Malaysia Solar Power Market Outlook to 2029
, By Regional Distribution, By Consumer Segments, and By Government Policies
- Product Code: TDR0098
- Region: Asia
- Published on: December 2024
- Total Pages: 80-100
Report Summary
The report titled “Malaysia Solar Power Market Outlook to 2029 - By Market Structure, By Types of Solar Panels, By Applications, By Regional Distribution, By Consumer Segments, and By Government Policies” provides a comprehensive analysis of the solar power market in Malaysia. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of installed capacity and revenue, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer level profiling, issues and challenges, and a comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the solar power market. The report concludes with future market projections based on installed capacity, revenue, by market segments, regions, cause and effect relationship, and success case studies highlighting the major opportunities and cautions.
Malaysia Solar Power Market Overview and Size
The Malaysia solar power market reached a valuation of MYR 8 billion in 2023, driven by increasing investments in renewable energy, favorable government policies, and growing awareness of sustainability among businesses and consumers. The market is characterized by major players such as Solarvest, Plus Solar, Sunseap Group, Ditrolic Solar, and Pekat Group. These companies are recognized for their extensive expertise in solar installations, strong focus on innovation, and customer-centric solutions.
In 2023, Solarvest expanded its operations with the launch of a new solar farm project in Selangor, aimed at increasing the overall renewable energy capacity in Malaysia. Key regions driving growth include Selangor, Johor, and Penang due to their high energy consumption and advanced infrastructure.
Market Size for Malaysia Solar Power Industry on the Basis of Installed Capacity in MW, 2018–2024
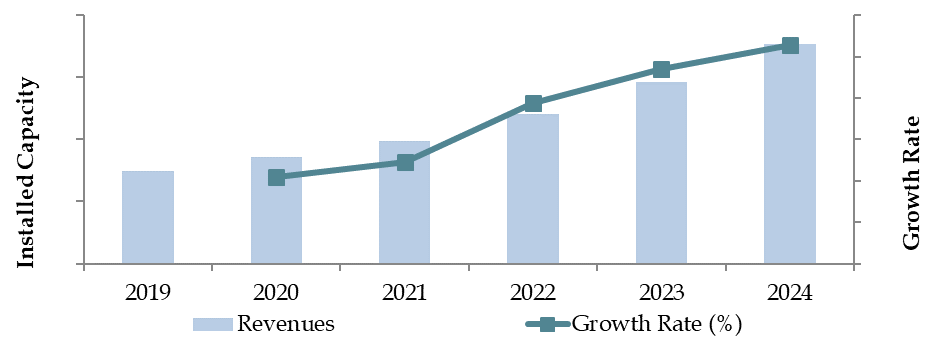
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Malaysia Solar Power Market:
Government Policies and Incentives: The Malaysian government’s push towards renewable energy, exemplified by initiatives like the Large Scale Solar (LSS) program and tax incentives for solar installations, has been a key driver. In 2023, approximately 25% of newly installed energy capacity in Malaysia was derived from solar energy, showcasing the impact of these policies.
Cost Reductions in Solar Technology: The declining cost of solar panels and increased efficiency of photovoltaic (PV) technology have made solar power a more attractive option for residential and commercial consumers. Between 2018 and 2023, the cost of solar panel installations in Malaysia fell by nearly 30%, further incentivizing adoption.
Corporate Sustainability Goals: A growing number of Malaysian businesses are committing to sustainability goals, leading to increased investments in rooftop solar systems. In 2023, corporate solar installations accounted for 40% of the country’s total solar capacity, highlighting a shift towards clean energy adoption among enterprises.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of Malaysia Solar Power Market
Intermittent Energy Supply: One of the primary challenges of solar power is its reliance on sunlight, which results in intermittent energy production. In Malaysia, frequent cloud cover and seasonal rainfall can reduce solar panel efficiency by up to 20%, creating challenges in ensuring consistent energy supply and reliability.
High Initial Costs: Despite declining costs, the upfront investment required for solar power systems remains a significant barrier for residential and small commercial consumers. According to a 2023 market survey, approximately 35% of potential customers cited high installation costs as the primary reason for not adopting solar solutions.
Regulatory and Permitting Delays: Lengthy approval processes for solar project permits and grid connections have slowed the pace of market expansion. In 2023, over 15% of proposed solar projects experienced delays exceeding six months due to regulatory bottlenecks, particularly in regions with stricter compliance standards.
