Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market Outlook to 2030
By Service Type, By Client Type, By Vehicle Class, By Channel, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0382
- Region: Middle East
- Published on: November 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market Outlook to 2030 - By Service Type, By Client Type, By Vehicle Class, By Channel, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the car rental and leasing market in Kuwait. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer level profiling, issues and challenges, and competitive landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the car rental and leasing market. The report concludes with future market projections based on fleet volumes, service categories, client types, regions, cause-and-effect relationships, and success case studies highlighting the major opportunities and cautions.
Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market Overview and Size
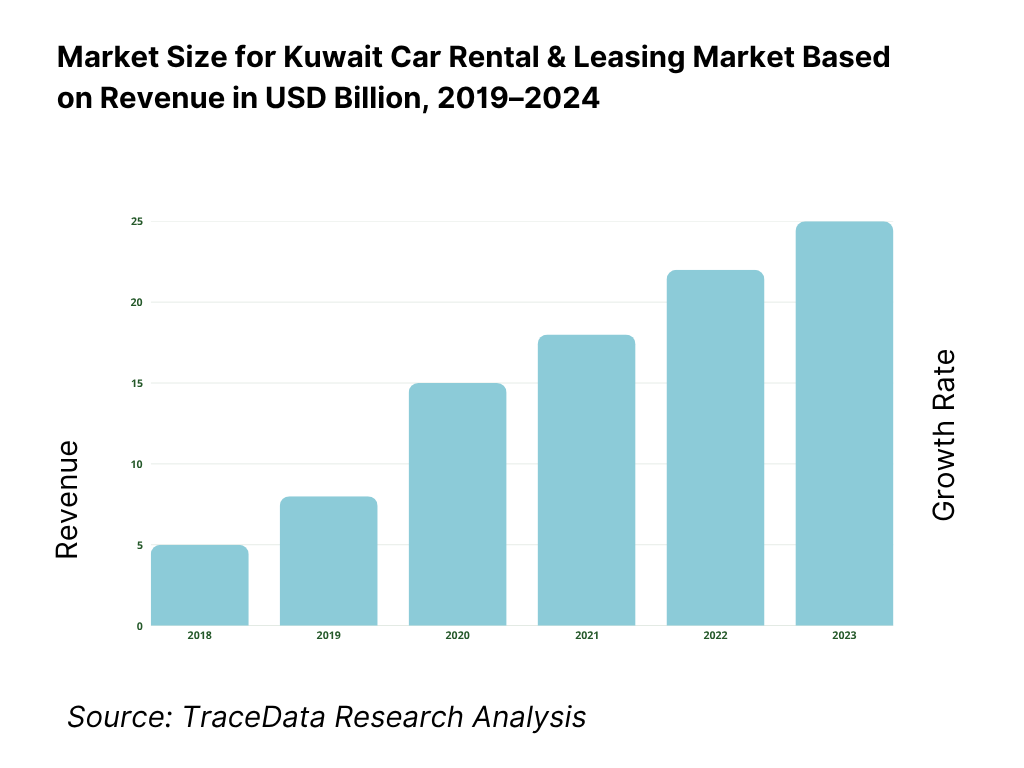
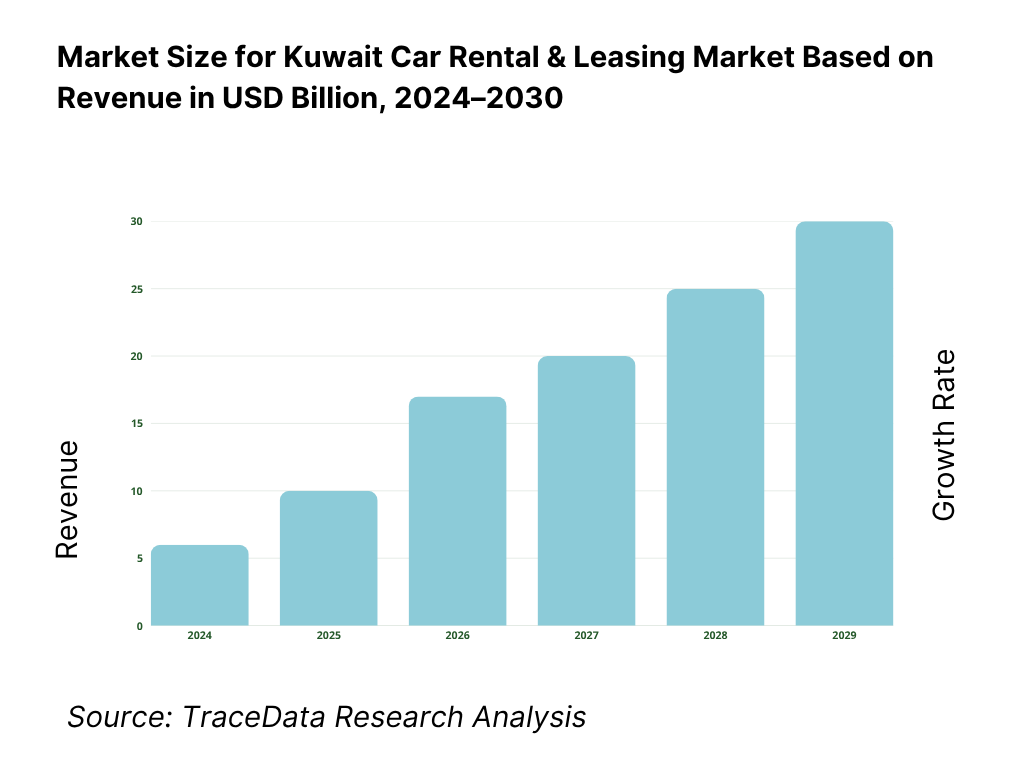
The Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing market is valued at approximately USD 1.20 billion, anchored by robust growth in tourism, rising incomes, and expansion in corporate mobility procurement. This valuation comes from bottom-up aggregation of fleet rental, lease, subscription, and ancillary services revenues across corporate and retail segments in Kuwait. Demand is driven by greater preference for flexible mobility solutions, a growing expatriate population requiring mobility, and uptick in airport arrivals which feed short-term rentals.
Key urban centers such as Kuwait City (Al Asimah Governorate) dominate the market, as it is the hub of business, diplomatic presence, and international arrivals. Likewise, coastal governorates like Hawalli and Ahmadi show dominant lease and rental penetration because they host oil & gas firms, industrial zones, and high expatriate residential density. These localities concentrate demand for city-branch pickup/drop, corporate fleet deployment, and airport-adjacent operations, giving them structural advantages in volume and higher yield per kilometer.
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market:
Air passenger throughput and airport-linked rentals: Kuwait International Airport’s traffic is a direct pump-primer for short-term rentals and corporate meets. The airport handled 1,150,000 passengers in one month, alongside 20,400 tonnes of cargo and 9,959 aircraft movements—a sustained flow that feeds airport counters, city branches, and corporate pick-ups through the year. These flows translate into high vehicle-day turns, especially for compact sedans and SUVs that match business and family travel profiles. Continuous aviation activity underpins demand for replacement vehicles and rapid fleet rotation, keeping utilization structurally elevated in Kuwait’s rental ecosystem.
