KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market Outlook to 2035
By Welding Technology, By Application Area, By Automation Level, By End-User Segment, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0529
- Region: Middle East
- Published on: January 2026
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market Outlook to 2035 – By Welding Technology, By Application Area, By Automation Level, By End-User Segment, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the automotive welding equipment industry in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The report covers an overview and genesis of the market, overall market size in terms of value, detailed market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory and industrial policy landscape, buyer-level demand profiling, key issues and challenges, and competitive landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players active in the KSA automotive welding equipment market. The report concludes with future market projections based on domestic automotive manufacturing localization, EV and advanced mobility investments, OEM and Tier-1 capacity expansion, industrial automation adoption, regional demand drivers, cause-and-effect relationships, and case-based illustrations highlighting the major opportunities and cautions shaping the market through 2035.
KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market Overview and Size
The KSA automotive welding equipment market is valued at approximately ~USD ~ million, representing the supply of welding systems and solutions used across vehicle body, chassis, powertrain, and component manufacturing. This includes resistance spot welding systems, arc welding equipment (MIG/MAG, TIG), laser welding systems, friction and solid-state welding technologies, welding robots, power sources, fixtures, and associated automation, safety, and quality monitoring solutions.
Automotive welding equipment plays a critical role in ensuring structural integrity, dimensional accuracy, productivity, and repeatability in vehicle manufacturing and component assembly. In Saudi Arabia, demand is increasingly linked to the Kingdom’s push toward industrial localization, the development of domestic automotive assembly and component manufacturing capabilities, and the broader transformation of the manufacturing sector under Vision 2030.
The market is anchored by emerging vehicle assembly projects, localization initiatives for automotive components, investments in industrial clusters, and the gradual shift toward higher automation levels in manufacturing. While the current automotive production base in KSA is smaller than mature global markets, the welding equipment market benefits from greenfield investments, technology leapfrogging, and the adoption of modern, automated welding lines rather than legacy systems.
Regionally, demand is concentrated in the Western and Central regions, driven by industrial zones around Jeddah, King Abdullah Economic City (KAEC), Riyadh, and surrounding manufacturing hubs. These areas benefit from proximity to ports, logistics infrastructure, and government-backed industrial cities. The Eastern region contributes through industrial manufacturing capabilities and supplier ecosystems linked to heavy industry and advanced fabrication. Other regions remain nascent but are expected to see gradual demand as localized component manufacturing expands.
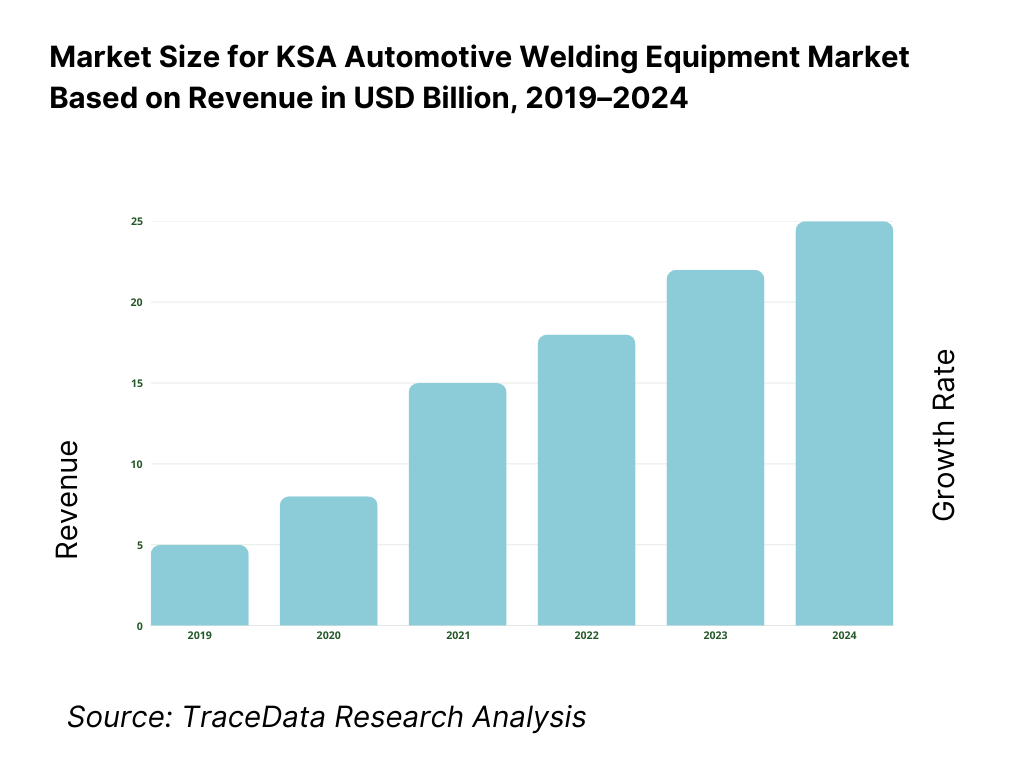
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market:
Automotive manufacturing localization and Vision 2030 initiatives strengthen structural demand: Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 places strong emphasis on building domestic manufacturing capabilities, reducing import dependence, and developing high-value industrial sectors, including automotive and mobility. As vehicle assembly plants, CKD/SKD operations, and component manufacturing facilities are established, demand for modern welding equipment increases across body-in-white, chassis, exhaust systems, frames, and sub-assemblies. Welding equipment suppliers benefit from greenfield projects where OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers specify new-generation welding systems aligned with global quality and productivity standards.
