KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market Outlook to 2035
KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market Outlook to 2035 – By Service Type, By Vehicle Type, By Service Channel, By Ownership Model, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0464
- Region: Central and South America
- Published on: January 2026
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market Outlook to 2035 – By Service Type, By Vehicle Type, By Service Channel, By Ownership Model, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the automotive repair and maintenance ecosystem in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA). The report covers an overview and genesis of the market, overall market size in terms of value, detailed market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory and inspection landscape, buyer-level demand profiling, key issues and challenges, and the competitive landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players operating in the KSA automotive aftermarket.
The report concludes with future market projections based on vehicle parc growth, aging vehicle population, rising utilization intensity, post-warranty servicing trends, localization of spare parts, digital service platforms, Saudization and workforce reforms, and regional demand drivers, supported by cause-and-effect relationships and case-based illustrations highlighting the major opportunities and cautions shaping the market through 2035.
KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market Overview and Size
The KSA automotive repair and maintenance market is valued at approximately ~USD ~ billion, representing expenditures on periodic servicing, mechanical and electrical repairs, body and paint work, tire and battery replacement, diagnostics, and value-added services across passenger vehicles and commercial fleets. The market encompasses authorized OEM service centers, independent workshops, quick-service chains, dealership-linked facilities, and emerging digital or aggregator-led service models.
The market is anchored by Saudi Arabia’s large and expanding vehicle parc, high vehicle ownership per household, long average vehicle holding periods, and extreme climatic conditions that accelerate wear and tear on critical components such as batteries, tires, cooling systems, and suspension parts. High annual mileage driven by intercity travel, limited public transport coverage outside major metros, and strong reliance on personal vehicles further intensify maintenance demand.
Passenger cars account for the largest share of service value, driven by routine servicing, consumables replacement, and post-warranty repairs. However, light commercial vehicles (LCVs) and heavy commercial vehicles (HCVs) represent a structurally important segment due to higher ticket sizes per service event, especially for fleet-operated vehicles in logistics, construction, oil & gas support services, and municipal applications.
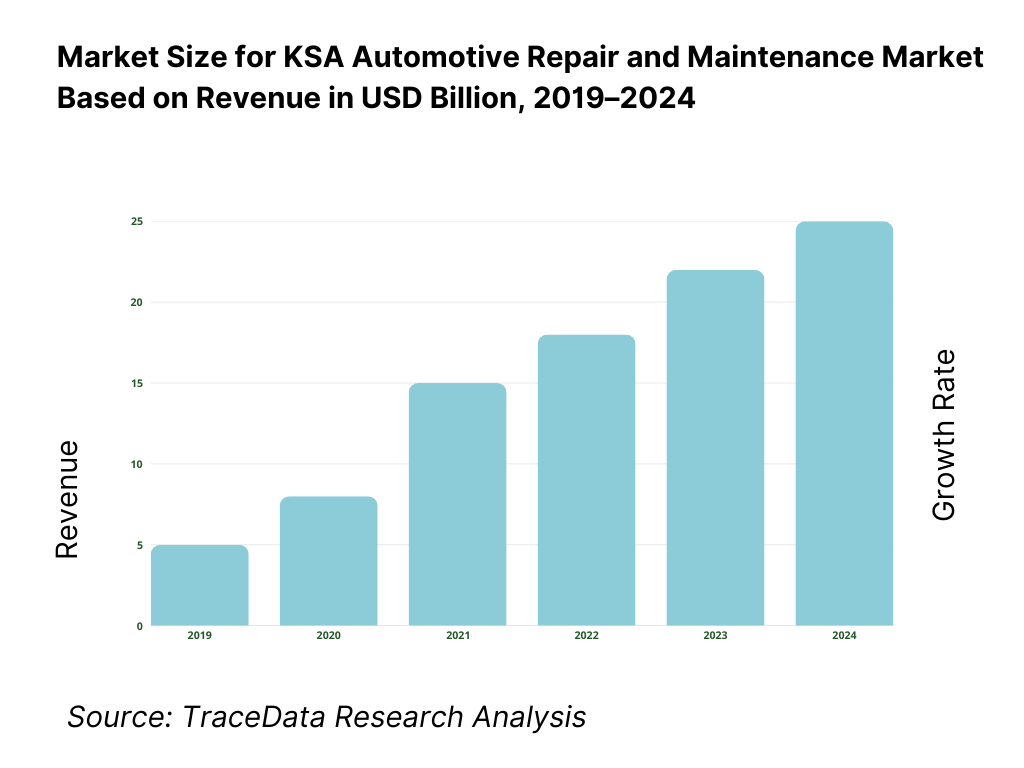
Regionally, the Central Region (Riyadh) and Western Region (Makkah–Madinah–Jeddah corridor) represent the largest demand centers due to vehicle density, population concentration, and higher penetration of organized service formats. The Eastern Region benefits from commercial fleet activity linked to energy, industrial, and port-led logistics. Southern and Northern regions remain more fragmented and informal but are gradually witnessing organized workshop expansion supported by urbanization and regulatory enforcement.