What Are the Regulations and Initiatives Governing the Market:
Net Energy Metering (NEM) Program: The Malaysian government has implemented the NEM program to allow consumers to export excess solar energy back to the grid in exchange for credits on their electricity bills. By 2023, over 1,200 MW of solar energy had been installed under the NEM program, benefiting residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
Feed-in Tariff (FiT) System: Malaysia’s FiT system incentivizes renewable energy adoption by guaranteeing fixed payments for energy generated by solar projects. In 2023, solar installations under the FiT scheme accounted for approximately 18% of the nation’s total renewable energy capacity.
Large Scale Solar (LSS) Program: The LSS program, aimed at utility-scale solar projects, has driven significant growth in the sector. The fourth phase (LSS4) awarded contracts for over 823 MW of new solar capacity in 2023, further cementing Malaysia’s commitment to renewable energy targets.
Malaysia Solar Power Market Segmentation
By Market Structure: Independent solar solution providers dominate the market due to their localized expertise, competitive pricing, and customer-focused services. These providers cater to small- and medium-scale installations, offering customized solutions and quicker deployment. Established energy companies and multinational corporations hold a significant share, focusing on large-scale projects and leveraging advanced technologies and economies of scale to meet industrial and commercial demand.
By Types of Solar Panels: Monocrystalline panels lead the market due to their superior efficiency and compact design, making them ideal for residential rooftops and high-performance commercial installations. Polycrystalline panels follow closely, offering cost-effective solutions with slightly lower efficiency. Thin-film panels have a niche presence, primarily used in large-scale utility projects where flexibility and affordability outweigh efficiency considerations.
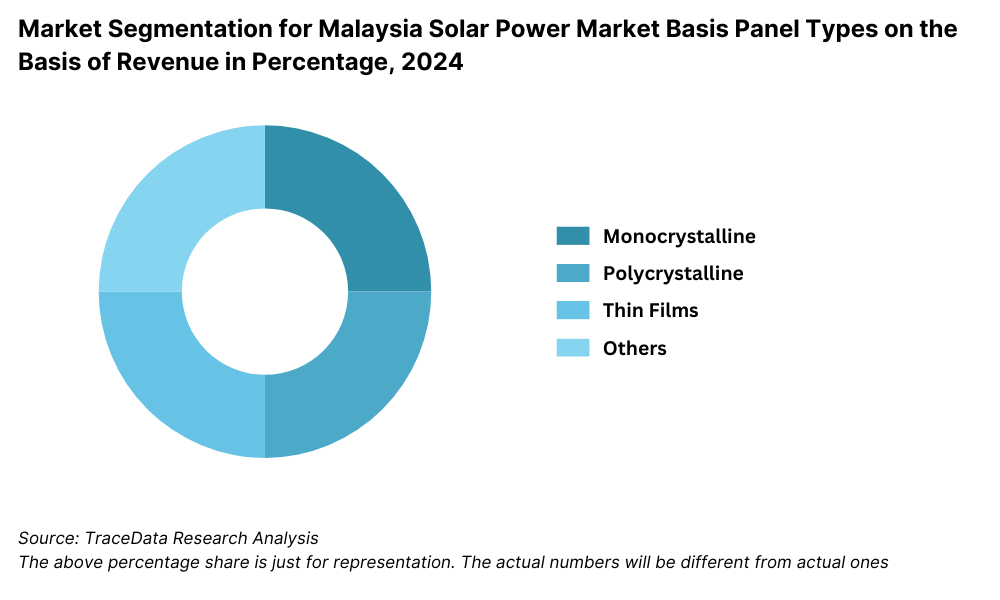
By Applications: Residential installations dominate due to increasing consumer interest in reducing electricity bills and government incentives like the Net Energy Metering (NEM) program. Commercial and industrial applications, however, hold a strong position due to businesses striving to achieve sustainability goals and reduce operational costs. Utility-scale projects are growing steadily, driven by government tenders under the Large Scale Solar (LSS) program.
Competitive Landscape in Malaysia Solar Power Market
The Malaysia solar power market is relatively concentrated, with key players leading the industry. However, new entrants and innovative startups are increasing competition, alongside the expansion of major corporations. Established companies such as Solarvest, Plus Solar, Sunseap Group, Ditrolic Solar, and Pekat Group dominate the market, supported by their technological advancements, strategic partnerships, and focus on sustainability.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
|---|---|---|
| Solarvest Holdings Berhad | 2012 | Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia |
| Ditrolic Solar | 2009 | Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia |
| Plus Xnergy | 2013 | Petaling Jaya, Malaysia |
| Verdant Solar | 2013 | Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia |
| Pekat Solar | 1999 | Shah Alam, Malaysia |
| First Solar Malaysia Sdn. Bhd. | 2007 | Kulim, Malaysia |
| Jinko Solar Technology Sdn. Bhd. | 2015 | Penang, Malaysia |
| JA Solar Malaysia Sdn. Bhd. | 2015 | Penang, Malaysia |
| LONGi Malaysia Sdn. Bhd. | 2016 | Kuching, Malaysia |
| SunPower Malaysia Manufacturing Sdn. Bhd. | 2010 | Melaka, Malaysia |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
Solarvest: A leading provider of solar solutions, Solarvest reported a 20% increase in annual revenue in 2023. The company expanded its portfolio by completing two utility-scale solar projects under the LSS program, further cementing its position in the market.