Emergence of EVs and advanced mobility platforms drives technology-intensive welding adoption: The Kingdom’s ambitions to participate in electric vehicle and advanced mobility manufacturing are reshaping welding technology requirements. EV platforms require precise welding of lightweight materials such as aluminum alloys, advanced high-strength steels, and mixed-material structures. This drives demand for laser welding, advanced arc welding, and digitally controlled resistance welding systems with higher accuracy and quality monitoring capabilities. Compared to conventional internal combustion vehicle manufacturing, these platforms accelerate the shift toward higher-specification welding equipment and automation-ready solutions.
Increasing adoption of automation and robotics in manufacturing improves productivity and consistency: Saudi manufacturers are increasingly adopting robotic and automated welding cells to address productivity targets, quality consistency, and long-term workforce optimization. Automotive welding is particularly suited to automation due to repetitive weld patterns, stringent quality requirements, and high throughput needs. As a result, demand is rising for integrated welding robots, automated fixtures, inline inspection systems, and digitally monitored welding processes. This trend supports higher average selling prices for welding equipment and favors suppliers offering turnkey automation solutions rather than standalone machines.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of the KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market:
Limited scale and phased ramp-up of domestic automotive production impacts equipment utilization and investment certainty: While Saudi Arabia has articulated strong ambitions to localize automotive manufacturing, the current production base is still in an early-stage ramp-up phase. Automotive welding equipment—particularly robotic and laser-based systems—requires high utilization rates to justify capital investment. Delays in project commissioning, phased production starts, or slower-than-expected volume ramp-ups can lead OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers to defer or stagger welding equipment purchases. This creates uneven demand cycles for equipment suppliers and increases reliance on modular, scalable systems rather than fully integrated high-capex welding lines.
Dependence on imported technology and limited local service capability increases lifecycle costs: Most advanced automotive welding technologies used in Saudi Arabia are imported from Europe, East Asia, or North America. While this ensures access to high-quality equipment, it also increases exposure to import lead times, spare parts availability, and reliance on overseas technical support. Limited local availability of certified welding automation engineers, robot programmers, and laser system specialists can extend commissioning timelines and raise after-sales service costs. For manufacturers, these factors increase total cost of ownership and may slow the adoption of highly sophisticated welding systems in favor of simpler, semi-automated solutions.
Workforce skill gaps in advanced welding automation and robotics create operational constraints: Automotive welding increasingly depends on digitally controlled processes, robotic cells, and real-time quality monitoring. However, the availability of locally trained technicians and engineers with hands-on experience in robotic welding, laser welding, and inline inspection systems remains limited. This skills gap can result in longer training cycles, reliance on expatriate expertise, and higher operating risk during early production phases. In some cases, manufacturers delay full automation deployment until internal teams are sufficiently trained, affecting near-term equipment demand.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
Industrial localization policies and Vision 2030 manufacturing initiatives shaping investment priorities: Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 and associated industrial strategies actively encourage domestic manufacturing, technology transfer, and localization of automotive and mobility-related value chains. These initiatives influence OEM and supplier investment decisions, including the specification of welding equipment that aligns with long-term localization plans. Preference is often given to equipment suppliers willing to establish local assembly, service partnerships, or training centers, shaping competitive dynamics beyond pure equipment performance.
Industrial safety, welding standards, and workplace compliance requirements influencing system design: Automotive welding operations in KSA must comply with national industrial safety regulations covering electrical safety, laser safety, fume extraction, operator protection, and machine guarding. Compliance with international welding and quality standards—such as ISO-based welding procedure qualification, traceability, and documentation—directly affects equipment selection. As manufacturers aim to meet global OEM quality benchmarks, welding systems increasingly incorporate advanced monitoring, data logging, and defect detection features to support audit and compliance requirements.
