arid environment of Saudi Arabia, agricultural productivity is closely tied to efficient water usage rather than land availability alone. Equipment that supports precise water delivery, reduced evaporation losses, and controlled nutrient application commands priority in farm investment decisions. Land preparation and planting remain essential baseline activities, while harvesting equipment adoption is concentrated among larger, commercial farms with scale-driven economics. Post-harvest mechanization remains comparatively limited but is gradually expanding alongside integrated agribusiness models.
Competitive Landscape in KSA Agricultural Equipment Market
The KSA agricultural equipment market exhibits moderate concentration, characterized by a mix of global agricultural machinery manufacturers, international irrigation system providers, and regional distributors with localized service networks. Market leadership is driven by equipment durability, adaptability to arid conditions, after-sales service strength, spare parts availability, and alignment with government subsidy programs. While global brands dominate tractors and harvesting machinery, irrigation equipment sees stronger participation from specialized technology providers and regional players. Local distributors play a critical role in bridging supplier capabilities with farm-level demand, particularly through financing support, installation services, and maintenance coverage.
Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
John Deere | 1837 | Illinois, USA |
CNH Industrial (Case IH / New Holland) | 2013 | London, UK |
AGCO Corporation (Massey Ferguson) | 1990 | Georgia, USA |
Kubota Corporation | 1890 | Osaka, Japan |
Netafim | 1965 | Tel Aviv, Israel |
Valmont Industries (Irrigation Division) | 1946 | Nebraska, USA |
Mahindra & Mahindra (Farm Equipment) | 1945 | Mumbai, India |
Alkhorayef Group (Agricultural Solutions) | 1957 | Riyadh, Saudi Arabia |
Al-Bahar / Regional Equipment Distributors | ~ | Saudi Arabia |
Some of the Recent Competitor Trends and Key Information About Competitors Include:
John Deere: John Deere maintains a strong position in the Saudi agricultural equipment market through its reputation for durability, high-performance tractors, and advanced precision agriculture capabilities. The brand is particularly favored by large commercial farms and government-supported agricultural projects where reliability, dealer support, and lifecycle performance are prioritized. Deere’s growing emphasis on digital farm management tools further strengthens its positioning among technologically progressive operators.
CNH Industrial (Case IH / New Holland): CNH Industrial brands compete strongly in mid- to high-horsepower tractor segments and harvesting equipment, offering a balance between performance and cost competitiveness. Their equipment is widely adopted in large-scale cereal and fodder farming operations, supported by established regional distributor networks that provide training, servicing, and spare parts availability across major agricultural regions.
AGCO Corporation (Massey Ferguson): Massey Ferguson has a broad footprint in Saudi Arabia, particularly among medium-sized farms seeking robust and relatively cost-efficient mechanization solutions. The brand’s strength lies in versatility across multiple crop types and farm sizes, making it suitable for diversified agricultural operations common in KSA’s evolving farming landscape.
Kubota Corporation: Kubota is strongly positioned in compact and mid-sized equipment categories, serving greenhouse farms, horticulture operations, and smaller mechanized plots. Its equipment is valued for fuel efficiency, ease of operation, and suitability for controlled-environment agriculture, a segment that is expanding rapidly in Saudi Arabia.
Netafim: Netafim plays a pivotal role in shaping the irrigation equipment segment in KSA, with drip irrigation and precision water management solutions aligned closely with national water conservation goals. The company’s competitive edge is driven by technology leadership, project-based installations, and strong alignment with government-led agricultural sustainability initiatives.
Valmont Industries: Valmont’s irrigation solutions, particularly center-pivot and large-scale sprinkler systems, are widely used in extensive commercial farms and fodder cultivation projects. The company benefits from long-term relationships with large landholders and public-sector projects where scale, reliability, and water-use optimization are critical decision factors.
What Lies Ahead for KSA Agricultural Equipment Market?
The Saudi Arabia agricultural equipment market is expected to expand steadily through 2035, supported by long-term food security priorities, continued mechanization of commercial farms, and increasing reliance on water-efficient and technology-enabled agricultural practices. Growth momentum is reinforced by government-backed agricultural investment programs, expansion of controlled-environment farming, and the structural need to improve productivity under severe climatic and water constraints. As agriculture in KSA continues to shift from labor-intensive and water-intensive models toward capital-intensive and efficiency-driven systems, agricultural equipment will remain a foundational enabler of sustainable domestic food production.