Plus Solar: Known for its innovative solar monitoring systems, Plus Solar recorded a 15% increase in installations in 2023, primarily driven by corporate demand for energy efficiency solutions. Its proprietary software offering real-time energy tracking has been a key differentiator.
Sunseap Group: Leveraging its regional expertise, Sunseap reported a 30% growth in its Malaysia operations in 2023. Its focus on cross-border renewable energy solutions and large-scale commercial projects has been instrumental in capturing market share.
Ditrolic Solar: Specializing in custom solar solutions for industrial applications, Ditrolic Solar achieved a 25% growth in installations in 2023. The company’s partnerships with multinational corporations have helped it tap into larger projects and expand its reach.
Pekat Group: With a legacy of over two decades, Pekat Group remains a prominent player in the solar market. In 2023, the company completed over 1,000 rooftop installations and expanded its operations to underserved regions like Sabah and Sarawak, marking a 10% growth in revenue.

What Lies Ahead for Malaysia Solar Power Market?
The Malaysia solar power market is projected to grow significantly by 2029, exhibiting a strong CAGR during the forecast period. This growth will be driven by supportive government policies, increasing corporate sustainability goals, and advancements in solar technology.
Expansion of Utility-Scale Solar Projects: With the continued implementation of the Large Scale Solar (LSS) program, utility-scale solar projects are expected to account for a larger share of Malaysia's renewable energy capacity. These projects will play a pivotal role in meeting the country's renewable energy targets under its 2050 Net Zero Carbon emissions agenda.
Rising Adoption of Rooftop Solar Solutions: Residential and commercial rooftop installations are anticipated to grow, supported by government incentives such as the Net Energy Metering (NEM) program. These solutions are becoming increasingly popular among consumers seeking energy independence and cost savings.
Integration of Advanced Energy Storage Systems: The adoption of battery storage technologies is expected to enhance the reliability of solar power systems by addressing issues related to intermittent energy supply. These advancements will facilitate greater integration of solar power into the national grid, improving overall energy efficiency and stability.
Development of Green Financing Models: With increasing interest in sustainability, green financing models such as low-interest loans and solar leasing programs are likely to expand. These financial solutions will make solar power more accessible to households and small businesses, accelerating market penetration.
Future Outlook and Projections for Malaysia Solar Power Market on the Basis of Revenues in USD Billion, 2024-2029


Malaysia Solar Power Market Segmentation
- By Market Structure:
- Utility-Scale Solar Projects
- Residential Rooftop Installations
- Commercial and Industrial Installations
- Solar Farms
- Off-Grid Solar Systems
- By Types of Solar Panels:
- Monocrystalline Solar Panels
- Polycrystalline Solar Panels
- Thin-Film Solar Panels
- By Applications:
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
- Agricultural
- Public Sector
- By Regional Distribution:
- Northern
- Southern
- Central
- Eastern (Sabah & Sarawak)
- By Consumer Segment:
- Residential Consumers
- Corporate and Industrial Entities
- Government and Municipalities
Players Mentioned in the Report:
- Solarvest Holdings Berhad
- Ditrolic Solar
- Plus Xnergy
- Verdant Solar
- Pekat Solar
- First Solar Malaysia Sdn. Bhd.
- Jinko Solar Technology Sdn. Bhd.
- JA Solar Malaysia Sdn. Bhd.
- LONGi Malaysia Sdn. Bhd.
- SunPower Malaysia Manufacturing Sdn. Bhd.
