KSA Circuit Breakers Market Outlook to 2035
By Voltage Level, By Product Type, By End-Use Sector, By Installation Type, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0453
- Region: Middle East
- Published on: January 2026
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “KSA Circuit Breakers Market Outlook to 2035 – By Voltage Level, By Product Type, By End-Use Sector, By Installation Type, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the circuit breakers industry in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The report covers an overview and genesis of the market, overall market size in terms of value, detailed market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory and standards landscape, buyer-level demand profiling, key issues and challenges, and competitive landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the KSA circuit breakers market. The report concludes with future market projections based on power sector investments, grid modernization programs, renewable energy integration, industrial capacity expansion, urban infrastructure development, regional demand drivers, cause-and-effect relationships, and case-based illustrations highlighting the major opportunities and cautions shaping the market through 2035.
KSA Circuit Breakers Market Overview and Size
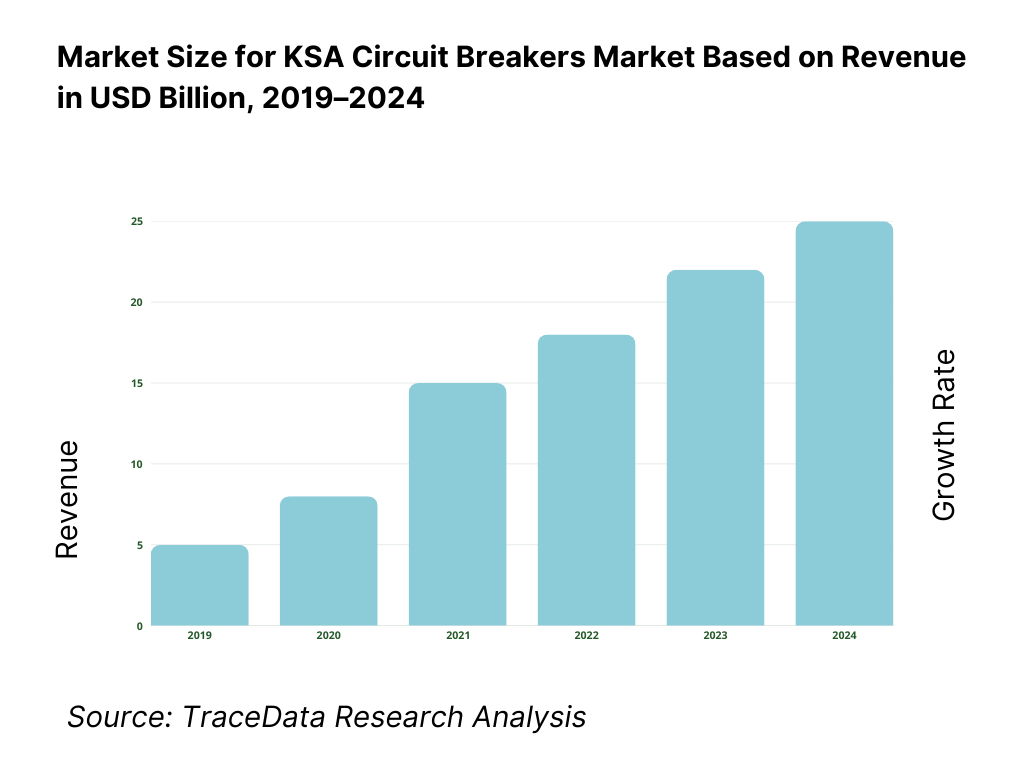
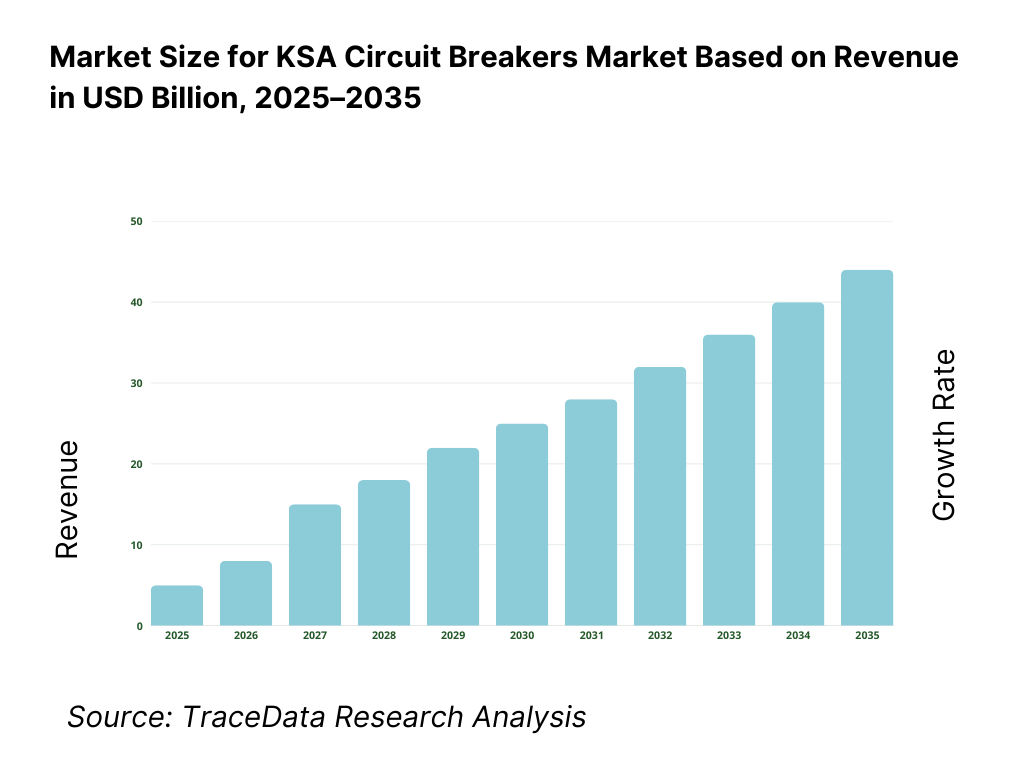
The Saudi Arabia circuit breakers market is valued at approximately ~USD ~ billion, representing the supply of electrical protection devices designed to automatically interrupt electrical circuits during overloads, short circuits, and fault conditions. Circuit breakers are critical components across power generation, transmission, distribution, industrial facilities, commercial buildings, and residential infrastructure, ensuring electrical safety, system reliability, and asset protection.
The market is underpinned by Saudi Arabia’s large and expanding power infrastructure base, sustained investments in transmission and distribution (T&D) networks, rapid urban development, and industrial diversification initiatives aligned with Vision 2030. Circuit breakers are widely deployed across low-voltage (LV), medium-voltage (MV), and high-voltage (HV) applications, with demand driven by both new installations and replacement of aging electrical assets across utilities and end-user facilities.
The Central and Western regions represent the largest demand centers due to concentration of population, commercial construction, industrial zones, and large-scale infrastructure projects. The Eastern Province remains a structurally important market supported by oil & gas facilities, petrochemical complexes, utilities, and industrial clusters that require high-reliability electrical protection systems. The Southern and Northern regions show growing incremental demand driven by grid expansion, renewable energy projects, and public-sector infrastructure development, although volumes remain smaller compared to core urban and industrial hubs.