Large urban customer base and expatriate mobility: Rental and operating-lease demand concentrates in Kuwait’s dense urban core and among expatriates requiring flexible mobility. The country’s urban population stands at 4,973,860 people—a critical customer pool for city-branch rentals, last-mile corporate mobility, and subscription use-cases. The total population is approximately 4.92 million, with expatriates forming a sizeable base that disproportionately relies on leased cars versus ownership during work tenures. This blend of urban density and mobile expatriate cohorts sustains high inquiry volumes, faster contract churn, and consistent replacement demand across corporate and retail channels.
Robust vehicle import pipeline supporting fleet refresh: Kuwait’s leasing and rental operators depend on imports to refresh and expand fleets. The nation recorded total merchandise imports of USD 37,489.8 million, with motor cars accounting for USD 1,636.7 million—a direct indicator of continuous passenger-vehicle inflows that enable fleet modernization, trim optimization, and uptime gains via newer, more reliable units. The breadth of import channels and volumes shortens replacement cycles and improves serviceability, directly sustaining availability for airport, corporate, and long-term lease contracts.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of the Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market:
Extreme heat elevates maintenance load and downtime risks: Vehicle operations in Kuwait run through extreme summer conditions that stress powertrains, tires, HVAC systems, and batteries. Maximum temperatures at Kuwait International Airport have reached 51.3 °C in historical records, with current daily maxima frequently in the high-40s during peak months. Such conditions accelerate wear, compress service intervals, and increase idling for cabin cooling—raising workshop throughput, spare-part consumption, and downtime windows that impact utilization and service-level compliance for corporate leases.
Urban concentration strains parking, handover logistics, and turnaround: A highly urbanized demand center means more vehicles competing for the same curb space, parking assets, and service bays, slowing pick-up/drop-off cycles and increasing turnaround friction. With nearly five million urban residents concentrated in Kuwait City and nearby governorates, demand density elevates dwell times near branches, increases repositioning mileage between constrained lots, and stretches valet and shuttle resources, especially during peak travel periods. These logistical pressures translate into higher non-revenue kilometers, longer check-in queues, and tighter inspection slotting, diluting daily rotation capacity.