Energy efficiency, sustainability goals, and emissions reduction initiatives affecting equipment choices: Saudi Arabia’s broader sustainability and energy efficiency agenda is beginning to influence industrial equipment procurement. Automotive manufacturers are increasingly evaluating welding systems based on energy consumption, process efficiency, and waste reduction. Technologies such as laser welding and modern inverter-based power sources gain relevance due to lower energy use, reduced rework, and improved material efficiency. Over time, sustainability considerations are expected to become a stronger differentiator in welding equipment specification and supplier selection.
KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market Segmentation
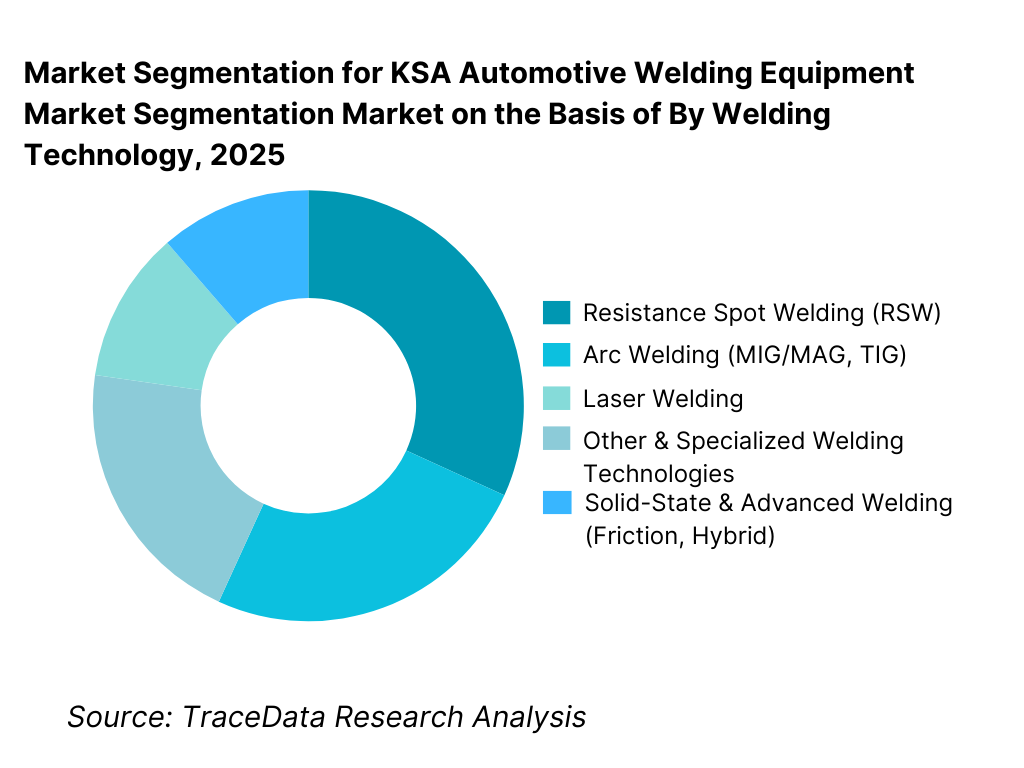
By Welding Technology: Resistance spot welding and arc welding dominate current demand. This is because conventional vehicle body structures, chassis assemblies, and component manufacturing in Saudi Arabia continue to rely heavily on resistance spot welding (RSW) and arc welding (MIG/MAG) technologies. These methods are well-established, cost-effective, and suitable for steel-intensive vehicle architectures that dominate early-stage localization programs. As domestic manufacturing ramps up, these technologies benefit from operator familiarity, lower capital intensity, and compatibility with semi-automated and fully automated setups. Advanced technologies such as laser welding and solid-state welding are gaining traction but remain concentrated in higher-end platforms and EV-related applications.