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the KSA Circuit Breakers Market
Expansion and reinforcement of power transmission and distribution infrastructure strengthens baseline demand: Saudi Arabia continues to invest heavily in expanding and upgrading its electricity transmission and distribution networks to support rising power consumption, urban expansion, and industrial load growth. Grid reinforcement projects, substation additions, and feeder upgrades require extensive deployment of circuit breakers across HV, MV, and LV levels. Utilities prioritize equipment that meets high reliability, safety, and climatic performance standards, directly supporting steady demand for advanced circuit breaker technologies.
Large-scale infrastructure and real estate development drives low- and medium-voltage installations: Ongoing development of residential communities, commercial buildings, transport infrastructure, healthcare facilities, and education campuses increases consumption of LV and MV circuit breakers. These projects require standardized, code-compliant protection devices integrated into switchboards, panels, and substations. The scale and phasing of construction projects create repeat demand across contractors, EPC firms, and electrical distributors serving the construction ecosystem.
Industrial diversification and manufacturing capacity expansion increase demand for high-performance protection systems: Industrial growth across sectors such as metals, cement, chemicals, food processing, logistics, and data centers drives adoption of circuit breakers designed for higher fault levels, continuous operation, and specialized industrial environments. Manufacturing facilities prioritize equipment reliability and uptime, increasing demand for molded-case circuit breakers (MCCBs), air circuit breakers (ACBs), and MV switchgear-integrated breakers capable of handling heavy loads and harsh operating conditions.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of the KSA Circuit Breakers Market:
Price competition and margin pressure in low-voltage segments impact supplier profitability and market discipline: The low-voltage circuit breakers segment in Saudi Arabia is highly competitive, with strong price sensitivity among contractors, panel builders, and distributors. Large volumes of standardized MCBs and MCCBs are often procured primarily on price, particularly in residential, commercial, and small industrial projects. Intense competition from multiple international brands and regional suppliers compresses margins and limits differentiation beyond basic compliance. This pricing pressure can discourage long-term investments in local stocking, service capabilities, and advanced product features, particularly among smaller suppliers operating in commoditized segments.