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market
Growth in vehicle parc and rising average vehicle age strengthen baseline service demand: Saudi Arabia continues to add vehicles annually, supported by population growth, rising female driver participation, improving credit access, and expanding suburban mobility. At the same time, average vehicle age remains elevated due to extended ownership cycles and high resale value of used vehicles. Older vehicles require more frequent mechanical repairs, replacement of wear-and-tear parts, and corrective maintenance, structurally expanding demand for independent workshops and non-warranty service providers.
Extreme climate conditions increase maintenance intensity per vehicle: High ambient temperatures, sand and dust exposure, and long-distance driving conditions significantly accelerate component degradation. Batteries, tires, brake systems, air conditioning units, cooling systems, and filters experience shorter replacement cycles compared to temperate markets. This climatic reality creates a structurally higher service frequency per vehicle, benefiting both quick-service chains and full-service workshops across regions.
Post-warranty servicing shifts volume from dealers to independent and organized aftermarket players: While authorized dealerships dominate warranty-period servicing, a substantial share of vehicles transitions to independent workshops once warranties expire. Price sensitivity, wider availability of aftermarket spare parts, and increasing trust in organized multi-brand service chains are driving this shift. Organized players offering transparent pricing, digital booking, service packages, and standardized processes are gradually formalizing a market that was historically fragmented.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of the KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market:
Fragmentation of workshops and uneven service quality impacts customer trust and price transparency: The Saudi automotive repair and maintenance market remains highly fragmented, with a large base of small, independent workshops operating alongside authorized dealerships and organized service chains. Many unorganized garages lack standardized processes, trained technicians, or advanced diagnostic tools, leading to inconsistent service quality and pricing opacity. This fragmentation creates trust issues among vehicle owners, increases perceived risk of overcharging or improper repairs, and slows the shift toward formal, scalable service models—particularly outside major urban centers.
Shortage of skilled technicians and Saudization pressures affect operational efficiency: The sector is labor-intensive and heavily dependent on technically skilled mechanics, electricians, and diagnostic specialists. Workforce localization initiatives and tightening regulations around expatriate labor have increased hiring and training costs for workshop operators. Many service providers face challenges in recruiting, retaining, and upskilling Saudi technicians, which impacts service turnaround times, limits capacity expansion, and raises operating costs—especially for workshops offering advanced diagnostics or fleet servicing.
Rising spare parts costs and supply variability impact margins and service affordability: Automotive repair operations are sensitive to spare parts pricing and availability, particularly for fast-moving consumables such as batteries, tires, brake components, filters, and cooling system parts. Fluctuations in import costs, currency exposure for non-localized parts, and supply chain disruptions can compress workshop margins or force price increases for end customers. Smaller workshops with limited purchasing power are especially vulnerable, reducing their competitiveness against larger chains and dealer networks.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
Workshop licensing, inspection standards, and vehicle roadworthiness regulations shaping formalization: Automotive repair and maintenance providers in KSA are required to operate under licensing frameworks that govern workshop registration, safety compliance, waste disposal, and operational standards. Periodic vehicle inspection programs linked to registration renewal reinforce the need for compliant repairs and maintenance, gradually pushing vehicle owners toward licensed service providers. Enforcement intensity varies by region, but overall regulatory oversight is contributing to the gradual formalization of the aftermarket.
Environmental, waste management, and safety regulations influencing workshop operations: Regulations related to disposal of used oils, batteries, tires, and other hazardous automotive waste affect workshop design and operating procedures. Compliance with environmental and occupational safety standards requires investments in equipment, storage, and documentation, particularly for larger workshops and chains. While these requirements improve industry standards, they also increase fixed costs for smaller operators and influence consolidation dynamics within the market.