Key Target Audience:
- Solar Installation Companies
- Renewable Energy Solution Providers
- Energy Financing Companies
- Government Bodies (e.g., Sustainable Energy Development Authority - SEDA)
- Research and Development Institutions
- Corporate Sustainability Teams
Time Period:
- Historical Period: 2018–2023
- Base Year: 2024
- Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, Margins and Challenges they Face
4.2. Revenue Streams for Malaysia Solar Power Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Malaysia Solar Power Market
5.1. Malaysia Renewable Energy Market Overview, 2018-2024
5.2. Solar Power Market Share in Renewable Energy Mix, 2018-2024
5.3. Government Spending on Renewable Energy in Malaysia, 2024
5.4. Cost Dynamics to Setup Solar Power Plant in Malaysia-Segregated by Residential, Commercial, Industrial and Utility
8.1. Installed Capacity in MW, 2018-2024
8.2. Revenue Generated, 2018-2024
9.1. By Solar Panel Type (Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline, Thin-Film and others), 2023-2024P
9.2. By Region (Northern, Southern, Central, Eastern), 2023-2024P
9.3. By Application (Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Agricultural), 2023-2024P
9.4. By Consumer Segment (Households, Corporates, Public Sector), 2023-2024P
10.1. Customer Landscape and Cohort Analysis
10.2. Adoption Trends and Consumer Motivations
10.3. Need, Desire, and Pain Point Analysis
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11.1. Trends and Developments in Malaysia Solar Power Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Malaysia Solar Power Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Malaysia Solar Power Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges for Malaysia Solar Power Market
11.5. Government Regulations for Malaysia Solar Power Market
12.1. Market Size and Future Potential for Off-Grid Systems, 2018-2029
12.2. Business Model and Revenue Streams
12.3. Cross Comparison of Leading Off-Grid Solar Companies Basis Operational and Financial Indicators
15.1. Market Share of Key Players in Malaysia Solar Power Market, 2024
15.2. Benchmark of Key Competitors in Malaysia Solar Power Market Basis Operational and Financial Parameters
15.3. Strengths and Weaknesses of Key Players
15.4. Operating Model Analysis Framework
15.5. Innovation and Sustainability Analysis
16.1. Installed Capacity in MW, 2025-2029
16.2. Revenue Projections, 2025-2029
17.1. By Solar Panel Type (Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline, Thin-Film), 2025-2029
17.2. By Region (Northern, Southern, Central, Eastern), 2025-2029
17.3. By Application (Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Agricultural), 2025-2029
17.4. By Consumer Segment (Households, Corporates, Public Sector), 2025-2029
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all demand-side and supply-side entities for the Malaysia Solar Power Market. Basis this ecosystem, we will shortlist leading 5-6 companies in the country based on their financial information, installed capacity, and technological expertise.
Sourcing is made through industry articles, government reports, and multiple secondary and proprietary databases to perform desk research around the market and collate industry-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
Engage in an exhaustive desk research process by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This approach enables us to conduct a thorough analysis of the market, aggregating industry-level insights. Key focus areas include installed capacity, growth trends, key players, and policy analysis.
Supplement this with detailed examinations of company-level data using sources such as press releases, annual reports, and project feasibility studies to establish a foundational understanding of the market landscape and key participants.
Step 3: Primary Research
Conduct in-depth interviews with C-level executives and other stakeholders representing various companies and entities involved in the Malaysia Solar Power Market, including solar project developers, government authorities, and consumers.
Validate market hypotheses, authenticate statistical data, and extract valuable insights into operational and financial trends. A bottom-to-top approach is used to evaluate installed capacity and financial performance for each player, aggregating this data to determine the overall market size.
As part of our validation strategy, our team executes disguised interviews, approaching companies as potential clients to confirm operational and financial information shared by executives and corroborate this against secondary sources. These interactions also provide insights into the value chain, pricing, and processes in the market.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- Bottom-to-top and top-to-bottom analyses, combined with market size modeling exercises, are undertaken to assess the consistency and reliability of the findings and ensure accuracy in market projections.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Malaysia Solar Power Market?
The Malaysia solar power market is poised for significant growth, with a projected valuation of MYR 12 billion by 2029. Growth is driven by government policies, corporate sustainability initiatives, and increasing consumer awareness of renewable energy. Utility-scale solar projects and rooftop installations are expected to dominate, contributing substantially to Malaysia’s renewable energy targets.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Malaysia Solar Power Market?
The Malaysia Solar Power Market features several key players, including Solarvest, Plus Solar, and Pekat Group. These companies are industry leaders due to their strong portfolios of completed projects, technological innovation, and expertise in solar energy solutions. Other notable players include Ditrolic Solar and Sunseap Group.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Malaysia Solar Power Market?
Primary growth drivers include government initiatives like the Net Energy Metering (NEM) and Large Scale Solar (LSS) programs, declining costs of solar technology, and increasing adoption of renewable energy by corporations. Additionally, advancements in energy storage and grid connectivity are expected to further boost market growth.
4. What are the Challenges in the Malaysia Solar Power Market?
Challenges include intermittent energy supply due to weather dependency, high initial installation costs for smaller consumers, and regulatory delays in project approvals. Moreover, a lack of skilled workforce for installation and maintenance poses operational challenges, while limited awareness in certain regions can hinder adoption.