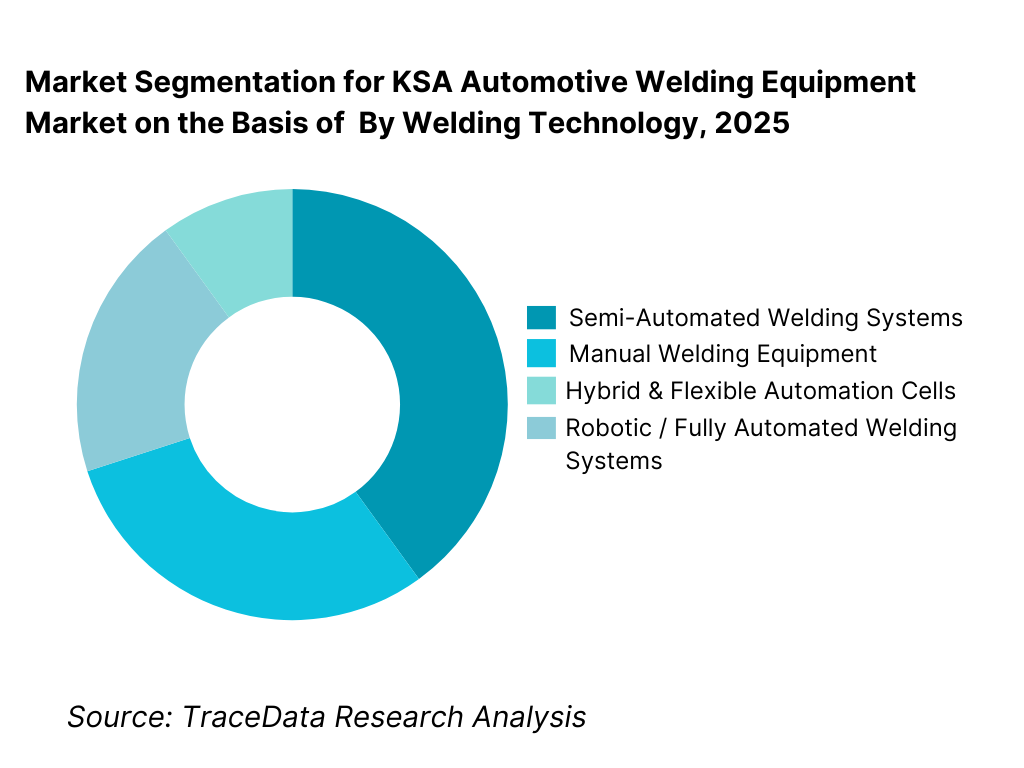
By Automation Level: Semi-automated and robotic welding systems lead the market. Saudi automotive manufacturers increasingly favor semi-automated and robotic welding systems to balance productivity, quality consistency, and workforce availability. While fully manual welding remains relevant for low-volume components, prototypes, and aftermarket fabrication, the strategic direction clearly favors automation to meet global OEM quality standards. Robotic welding cells are particularly common in body-in-white, exhaust systems, frames, and repetitive component assemblies where cycle time, repeatability, and defect reduction are critical.
Competitive Landscape in KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market
The KSA automotive welding equipment market exhibits low to moderate concentration, characterized by the presence of global welding equipment manufacturers, robotic automation leaders, and regional system integrators. Market leadership is driven by technology reliability, automation integration capability, global OEM approvals, local service availability, and the ability to support greenfield plant commissioning. International brands dominate high-specification and automated welding lines, while regional distributors and integrators play a critical role in installation, commissioning, and after-sales support.
While large global suppliers are favored for OEM and Tier-1 projects, localized system integrators remain competitive by offering faster response times, customization, and cost-effective solutions for mid-scale component manufacturers.
Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
Lincoln Electric | 1895 | Cleveland, Ohio, USA |
Fronius International | 1945 | Pettenbach, Austria |
Panasonic Welding Systems | 1918 | Osaka, Japan |
ABB Robotics | 1988 | Zurich, Switzerland |
KUKA Robotics | 1898 | Augsburg, Germany |
ESAB | 1904 | Gothenburg, Sweden |
OTC Daihen | 1919 | Osaka, Japan |
Yaskawa Motoman | 1915 | Kitakyushu, Japan |
CLOOS Welding Technology | 1919 | Haiger, Germany |
Some of the Recent Competitor Trends and Key Information About Competitors Include:
Lincoln Electric: Lincoln Electric maintains a strong presence through its broad portfolio of arc welding power sources, automation solutions, and global service infrastructure. In the KSA market, the company benefits from strong brand recognition, robust training programs, and suitability for both manual and automated welding applications across automotive and component manufacturing.
Fronius International: Fronius is positioned as a premium technology supplier, particularly in digitally controlled arc welding and high-precision automotive applications. Its strength lies in advanced process control, energy efficiency, and suitability for lightweight materials and complex joints increasingly used in modern vehicle platforms.
ABB Robotics: ABB plays a critical role in robotic welding automation, supplying integrated robot-welding systems for body-in-white and high-volume component manufacturing. Its competitive advantage is driven by system integration expertise, global OEM acceptance, and scalable automation architectures suitable for greenfield Saudi plants.