Saudization policies and vocational training initiatives impacting workforce structure: National employment policies aimed at increasing Saudi participation in technical and service roles are reshaping labor models within the automotive repair sector. Workshops are increasingly required to invest in training, certification, and structured career pathways for local technicians. Government-supported vocational programs and partnerships with training institutes are gradually improving skill availability, but short-term productivity gaps and higher labor costs remain key considerations for operators.
KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market Segmentation
By Service Type: The periodic maintenance and mechanical repair segment holds dominance in the KSA automotive repair and maintenance market. This is because the Saudi vehicle parc is characterized by high average vehicle age, extended ownership cycles, and intensive usage patterns driven by long-distance travel and limited public transport alternatives outside major cities. Routine servicing—including oil changes, brake servicing, suspension repair, cooling system maintenance, and AC servicing—accounts for a large share of workshop visits and repeat customer traffic. While body & paint, electrical diagnostics, and specialty services are growing, periodic maintenance continues to benefit from volume-driven demand and recurring service cycles.

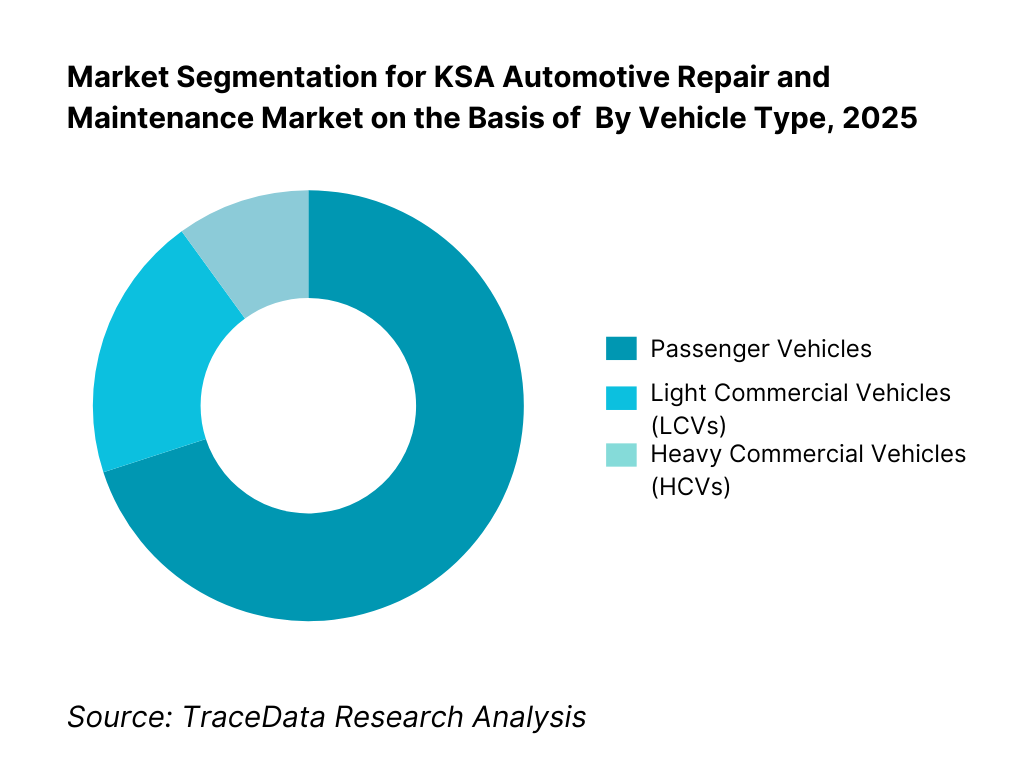
By Vehicle Type: Passenger vehicles dominate the KSA automotive repair and maintenance market, supported by high private vehicle ownership, multi-car households, and increasing participation of female drivers. Passenger cars generate steady demand for routine servicing and consumable replacements across both authorized and independent workshops. Commercial vehicles—particularly light commercial vehicles (LCVs)—represent a structurally important segment due to higher service intensity, mileage accumulation, and fleet-driven maintenance contracts. Heavy commercial vehicles contribute lower volume but higher ticket-size repairs.
