Lebanon Logistics and warehousing Market Outlook to 2029
By Mode of Transport (Road, Air, Sea), By Type of Warehousing (General, Cold Chain, Bonded), By End User Industry (Retail, Pharma, FMCG, Manufacturing, Others), and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0290
- Region: Middle East
- Published on: September 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Lebanon Logistics and Warehousing Market Outlook to 2029 – By Mode of Transport (Road, Air, Sea), By Type of Warehousing (General, Cold Chain, Bonded), By End User Industry (Retail, Pharma, FMCG, Manufacturing, Others), and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the logistics and warehousing market in Lebanon. The report includes the genesis and overview of the industry, market size in terms of revenue, segmentation by transport modes and storage types, trends and developments, regulatory framework, customer and operator profiling, major challenges, and comparative landscape featuring leading market participants. The study concludes with future projections, key growth drivers, and illustrative case studies capturing opportunities and strategic insights.
Lebanon Logistics and Warehousing Market Overview and Size
The Lebanon logistics and warehousing market was valued at USD 1.2 billion in 2023, driven by increasing trade activities, rising e-commerce penetration, and infrastructure investments. Despite geopolitical challenges, the logistics sector remains critical due to Lebanon's strategic location as a gateway to the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region.
Key players in the Lebanese market include LibanPost, Aramex Lebanon, DHL, Medlog, and Ghellal Logistics, which offer integrated logistics solutions across multiple industries. Beirut remains the central logistics hub due to its proximity to the Port of Beirut and the Beirut–Rafic Hariri International Airport.
In 2023, LibanPost expanded its warehousing capacity to accommodate rising parcel volume from online retail, while Aramex invested in digital infrastructure to optimize last-mile delivery and customer experience.
%2C%202019-2024.png)
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Lebanon Logistics and Warehousing Market
Strategic Geographic Position: Lebanon’s location on the eastern Mediterranean coast allows it to act as a regional logistics hub for goods flowing between Europe, the Middle East, and Africa. This geographical advantage has led to increased transshipment and bonded warehousing operations at the Port of Beirut.
Surge in E-commerce: With more than 55% internet penetration and a young, tech-savvy population, e-commerce is rapidly growing. This shift has heightened demand for modern fulfillment centers and last-mile delivery networks, particularly in Beirut and Tripoli.
Revival of Port Infrastructure: Following the 2020 Port of Beirut explosion, significant rebuilding efforts have been undertaken with support from international donors. The reconstruction of port terminals and digitalization of customs processes have improved cargo handling capacity, thereby boosting logistics efficiency.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for Lebanon Logistics and Warehousing Market
Geopolitical Instability and Currency Volatility: Lebanon’s prolonged political and economic crisis, including sharp currency devaluation, has disrupted supply chains and reduced import volumes. According to industry estimates, logistics costs surged by over 35% between 2019 and 2023, making it difficult for logistics providers to maintain margins and service levels.
Infrastructure Constraints: Lebanon faces significant infrastructure deficits, particularly in road quality, power availability, and storage facilities. A 2023 logistics assessment revealed that nearly 40% of warehousing facilities lack basic automation or climate control, hindering efficient storage, especially for cold chain and pharmaceuticals.
Fragmentation of Logistics Providers: The logistics sector in Lebanon is highly fragmented, with many small, unorganized players operating without standardized service levels. This fragmentation leads to inconsistent pricing, lack of service reliability, and limited scalability, particularly for 3PL solutions. It is estimated that only 15% of logistics transactions in 2023 were handled by integrated providers.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market
Customs Modernization (ASYCUDA World Implementation): Lebanon’s Customs Administration adopted the UNCTAD-supported ASYCUDA World system to digitize and expedite customs clearance. By 2023, over 85% of import-export declarations were processed digitally, reducing average clearance time by 2-3 days and improving operational efficiency.
Free Zones and Bonded Warehousing Policies: The government has promoted bonded warehousing and free zone development, particularly around the Port of Beirut and Tripoli Port, to attract transshipment and regional logistics operations. These zones offer deferred duty benefits and simplified customs procedures, helping boost throughput by 12% year-on-year in 2023.
Rehabilitation of Critical Infrastructure: With support from international donors like the World Bank and UNDP, Lebanon has initiated rehabilitation projects for roads, port terminals, and warehousing clusters. The Port of Beirut modernization project, slated for completion in 2025, is expected to increase container handling capacity by 25%.