KUKA Robotics: KUKA remains closely associated with automotive manufacturing worldwide and continues to be a preferred supplier for highly automated welding lines. In Saudi Arabia, its relevance is strongest in OEM-linked projects where full automation, digital twins, and flexible production cells are specified from the outset.
Panasonic Welding Systems: Panasonic differentiates through integrated welding robot solutions combining power sources, robots, and process control. Its strength lies in precision welding, stable arc characteristics, and long-term reliability, making it attractive for Tier-1 suppliers focused on consistent quality and uptime.
What Lies Ahead for KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market?
The KSA automotive welding equipment market is expected to expand steadily through 2035, supported by Saudi Arabia’s long-term automotive manufacturing localization agenda, investments in EV and advanced mobility platforms, and the broader industrial transformation under Vision 2030. Growth momentum will be driven by greenfield vehicle assembly plants, Tier-1 and Tier-2 component localization, and increasing adoption of automation to meet global OEM quality, productivity, and safety benchmarks. As Saudi manufacturers prioritize scalable, future-ready production systems over legacy setups, automotive welding equipment will remain a foundational element in the Kingdom’s evolving automotive manufacturing ecosystem.
Transition Toward Higher Automation and Digitally Controlled Welding Systems: The future of the KSA automotive welding equipment market will see a clear shift from manual and basic semi-automatic welding toward robotic and digitally controlled welding systems. Body-in-white operations, chassis assemblies, exhaust systems, and structural components increasingly require consistent weld quality, traceability, and repeatability. Advanced resistance spot welding, robotic arc welding, and laser welding systems with integrated monitoring and data logging will gain importance as manufacturers align with global OEM production standards. Suppliers capable of delivering automation-ready, upgradeable systems will capture higher-value opportunities.
Increasing Adoption of EV-Oriented and Lightweight Material Welding Technologies: As Saudi Arabia positions itself within the EV and advanced mobility value chain, demand will grow for welding technologies suitable for aluminum alloys, advanced high-strength steels, and mixed-material architectures. Laser welding, hybrid welding, and advanced inverter-based arc welding systems will see rising adoption due to their precision, lower heat input, and suitability for lightweight structures. This shift will gradually change the technology mix of the market, increasing average system complexity and favoring suppliers with strong R&D and application engineering capabilities.
Growing Emphasis on Turnkey Automation, Integration, and Lifecycle Support: Automotive manufacturers in KSA increasingly prefer turnkey welding solutions that integrate robots, power sources, fixtures, safety systems, and quality monitoring into a single production cell. Beyond equipment supply, buyers place growing importance on commissioning support, operator training, predictive maintenance, and local after-sales service. Through 2035, suppliers that establish strong local integration partnerships, service infrastructure, and technical training capabilities will be better positioned to support long-term customer relationships and recurring revenue streams.
Alignment with Industrial Sustainability, Energy Efficiency, and Safety Objectives: Energy efficiency, workplace safety, and emissions reduction will become more prominent considerations in welding equipment selection. Modern inverter-based power sources, laser systems with reduced material waste, and fume extraction-integrated welding cells will gain traction as manufacturers align with broader sustainability and ESG objectives. While cost remains a key decision factor, lifecycle efficiency and compliance readiness are expected to increasingly influence procurement decisions, particularly for export-oriented and OEM-aligned manufacturing facilities.
KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market Segmentation
By Welding Technology
• Resistance Spot Welding
• Arc Welding (MIG/MAG, TIG)
• Laser Welding
• Solid-State & Advanced Welding Technologies
• Other & Specialized Welding Processes
By Automation Level
• Robotic / Fully Automated Welding Systems
• Semi-Automated Welding Systems
• Manual Welding Equipment
• Hybrid & Flexible Automation Cells
By Application Area
• Body-in-White (BIW)
• Chassis and Frame Welding
• Exhaust and Powertrain Components
• Structural and Safety Components
• General Automotive Component Fabrication
By End-User Segment
• OEM Vehicle Manufacturers
• Tier-1 Automotive Component Suppliers
• Tier-2 & Tier-3 Component Manufacturers
• Maintenance, Retrofit & Others
By Region
• Central Region
• Western Region
• Eastern Region
• Southern and Northern Regions
Players Mentioned in the Report:
• Lincoln Electric
• Fronius International
• ABB Robotics
• KUKA Robotics
• Panasonic Welding Systems
• ESAB
• OTC Daihen
• Yaskawa Motoman
• CLOOS Welding Technology
• Regional welding automation integrators and industrial equipment distributors in KSA
Key Target Audience
• Automotive OEMs and vehicle assembly companies
• Tier-1, Tier-2, and Tier-3 automotive component manufacturers
• Welding equipment manufacturers and automation solution providers
• Industrial system integrators and engineering firms
• Industrial zone developers and manufacturing investors
• Government bodies supporting automotive localization and industrial development
• Private equity and strategic investors focused on manufacturing and mobility
Time Period:
Historical Period: 2019–2024
Base Year: 2025
Forecast Period: 2025–2035
Report Coverage
1. Executive Summary
2. Research Methodology
3. Ecosystem of Key Stakeholders in KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market
4. Value Chain Analysis
4.1 Delivery Model Analysis for Automotive Welding Equipment including manual welding systems, semi-automated systems, robotic welding cells, and fully integrated automation lines with margins, preferences, strengths, and weaknesses
4.2 Revenue Streams for Automotive Welding Equipment Market including equipment sales, automation integration, software and controls, spare parts, maintenance services, and training support
4.3 Business Model Canvas for Automotive Welding Equipment Market covering equipment manufacturers, robotic automation providers, system integrators, distributors, OEMs, Tier-1 suppliers, and service partners
5. Market Structure
5.1 Global Welding Equipment and Automation Players vs Regional and Local Integrators including Lincoln Electric, Fronius, ABB, KUKA, Panasonic, ESAB, and regional system integrators
5.2 Investment Model in Automotive Welding Equipment Market including greenfield plant investments, automation upgrades, capacity expansion, and retrofit or modernization projects
5.3 Comparative Analysis of Welding Equipment Deployment by Manual, Semi-Automated, and Robotic Production Lines including flexibility, cost, and productivity considerations
5.4 Automotive Manufacturing Cost Allocation comparing welding equipment investment versus stamping, machining, assembly, and painting with average capital spend per production line
6. Market Attractiveness for KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market including automotive localization initiatives, EV manufacturing plans, industrial automation adoption, workforce availability, and technology readiness
7. Supply-Demand Gap Analysis covering demand for advanced welding automation, availability of skilled operators and integrators, technology localization gaps, and service capability constraints
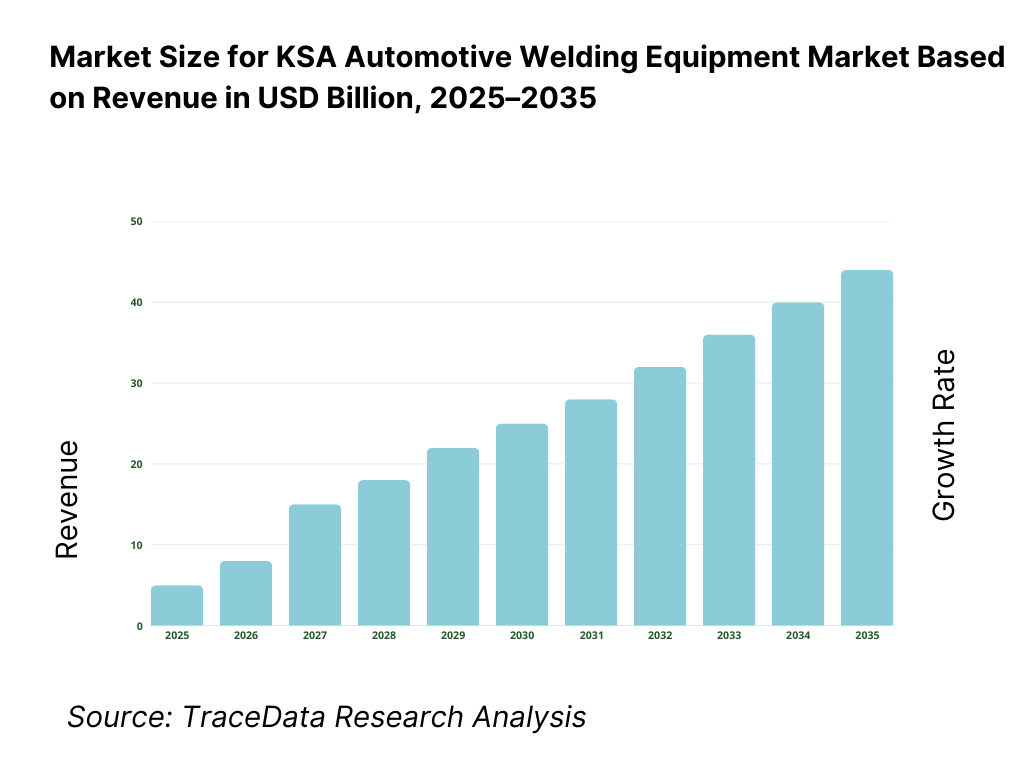
8. Market Size for KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market Basis
8.1 Revenues from historical to present period
8.2 Growth Analysis by welding technology and by automation level
8.3 Key Market Developments and Milestones including OEM plant announcements, EV projects, automation investments, and industrial policy updates
9. Market Breakdown for KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market Basis
9.1 By Market Structure including global equipment suppliers, regional distributors, and local system integrators
9.2 By Welding Technology including resistance spot welding, arc welding, laser welding, and solid-state or advanced welding technologies
9.3 By Automation Level including manual, semi-automated, robotic, and flexible automation cells
9.4 By End-User Segment including OEMs, Tier-1 suppliers, Tier-2 and Tier-3 component manufacturers
9.5 By Application Area including body-in-white, chassis and frame, exhaust and powertrain, and structural components
9.6 By Material Type including steel, aluminum, mixed materials, and advanced alloys