Competitive Landscape in KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market
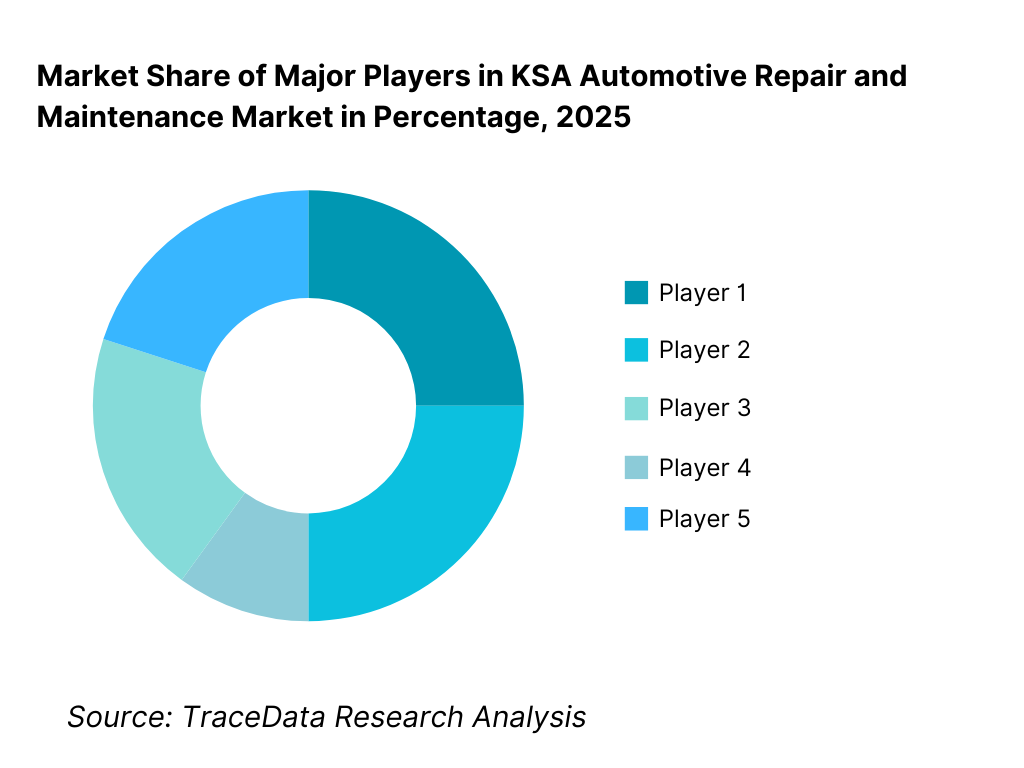
The KSA automotive repair and maintenance market is highly fragmented with low-to-moderate concentration, characterized by a large base of small independent garages alongside authorized dealer networks and a growing presence of organized multi-brand service chains. Competitive positioning is driven by pricing, turnaround time, parts availability, service credibility, insurer and fleet tie-ups, and geographic coverage. While dealerships dominate warranty-linked and premium servicing, independent and organized players compete aggressively in post-warranty and mass-market segments.
Key Players and Service Networks in KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market
Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
Petromin | 1968 | Jeddah, Saudi Arabia |
Abdul Latif Jameel Motors Service Network | 1945 | Jeddah, Saudi Arabia |
SAMACO Automotive Service | 1976 | Riyadh, Saudi Arabia |
Aljomaih Automotive Services | 1936 | Dammam, Saudi Arabia |
Bosch Car Service Saudi Arabia | 1921 | Riyadh, Saudi Arabia |
Fast Fit Auto Centers | 2009 | Saudi Arabia |
Zain Auto Services | 2012 | Saudi Arabia |
Some of the Recent Competitor Trends and Key Information About Competitors Include:
Petromin: Petromin continues to strengthen its position as one of the largest organized automotive service platforms in Saudi Arabia, leveraging its nationwide footprint, multi-brand servicing capability, and integrated fuel and lubricant ecosystem. The company benefits from strong brand recognition, standardized service offerings, and growing partnerships with insurers and fleet operators, positioning it well for post-warranty and mass-market demand.
Abdul Latif Jameel Motors – Service Network: As one of the largest automotive distributors in the Kingdom, ALJ’s service network remains dominant in the authorized dealership segment, particularly for Japanese passenger vehicles. Its competitive advantage lies in OEM-certified technicians, strong spare parts availability, and high customer retention during warranty and extended service periods.