Lengthy qualification cycles and technical approval requirements slow market entry and project execution: Utility-scale, infrastructure, and large industrial projects in Saudi Arabia typically require extensive technical qualification, vendor registration, and product testing before circuit breakers can be approved for use. These processes involve compliance verification with utility standards, factory audits, type-test certifications, and site-specific technical reviews. While these requirements ensure reliability and safety, they can extend procurement timelines, delay project awards, and create entry barriers for new or lesser-known suppliers. As a result, approved vendor lists tend to be concentrated among established players, limiting competitive intensity in higher-voltage and critical applications.
Dependence on imported equipment and long lead times create supply-chain and project scheduling risks: A significant share of medium- and high-voltage circuit breakers used in Saudi Arabia is imported, particularly for advanced applications such as gas-insulated switchgear, high fault-level substations, and renewable energy interconnections. Manufacturing lead times, shipping schedules, customs clearance, and logistics coordination can introduce delays, especially during periods of strong infrastructure spending or global supply-chain disruption. These delays can impact commissioning schedules for power plants, substations, and industrial facilities, increasing project risk for EPC contractors and asset owners.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
Electrical safety standards and grid compliance requirements governing circuit breaker performance and reliability: Circuit breakers deployed across Saudi Arabia must comply with established international standards, primarily IEC specifications, covering breaking capacity, insulation levels, temperature rise, mechanical endurance, and short-circuit performance. Utilities and large industrial users impose additional grid-specific requirements related to fault coordination, protection selectivity, and operational reliability under harsh climatic conditions. Compliance with these standards directly influences product design, testing requirements, and supplier eligibility for utility and infrastructure projects.
Energy efficiency, grid modernization, and digitalization initiatives shaping product specifications: Ongoing grid modernization programs encourage the adoption of circuit breakers compatible with advanced protection schemes, digital monitoring, and remote operation. Utilities increasingly specify equipment that supports condition monitoring, communication interfaces, and integration with supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems. While these initiatives improve grid resilience and operational efficiency, they raise technical thresholds for suppliers and increase the complexity and cost of compliant products, particularly in MV and HV segments.
Public-sector procurement frameworks and local content initiatives influencing supplier selection: Government-linked projects in power transmission, utilities, transport infrastructure, and public buildings follow structured procurement processes emphasizing prequalification, technical compliance, and commercial transparency. Increasing focus on local content, regional value addition, and long-term service support influences specification decisions and vendor evaluation. While these initiatives aim to strengthen domestic capabilities and supply resilience, they can add documentation requirements and compliance costs for suppliers, particularly those without established local operations or partnerships.
KSA Circuit Breakers Market Segmentation
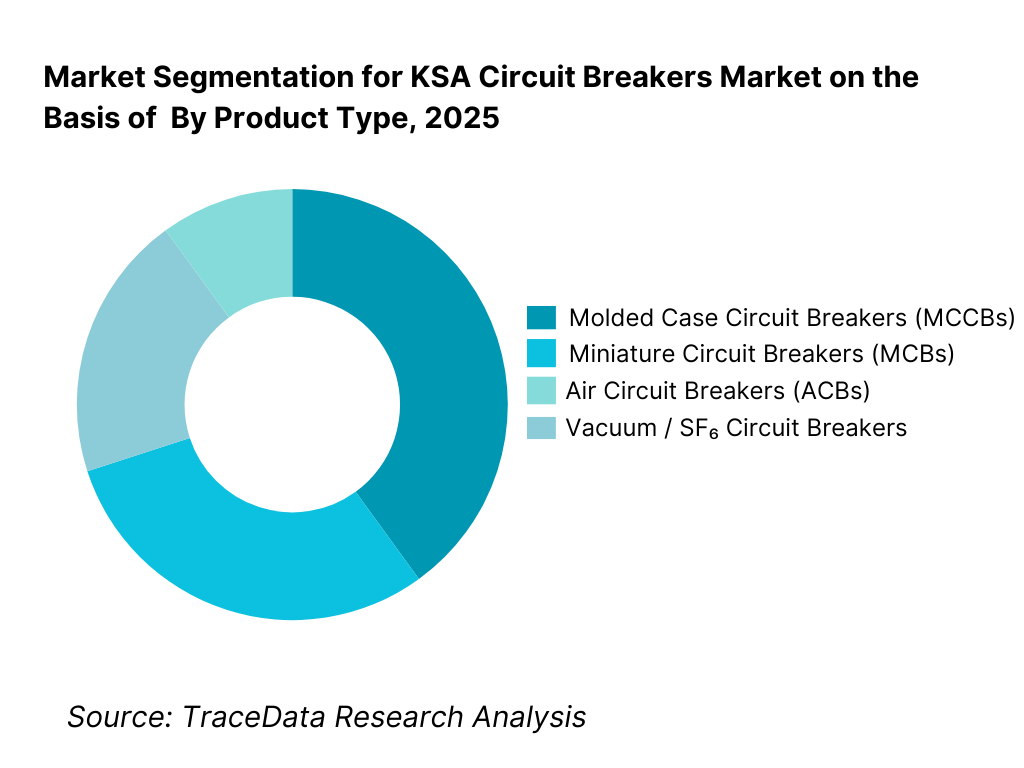
By Product Type: Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs) dominate the KSA circuit breakers market due to their broad applicability across commercial buildings, industrial plants, utilities, and infrastructure projects. MCCBs offer flexibility in current ratings, adjustable protection settings, and compatibility with modern panel systems, making them the preferred choice for contractors and industrial buyers. Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) account for large volumes in residential and small commercial projects, while Air Circuit Breakers (ACBs) and Vacuum Circuit Breakers (VCBs) are used in higher-capacity industrial and utility environments.