9.7 By Production Scale including pilot lines, low-volume assembly, and high-volume manufacturing
9.8 By Region including Central, Western, Eastern, Northern, and Southern regions of KSA
10. Demand Side Analysis for KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market
10.1 Automotive Manufacturing Landscape and Production Capacity Analysis
10.2 Welding Technology Selection and Purchase Decision Making influenced by quality standards, automation needs, cost, and OEM approvals
10.3 Productivity, Quality, and ROI Analysis measuring cycle time, defect rates, uptime, and lifecycle cost
10.4 Gap Analysis Framework addressing automation readiness, skills availability, and service localization gaps
11. Industry Analysis
11.1 Trends and Developments including rise of robotic welding, laser welding adoption, EV-oriented processes, and digital quality monitoring
11.2 Growth Drivers including automotive localization, EV manufacturing, automation adoption, and industrial policy support
11.3 SWOT Analysis comparing global technology leadership versus regional integration and localization capability
11.4 Issues and Challenges including high capital costs, skill shortages, commissioning complexity, and reliance on imported technology
11.5 Government Regulations covering industrial safety standards, welding compliance requirements, localization policies, and manufacturing incentives in KSA
12. Snapshot on Industrial Automation and Robotics Market in KSA
12.1 Market Size and Future Potential of robotic welding systems and industrial automation
12.2 Business Models including turnkey automation projects, modular upgrades, and service-led engagement models
12.3 Delivery Models and Type of Solutions including robotic cells, flexible automation, and digitally monitored welding lines
13. Opportunity Matrix for KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market highlighting EV manufacturing, Tier-1 localization, robotic welding adoption, and aftermarket automation upgrades
14. PEAK Matrix Analysis for KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market categorizing players by process excellence, automation capability, application expertise, and market reach
15. Competitor Analysis for KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market
15.1 Market Share of Key Players by revenues and by installed base
15.2 Benchmark of 15 Key Competitors including Lincoln Electric, Fronius, ABB, KUKA, Panasonic, ESAB, OTC Daihen, Yaskawa Motoman, CLOOS, and regional automation integrators
15.3 Operating Model Analysis Framework comparing global equipment-led models, automation-integrator-led models, and localized service-driven models
15.4 Gartner Magic Quadrant positioning global leaders and regional challengers in welding automation and robotics
15.5 Bowman’s Strategic Clock analyzing competitive advantage through technology differentiation versus cost-led automation strategies
16. Future Market Size for KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market Basis
16.1 Revenues with projections
17. Market Breakdown for KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market Basis Future
17.1 By Market Structure including global suppliers, regional distributors, and local integrators
17.2 By Welding Technology including resistance, arc, laser, and advanced welding processes
17.3 By Automation Level including manual, semi-automated, and robotic systems
17.4 By End-User Segment including OEMs, Tier-1, and Tier-2/3 suppliers
17.5 By Application Area including body-in-white, chassis, and components
17.6 By Material Type including steel and lightweight materials
17.7 By Production Scale including low-volume and high-volume manufacturing
17.8 By Region including Central, Western, Eastern, Northern, and Southern KSA
18. Recommendations focusing on automation strategy, technology localization, workforce upskilling, and service infrastructure development
19. Opportunity Analysis covering EV manufacturing, robotic welding adoption, Tier-1 supplier localization, and industrial automation expansion
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
We begin by mapping the complete ecosystem of the KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market across demand-side and supply-side entities. On the demand side, entities include vehicle OEMs, EV manufacturers, Tier-1 automotive component suppliers, Tier-2 and Tier-3 component manufacturers, industrial fabrication units, and automotive-focused industrial clusters operating within economic cities and special zones. Demand is further segmented by application area (body-in-white, chassis, exhaust, structural components), production scale (pilot lines, low-volume assembly, high-volume manufacturing), and automation intensity (manual, semi-automated, robotic).