SAMACO Automotive Services: SAMACO operates primarily in the premium and luxury vehicle servicing segment, where technical expertise, diagnostic sophistication, and brand trust are critical. Its service operations are closely aligned with high-end OEM standards, making it a preferred choice for customers prioritizing quality assurance over price sensitivity.
Bosch Car Service Saudi Arabia: The Bosch Car Service network is expanding gradually as a structured multi-brand alternative to unorganized workshops. Its differentiation is built around standardized diagnostics, global process benchmarks, technician training, and transparent service practices, appealing to urban customers seeking reliability without dealership pricing.
Fast Fit Auto Centers: Fast Fit focuses on quick-service formats such as tires, batteries, brakes, and routine maintenance, targeting high-frequency service needs. The brand’s growth is supported by convenience-driven locations, faster turnaround times, and increasing demand for express maintenance services in urban centers.
What Lies Ahead for KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market?
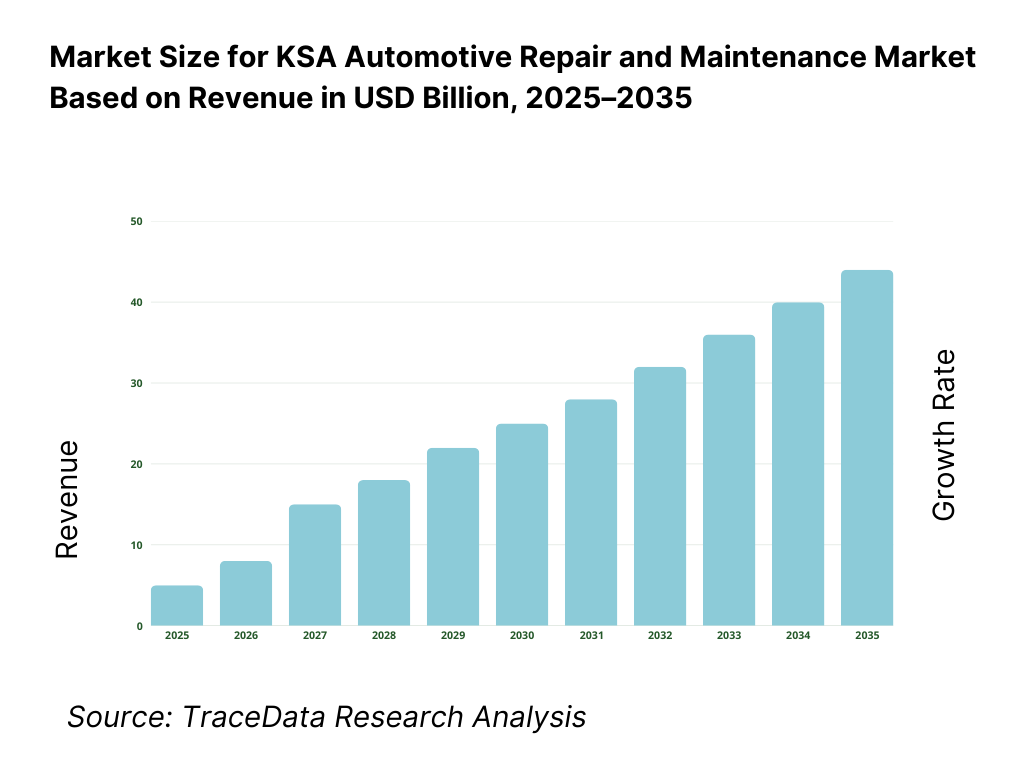
The KSA automotive repair and maintenance market is expected to expand steadily through 2035, supported by continued growth in the national vehicle parc, rising average vehicle age, and sustained dependence on private mobility across regions. Market momentum will be reinforced by high vehicle utilization, extreme climatic conditions that accelerate component wear, and increasing regulatory enforcement around vehicle inspections and roadworthiness. As Saudi vehicle owners continue to retain vehicles for longer periods and seek cost-efficient post-warranty servicing, repair and maintenance will remain a structurally resilient segment of the automotive value chain.