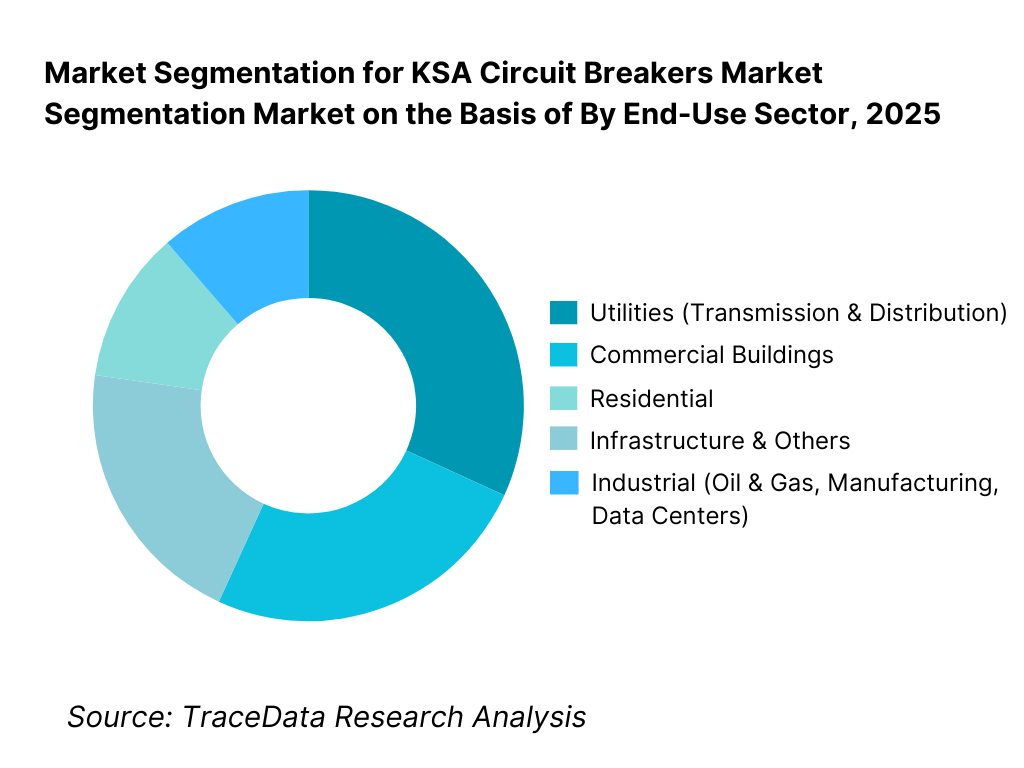
By End-Use Sector: Utilities and industrial sectors dominate the KSA circuit breakers market. Utilities account for a significant share due to continuous investments in power transmission, substations, and grid reinforcement projects. Industrial users—including oil & gas, petrochemicals, metals, cement, manufacturing, and data centers—require high-reliability protection systems to ensure operational continuity and asset safety. Commercial and residential segments contribute steady volume demand, largely driven by construction activity and urban expansion.
