Morocco Auto Finance Market Outlook to 2029
By Type of Financing Institution, By Vehicle Type, By Loan Tenure, By Vehicle Condition (New vs Used), and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0157
- Region: North America
- Published on: April 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Morocco Auto Finance Market Outlook to 2029 – By Type of Financing Institution, By Vehicle Type, By Loan Tenure, By Vehicle Condition (New vs Used), and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the auto finance market in Morocco. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of credit disbursed and outstanding loans, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer level profiling, issues and challenges, and a comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the Auto Finance Market. The report concludes with future market projections based on credit disbursed, by market segment, vehicle type, region, cause and effect relationships, and success case studies highlighting the major opportunities and strategic risks.
Morocco Auto Finance Market Overview and Size
The Morocco auto finance market reached a valuation of MAD 45 Billion in outstanding auto loans in 2023, supported by steady vehicle demand, a growing urban population, and increasing access to consumer credit. The country’s automotive sector is anchored by both domestic demand and its position as a key vehicle assembly hub in North Africa, with car ownership steadily rising across middle-income and young consumer segments.
Key players in the Moroccan auto finance landscape include Attijariwafa Bank, Banque Populaire, BMCE Bank of Africa, Wafasalaf, Eqdom (a subsidiary of Société Générale), and Maroc Leasing. These institutions offer structured financing products targeted at both new and used vehicles, often in collaboration with authorized dealerships and OEMs such as Renault, Dacia, and Peugeot.
In 2023, Wafasalaf launched a digitized auto loan application process integrated with dealership networks in Rabat and Casablanca, reducing loan approval times to under 48 hours. Casablanca, Rabat, and Marrakech remain the key markets due to their higher income levels, population density, and extensive dealership presence.
Market Size for Morocco Auto Finance Industry on the Basis of Credit Disbursed in USD Billion, 2018-2023
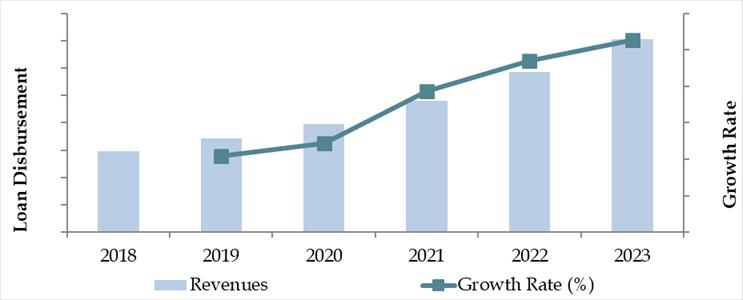
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Morocco Auto Finance Market:
Economic Factors: Morocco’s auto finance sector is benefiting from a recovering economy and a renewed consumer appetite for personal mobility post-pandemic. In 2023, over 60% of vehicle purchases were supported by structured financing. The growing presence of salaried professionals and small business owners in urban areas continues to drive the demand for auto loans.
Growing Middle-Class & Youth Demographics: Morocco has witnessed a steady rise in its middle-class population along with a relatively young median age of 29.4 years. This demographic is increasingly seeking asset ownership through manageable financing options. Used vehicle loans have become a preferred route to first-time vehicle ownership, especially among younger consumers.
Digitalization: The adoption of mobile-first lending platforms and digitized loan processing by banks and captive finance companies has streamlined the borrower experience. In 2023, an estimated 35% of auto loan applications in urban centers were initiated through online or mobile banking portals. Fintech integration and digital KYC protocols are improving access and reducing turnaround times.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for Morocco Auto Finance Market
High Interest Rates for Used Vehicle Loans: One of the key challenges in Morocco’s auto finance market is the relatively higher interest rates applied to used vehicle loans. As of 2023, average interest rates for used cars ranged between 9%–11% annually, significantly higher than rates for new vehicles. This disparity reduces affordability and discourages financing among low- to mid-income consumers, who often prefer used cars due to price constraints.
Low Penetration in Semi-Urban and Rural Areas: While urban centers such as Casablanca and Rabat enjoy well-developed financing ecosystems, semi-urban and rural regions remain underserved. A 2023 report indicated that less than 30% of vehicle buyers in peripheral regions accessed formal financing channels. The absence of dedicated lender branches, limited dealership presence, and lack of digital financial literacy contribute to this gap.