Lebanon Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
By Market Structure: The Lebanese logistics sector is largely dominated by unorganized and small-scale operators, especially in road transport and general warehousing. These providers offer competitive pricing and localized solutions but often lack advanced technology and standardized service delivery. In contrast, organized 3PL and integrated service providers such as Aramex, DHL, and Medlog are steadily growing in market share due to their investment in digital tracking, automation, and cold chain capabilities. These organized players appeal especially to multinational clients, pharmaceutical companies, and e-commerce businesses looking for scalable and reliable solutions.
%2C%202023.png)
By Mode of Transport: Road transport remains the dominant mode of logistics in Lebanon, accounting for a major portion of domestic freight movement due to its cost-effectiveness and last-mile reach. Sea transport plays a crucial role in international logistics via the Port of Beirut and Tripoli, especially for containerized and bulk cargo. Air freight, while costlier, is critical for high-value and time-sensitive shipments, especially for sectors like pharma, electronics, and perishables.
%2C%202023.png)
By Type of Warehousing: General warehousing leads the market, serving sectors such as retail, FMCG, and textiles with dry storage needs. Cold chain warehousing has witnessed significant growth due to rising pharmaceutical and perishable goods demand. Bonded warehouses, mostly located in and around free zones, are used for international transshipment and customs clearance processes.
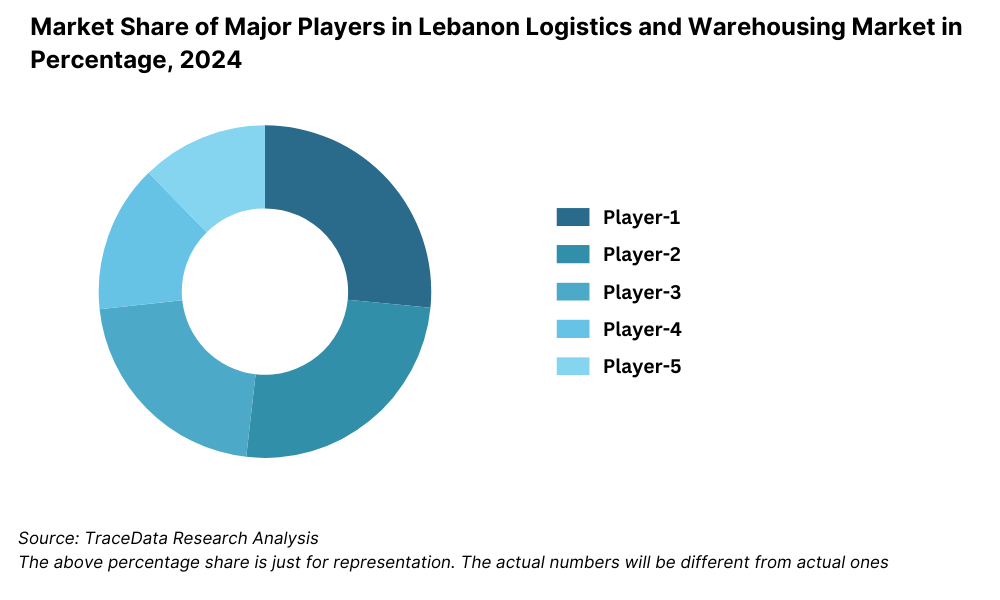
Competitive Landscape in Lebanon Logistics and Warehousing Market
The Lebanon logistics and warehousing market is moderately fragmented, with a mix of international logistics companies and local service providers operating across transport, freight forwarding, and storage. While global players offer integrated logistics solutions with advanced infrastructure, local firms continue to dominate last-mile delivery and domestic warehousing due to their regional familiarity and cost competitiveness.
Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
LibanPost | 1998 | Beirut, Lebanon |
Aramex Lebanon | 1982 | Beirut, Lebanon |
DHL Express | 1969 | Beirut, Lebanon |
Medlog Lebanon | 2000 | Beirut, Lebanon |
Ghellal Logistics | 1995 | Tripoli, Lebanon |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
LibanPost: As the national postal and logistics provider, LibanPost has expanded its B2B offerings, with warehouse capacity growing by 18% in 2023 to support rising parcel volumes. The company also upgraded its digital tracking system and introduced a cross-border e-commerce logistics solution targeting regional exporters.
Aramex Lebanon: A leading player in express logistics and freight forwarding, Aramex reported a 22% growth in e-commerce parcel volume in 2023. It has invested heavily in tech-enabled last-mile delivery and offers smart locker solutions in major cities like Beirut and Sidon.
DHL Express: DHL Lebanon continues to serve multinational clients with temperature-controlled shipping and air freight services. In 2023, it opened a new 2000 sq. meter bonded warehouse near Beirut Airport, aiming to reduce lead times for pharmaceutical and electronics shipments.
Medlog Lebanon: The logistics arm of Mediterranean Shipping Company (MSC), Medlog has expanded its intermodal capabilities by partnering with local trucking firms. Its container handling operations at Tripoli Port grew by 15% year-on-year, driven by increased demand for FMCG and construction imports.