Competitive Landscape in KSA Circuit Breakers Market
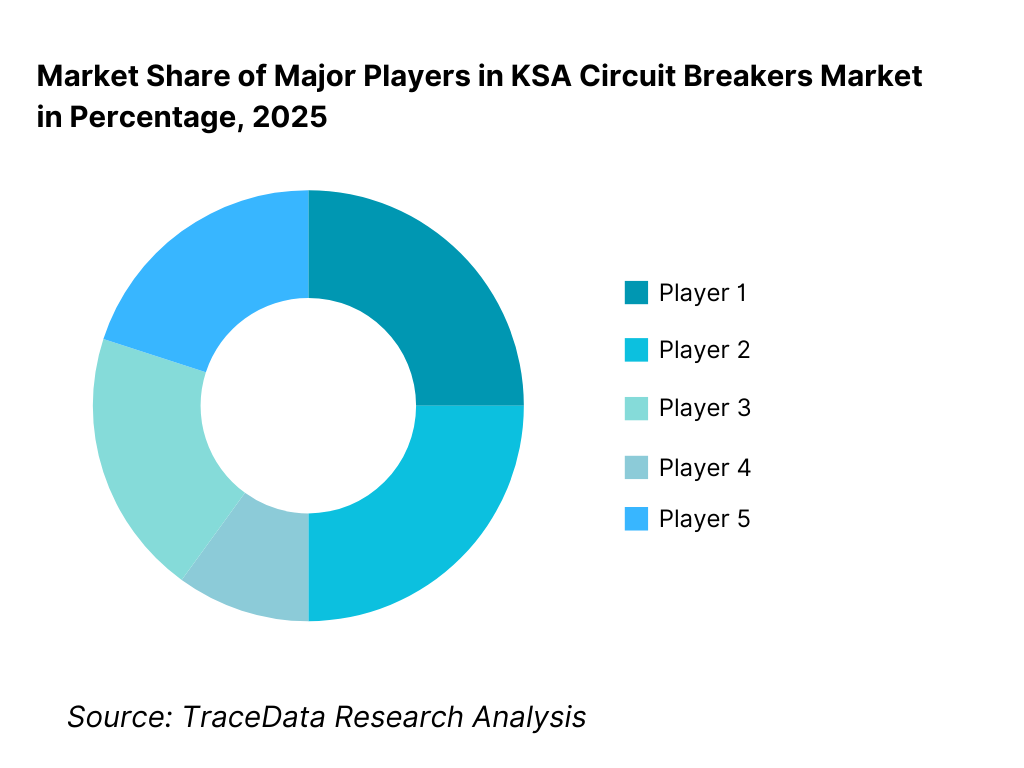
The Saudi Arabian circuit breakers market exhibits moderate-to-high concentration, characterized by the strong presence of multinational electrical equipment manufacturers with established regional operations, approved vendor status with utilities, and long-standing relationships with EPC contractors. Market leadership is driven by technical compliance, brand reliability, product breadth across voltage levels, after-sales service capability, and alignment with utility qualification requirements. While global brands dominate utility-scale and high-voltage projects, regional suppliers and distributors remain competitive in price-sensitive LV segments and construction-led demand.
Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
Schneider Electric | 1836 | Rueil-Malmaison, France |
ABB | 1883 | Zurich, Switzerland |
Siemens | 1847 | Munich, Germany |
Eaton | 1911 | Dublin, Ireland |
Mitsubishi Electric | 1921 | Tokyo, Japan |
LS Electric | 1974 | Anyang, South Korea |
Hyundai Electric | 1977 | Seongnam, South Korea |
Alfanar Electric | 1976 | Riyadh, Saudi Arabia |
Some of the Recent Competitor Trends and Key Information About Competitors Include:
Schneider Electric: Schneider Electric maintains a strong competitive position in Saudi Arabia through its broad LV, MV, and digital circuit breaker portfolio, deep engagement with utilities, and alignment with grid modernization initiatives. The company emphasizes smart protection devices, digital monitoring, and integration with energy management platforms, making it a preferred supplier for large infrastructure and industrial projects.
ABB: ABB continues to compete strongly in utility and industrial segments, particularly in MV and HV circuit breakers used in substations and grid applications. Its strengths lie in product reliability, extensive type-testing credentials, and long-term service support, which align the company closely with utility procurement requirements and large EPC-led projects.
Siemens: Siemens is well positioned in high-specification projects, including utilities, data centers, and industrial facilities requiring advanced protection coordination and digital integration. The company leverages its automation and grid technology expertise to offer integrated solutions rather than standalone components, strengthening its value proposition in complex installations.
Eaton: Eaton’s presence in Saudi Arabia is driven largely by its LV and MV circuit breaker offerings for commercial buildings, infrastructure, and industrial facilities. The company competes on robust product design, compliance with international standards, and compatibility with modern panel and switchgear systems used by regional contractors.
