Kuwait Logistics and warehousing Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Structure, By Mode of Transport (Road, Sea, Air), By End Users (Retail, Oil & Gas, E-commerce, FMCG, Construction), By Services (Freight Forwarding, Warehousing, Express Logistics), and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0288
- Region: Middle East
- Published on: September 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Kuwait Logistics and Warehousing Market Outlook to 2029 - By Market Structure, By Mode of Transport (Road, Sea, Air), By End Users (Retail, Oil & Gas, E-commerce, FMCG, Construction), By Services (Freight Forwarding, Warehousing, Express Logistics), and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the logistics and warehousing industry in Kuwait. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation, key trends and developments, regulatory environment, end-user behavior analysis, challenges and issues, and a comparative landscape including market competition, cross-sector dynamics, growth drivers and roadblocks, and company profiling of major players in the logistics and warehousing space. The report concludes with future projections for the market based on revenue, segmented by service type, mode of transport, region, and end-use sectors, supported by cause-effect relationships and select case studies of success and disruption.
Kuwait Logistics and Warehousing Market Overview and Size
The Kuwait logistics and warehousing market was valued at KWD 1.3 Billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% during 2024–2029. The sector has gained traction due to the country’s strong oil exports, growing non-oil economy, government initiatives like “Vision 2035”, and its role as a regional transit hub for Iraq and GCC countries.
Kuwait’s logistics market is predominantly driven by road and sea freight, supported by ongoing infrastructure investments such as Mubarak Al-Kabeer Port, expansion of Shuwaikh and Shuaiba Ports, and digitalization of customs and logistics processes. Major players include Agility Logistics, Kuwait Transcontinental Shipping, KGL Logistics, DHL, and Aramex, offering integrated logistics and warehousing services across retail, FMCG, oil & gas, and construction industries.
In 2023, Agility Logistics announced the development of a smart warehousing zone in Mina Abdullah, utilizing automation, IoT, and green energy, catering to e-commerce and FMCG players.
%2C%202024-2030.png)
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Kuwait Logistics and Warehousing Market
Strategic Location and Trade Connectivity: Kuwait’s strategic location near the northern tip of the Arabian Gulf makes it a key transit hub for regional trade, especially for Iraq and Northern Saudi Arabia. Government investments in multi-modal logistics zones have significantly enhanced cross-border trade efficiency.
Diversification of Economy (Vision 2035): Kuwait’s National Development Plan emphasizes reducing dependency on oil by enhancing logistics and trade infrastructure. Non-oil sectors such as retail, FMCG, and industrial manufacturing are now actively driving the need for organized logistics and warehousing support.
Boom in E-commerce and Digital Retail: The rise of e-commerce players like Tamatem, Xcite, and international platforms has fueled demand for last-mile delivery services and warehousing capacity. In 2023, e-commerce logistics accounted for 18% of Kuwait's logistics sector revenue, up from 11% in 2020.
What Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of Kuwait Logistics and Warehousing Market
Infrastructure Constraints: Despite Kuwait’s strategic location, infrastructure limitations such as congestion at ports and outdated storage facilities remain significant bottlenecks. As of 2023, over 35% of warehousing facilities in Kuwait were operating below international efficiency standards, leading to increased turnaround time and logistics costs for businesses.
High Dependency on Imports: Kuwait relies heavily on imported goods, and this dependency makes the logistics sector vulnerable to global disruptions. The COVID-19 pandemic and the Red Sea shipping crisis revealed this fragility, with over 40% of logistics firms reporting delays and increased freight costs due to international shipping disruptions.
Talent Shortage and Skill Gaps: The sector faces a shortage of skilled labor in areas such as inventory management, automation technologies, and cold chain operations. Industry reports from 2023 show that nearly 28% of logistics service providers identified workforce training and recruitment as one of their top operational challenges, particularly in advanced warehousing functions.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market
Kuwait Vision 2035 Logistics Reforms: Under Kuwait’s Vision 2035, the government is prioritizing logistics infrastructure development to transform the country into a regional trade hub. Initiatives include expanding Mubarak Al Kabeer Port, enhancing the Kuwait Free Trade Zone, and easing customs clearance through digital transformation. In 2023, over KWD 2 billion was allocated to logistics-related infrastructure upgrades.