Transition Toward Water-Efficient, Precision-Oriented, and Climate-Adapted Equipment Solutions: The future of the KSA agricultural equipment market will see a sustained shift away from basic mechanization toward precision-oriented and purpose-specific equipment designed for arid environments. Demand will increasingly favor drip and micro-irrigation systems, automated fertigation units, precision planters, and equipment optimized for controlled water delivery and minimal wastage. Greenhouse and hydroponic farming expansion will further drive adoption of climate-controlled machinery, sensors, and automated handling systems. Suppliers that offer integrated solutions combining equipment, monitoring, and control capabilities tailored to Saudi climatic realities will capture higher-value demand and strengthen long-term customer relationships.
Rising Importance of Mechanization to Offset Labor Constraints and Improve Operational Predictability: Labor availability and rising operating costs will continue to push farm operators toward higher levels of mechanization and selective automation. Tractors, harvesting equipment, and crop care machinery that reduce manual intervention and improve consistency will see growing preference, particularly among medium and large commercial farms. Through 2035, buyers will increasingly evaluate equipment based on total cost of ownership, uptime reliability, and service responsiveness rather than upfront purchase price alone. This trend favors suppliers with strong after-sales networks, readily available spare parts, and localized technical support.
Expansion of Controlled-Environment and Commercial-Scale Farming Programs: A growing share of agricultural investment in KSA is directed toward greenhouses, net houses, vertical farming pilots, and large-scale commercial farms focused on vegetables, fruits, and animal feed. These operations require specialized equipment for planting, irrigation, climate management, and harvesting that differs significantly from traditional open-field farming machinery. As these farming models scale, equipment demand will become more project-driven and specification-led, benefiting suppliers capable of delivering turnkey or semi-integrated equipment packages aligned with commercial production requirements.
KSA Agricultural Equipment Market Segmentation
By Equipment Type
- Tractors (Low HP, Medium HP, High HP)
- Tillage & Land Preparation Equipment (Ploughs, Harrows, Cultivators, Levelers)
- Planting & Seeding Machinery (Seed Drills, Planters, Transplanters)
- Irrigation Equipment (Drip, Sprinkler, Micro-Irrigation, Pumps, Controllers, Fertigation Systems)
- Harvesting Equipment (Combine Harvesters, Forage Harvesters, Specialty Harvesters)
- Crop Protection Equipment (Sprayers, Spreaders, Dusters)
- Post-Harvest & Handling Equipment (Balers, Graders, Conveyors, Storage & Handling Systems)
By Power Source
- Diesel-Powered Equipment
- Electric-Powered Equipment
- Solar-Powered / Solar-Assisted Irrigation Systems
- Hybrid / Alternative Energy-Based Equipment
By Sales & Delivery Model
- Manufacturer–Authorized Dealer Network Model
- Direct-to-Farm / Direct-to-Agribusiness Model
- Distributor–Integrator Model (Equipment + Installation + Service)
- Government / Public Procurement & Subsidy-Linked Model
By End-Use Sector
- Commercial & Corporate Farms
- Integrated Agribusiness & Food Producers
- Greenhouse, Hydroponic & Controlled-Environment Farms
- Government & Public Sector Agricultural Projects
- Smallholder & Traditional Farms
By Region
- Riyadh Province
- Al-Qassim Province
- Eastern Province
- Asir Province
- Jazan Province
- Rest of Saudi Arabia
Players Mentioned in the Report
- John Deere
- CNH Industrial (Case IH / New Holland)
- AGCO (Massey Ferguson)
- Kubota Corporation
- Mahindra Farm Equipment
- Netafim
- Valmont Industries (Irrigation Division)
- Alkhorayef Group (Agricultural & Irrigation Solutions)
- Regional agricultural equipment distributors, irrigation contractors, and service providers in KSA
Key Target Audience
- Agricultural equipment manufacturers and OEMs
- Irrigation system providers and water management solution companies
- Local distributors, dealers, and after-sales service networks
- Commercial farms, agribusiness corporations, and food producers
- Government agencies and public-sector agricultural development bodies
- Greenhouse, hydroponic, and controlled-environment farming operators
- Agri-finance companies, leasing firms, and subsidy-linked financiers
- EPC firms and farm infrastructure developers
- Private equity, strategic investors, and food security-focused stakeholders
Time Period
Historical Period: 2019–2024
Base Year: 2025
Forecast Period: 2025–2035
Report Coverage
Executive Summary
Research Methodology
Ecosystem of Key Stakeholders in KSA Agricultural Equipment Market
Value Chain Analysis
4.1 Delivery Model Analysis for Agricultural Equipment-OEM Manufacturing, Dealer Distribution, Direct Sales, EPC/Turnkey [Margins, Preference, Strength & Weakness]
4.2 Revenue Streams for KSA Agricultural Equipment Market [Equipment Sales, Spare Parts, AMC & Services, Leasing, Financing, Turnkey Projects]
4.3 Business Model Canvas for KSA Agricultural Equipment Market [Key Partners, Key Activities, Value Propositions, Customer Segments, Cost Structure, Revenue Streams]Market Structure