Compliance-intensive environment across licensing, inspection, and insurance: Leasing and rental operators must navigate multiple, recurring compliance steps that consume operational time and administrative effort. Regulations mandate technical vehicle checks before license renewal, compulsory third-party liability coverage, and complete documentation for new vehicle licensing—all prerequisites for commercial fleet operation. These steps are essential for safety and consumer protection but add predictable queues and paperwork to fleet rotation plans, particularly when scaling delivery batches. For airport-based operators, additional aviation liability and safety obligations apply to airside shuttle and service vehicles.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
Insurance regulation and compulsory cover for motor use: Kuwait’s insurance framework is governed by Law No. 125 of 2019 on Insurance Regulation, which established the Insurance Regulatory Unit and formalized operational requirements for insurers and intermediaries. For mobility operators, this framework enforces compulsory third-party liability coverage for all vehicles as a condition for registration and operation. The legislation streamlines oversight, strengthens risk management, and aligns insurance compliance across both rental and leasing fleets, ensuring standardized protection and accountability.
Driver and vehicle licensing administered by MOI/Traffic: Operational compliance for fleets and chauffeurs is managed by the Ministry of Interior’s Traffic Department. The ministry oversees the issuance and renewal of public driving licenses, license conversions, and technical inspections prior to vehicle registration renewal. These measures directly support safety assurance by ensuring all commercial drivers and high-mileage vehicles meet Kuwait’s regulatory standards before being deployed into service. This framework also facilitates traceability, uniform recordkeeping, and enforcement under the national traffic law.
Airport-side operating obligations where car-rental interfaces occur: Car rental and leasing operators located at or servicing Kuwait International Airport must comply with the Kuwait Civil Aviation Safety Regulations, which define liability insurance requirements and ground-handling procedures for vehicle movements within restricted airport zones. These regulations affect shuttle fleet insurance thresholds, driver certification, and operational clearances for vehicle access to ramps and service roads. Compliance with these standards enhances safety governance for rental and lease operators functioning within or adjacent to aviation facilities.
Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market Segmentation
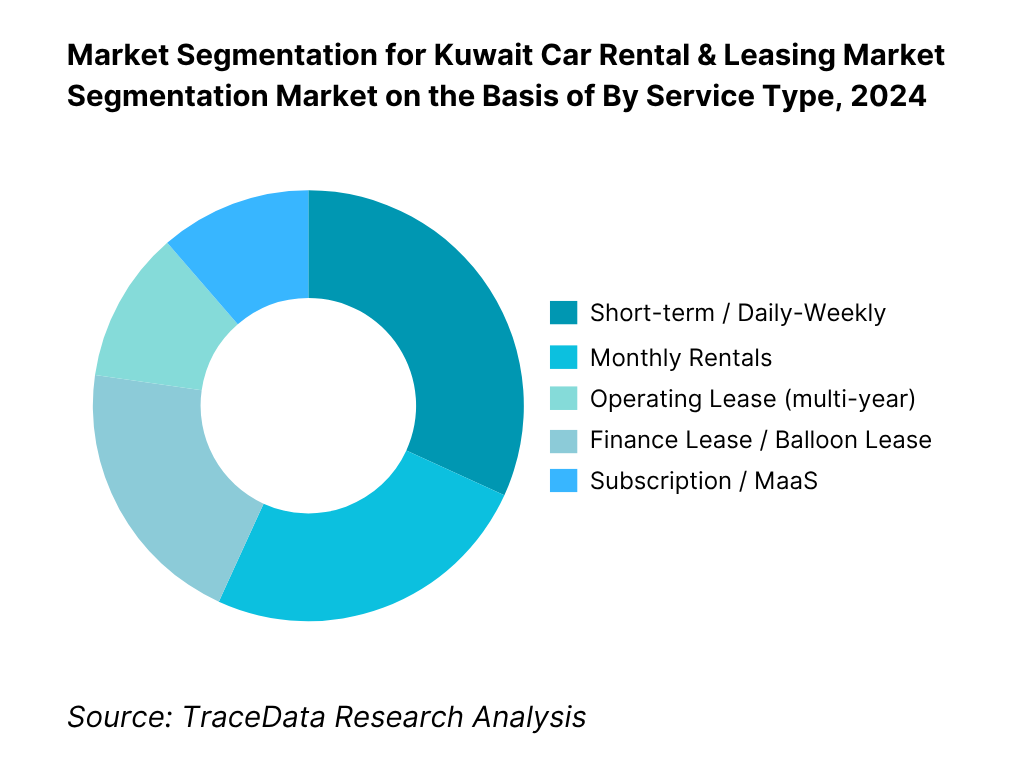
By Service Type: In Kuwait, short-term / daily-weekly rentals command the largest share, because of high airport passenger volumes and tourist turnover. Many international and regional tourists prefer renting cars upon arrival, fueling spot rentals. Additionally, expatriate residents often opt for short-term rentals for temporary assignments or weekend use. The flexibility and minimal commitment make this the default for many users, especially in a climate of uncertain stays. Meanwhile, operating leases are gaining traction among corporates and government entities seeking predictable costs and fleet management outsourcing, but still trail the spot rental dominance in sheer volume of transactions.