On the supply side, the ecosystem includes global welding equipment manufacturers, robotic automation providers, regional distributors, system integrators, fixture and tooling suppliers, robot programming and commissioning partners, industrial safety solution providers, training and certification bodies, and local service and maintenance contractors. From this mapped ecosystem, we shortlist 6–10 leading welding equipment and automation suppliers based on technology breadth, OEM approvals, automation capability, regional presence, and installed base relevance within automotive manufacturing. This step establishes how value is created and captured across equipment supply, system integration, commissioning, production ramp-up, and lifecycle support.
Step 2: Desk Research
An exhaustive desk research process is undertaken to analyze the structure and evolution of the KSA automotive welding equipment market. This includes reviewing Saudi Arabia’s automotive localization roadmap, EV and advanced mobility announcements, industrial investment pipelines, and capacity build-out within economic cities and manufacturing zones. We analyze technology adoption trends across welding processes, automation levels, and material compatibility, particularly in relation to lightweight structures and EV platforms.
Company-level analysis includes review of welding equipment portfolios, automation offerings, regional distribution models, service infrastructure, and training capabilities. We also examine industrial safety regulations, quality standards, and sustainability initiatives influencing welding equipment specification and procurement. The outcome of this stage is a robust industry foundation that defines segmentation logic and establishes the assumptions required for market sizing and long-term outlook modeling.
Step 3: Primary Research
We conduct structured interviews with automotive OEM representatives, Tier-1 and Tier-2 component manufacturers, welding automation integrators, equipment distributors, plant engineers, and production managers. The objectives are threefold:
(a) validate assumptions around demand concentration, technology mix, and automation adoption,
(b) authenticate segment splits by welding technology, automation level, and end-user category, and
(c) gather qualitative insights on capital investment behavior, commissioning timelines, workforce readiness, service expectations, and total cost of ownership considerations.
A bottom-to-top approach is applied by estimating production line counts, average welding cell value, and equipment density across different manufacturing setups, which are aggregated to form the overall market view. In selected cases, buyer-style interactions are conducted with system integrators and distributors to validate field-level realities such as installation timelines, integration challenges, spare parts availability, and after-sales responsiveness.
Step 4: Sanity Check
The final stage integrates bottom-to-top and top-to-down approaches to cross-validate market estimates, segmentation splits, and forecast assumptions. Demand projections are reconciled with macro indicators such as automotive production targets, EV manufacturing timelines, industrial investment commitments, and localization milestones under Vision 2030. Assumptions around automation penetration, workforce capability development, and service localization are stress-tested to understand their impact on adoption pace.
Sensitivity analysis is conducted across key variables including speed of automotive project execution, EV platform adoption, supplier localization depth, and automation intensity. Market models are refined until alignment is achieved between supplier capacity, integrator throughput, and buyer investment plans, ensuring internal consistency and a robust directional forecast through 2035.
FAQs
01 What is the potential for the KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market?
The KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market holds strong long-term potential, supported by Saudi Arabia’s automotive localization strategy, investments in EV and advanced mobility manufacturing, and the broader industrial transformation agenda under Vision 2030. As vehicle and component manufacturing capacity expands, demand for modern, automated, and high-precision welding equipment is expected to grow steadily. The shift toward higher automation and advanced materials further increases the value intensity of welding systems through 2035.
02 Who are the Key Players in the KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market?
The market features a mix of global welding equipment manufacturers, robotic automation leaders, and regional system integrators. Competition is shaped by technology capability, OEM approvals, automation integration expertise, and availability of local service and commissioning support. While international suppliers dominate high-specification and automated welding lines, regional integrators play a critical role in localization, installation, and lifecycle support.
03 What are the Growth Drivers for the KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market?
Key growth drivers include the establishment of domestic vehicle assembly plants, expansion of Tier-1 and Tier-2 component manufacturing, increasing automation adoption to meet global quality standards, and the emergence of EV-oriented production platforms. Additional momentum comes from government-backed industrial zones, incentives for manufacturing localization, and rising focus on productivity, safety, and energy efficiency in welding operations.
04 What are the Challenges in the KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market?
Challenges include the early-stage scale of automotive production, dependence on imported welding technologies, limited local availability of advanced automation skills, and extended commissioning timelines for complex systems. Production variability and multi-platform manufacturing can also reduce standardization benefits. Over time, these challenges are expected to moderate as production volumes increase, supplier ecosystems mature, and workforce capabilities deepen.