5.1 Local Players vs Global Vendors [Regional Distributors vs Global OEMs such as John Deere, CNH, AGCO, etc.]
5.2 Investment Model in KSA Agricultural Equipment Market [Government Subsidies, Private Investments, Leasing & Financing, Public-Private Partnerships]
5.3 Comparative Analysis of Equipment Adoption in Commercial vs Government Farms [Procurement Models, Use Cases, ROI Benchmarks]
5.4 Equipment Budget Allocation by Farm Size [Large Farms, Medium Farms, Smallholder Farms]Market Attractiveness for KSA Agricultural Equipment Market
Supply-Demand Gap Analysis
Market Size for KSA Agricultural Equipment Market Basis
8.1 Revenues (Historical Trend)
Market Breakdown for KSA Agricultural Equipment Market Basis
9.1 By Market Structure (Owned Equipment vs Leased/Rented Equipment)
9.2 By Equipment Type (Tractors, Tillage, Planting & Seeding, Irrigation, Harvesting, Crop Protection)
9.3 By Application (Land Preparation, Planting, Irrigation & Water Management, Crop Protection, Harvesting, Post-Harvest Handling)
9.4 By Farm Size (Large Commercial Farms, Medium Farms, Smallholder Farms)
9.5 By Power Source (Diesel, Electric, Solar-Assisted, Hybrid)
9.6 By Sales & Delivery Model (Dealer Network, Direct Sales, EPC/Turnkey, Public Procurement)
9.7 By New vs Refurbished Equipment
9.8 By Region (Riyadh, Al-Qassim, Eastern Province, Asir, Jazan, Rest of Saudi Arabia)Demand-Side Analysis for KSA Agricultural Equipment Market
10.1 Farm & Agribusiness Landscape and Cohort Analysis
10.2 Equipment Adoption Drivers & Decision-Making Process
10.3 Equipment Performance, Productivity Impact & ROI Analysis
10.4 Gap Analysis FrameworkIndustry Analysis
11.1 Trends & Developments in KSA Agricultural Equipment Market
11.2 Growth Drivers for KSA Agricultural Equipment Market
11.3 SWOT Analysis for KSA Agricultural Equipment Market
11.4 Issues & Challenges for KSA Agricultural Equipment Market
11.5 Government Regulations for KSA Agricultural Equipment MarketSnapshot on Irrigation & Precision Agriculture Equipment Market in KSA
12.1 Market Size and Future Potential for Precision & Water-Efficient Equipment in KSA
12.2 Business Models & Revenue Streams [Equipment Sales, Turnkey Projects, O&M Contracts]
12.3 Delivery Models & Equipment Applications Offered [Drip Systems, Sprinklers, Automation, Smart Controllers]Opportunity Matrix for KSA Agricultural Equipment Market
PEAK Matrix Analysis for KSA Agricultural Equipment Market
Competitor Analysis for KSA Agricultural Equipment Market
15.1 Market Share of Key Players in KSA Agricultural Equipment Market (By Revenues)
15.2 Benchmark of Key Competitors [Company Overview, USP, Business Strategies, Business Model, Product Portfolio, Revenues, Pricing Models, Technology Used, Best-Selling Equipment, Major Clients, Strategic Tie-ups, Marketing Strategy, Recent Developments]
15.3 Operating Model Analysis Framework
15.4 Gartner Magic Quadrant for Agricultural Equipment & Precision Farming Providers
15.5 Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive AdvantageFuture Market Size for KSA Agricultural Equipment Market Basis
16.1 Revenues (Projections)
Market Breakdown for KSA Agricultural Equipment Market Basis
17.1 By Market Structure (Owned vs Leased Equipment)
17.2 By Equipment Type (Tractors, Tillage, Planting, Irrigation, Harvesting, Crop Protection)
17.3 By Application (Land Prep, Planting, Irrigation, Crop Care, Harvesting, Post-Harvest)
17.4 By Farm Size (Large, Medium, Smallholder Farms)
17.5 By Power Source (Diesel, Electric, Solar, Hybrid)
17.6 By Sales & Delivery Model (Dealer, Direct, EPC, Public Procurement)
17.7 By New vs Refurbished Equipment
17.8 By Region (Riyadh, Al-Qassim, Eastern Province, Asir, Jazan, Rest of Saudi Arabia)Recommendations
Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
We begin by mapping the complete ecosystem of the KSA Agricultural Equipment Market across demand-side and supply-side entities. On the demand side, entities include large commercial farms, integrated agribusiness companies, greenhouse and controlled-environment agriculture operators, livestock and fodder producers, small and medium farm owners, and government-backed agricultural development projects. Demand is further segmented by farm size (smallholder, medium commercial, large corporate/government farms), application (land preparation, planting, irrigation, crop protection, harvesting, post-harvest handling), and procurement model (outright purchase, dealer-financed purchase, leasing, subsidy-linked procurement, and public tenders). On the supply side, the ecosystem includes global agricultural equipment OEMs, irrigation and precision farming solution providers, local distributors and dealers, system integrators, spare-parts suppliers, after-sales service providers, financing and leasing institutions, and government agencies involved in subsidies and approvals. From this mapped ecosystem, we shortlist 8–12 leading OEMs and regional distributors based on product portfolio, suitability for arid conditions, geographic coverage, service network strength, and presence across key crop and farm segments. This step establishes how value is created and captured across equipment manufacturing, distribution, installation, servicing, and lifecycle support.