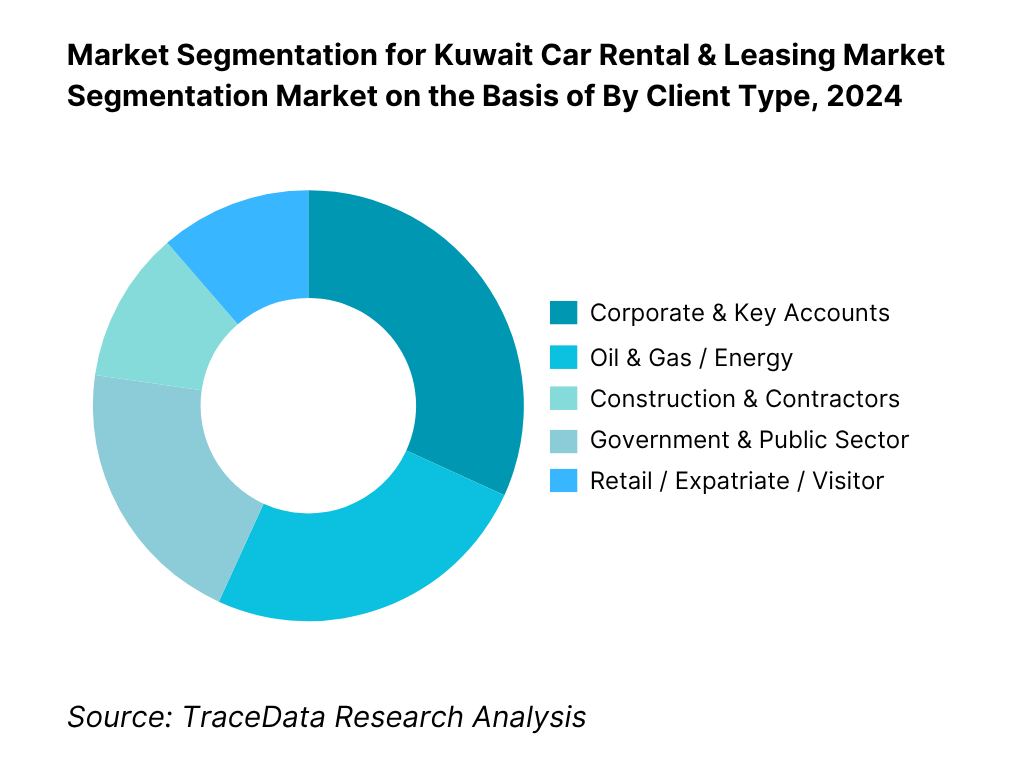
By Client Type: The corporate & key accounts segment dominates this axis because of large volume contracts, renewal agreements, and multi-year leases. Corporations prefer outsourced leasing and fleet management to reduce internal capex burden. In Kuwait, many multinational firms, banks, telecoms, and logistics companies maintain sizable mobility needs and negotiate aggregated contracts. These high-ticket contracts often come with higher margins, service level agreements, and stable revenue streams. The oil & gas sector is a close second, driven by project-based deployments, crew mobility, and specialized vehicle needs (4×4, crew transport), but the corporate segment’s sheer breadth gives it overarching dominance.