Alfanar Electric: As a major regional electrical equipment manufacturer, Alfanar benefits from strong local manufacturing, established distribution networks, and alignment with local content initiatives. The company remains highly competitive in LV and selected MV segments, particularly in construction-led projects where pricing, availability, and local support are key decision factors.
What Lies Ahead for KSA Circuit Breakers Market?
The KSA circuit breakers market is expected to expand steadily through 2035, supported by sustained investments in power transmission and distribution infrastructure, continued urban and industrial development, and the Kingdom’s long-term energy transition agenda under Vision 2030. Growth momentum will be reinforced by grid expansion projects, modernization of aging electrical assets, rising electricity demand from population growth and industrial diversification, and the integration of renewable energy into the national power system. As utilities, EPC contractors, and industrial buyers increasingly prioritize reliability, safety, and lifecycle performance, circuit breakers will remain a critical component across Saudi Arabia’s electrical infrastructure landscape.
Transition Toward Higher-Reliability and Application-Specific Circuit Breaker Solutions: The future market will see a gradual shift from basic, standardized protection devices toward higher-reliability and application-specific circuit breakers. Utilities and large industrial users are increasingly specifying products designed for high fault levels, harsh environmental conditions, and continuous-duty operation. Medium- and high-voltage breakers engineered for substations, renewable energy interconnections, and industrial plants will see growing demand, particularly where operational continuity and system protection are mission-critical.
Growing Emphasis on Grid Modernization, Digital Protection, and Smart Monitoring: Saudi Arabia’s grid modernization initiatives are driving demand for circuit breakers that support digital protection schemes, condition monitoring, and remote operation. Utilities are increasingly adopting smart substations and advanced distribution management systems, requiring breakers compatible with SCADA, communication protocols, and predictive maintenance frameworks. Suppliers offering digitally enabled circuit breakers with diagnostics, monitoring, and integration capabilities will be better positioned to capture higher-value utility and infrastructure demand.
Expansion of Industrial, Data Center, and Energy-Intensive Facilities Driving MV and HV Demand: Industrial expansion across oil & gas, petrochemicals, metals, cement, mining, and emerging data center infrastructure will support sustained demand for medium- and high-voltage circuit breakers. These facilities require robust protection systems capable of handling high loads, fault currents, and complex coordination requirements. As energy-intensive facilities expand or upgrade electrical systems, demand will increasingly favor proven, high-specification breaker technologies over low-cost alternatives.
Continued Volume Growth in Low-Voltage Segments Driven by Construction Activity: Low-voltage circuit breakers will continue to account for the largest share of unit volumes, supported by residential, commercial, and public-sector construction. Housing developments, healthcare facilities, education campuses, retail centers, and transport infrastructure will generate recurring demand for MCBs and MCCBs. While pricing pressure will remain a feature of this segment, consistent construction pipelines will ensure stable baseline demand through the forecast period.
KSA Circuit Breakers Market Segmentation
By Voltage Level
• Low Voltage (LV – MCBs, MCCBs, ACBs)
• Medium Voltage (MV – Vacuum & SF₆ Circuit Breakers)
• High Voltage (HV – Transmission & Grid-Level Circuit Breakers)
By Product Type
• Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs)
• Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs)
• Air Circuit Breakers (ACBs)
• Vacuum Circuit Breakers (VCBs)
• SF₆ and Gas-Insulated Circuit Breakers
By End-Use Sector
• Utilities (Transmission & Distribution)
• Industrial (Oil & Gas, Manufacturing, Data Centers, Mining)
• Commercial Buildings
• Residential
• Infrastructure & Others
By Installation Type
• New Installations
• Replacement & Retrofit
By Region
• Central Region
• Western Region
• Eastern Province
• Southern Region
• Northern Region
Players Mentioned in the Report:
• Schneider Electric
• ABB
• Siemens
• Eaton
• Mitsubishi Electric
• LS Electric
• Hyundai Electric
• Alfanar Electric
• Regional electrical equipment manufacturers and authorized distributors
Key Target Audience
• Circuit breaker manufacturers and electrical equipment suppliers
• Utilities and power transmission & distribution companies
• EPC contractors and system integrators
• Industrial plant owners and operators
• Commercial and residential real estate developers
• Panel builders and electrical contractors
• Government agencies and public-sector procurement bodies
• Investors and infrastructure-focused stakeholders
Time Period:
Historical Period: 2019–2024
Base Year: 2025
Forecast Period: 2025–2035
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4. 1 Delivery Model Analysis for Circuit Breakers-Direct Utility Supply, EPC-Driven Supply, Distributor-Led Supply, Panel Builder Integration [Margins, Preference, Strength & Weakness]
4. 2 Revenue Streams for KSA Circuit Breakers Market [Product Sales, EPC Supply Contracts, Panel Integration, After-Sales & Services, Replacement & Retrofit]
4. 3 Business Model Canvas for KSA Circuit Breakers Market [Key Partners, Key Activities, Value Propositions, Customer Segments, Cost Structure, Revenue Streams]
5. 1 Local Players vs Global Manufacturers [Alfanar vs Schneider/ABB/Siemens etc.]