Ghellal Logistics: A regional warehousing and distribution specialist, Ghellal focuses on serving North Lebanon, particularly Tripoli and Zgharta. In 2023, it launched a new cold chain warehousing unit with a 1000-pallet capacity, targeting the pharmaceutical and food sectors.
What Lies Ahead for Lebanon Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Lebanon logistics and warehousing market is projected to grow steadily through 2029, with an anticipated CAGR of 5.8%, supported by improvements in trade facilitation, infrastructure recovery efforts, and digital transformation. Despite ongoing macroeconomic uncertainties, the sector is expected to witness gradual modernization and increasing private sector participation.
Expansion of E-Commerce Logistics: With Lebanon’s growing internet and smartphone penetration, the expansion of e-commerce platforms is set to boost demand for last-mile delivery, urban warehouses, and fulfillment centers. This segment is likely to drive significant investment in route optimization technologies and fleet modernization.
Growth in Cold Chain Infrastructure: Demand for cold storage facilities is expected to rise, particularly from the pharmaceutical, food, and agriculture sectors. As Lebanon increases its focus on food security and vaccine distribution readiness, modern cold chain warehousing will play a pivotal role in ensuring product integrity.
Revival of Port-Centric Logistics: Reconstruction of the Port of Beirut and expansion at Tripoli Port will catalyze port-centric logistics, including bonded warehousing and free zone operations. These improvements will reduce turnaround time, lower logistics costs, and position Lebanon as a regional re-export hub.
Digital Transformation of Logistics Operations: Logistics companies are increasingly adopting cloud-based fleet management, real-time tracking, and AI-driven demand forecasting. These innovations are expected to enhance service quality, improve route planning, and offer better visibility across the supply chain.
%2C%202024-2030.png)
Lebanon Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
- By Market Structure:
o Local Transporters
o Regional Freight Forwarders
o Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Providers
o Multinational Logistics Companies
o Organized Warehousing Operators
o Unorganized Sector Operators
o Cold Chain Providers - By Mode of Transport:
o Road Freight
o Sea Freight
o Air Freight
o Multimodal Transport - By Type of Warehousing:
o General Warehousing
o Cold Chain Warehousing
o Bonded Warehousing
o Distribution Centers
o Urban Fulfillment Centers - By End-User Industry:
o Retail and FMCG
o Pharmaceuticals and Healthcare
o E-commerce
o Automotive and Spare Parts
o Food and Agriculture
o Construction Materials
o Industrial Manufacturing - By Region:
o Beirut
o Mount Lebanon
o North Lebanon (including Tripoli)
o Bekaa Valley
o South Lebanon
Players Mentioned in the Report:
- LibanPost
- Aramex Lebanon
- DHL Express
- Medlog Lebanon
- Ghellal Logistics
- Net Logistics
- Transglobal Logistics
- Speed Couriers
Key Target Audience:
- Logistics Companies
- Freight Forwarders
- Warehouse Developers and Operators
- E-commerce Companies
- Cold Chain Operators
- Industrial and Retail Enterprises
- Infrastructure and Investment Funds
- Government and Regulatory Bodies (e.g., Lebanese Customs, Ministry of Public Works and Transport)
Time Period:
- Historical Period: 2018–2023
- Base Year: 2024
- Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and Challenges They Face
4.2. Revenue Streams for Lebanon Logistics Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Lebanon Logistics Ecosystem
4.4. Supply Chain Mapping and Flow
4.5. Procurement and Fulfillment Decision-Making Process
5.1. Volume of Cargo Handled by Port of Beirut and Tripoli, 2018-2024
5.2. Share of Transport Modes in Total Freight Movement
5.3. Spending on Logistics Infrastructure, 2018-2024
5.4. Number of Warehouses and Logistics Providers by Region
8.1. Revenues, 2018-2024
8.2. Volume Handled (MT/TEU), 2018-2024
9.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized Sector), 2023-2024P
9.2. By Mode of Transport (Road, Air, Sea), 2023-2024P
9.3. By Type of Warehousing (General, Cold Chain, Bonded, Distribution Centers), 2023-2024P
9.4. By End-User Industry (Retail, FMCG, Pharma, Manufacturing, Others), 2023-2024P
9.5. By Region (Beirut, Mount Lebanon, North, South, Bekaa), 2023-2024P
10.1. Customer Segments and Logistics Needs
10.2. Delivery Preferences and SLA Expectations
10.3. Industry-Specific Logistics Requirements
10.4. Decision-Making Framework for Logistics Partner Selection
11.1. Trends and Developments for Lebanon Logistics and Warehousing Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Lebanon Logistics Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis
11.4. Issues and Challenges
11.5. Government Regulations and Trade Facilitation Initiatives
12.1. Market Size and Future Potential for E-commerce Logistics, 2018-2029
12.2. Cold Chain Infrastructure and Gaps
12.3. Emerging Trends in Last-Mile Delivery
12.4. Cross Comparison of Leading E-commerce Logistics Players
13.1. Investment in Logistics Infrastructure by Private and Public Entities
13.2. Trends in Warehouse Leasing and Build-to-Suit Models
13.3. Role of Development Finance Institutions
13.4. Sources of Financing for Logistics Startups and Asset Owners