Dependence on Traditional Underwriting Models: Most Moroccan banks and finance institutions continue to rely on traditional documentation-heavy underwriting processes. This limits credit access for informal sector workers and self-employed individuals who lack verifiable income documents. According to industry feedback, nearly 40% of loan rejections in 2023 were due to incomplete documentation or insufficient credit history.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
Central Bank Oversight on Auto Lending: The Bank Al-Maghrib (Morocco’s central bank) regulates interest rate ceilings, consumer protection norms, and credit reporting standards for auto loans. Since 2022, new guidelines were introduced to enhance borrower disclosures, standardize processing fees, and improve pre-approval transparency. This has gradually improved trust in the formal lending system.
Digitalization Initiatives for Financial Inclusion: In partnership with Morocco’s Ministry of Digital Transition, several public-private programs were rolled out to promote fintech integration in consumer lending. The “Digital Finance Acceleration Initiative” aims to onboard at least 1 million unbanked Moroccans to formal credit platforms by 2026, including those seeking auto loans.
EV Financing Support Schemes: As part of its national green mobility agenda, Morocco has introduced reduced VAT and import duty exemptions on electric vehicles (EVs). In 2023, some banks began offering “Green Auto Loans” with lower interest rates and longer tenures for hybrid and electric vehicles, in line with the government’s 2030 climate roadmap.
Morocco Auto Finance Market Segmentation
By Type of Financing Institution: Commercial banks dominate the Moroccan auto finance market owing to their established presence, broader product offerings, and trust among consumers. Major banks such as Attijariwafa Bank, Banque Populaire, and BMCE Bank of Africa offer structured auto loans with competitive rates and tie-ups with dealerships. Non-banking financial institutions such as Wafasalaf, Eqdom, and Maroc Leasing are gaining momentum by offering quicker processing times, flexible eligibility criteria, and digitized application experiences. Captive finance companies linked to OEMs like Renault and Stellantis are also playing a growing role by supporting dealer-driven loan programs.
By Vehicle Type: Passenger vehicles form the core of the financed vehicle portfolio in Morocco, particularly compact sedans, hatchbacks, and entry-level SUVs, driven by first-time buyers and salaried professionals. Financing of light commercial vehicles such as vans and pickups is also gaining momentum due to rising demand from small businesses and delivery startups. Meanwhile, electric and hybrid vehicles, though currently a small fraction, are expected to gain share with supportive government policies and green lending products.
By Loan Tenure: Loans with tenures between 36 to 60 months remain the most popular, providing a balance between monthly affordability and total interest cost. New vehicle buyers, particularly from salaried segments, prefer longer tenures for lower EMIs. In contrast, buyers of used vehicles, especially in lower-income groups, opt for shorter tenures of 12–24 months to limit long-term financial commitments.
Competitive Landscape in Morocco Auto Finance Market
The Morocco auto finance market is moderately competitive, with a strong presence of established banks and non-banking financial institutions. While traditional players continue to lead in terms of disbursed credit volume, the market has seen increasing digitalization and new product development across both captive and independent financing entities. The rise of dealer-OEM tie-ups and fintech-led initiatives is also gradually reshaping customer experience and broadening access.
| Company Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
| Attijariwafa Bank | 2003 | Casablanca, Morocco |
| Bank of Africa (BOA) | 1959 | Casablanca, Morocco |
| Banque Centrale Populaire (BCP) | 1961 | Casablanca, Morocco |
| CIH Bank | 1920 | Casablanca, Morocco |
| BMCI (BNP Paribas subsidiary) | 1964 | Casablanca, Morocco |
| Mobilize Financial Services Morocco | 2021 | Casablanca, Morocco |
| FCA Capital Maroc | 2021 | Casablanca, Morocco |
| BAG Capital | 2024 | Casablanca, Morocco |
| Umnia Bank | 2017 | Casablanca, Morocco |
| Autochek Morocco | 2020 | Casablanca, Morocco |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
Attijariwafa Bank: The largest financial institution in Morocco, Attijariwafa Bank continues to dominate the auto loan market through its “Crédit Auto” program. In 2023, the bank expanded its financing reach through digital loan approvals, offering pre-approved limits via its mobile app for eligible clients. Partnerships with local dealerships have improved point-of-sale financing adoption.