5. 2 Investment Model in KSA Circuit Breakers Market [Government Utility Capex, Industrial Capex, EPC Investments, Localization & Manufacturing Initiatives]
5. 3 Comparative Analysis of Circuit Breaker Adoption in Utilities vs Industrial & Commercial Users [Procurement Models, Use Cases, Reliability & Cost Benchmarks]
5. 4 Electrical Protection Budget Allocation by End-User Type [Utilities, Industrial, Commercial, Residential]
8. 1 Revenues (Historical Trend)
9. 1 By Market Structure (Utility Procurement vs EPC/Contractor-Led vs Distributor-Led Sales)
9. 2 By Product Type (MCBs, MCCBs, ACBs, VCBs, SF₆ Circuit Breakers)
9. 3 By Voltage Level (Low Voltage, Medium Voltage, High Voltage)
9. 4 By End-Use Sector (Utilities, Industrial, Commercial, Residential, Infrastructure)
9. 5 By Application (Power Generation, Transmission, Distribution, Building Electrical Systems, Industrial Protection)
9. 6 By Installation Type (New Installation, Replacement & Retrofit)
9. 7 By Standardized vs Customized Circuit Breakers
9. 8 By Region (Central Region, Western Region, Eastern Province, Southern Region, Northern Region)
10. 1 Utility, Industrial & Commercial Buyer Landscape and Cohort Analysis
10. 2 Circuit Breaker Adoption Drivers & Decision-Making Process
10. 3 Performance, Reliability & Lifecycle Cost Analysis
10. 4 Gap Analysis Framework
11. 1 Trends & Developments in KSA Circuit Breakers Market
11. 2 Growth Drivers for KSA Circuit Breakers Market
11. 3 SWOT Analysis for KSA Circuit Breakers Market
11. 4 Issues & Challenges for KSA Circuit Breakers Market
11. 5 Government Regulations and Electrical Standards for KSA Circuit Breakers Market
12. 1 Market Size and Future Potential for Smart Circuit Breakers in KSA
12. 2 Business Models & Revenue Streams [Digital Protection, Monitoring, Lifecycle Services]
12. 3 Delivery Models & Applications Offered [Smart LV Panels, Digital Substations, SCADA-Integrated Breakers]
15. 1 Market Share of Key Players in KSA Circuit Breakers Market (By Revenues)
15. 2 Benchmark of Key Competitors [Company Overview, USP, Business Strategies, Business Model, Manufacturing Footprint, Revenues, Pricing Strategy, Technology Portfolio, Key Products, Major Clients, Strategic Tie-ups, Marketing Strategy, Recent Developments]
15. 3 Operating Model Analysis Framework
15. 4 Gartner Magic Quadrant for Circuit Breaker & Electrical Equipment Providers
15. 5 Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
16. 1 Revenues (Projections)
17. 1 By Market Structure (Utility, EPC, Distributor & Panel Builder Channels)
17. 2 By Product Type (MCBs, MCCBs, ACBs, VCBs, SF₆ Breakers)
17. 3 By Voltage Level (Low, Medium, High Voltage)
17. 4 By End-Use Sector (Utilities, Industrial, Commercial, Residential, Infrastructure)
17. 5 By Application (Generation, Transmission, Distribution, Buildings, Industrial Systems)
17. 6 By Installation Type (New Installations, Replacement & Retrofit)
17. 7 By Standardized vs Customized Solutions
17. 8 By Region (Central, Western, Eastern, Southern, Northern)
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
We begin by mapping the complete ecosystem of the KSA Circuit Breakers Market across demand-side and supply-side entities. On the demand side, entities include electric utilities (transmission and distribution), power generation companies, industrial operators (oil & gas, petrochemicals, metals, cement, mining, manufacturing), EPC contractors, data center developers, commercial real estate developers, residential builders, and public-sector agencies commissioning infrastructure, transport, healthcare, and education projects. Demand is further segmented by voltage level (LV, MV, HV), application type (new installation, replacement, retrofit), and project nature (utility grid expansion, industrial capacity addition, building construction).