Competitive Landscape in Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market
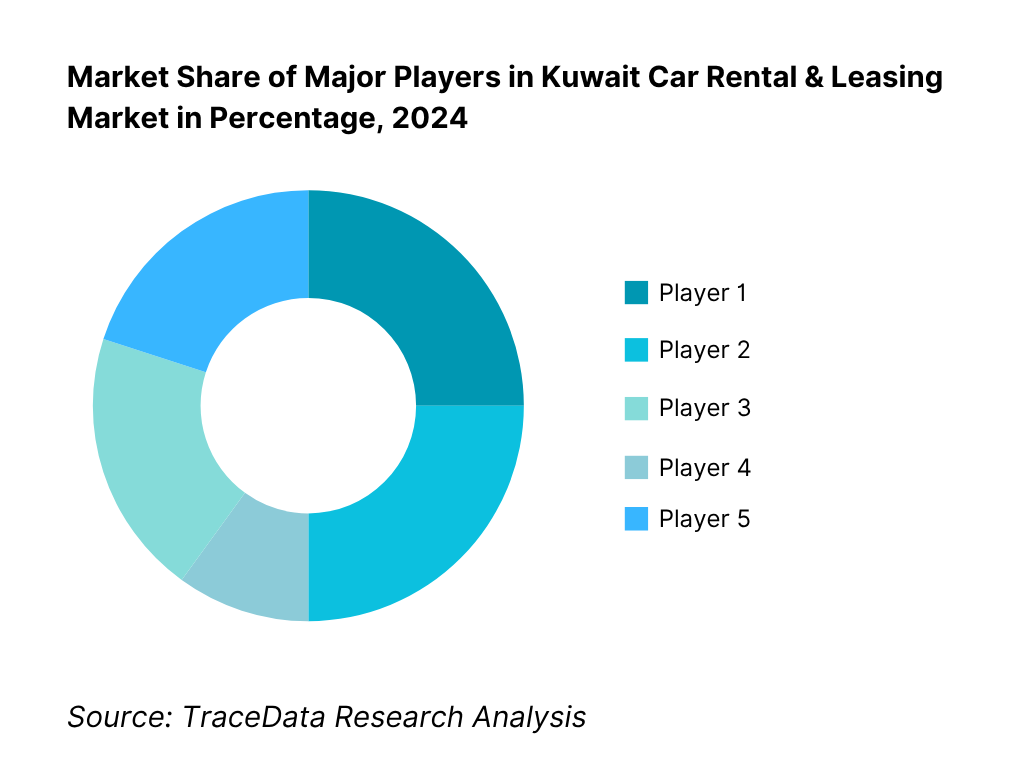
The Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing market is moderately consolidated, with a mix of global brands and strong local players. International names such as Hertz, Avis, Sixt, and Enterprise compete alongside home-grown firms like Al Mulla Rental & Leasing, Al Sayer Car Rental & Leasing, Automak, and Aayan Leasing. This mix ensures both scale and local network depth, and gives rise to strategic alliances, digital investments, and fleet specialization.
Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
Al Mulla Rental & Leasing | 1950 | Kuwait City, Kuwait |
Al Sayer Car Rental & Leasing | 1970 s | Kuwait City, Kuwait |
Automak Automotive | 2000 s | Kuwait City, Kuwait |
Aayan Leasing & Investment | 1999 | Kuwait City, Kuwait |
Hertz Kuwait | 1918 | Florida, USA / Kuwait City |
Avis Kuwait | 1946 | Parsippany, USA |
Budget Kuwait | 1958 | New Jersey, USA |
Europcar Kuwait | 1949 | Paris, France / Kuwait City |
Sixt Kuwait | 1912 | Munich, Germany |
Thrifty Kuwait | 1958 | Estero, USA / Kuwait City |
Dollar Rent A Car Kuwait | 1965 | Estero, USA / Kuwait City |
Enterprise / National Kuwait | 1957 | St. Louis, USA / Kuwait City |
Behbehani Car Rental & Leasing | 1960 s | Kuwait City, Kuwait |
Mustafa Karam Rent-A-Car | 1973 | Kuwait City, Kuwait |
Al Daman Vehicle Services | 2005 | Kuwait City, Kuwait |
Some of the Recent Competitor Trends and Key Information About Competitors Include:
Al Mulla Rental & Leasing: As one of Kuwait’s largest integrated mobility service providers, Al Mulla Rental & Leasing has expanded its long-term operating lease portfolio across oil & gas, construction, and government accounts. In 2024, the company introduced telematics-enabled fleet management and predictive-maintenance solutions, improving fleet uptime and safety compliance across over 3,000 vehicles. Al Mulla has also invested in hybrid-vehicle pilots to align with Kuwait’s sustainability roadmap and reduce fleet emissions intensity.
Al Sayer Car Rental & Leasing: A division of the Al Sayer Group, the firm enhanced its corporate leasing model with flexible tenure and subscription-style options for SME clients. In 2023, Al Sayer added new SUVs and hybrid sedans to its fleet, reflecting customer preference for fuel-efficient and comfort-oriented vehicles. The company also partnered with leading insurance providers to offer bundled TPL + comprehensive coverage, improving convenience and cost predictability for enterprise clients.
Automak Automotive: Automak continued to strengthen its position as a preferred fleet partner for large infrastructure and logistics projects. The company deployed a refreshed vehicle lineup tailored for desert and industrial operations, with 4×4 and LCV units comprising a substantial portion of its lease base. During 2023, Automak digitized its client portal to allow contract renewals, service requests, and driver tracking online—reflecting an industry-wide pivot toward operational transparency and customer self-service.