Customs Clearance Reforms: The General Administration of Customs has introduced new digital platforms for customs declarations and real-time tracking of shipments. These changes aim to reduce import processing times by 30% by 2025. Early pilot implementations in 2023 already reduced container clearance times at Shuwaikh Port by an average of 1.2 days.
Investment Incentives for Warehousing Projects: To attract foreign investment, the Kuwait Direct Investment Promotion Authority (KDIPA) has introduced incentives such as tax exemptions, 100% foreign ownership for logistics companies, and land lease options in logistics zones. As of 2023, five new warehousing and distribution centers have been approved under this initiative, especially in areas like Mina Abdullah and Doha Port.
Kuwait Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
By Market Structure: The Kuwaiti logistics market is primarily dominated by local logistics service providers due to their established relationships with regional clients, cost-effective operations, and deep understanding of Kuwait’s regulatory and operational environment. These firms handle a significant portion of last-mile deliveries and offer customized warehousing solutions. International 3PL players like Agility, DHL, and DB Schenker also maintain a strong foothold, especially in high-value, cross-border logistics and sectors requiring specialized infrastructure (cold chain, oil & gas logistics, etc.). Their advanced tech systems, global connectivity, and capacity to handle complex supply chains make them preferred partners for large corporations and multinational clients.
%2C%202023.png)
By Mode of Transport: Road transport is the most widely used logistics mode in Kuwait, accounting for the majority of domestic freight movement due to the country’s compact geography and efficient road infrastructure. It plays a vital role in last-mile connectivity and inland transport from ports to industrial zones. Sea freight is critical for Kuwait’s import-dependent economy, with major volumes routed through Shuwaikh and Shuaiba ports. These ports serve as key entry points for goods, especially bulk commodities, construction materials, and machinery. Air freight caters predominantly to high-value and time-sensitive shipments, such as electronics, pharmaceuticals, and automotive parts. Kuwait International Airport acts as a regional transshipment hub with growing investment in air cargo infrastructure.
%20%E2%80%93%20Share%20in%20Freight%20Movement%20(%25)%2C%202023.png)
By End-User Industry: The oil & gas sector is the largest contributor to the logistics demand in Kuwait, driven by the country’s reliance on petroleum exports and related industrial activity. Logistics operations in this sector often require specialized handling, hazardous material protocols, Retail and FMCG sectors are key consumers of warehousing and distribution services, especially in urban areas like Kuwait City. The rise of modern trade and supermarkets has boosted demand for Grade A warehousing.
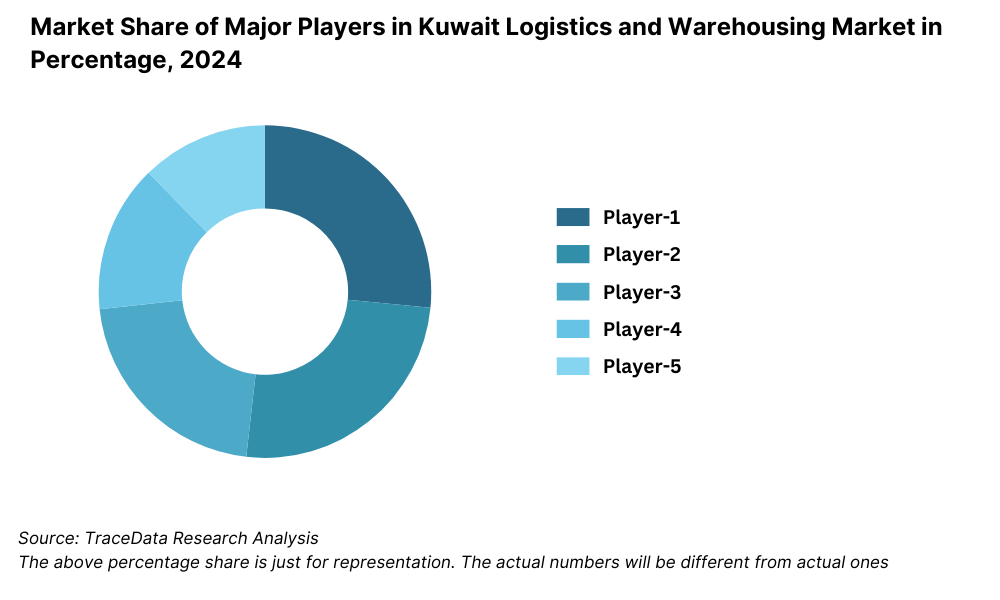
Competitive Landscape in Kuwait Logistics and Warehousing Market
The Kuwait logistics and warehousing market is moderately concentrated, with a mix of local and global players operating across freight forwarding, contract logistics, warehousing, and last-mile delivery services. Key players include Agility Logistics, KGL Logistics, DHL Express, Aramex, UPS Kuwait, CEVA Logistics, and Posta Plus. The increasing adoption of digital logistics platforms and demand for specialized logistics (cold chain, e-commerce delivery) have encouraged both expansion of established players and entry of new competitors.
Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
Agility Logistics | 1979 | Sulaibiya, Kuwait |
KGL Logistics | 2005 | Kuwait City, Kuwait |
DHL Express | 1969 | Bonn, Germany (Kuwait Ops) |
Aramex | 1982 | Dubai, UAE (Kuwait Branch) |
UPS Kuwait | 1907 | Atlanta, USA (Kuwait Branch) |
CEVA Logistics | 2006 | Marseille, France |
Posta Plus | 2005 | Kuwait City, Kuwait |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key developments include:
Agility Logistics: As one of Kuwait’s flagship logistics companies, Agility has invested heavily in digital supply chain platforms and sustainable warehousing. In 2023, the company launched a new 26,000 sqm logistics park in Mina Abdullah aimed at serving FMCG and pharmaceutical clients with advanced automation and cold storage capabilities.
KGL Logistics: Known for its strong presence in contract logistics and defense logistics support, KGL reported a 12% YoY growth in 2023. The firm has expanded its fleet size and upgraded its tracking systems to support real-time visibility and higher service reliability.
DHL Express: DHL remains a leader in international express services in Kuwait. In 2023, DHL launched a new shipment center in Shuwaikh and introduced green delivery initiatives using electric vans in urban zones to reduce carbon footprint.
Aramex: Leveraging its regional network, Aramex has been scaling up e-commerce logistics in Kuwait. In 2023, the company expanded its last-mile delivery services and added new fulfillment centers to meet growing online retail demand.
UPS Kuwait: UPS continues to focus on high-value supply chains like healthcare and electronics. In 2023, the company upgraded its customs brokerage services and launched temperature-controlled solutions for sensitive cargo.
CEVA Logistics: CEVA, part of the CMA CGM Group, has deepened its involvement in project logistics and oil & gas supply chains. In 2023, CEVA secured a major logistics contract with a petrochemical client in southern Kuwait.
Posta Plus: A growing local player, Posta Plus has been rapidly gaining share in the last-mile and express delivery segment. In 2023, it processed over 15 million shipments, marking a 20% increase from 2022, driven by rising e-commerce volumes and improved customer service systems.
What Lies Ahead for Kuwait Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Kuwait logistics and warehousing market is expected to witness steady growth through 2029, driven by increased trade activity, expanding infrastructure, and rising demand from sectors like retail, oil & gas, and e-commerce. A favorable investment climate under Kuwait Vision 2035 and increasing technological adoption are projected to support a positive CAGR during the forecast period.
Expansion of Logistics Infrastructure: Major infrastructure investments, including the ongoing development of Mubarak Al Kabeer Port and logistics zones near Shuwaikh and Mina Abdullah, will significantly enhance Kuwait’s cargo handling and storage capacity. These projects are expected to reduce operational bottlenecks and attract regional transshipment activity.
Rising Demand for Grade A Warehousing: With the growth of organized retail and multinational corporations in Kuwait, there is increasing demand for high-standard, temperature-controlled, and automated warehouses. Developers are expected to focus on modern logistics parks with integrated inventory management, smart lighting, and energy-efficient designs.
E-commerce Logistics Boom: Online retail is expected to be a major driver of logistics demand, particularly for last-mile delivery services. As internet penetration surpasses 99% and consumer preference shifts toward digital platforms, logistics firms will scale operations to support same-day delivery and real-time tracking features across urban centers.