16.1. Benchmark of Key Players-Company Overview, Services, Fleet Size, Warehouse Capacity, Technology Adoption
16.2. Strengths and Weaknesses
16.3. Operating Model Assessment
16.4. Market Positioning and Competitive Strategy
16.5. Bowmans Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
17.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
17.2. Volume Handled (MT/TEU), 2025-2029
18.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized Sector), 2025-2029
18.2. By Mode of Transport (Road, Air, Sea), 2025-2029
18.3. By Type of Warehousing, 2025-2029
18.4. By End-User Industry, 2025-2029
18.5. By Region, 2025-2029
18.6. Key Recommendations and Strategic Insights
18.7. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand-side and supply-side entities relevant to the Lebanon Logistics and Warehousing Market. This includes logistics service providers, warehousing companies, freight forwarders, third-party logistics (3PL) operators, e-commerce players, and end-user industries like FMCG, retail, pharma, and manufacturing.
Based on this mapping, we shortlist 5–6 key logistics and warehousing companies operating in Lebanon, selected on the basis of operational scale, fleet/warehouse capacity, and financial data.
Sourcing is carried out through industry publications, government portals, trade reports, company websites, and multiple secondary and proprietary databases to collate ecosystem-level insights.
Step 2: Desk Research
We conduct exhaustive secondary research using proprietary and public databases to build a foundational understanding of the market. This involves aggregation of industry-level information, including sector size, number of operators, volume of goods transported, warehousing trends, and pricing benchmarks.
Company-specific insights are gathered through press releases, annual reports, regulatory filings, and interviews with stakeholders published in trade magazines. The objective is to assess revenue estimates, service portfolios, operational presence, and strategic developments.
Step 3: Primary Research
We conduct in-depth interviews with C-level executives and logistics managers from leading companies in the Lebanon logistics and warehousing ecosystem. Additional discussions are held with end-user industry players such as retailers, pharma companies, and exporters to validate demand-side trends.
These interviews serve to validate hypotheses, reconcile discrepancies in secondary data, and gain deep operational insights.
A bottom-up estimation approach is used to arrive at volume and value-based market size figures by aggregating individual company operations.
Additionally, disguised interviews are carried out under the guise of potential customers to verify information such as pricing, services offered, storage capacity, delivery timelines, and technological readiness.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- A comprehensive bottom-up and top-down triangulation is conducted to validate the final market size and segmentation. Market modeling and forecasting exercises are undertaken using historical growth patterns, demand triggers, infrastructure investments, and macroeconomic indicators to ensure logical consistency and accuracy.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Lebanon Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Lebanon logistics and warehousing market holds strong growth potential, reaching a valuation of USD 1.2 Billion in 2023. Growth is expected to be driven by Lebanon’s strategic geographic location, the recovery and modernization of key infrastructure such as the Port of Beirut, and the expanding e-commerce sector. Rising demand for cold chain logistics, increasing digital adoption, and international support for supply chain improvements are also key enablers of long-term market potential.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Lebanon Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The market includes a combination of international and domestic players such as LibanPost, Aramex Lebanon, DHL Express, Medlog Lebanon, and Ghellal Logistics. These companies offer a mix of freight forwarding, courier services, warehousing, and last-mile delivery solutions. Their growing investments in technology and storage capacity are strengthening their market positions.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Lebanon Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Key growth drivers include the rise of e-commerce and last-mile delivery needs, reconstruction and digitalization efforts at the Port of Beirut, and increasing demand from retail, pharma, and food industries. The implementation of customs modernization tools like ASYCUDA World, and public-private partnerships for infrastructure development, are also contributing significantly to market expansion.
4. What are the Challenges in the Lebanon Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The sector faces several challenges including political instability, currency devaluation, and underdeveloped infrastructure, particularly in road networks and energy supply. The dominance of unorganized players, lack of standardization, and limited access to financing also restrict scalability and investment in modern technologies. Additionally, fluctuating import volumes and regulatory inefficiencies can hinder logistics flow and capacity utilization.