Aayan Leasing & Investment: Operating as both a financial lessor and a fleet operator, Aayan expanded its lease-finance offerings to support SMEs and mid-tier corporates facing high vehicle-acquisition costs. The company’s 2023 strategy centered on integrating financing with fleet services under a unified digital platform. Aayan also partnered with local workshops to expand maintenance coverage across the Ahmadi and Hawalli governorates, ensuring lower turnaround times and better asset utilization.
Hertz Kuwait (Franchise of Hertz International): Hertz Kuwait introduced mobile-app-based booking, real-time vehicle availability, and keyless pickup technology in 2023, targeting business travelers and short-term renters. The brand leveraged Kuwait International Airport’s passenger recovery to restore its daily-rental volumes above pre-pandemic levels. Fleet modernization also took priority, with the inclusion of hybrid models and compact sedans aimed at both sustainability compliance and cost efficiency in daily operations.
What Lies Ahead for Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market?
The Kuwait car rental & leasing market is poised for sustained expansion over the coming years, underpinned by growing tourism, increasing expatriate mobility, and higher outsourcing of corporate and government fleets. As digital technologies and mobility models converge, the sector will evolve beyond traditional rentals into integrated mobility ecosystems, offering diversified services and deeper customer engagement. Below are key directional themes shaping its future.
Rise of Flexible Subscription & Hybrid Leasing Models: The paradigm will shift from rigid long-term leases or per-day rentals to hybrid subscription models that blend short-term access, vehicle swaps, and flexible contract tenors. Operators will increasingly offer packages where users can swap vehicle types mid-term (e.g., switching from sedan to SUV) or pause service during downtime. This flexibility appeals to expatriate professionals, project staff, and SMEs reluctant to commit to multi-year contracts without agility. The blending of rental and lease economics will help providers smooth utilization spikes and reduce idle inventory.
Outcome-based Performance & Usage-Linked Pricing: Operators will adopt outcome-oriented pricing, shifting from flat lease or daily rates to usage-linked models (e.g., pay per km, idle time surcharges, service bonus credits). This aligns operator risk with client behavior and encourages efficient usage. Fleet providers will integrate telematics, driver scoring, and performance dashboards into contracts so corporate clients see real ROI: reduced fuel waste, optimized routes, and lower downtime. The contract’s ROI focus will attract clients who demand accountability and data transparency.
Fleet Electrification and Green Mobility Adoption: The transition toward electric and hybrid vehicles in fleets will accelerate, driven by global ESG pressures, regional energy policies, and cost arbitrage from rising fuel costs. Leasing operators will pilot EVs, integrate charging infrastructure, and partner with utilities for load management. They will package “green fleet” services—charging, battery health, and carbon tracking—into lease agreements. This move positions operators for regulatory benefits, improved brand sustainability, and access to corporates emphasizing carbon goals.
Sector-Specific Mobility Solutions: Mobility providers will tailor services to specific verticals—for instance, crew transfer services for oil & gas sites, construction site vehicle rentals for EPC firms, airport shuttle fleets for hospitality, and municipal mobility for public sector contracts. These verticalized offerings permit premium pricing, lower risk of cannibalization, and deeper client lock-in via value-adds (e.g., site safety package, dust protection kits). Operators will embed domain expertise in service design.
Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market Segmentation
By Service Type (In Value %)
Short-Term / Daily–Weekly Rentals
Monthly Rentals
Operating Lease (Multi-Year)
Finance Lease / Balloon Lease
Vehicle Subscription & Chauffeur Services
By Client Type (In Value %)
Corporate & Key Accounts
Oil & Gas & Energy Operators
Construction & Infrastructure Contractors
Government & Public Sector Entities
Retail / Expatriate & Visitors
By Vehicle Class (In Value %)
Economy & Compact Sedans
Mid-Size / Full-Size Sedans
SUVs & 4×4 Utility Vehicles
Pick-Ups / LCVs / Vans
Luxury & Executive Vehicles
By Channel (In Value %)
Airport Counters
City Branches
Hotel Desks & Tour Operator Alliances
Corporate / Key-Account Contracts
Online & Aggregator Platforms
By Region (In Value %)
Al Asimah (Greater Kuwait City)
Hawalli Governorate
Al Farwaniya
Al Ahmadi
Al Jahra & Mubarak Al-Kabeer
Players Mentioned in the Report:
Al Mulla Rental & Leasing
Al Sayer Car Rental & Leasing
Automak Automotive (leasing & rental arm)
Aayan Leasing & Investment
Hertz Kuwait
Avis Kuwait
Budget Kuwait
Europcar Kuwait
Sixt Kuwait
Thrifty Kuwait
Dollar Rent A Car Kuwait
Enterprise / National Kuwait
Behbehani Car Rental & Leasing
Mustafa Karam Rent-A-Car
Al Daman Vehicle Services (adjacent support services)
Key Target Audience
Corporate fleet procurement heads
Oil & Gas & Energy sector mobility managers
Infrastructure & Construction companies’ transport heads
Government ministries / transportation agencies (e.g., Ministry of Interior – Traffic Department, Ministry of Commerce)
Airport concession & operations departments
Auto OEMs and dealer groups with leasing arms
Banks and specialized vehicle finance / leasing arms
Investments & venture capital firms focusing on mobility and fleet services
Government and regulatory bodies
Time Period:
Historical Period: 2019-2024
Base Year: 2025
Forecast Period: 2025-2030
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Delivery Model Analysis for Car Rental & Leasing Market-Airport Counters, City Branches, Corporate Contracts and Online Channels
4.2. Revenue Streams for Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market
5.1. Freelance Drivers vs. Full-Time Drivers in Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market
5.2. Investment Model in Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market
5.3. Comparative Analysis of Fleet Procurement Processes by Private and Government Organizations in Kuwait
5.4. Fleet Budget Allocation by Company Size
8.1. Revenues, Historical Trend (2019-2024)
9.1. By Market Structure (In-House vs. Outsourced Fleet Management)
9.2. By Service Type (Daily/Weekly Rental, Monthly Rental, Operating Lease, Finance Lease, Subscription & Chauffeur)
9.3. By Industry Verticals (Oil & Gas, Construction, Government & SOEs, Hospitality & Tourism, Corporate Services)
9.4. By Company Size (Large Enterprise, Medium, SME Clients)
9.5. By Vehicle Class (Economy Sedan, SUV, LCV/Pick-Up, Luxury, Electric & Hybrid)
9.6. By Mode of Booking (Offline, Aggregator Platform, Direct Online, Corporate Portal)
9.7. By Program Type (Open vs. Customized Corporate Leasing Contracts)
9.8. By Region (Al Asimah, Hawalli, Farwaniya, Ahmadi, Jahra, Mubarak Al-Kabeer)
10.1. Corporate Client Landscape and Cohort Analysis
10.2. Fleet Procurement Needs and Decision-Making Process
10.3. Fleet Utilization Effectiveness and ROI Analysis
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework (Contract Renewals, Downtime, Utilization vs. Capacity)
11.1. Trends and Developments in Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges (Fleet Financing Costs, Residual Value Risk, Driver Shortages, Heat Stress Maintenance)
11.5. Government Regulations (TPL Insurance, Licensing, Inspection Cycle, GCC Conformity)
12.1. Market Size and Future Potential for Online Booking Platforms in Kuwait
12.2. Business Model and Revenue Streams of Digital Aggregators
12.3. Delivery Models and Vehicle Categories Offered via Online Platforms
15.1. Market Share of Key Players by Revenue and Fleet Size
15.2. Benchmark of Key Competitors Including Company Overview, USP, Business Strategies, Business Model, Fleet Composition, Pricing Basis Vehicle Type, Technology Used, Key Clients, Strategic Tie-Ups, Marketing Strategy, Recent Developments, and Digital Capabilities
15.3. Operating Model Analysis Framework (Branch Network, Fleet Rotation, Maintenance Operations, Driver Management)
15.4. Gartner Magic Quadrant (Performance vs. Innovation for Fleet Operators)
15.5. Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage (Pricing vs. Differentiation in Rental Services)
16.1. Revenues Forecast (2025-2030)
17.1. By Market Structure (In-House and Outsourced Fleet Management)
17.2. By Service Type (Daily, Monthly, Operating Lease, Finance Lease, Subscription & Chauffeur)
17.3. By Industry Verticals (Oil & Gas, Construction, Government, Hospitality, Corporate)
17.4. By Company Size (Large, Medium, SMEs)
17.5. By Vehicle Class (Economy, SUV, LCV/Pick-Up, Luxury, EV & Hybrid)
17.6. By Mode of Booking (Offline, Online, Aggregator, Corporate Portal)
17.7. By Program Type (Open vs. Customized Corporate Leasing Programs)
17.8. By Region (Al Asimah, Hawalli, Farwaniya, Ahmadi, Jahra, Mubarak Al-Kabeer)
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand-side and supply-side entities for the Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market. Based on this ecosystem, we will shortlist leading 5-6 rental and leasing operators in the country based on their financial information, fleet scale, market reach, and client base. Sourcing is conducted through industry articles, multiple secondary, and proprietary databases to perform desk research around the market to collate industry-level information. This includes government portals such as the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) for airport throughput data, Ministry of Interior (MOI) for licensing and registration information, and WTO/UN Comtrade for vehicle import statistics, along with verified company filings.