Shift Toward Organized, Standardized, and Multi-Brand Service Formats: The market will continue to transition gradually from highly fragmented, informal garages toward organized multi-brand service chains and professionally managed workshop networks. Customers are increasingly prioritizing pricing transparency, service consistency, digital booking, and warranty-backed repairs—particularly in major urban centers. Organized players that offer standardized service menus, trained technicians, and integrated spare parts sourcing will capture a growing share of post-warranty demand, while smaller independent workshops will face pressure to upgrade capabilities or consolidate.
Rising Importance of Fleet Servicing and Contract-Based Maintenance Models: Growth in logistics, last-mile delivery, ride-hailing, corporate leasing, and government fleets will increase demand for structured, contract-based maintenance services. Fleet operators prioritize uptime, preventive maintenance, predictable costs, and rapid turnaround times, favoring workshops that can deliver service-level agreements (SLAs), centralized billing, and mobile or on-site servicing. Through 2035, fleet-driven demand is expected to become a key profit pool for organized service providers and regional workshop groups.
Gradual Technology Transition and Capability Building for Hybrid and EV Servicing: While internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles will continue to dominate the Saudi vehicle parc in the medium term, the gradual penetration of hybrids and electric vehicles will reshape service requirements over the long run. Demand will increasingly shift toward advanced diagnostics, software-based fault detection, battery health monitoring, and high-voltage safety procedures. Workshops that invest early in training, tooling, and EV-ready infrastructure will be better positioned to participate in future growth segments as electrification adoption accelerates.
Digitalization of Customer Engagement, Diagnostics, and Workshop Operations: Digital tools will play a growing role in customer acquisition and retention, including online booking platforms, service reminders, digital inspection reports, and CRM-driven engagement. Internally, workshops are expected to adopt diagnostic software, inventory management systems, and workflow automation to improve efficiency and reduce turnaround times. Players that integrate digital interfaces across customer touchpoints and back-end operations will gain competitive advantage through improved transparency and operational control.
KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market Segmentation
By Service Type
• Periodic Maintenance & Preventive Servicing
• Mechanical Repairs (Engine, Transmission, Suspension)
• Electrical & Diagnostics (AC, Electronics, Sensors)
• Body Repair & Paint
• Tires, Batteries & Quick-Service Consumables
By Vehicle Type
• Passenger Vehicles
• Light Commercial Vehicles (LCVs)
• Heavy Commercial Vehicles (HCVs)
By Service Channel
• Independent Workshops
• Authorized OEM Service Centers
• Organized Multi-Brand Service Chains
• Mobile / On-Demand & Roadside Services
By Ownership Model
• Privately Owned / Family-Run Workshops
• Corporate-Owned & Franchise Chains
• Government & Semi-Government Workshops
By Region
• Central Region (Riyadh)
• Western Region (Makkah–Madinah–Jeddah)
• Eastern Region
• Southern Region
• Northern Region
Players Mentioned in the Report:
• National and regional organized automotive service chains
• Authorized OEM dealership service networks
• Independent and family-owned workshops
• Fleet-focused maintenance service providers
• Multi-brand diagnostic and quick-service networks
• Insurance-approved repair centers
Key Target Audience
• Automotive repair and maintenance service providers
• Organized multi-brand service chains and franchise operators
• Automotive dealerships and OEM service networks
• Fleet operators and logistics companies
• Motor insurance companies and claims administrators
• Spare parts distributors and aftermarket suppliers
• Automotive equipment, diagnostics, and tooling providers
• Private equity and strategic investors evaluating aftermarket consolidation
Time Period:
Historical Period: 2019–2024
Base Year: 2025
Forecast Period: 2025–2035
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4. 1 Delivery Model Analysis for Automotive Repair and Maintenance Services-Authorized Dealerships, Independent Workshops, Organized Multi-Brand Chains, Mobile Services [Margins, Preference, Strength & Weakness]
4. 2 Revenue Streams for KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market [Periodic Servicing, Mechanical Repairs, Body & Paint, Diagnostics, Consumables, Fleet Contracts]
4. 3 Business Model Canvas for KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market [Key Partners, Key Activities, Value Propositions, Customer Segments, Cost Structure, Revenue Streams]
5. 1 Local Players vs Global Service Networks [Local Workshops vs Bosch Car Service / Dealer Networks etc.]