Step 2: Desk Research
An exhaustive desk research process is undertaken to analyze the KSA agricultural equipment market structure, demand drivers, and segment behavior. This includes reviewing national food security strategies, water-use regulations, agricultural subsidy programs, crop-wise cultivation patterns, and mechanization trends across regions. We assess demand dynamics by equipment category such as tractors, irrigation systems, planting machinery, and harvesting equipment, along with buyer preferences related to durability, water efficiency, energy consumption, and total cost of ownership. Company-level analysis includes review of OEM product offerings, distributor models, pricing structures, financing options, and after-sales service capabilities. We also examine import regulations, standards, and certification requirements affecting equipment availability and cost. The outcome of this stage is a comprehensive industry foundation that defines the segmentation logic and creates the assumptions required for market sizing and long-term outlook modeling.
Step 3: Primary Research
We conduct structured interviews with agricultural equipment manufacturers, irrigation system providers, local distributors and dealers, agribusiness companies, commercial farm operators, greenhouse operators, and relevant government or institutional stakeholders. The objectives are threefold: (a) validate assumptions around demand concentration by farm size, crop type, and region, (b) authenticate segment splits by equipment type, application, and power source, and (c) gather qualitative insights on pricing behavior, financing adoption, replacement cycles, service expectations, and technology adoption barriers. A bottom-to-top approach is applied by estimating equipment penetration, average selling prices, and replacement demand across key segments and regions, which are aggregated to develop the overall market view. In selected cases, dealer-level interactions are used to validate on-ground realities such as lead times, availability constraints, spare-parts dependence, and subsidy-linked procurement timelines.
Step 4: Sanity Check
The final stage integrates bottom-to-top and top-to-down approaches to cross-validate the market size, segmentation splits, and forecast assumptions. Demand estimates are reconciled with macro indicators such as agricultural output trends, government spending on agriculture, water availability constraints, and farm mechanization benchmarks. Sensitivity analysis is conducted across key variables including subsidy continuity, water regulation stringency, energy costs, and adoption rates of precision and controlled-environment farming. Market models are refined until alignment is achieved between supplier capacity, distributor throughput, and farm-level demand, ensuring internal consistency and robust directional forecasting through 2035.
FAQs
01 What is the potential for the KSA Agricultural Equipment Market?
The KSA Agricultural Equipment Market holds strong long-term potential, driven by national food security objectives, increasing mechanization of commercial farms, and the shift toward water-efficient and controlled-environment agriculture. Demand is supported by government subsidies, expansion of greenhouse and precision irrigation projects, and the need to improve productivity under arid climatic conditions. As agriculture becomes more capital- and technology-intensive, equipment adoption is expected to remain a critical enabler through 2035.
02 Who are the Key Players in the KSA Agricultural Equipment Market?
The market features a mix of global agricultural equipment OEMs, international irrigation technology providers, and strong local distributors with established service networks. Competition is shaped by product reliability, suitability for local conditions, financing support, spare-parts availability, and after-sales service coverage. Local partners play a crucial role in market penetration, customer relationships, and ongoing maintenance support.
03 What are the Growth Drivers for the KSA Agricultural Equipment Market?
Key growth drivers include government-led food security initiatives, strict water-use regulations favoring efficient irrigation systems, rising labor costs pushing mechanization, and expansion of commercial and controlled-environment farming. Additional momentum comes from financing and subsidy programs, adoption of precision agriculture technologies, and replacement of aging equipment with more efficient and regulation-compliant machinery.
04 What are the Challenges in the KSA Agricultural Equipment Market?
Challenges include high upfront capital costs for advanced equipment, dependence on imported machinery, exposure to supply chain disruptions, and limited availability of skilled operators and technicians in certain regions. Variability in subsidy access and approval timelines can also affect procurement decisions. Despite these constraints, structural drivers continue to support steady long-term market growth.