On the supply side, the ecosystem includes multinational circuit breaker manufacturers, regional and local electrical equipment manufacturers, authorized distributors, panel builders, system integrators, EPC contractors, testing and certification bodies, logistics partners, and after-sales service providers. From this mapped ecosystem, we shortlist 6–10 leading circuit breaker suppliers active in Saudi Arabia based on voltage coverage, utility approvals, manufacturing and sourcing footprint, product reliability, service capability, and presence across utility, industrial, and construction-led segments. This step establishes how value is created and captured across product design, manufacturing, import/local assembly, distribution, installation, and lifecycle service.
Step 2: Desk Research
An exhaustive desk research process is undertaken to analyze the structure and dynamics of the Saudi Arabian circuit breakers market. This includes review of power sector investment plans, grid expansion and reinforcement programs, renewable energy capacity additions, industrial diversification initiatives, and construction activity across residential, commercial, and infrastructure segments. We assess demand behavior across voltage levels, product categories, and end-use sectors, along with procurement practices followed by utilities, EPC contractors, and large industrial buyers.
Company-level analysis includes review of product portfolios, voltage ratings, technology offerings, certifications, local presence, distributor networks, and participation in major projects. We also examine regulatory and standards frameworks governing electrical equipment deployment, including compliance requirements, testing protocols, and public-sector procurement processes. The outcome of this stage is a comprehensive industry foundation that defines segmentation logic and establishes the assumptions required for market sizing and outlook modeling.
Step 3: Primary Research
We conduct structured interviews with utilities, EPC contractors, industrial facility operators, panel builders, electrical consultants, distributors, and circuit breaker manufacturers operating in Saudi Arabia. The objectives are threefold: (a) validate assumptions around demand concentration by voltage level and end-use sector, (b) authenticate segmentation splits across utilities, industrial, commercial, and residential applications, and (c) gather qualitative insights on pricing dynamics, qualification timelines, lead times, supply-chain constraints, and buyer expectations around reliability and after-sales support.
A bottom-to-top approach is applied by estimating installation volumes and average equipment value across key end-use segments and regions, which are aggregated to derive the overall market view. In selected cases, buyer-style interactions with distributors and contractors are used to validate field-level realities such as availability, brand preferences, approval barriers, and typical decision drivers influencing product selection.
Step 4: Sanity Check
The final stage integrates bottom-to-top and top-to-down approaches to cross-validate market size estimates, segmentation splits, and forecast assumptions. Demand estimates are reconciled with macro indicators such as electricity demand growth, grid investment budgets, industrial expansion trajectories, and construction activity levels. Sensitivity analysis is conducted across key variables including utility capital expenditure cycles, renewable energy rollout pace, industrial project execution timelines, and replacement market acceleration. Market models are refined until alignment is achieved between supplier capacity, distributor throughput, and buyer-side project pipelines, ensuring internal consistency and robust directional forecasting through 2035.
FAQs
01 What is the potential for the KSA Circuit Breakers Market?
The KSA circuit breakers market holds strong long-term potential, supported by sustained investments in power transmission and distribution infrastructure, continued industrial diversification, and large-scale construction and infrastructure development. Grid modernization, renewable energy integration, and replacement of aging electrical assets further strengthen demand. Circuit breakers will remain a mission-critical component across utilities, industrial facilities, and buildings, supporting steady growth through 2035.
02 Who are the Key Players in the KSA Circuit Breakers Market?
The market is characterized by the presence of leading multinational electrical equipment manufacturers alongside regional and local players with strong distribution networks. Competition is shaped by utility approvals, voltage-level coverage, product reliability, service capability, and alignment with public-sector procurement requirements. Established global brands dominate MV and HV segments, while local and regional suppliers remain competitive in LV, construction-led applications.
03 What are the Growth Drivers for the KSA Circuit Breakers Market?
Key growth drivers include expansion and reinforcement of power grids, renewable energy capacity additions, industrial capacity expansion in energy-intensive sectors, and steady construction activity across residential, commercial, and public infrastructure. Increasing emphasis on electrical safety, reliability, and digital monitoring further supports adoption of advanced circuit breaker technologies across voltage levels.
04 What are the Challenges in the KSA Circuit Breakers Market?
Challenges include pricing pressure in commoditized low-voltage segments, lengthy qualification and approval cycles for utility projects, and dependence on imported equipment for advanced MV and HV applications. Supply-chain lead times and project execution risks can impact large infrastructure and industrial projects, particularly during periods of high capital spending and tight delivery schedules.