Adoption of Digital Supply Chain Solutions: The market is moving toward the widespread adoption of technologies like IoT, RFID, and AI for fleet tracking, predictive maintenance, and automated inventory control. These solutions will improve supply chain visibility, reduce turnaround time, and enhance operational efficiency for logistics providers.
%2C%202019-2024.png)
Kuwait Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
• By Market Structure:
o Freight Forwarding Companies
o 3PL & 4PL Service Providers
o Warehousing & Storage Operators
o Integrated Logistics Service Providers
o Express Delivery and Last-Mile Providers
o Organized Sector
o Unorganized Sector
• By Mode of Transport:
o Road
o Sea
o Air
o Rail (limited, mainly cross-border via GCC)
• By Type of Warehousing Services:
o General Warehousing
o Cold Storage
o Bonded Warehousing
o E-commerce Fulfillment Centers
o Industrial Warehousing
• By End-User Industry:
o Oil & Gas
o Retail & FMCG
o E-commerce
o Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare
o Automotive & Spare Parts
o Construction Materials
o Electronics
• By Ownership of Warehouses:
o Owned
o Leased
o Built-to-Suit (BTS)
• By Region:
o Kuwait City
o Shuwaikh Port Area
o Mina Abdullah Industrial Area
o Doha Port Region
o Al Ahmadi
o Jahra
Players Mentioned in the Report:
• Agility Logistics
• KGL Logistics
• DHL Express
• Aramex
• CEVA Logistics
• UPS Kuwait
• Posta Plus
• FedEx Kuwait
• Alghanim Freight
• GWC Logistics
Key Target Audience:
• Logistics & Supply Chain Companies
• Freight Forwarders and 3PL Providers
• E-commerce and Retail Firms
• Real Estate and Industrial Park Developers
• Investors and PE Firms Focused on Logistics
• Ministries and Regulatory Bodies (e.g., Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Customs Department)
• Transport Infrastructure Developers
• Technology Providers (IoT, Warehouse Automation, TMS/WMS)
Time Period:
• Historical Period: 2018–2023
• Base Year: 2024
• Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and Challenges They Face
4.2. Revenue Streams for Kuwait Logistics Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Logistics Players in Kuwait
4.4. Customer Decision-Making Process (Warehousing & Freight Services)
4.5. Supplier Decision-Making Process (Warehouse Developers, Transport Providers)
5.1. Imports and Exports Volume in Kuwait, 2018-2024
5.2. Share of Logistics Cost in Overall Supply Chain, 2024
5.3. Logistics Spend by Sector (Oil & Gas, Retail, FMCG, etc.), 2024
5.4. Number of Warehouses and Logistics Providers by Region
8.1. Revenues, 2018-2024
8.2. Freight Volume Handled, 2018-2024
8.3. Warehousing Space in SQM, 2018-2024
9.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized), 2023-2024P
9.2. By Mode of Transport (Road, Sea, Air), 2023-2024P
9.3. By End User (Retail, Oil & Gas, FMCG, E-commerce, Pharma, Automotive), 2023-2024P
9.4. By Type of Warehousing (Cold Storage, General, Bonded, E-fulfillment), 2023-2024P
9.5. By Region (Kuwait City, Mina Abdullah, Shuwaikh, Jahra, etc.), 2023-2024P
10.1. Customer Landscape and Sector-Wise Logistics Demand
10.2. Logistics Outsourcing Trends and Preferences
10.3. Service Pain Points and Pricing Sensitivity
10.4. Buyer Behavior and Vendor Selection Criteria
11.1. Trends and Developments for Kuwait Logistics Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Kuwait Logistics and Warehousing Sector
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Kuwait Logistics Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges for Logistics Operators