5. 2 Investment Model in KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market [Private Investment, Franchise Expansion, OEM-Led Investments, PE Participation]
5. 3 Comparative Analysis of Repair and Maintenance Adoption in Private vs Fleet Vehicles [Service Frequency, Cost Structure, SLA Models]
5. 4 Service Spend Allocation by Vehicle Ownership Type [Private Owners, Corporate Fleets, Government Fleets]
8. 1 Revenues (Historical Trend)
9. 1 By Market Structure (Authorized Service Centers vs Independent & Organized Workshops)
9. 2 By Service Type (Periodic Maintenance, Mechanical Repair, Electrical & Diagnostics, Body & Paint, Tires & Batteries)
9. 3 By Vehicle Type (Passenger Vehicles, Light Commercial Vehicles, Heavy Commercial Vehicles)
9. 4 By Ownership Model (Private Vehicles, Fleet Vehicles, Government Vehicles)
9. 5 By Service Channel (Dealerships, Independent Workshops, Organized Chains, Mobile Services)
9. 6 By Warranty Status (In-Warranty vs Post-Warranty Vehicles)
9. 7 By Price Positioning (Economy, Mid-Range, Premium Service Offerings)
9. 8 By Region (Central Region, Western Region, Eastern Region, Southern Region, Northern Region)
10. 1 Vehicle Owner & Fleet Operator Landscape and Cohort Analysis
10. 2 Repair and Maintenance Decision Drivers & Service Selection Process
10. 3 Cost Effectiveness & Lifecycle Value Analysis
10. 4 Gap Analysis Framework
11. 1 Trends & Developments in KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market
11. 2 Growth Drivers for KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market
11. 3 SWOT Analysis for KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market
11. 4 Issues & Challenges for KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market
11. 5 Government Regulations for KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market
12. 1 Market Size and Future Potential for Organized Automotive Service Platforms in KSA
12. 2 Business Models & Revenue Streams [Service Packages, AMC Contracts, Fleet SLAs, Digital Booking]
12. 3 Delivery Models & Service Offerings [Multi-Brand Workshops, Express Service, Mobile Repair, Fleet Servicing]
15. 1 Market Share of Key Players in KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market (By Revenues)
15. 2 Benchmark of Key Competitors [Company Overview, USP, Business Strategies, Business Model, Number of Service Outlets, Revenues, Pricing Strategy, Service Portfolio, Key Clients, Strategic Tie-ups, Marketing Strategy, Recent Developments]
15. 3 Operating Model Analysis Framework
15. 4 Competitive Positioning Matrix for Automotive Service Providers
15. 5 Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
16. 1 Revenues (Projections)
17. 1 By Market Structure (Authorized vs Independent & Organized Service Providers)
17. 2 By Service Type (Maintenance, Mechanical, Electrical, Body & Paint, Consumables)
17. 3 By Vehicle Type (Passenger Vehicles, LCVs, HCVs)
17. 4 By Ownership Model (Private, Fleet, Government Vehicles)
17. 5 By Service Channel (Dealerships, Independent Workshops, Organized Chains, Mobile Services)
17. 6 By Warranty Status (In-Warranty vs Post-Warranty)
17. 7 By Price Positioning (Economy, Mid-Range, Premium)
17. 8 By Region (Central, Western, Eastern, Southern, Northern Regions)
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
We begin by mapping the complete ecosystem of the KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market across demand-side and supply-side entities. On the demand side, entities include private passenger vehicle owners, multi-car households, premium vehicle owners, commercial fleet operators, logistics and last-mile delivery companies, ride-hailing platforms, corporate leasing firms, government and municipal fleets, and insurance-driven accident repair demand. Demand is further segmented by vehicle age (in-warranty vs post-warranty), service type (periodic maintenance, mechanical repair, body & paint, diagnostics), usage intensity (private vs fleet), and customer preference (price-led vs quality-led).
On the supply side, the ecosystem includes authorized OEM dealership service centers, organized multi-brand service chains, independent and family-owned workshops, quick-service outlets, mobile and roadside assistance providers, spare parts distributors, lubricant suppliers, diagnostic equipment vendors, workshop management software providers, and technical training institutes. Regulatory bodies overseeing workshop licensing, vehicle inspections, labor compliance, and environmental standards are also included. From this mapped ecosystem, we shortlist 8–12 leading organized service networks and dealership groups, along with a representative sample of independent workshops, based on outlet footprint, geographic coverage, service breadth, insurer and fleet tie-ups, and brand recognition. This step establishes how value is created and captured across customer acquisition, servicing, parts sourcing, labor deployment, and after-sales engagement.