Step 2: Desk Research
Subsequently, we engage in an exhaustive desk research process by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This approach enables us to conduct a thorough analysis of the market, aggregating industry-level insights. We delve into aspects like the number of rental and leasing companies, fleet utilization levels, vehicle import flows, and contract tenors. We supplement this with detailed examinations of company-level data, relying on sources like annual reports, press releases, and official statements of leading operators such as Al Mulla Rental & Leasing, Al Sayer Car Rental & Leasing, Automak Automotive, Aayan Leasing & Investment, Hertz, and Avis. This process aims to construct a foundational understanding of both the market and the entities operating within it, capturing revenue streams, client categories, pricing patterns, and operational models unique to Kuwait’s mobility landscape.
Step 3: Primary Research
We initiate a series of in-depth interviews with C-level executives and other stakeholders representing various Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market companies and end-users. This interview process serves a multi-faceted purpose: to validate market hypotheses, authenticate statistical data, and extract valuable operational and financial insights from these industry representatives. A bottom-to-top approach is undertaken to evaluate revenue contributions for each player, thereby aggregating to the overall market. As part of our validation strategy, our team executes disguised interviews wherein we approach each company under the guise of potential clients. This approach enables us to validate the operational and financial information shared by company executives, corroborating this data against what is available in secondary databases. These interactions also provide us with a comprehensive understanding of fleet utilization, lease duration, maintenance cost structures, pricing mechanisms, and other operational processes.
Step 4: Sanity Check
A bottom-to-top and top-to-bottom analysis along with market size modeling exercises is undertaken to assess the sanity of the process. National-level data points—such as total merchandise imports of USD 37,489.8 million (WTO), urban population of 4,973,860, and 1,150,000 monthly air passengers (DGCA)—are used as macro benchmarks to align the derived market values with Kuwait’s underlying mobility, population, and fleet metrics. This triangulation ensures that final estimates of the Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market are consistent with macroeconomic fundamentals, validated operator disclosures, and real-world fleet operations within Kuwait’s regulated transport ecosystem.
FAQs
01 What is the potential for the Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market?
The Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market holds strong potential, with the sector valued at approximately USD 0.9 billion based on a five-year historical assessment of fleet revenues, corporate lease contracts, and daily rental activity. Growth momentum stems from the expanding expatriate population (estimated at 3.3 million out of 4.9 million residents, PACI/World Bank) and the continued rise in inbound travel, as the Directorate General of Civil Aviation reported 1.15 million passengers through Kuwait International Airport in a single month. The market’s potential is further reinforced by corporate fleet outsourcing, government mobility tenders, and an accelerating shift toward flexible leasing and subscription models.
02 Who are the Key Players in the Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market?
The Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market features several prominent operators, including Al Mulla Rental & Leasing, Automak Automotive, and Al Sayer Car Rental & Leasing, which collectively dominate the long-term leasing and government fleet segments. International brands such as Hertz, Avis, Budget, Europcar, Sixt, and Enterprise/National maintain strong presence at airport and city-branch locations, catering to both tourists and corporate clients. Other notable players like Aayan Leasing & Investment, Mustafa Karam Rent-A-Car, and Behbehani Car Leasing contribute to competitive diversification across mid-tier and SME-focused offerings.
03 What are the Growth Drivers for the Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market?
Key growth drivers include macroeconomic and demographic factors such as Kuwait’s GDP of USD 175 billion supporting strong corporate activity and procurement budgets for mobility services. The urban population of 4,973,860 people fuels concentrated demand in city centers, while a robust import pipeline—valued at USD 1,636.7 million for passenger cars (WTO/UN Comtrade)—ensures continuous fleet renewal and modern vehicle availability. Additionally, stable fuel pricing and expanding aviation throughput create favorable operating conditions for short-term rentals and operating leases alike.
04 What are the Challenges in the Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market?
The Kuwait Car Rental & Leasing Market faces challenges stemming from climatic, logistical, and compliance-related factors. The Kuwait Meteorological Department records peak temperatures above 50 °C, significantly raising vehicle maintenance costs and downtime. Urban density—with nearly 5 million urban residents—intensifies parking shortages and turnaround bottlenecks for operators. Furthermore, regulatory complexity—covering technical inspections, compulsory third-party liability insurance (Law No. 125 of 2019), and driver licensing through the Ministry of Interior—creates administrative overhead and delays in fleet deployment, challenging scalability for both domestic and international operators.