11.5. Government Regulations and Initiatives-Vision 2035, Customs Reforms
12.1. Market Size and Forecast for Last-Mile and Fulfillment Logistics, 2018-2029
12.2. Business Models: COD, Fulfillment Centers, Reverse Logistics
12.3. Cross-Comparison of Major Players (Agility, Posta Plus, Aramex, etc.)
13.1. Warehousing Space Absorption by Industry, 2018-2029
13.2. Rental Trends and Leasing Models (Owned, BTS, Shared)
13.3. Adoption of Smart Warehousing & Automation
13.4. Cold Chain Infrastructure Analysis
13.5. Investment and Development Pipeline for Warehousing Parks
16.1. Benchmark of Key Players on Coverage, Fleet, Tech Adoption, Warehousing Size
16.2. Strengths and Weaknesses of Each Major Player
16.3. Operating Model Analysis Framework
16.4. Strategic Positioning-BCG Matrix
16.5. Bowmans Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
17.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
17.2. Freight Volume Handled, 2025-2029
17.3. Warehousing Capacity (in SQM), 2025-2029
18.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized), 2025-2029
18.2. By Transport Mode, 2025-2029
18.3. By Industry Vertical, 2025-2029
18.4. By Type of Warehousing, 2025-2029
18.5. By Region, 2025-2029
18.6. By Ownership (Owned, Leased, BTS), 2025-2029
18.7. Recommendation and Strategic Outlook
18.8. Opportunity Analysis and Investment Hotspots
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand-side and supply-side entities for the Kuwait Logistics and Warehousing Market. This includes logistics providers, freight forwarders, warehousing operators, e-commerce players, oil & gas companies, government bodies, and trade associations.
Sourcing is carried out through industry publications, trade portals, logistics-specific databases, government reports, and proprietary datasets to perform initial desk research around the market and to create a comprehensive ecosystem map.
Step 2: Desk Research
Subsequent to ecosystem mapping, we engage in detailed desk research using a combination of secondary and proprietary databases. The aim is to collect information related to overall market performance, freight volumes handled, warehousing capacity, technological penetration, and service pricing.
Key variables analyzed include market size (by volume and value), segmental splits, demand from end-user industries, growth trends, infrastructure development, and investment patterns. Company-level data such as operational footprint, fleet size, service offerings, and revenue contribution is extracted from annual reports, industry presentations, and government filings to build foundational intelligence.
Step 3: Primary Research
We conduct structured interviews with logistics managers, supply chain heads, C-suite executives, warehouse operators, and freight partners across the Kuwait market. The objective is to validate market estimates, identify ground-level trends, and obtain insights around logistics challenges, cost structures, and service quality benchmarks.
A bottom-to-top approach is employed to assess service volume handled by each major operator, which is then aggregated to arrive at the total market size.
To further validate information, disguised interviews are conducted—posing as prospective clients—to verify claims around storage capacity, pricing models, delivery turnaround, and value-added services. This helps corroborate findings with desk research and gain more candid insights from service providers.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- A combination of top-down and bottom-up approaches is applied for triangulation of market size. Scenario modeling, sensitivity analysis, and comparison with historical benchmarks and regional peers are carried out to ensure consistency and reliability of the findings.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Kuwait Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Kuwait logistics and warehousing market is poised for significant expansion, backed by infrastructure development, trade liberalization, and Vision 2035-driven reforms. The market is projected to grow steadily through 2029, supported by demand from the oil & gas, retail, FMCG, and e-commerce sectors. Strategic investments in port development and logistics zones are expected to position Kuwait as a regional logistics hub within the GCC.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Kuwait Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Major players in the market include Agility Logistics, KGL Logistics, DHL Express, Aramex, UPS Kuwait, and Posta Plus. These companies lead due to their wide operational coverage, integrated service offerings, and strong infrastructure. Global players such as CEVA Logistics and FedEx also have a growing presence, particularly in high-value and time-sensitive logistics segments.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Kuwait Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Key growth drivers include government investment in logistics infrastructure, increasing imports and consumer demand, digitalization of supply chain processes, and a surge in e-commerce activity. Kuwait’s strategic geographic location and the development of the Mubarak Al Kabeer Port are further expected to boost international logistics connectivity and transshipment volumes.
4. What are the Challenges in the Kuwait Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Challenges include infrastructure gaps in older warehousing facilities, reliance on imports making the supply chain vulnerable to global disruptions, shortage of skilled logistics labor, and rising operational costs. Additionally, regulatory complexities around customs procedures and licensing can impact speed and efficiency, especially for smaller logistics firms.