Step 2: Desk Research
An exhaustive desk research process is undertaken to analyze the structure, demand drivers, and service behavior within the KSA automotive repair and maintenance market. This includes assessment of vehicle parc growth, average vehicle age trends, mileage patterns, climatic impact on component wear, and regional vehicle density. We analyze service frequency by vehicle type, post-warranty servicing behavior, and the role of consumables such as tires, batteries, lubricants, and filters in driving repeat demand.
Company-level analysis includes review of service offerings, pricing structures, outlet formats, expansion strategies, franchise models, and digital service capabilities of organized players and dealership networks. We also examine regulatory and compliance dynamics, including vehicle inspection regimes, insurance-linked repair approvals, workshop licensing requirements, and workforce localization policies. The outcome of this stage is a comprehensive industry foundation that defines segmentation logic, service mix assumptions, and baseline demand parameters required for market sizing and forward-looking projections.
Step 3: Primary Research
We conduct structured interviews with authorized dealership service heads, organized multi-brand service chain operators, independent workshop owners, fleet maintenance managers, spare parts distributors, and insurance-linked repair coordinators. The objectives are threefold:
(a) validate assumptions around service demand concentration, channel share, and customer migration from dealers to independent workshops,
(b) authenticate segment splits by service type, vehicle type, service channel, and ownership model, and
(c) gather qualitative insights on pricing behavior, margin structures, technician availability, turnaround times, parts sourcing challenges, and customer expectations around transparency and service quality.
A bottom-to-top approach is applied by estimating service volumes, average ticket sizes, and outlet throughput across key vehicle and service segments, which are aggregated to develop the overall market view. In selected cases, disguised customer-style interactions are conducted with workshops and service chains to validate field-level realities such as service timelines, quotation practices, warranty terms, and differences between advertised and actual service delivery.
Step 4: Sanity Check
The final stage integrates bottom-to-top and top-to-down approaches to cross-validate the market size, segmentation splits, and forecast assumptions. Demand estimates are reconciled with macro indicators such as vehicle parc growth, new vehicle sales, used vehicle retention trends, fleet expansion, and insurance penetration. Assumptions around service frequency, spare parts replacement cycles, labor productivity, and regulatory enforcement are stress-tested to understand their impact on overall market growth.
Sensitivity analysis is conducted across key variables including changes in vehicle age distribution, pace of organized workshop penetration, fleet servicing adoption, and readiness for hybrid and EV maintenance. Market models are refined until alignment is achieved between service capacity, outlet density, parts supply, and observed demand behavior, ensuring internal consistency and robust directional forecasting through 2035.
FAQs
01 What is the potential for the KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market?
The KSA automotive repair and maintenance market holds strong long-term potential, supported by sustained growth in the vehicle parc, high average vehicle age, intensive vehicle usage, and climatic conditions that accelerate wear and tear. As vehicle owners retain cars for longer periods and seek cost-efficient post-warranty servicing, demand for repair and maintenance services is expected to remain resilient through 2035. Gradual formalization and organized service expansion will further enhance market depth.
02 Who are the Key Players in the KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market?
The market features a mix of authorized OEM dealership service networks, organized multi-brand service chains, and a large base of independent workshops. Dealerships dominate warranty-period and premium vehicle servicing, while independent and organized players compete aggressively in post-warranty and mass-market segments. Competitive differentiation is driven by service quality, pricing transparency, turnaround time, geographic reach, and insurer or fleet relationships.
03 What are the Growth Drivers for the KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market?
Key growth drivers include expansion of the national vehicle parc, increasing average vehicle age, high annual mileage, and environmental conditions that increase service frequency. Additional momentum comes from growth in logistics and fleet operations, rising insurance penetration, regulatory enforcement of vehicle inspections, and gradual customer shift toward organized service formats offering transparency and consistency.
04 What are the Challenges in the KSA Automotive Repair and Maintenance Market?
Challenges include market fragmentation, uneven service quality across independent workshops, shortages of skilled technicians under workforce localization policies, and rising spare parts and operating costs. Limited readiness for advanced vehicle technologies such as hybrids and EVs may also constrain long-term capability unless investments in training and infrastructure accelerate.