Banque Populaire: With a strong regional presence across Morocco, Banque Populaire focuses on financing new vehicles through dealer-driven campaigns. In 2023, the bank launched “Pack Auto Jeune” targeting first-time vehicle buyers under the age of 30 with preferential rates and lower down payments.
BMCE Bank of Africa: Known for its innovation in digital banking, BMCE has expanded its auto financing arm with simplified digital pre-approval services. The bank reported a 22% increase in disbursed auto credit in 2023, largely driven by its focus on mid-income professionals and salaried borrowers in urban centers.
Wafasalaf: A leading non-bank financial institution, Wafasalaf offers both new and used vehicle loans with customized repayment tenures. In 2023, the company integrated a fully digital loan application journey across its partner dealership network, enabling approvals within 48 hours. Its focus on rapid processing and flexible eligibility has made it popular among informal sector customers.
Eqdom: A subsidiary of Société Générale, Eqdom provides competitive interest rates and long tenures for auto loans, particularly for new vehicles. In 2023, Eqdom strengthened its collaboration with French OEMs such as Peugeot and Renault to expand captive financing schemes in Casablanca and Rabat.
Maroc Leasing: Specialized in leasing solutions, Maroc Leasing has grown its vehicle leasing and fleet financing business for SMEs and logistics firms. In 2023, the company expanded its operating lease solutions for light commercial vehicles, supporting Morocco’s rising e-commerce sector.
Sofac Crédit: With over 70 years of experience, Sofac Crédit remains a key player in the personal and vehicle loan space. Its emphasis on credit scoring tools and bundled insurance-financing offerings has helped expand its footprint among risk-conscious buyers.
What Lies Ahead for Morocco Auto Finance Market?
The Morocco auto finance market is projected to grow steadily by 2029, supported by a rising demand for vehicle ownership, digital financial services adoption, and strategic government incentives to encourage green mobility. The market is expected to register a healthy CAGR over the forecast period as both formal and informal lending ecosystems expand to serve new customer segments.
Rising Adoption of Electric Vehicles (EVs): With Morocco’s national strategy focused on sustainability and carbon neutrality, the demand for electric vehicles is expected to rise. This will be supported by new green loan products and preferential tax treatment. Financial institutions are likely to introduce EV-specific financing with low interest rates and longer repayment periods, boosting accessibility among environmentally conscious buyers.
Acceleration of Digital Auto Lending: Auto loan disbursals via digital channels are set to increase significantly by 2029. Banks and NBFCs will continue investing in mobile-first loan applications, AI-based credit scoring models, and paperless documentation processes. This digital transformation will particularly benefit young and tech-savvy consumers in urban centers such as Casablanca, Rabat, and Tangier.
Growth in Used Vehicle Financing: Used vehicles will remain the preferred option for cost-sensitive buyers, especially in the semi-urban and emerging middle-income segments. Financial institutions are expected to design targeted products for pre-owned car buyers, including trade-in loan schemes, shorter tenures, and bundled warranties. This will drive a larger share of total disbursed credit towards the used vehicle segment.
Expansion of Captive and OEM Financing: More automotive OEMs operating in Morocco, including Renault, Peugeot, and Volkswagen, are expected to scale their captive financing arms or enter into co-branded partnerships with local lenders. These efforts will improve dealership-level financing access and allow customized offerings like low down payments, zero interest for introductory periods, and loyalty programs.
Future Outlook and Projections for Morocco Car Finance Market Size on the Basis of Loan Disbursements in USD Billion, 2024-2029
Morocco Auto Finance Market Segmentation
• By Type of Financing Institution:
o Commercial Banks
o Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)
o Captive Finance Companies
o Microfinance Institutions
o Islamic Financing Institutions
o Digital Lending Platforms
• By Vehicle Type:
o Passenger Vehicles
o Light Commercial Vehicles
o Electric Vehicles
o Hybrid Vehicles
o Two-Wheelers (limited market share but growing)
• By Loan Tenure:
o <12 Months
o 12–24 Months
o 25–36 Months
o 37–60 Months
o >60 Months
• By Vehicle Condition:
o New Vehicles
o Used Vehicles
• By Borrower Type:
o Salaried Individuals
o Self-Employed / Informal Sector
o Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
o Taxi / Ride-Hailing Drivers
o Fleet Operators
• By Region:
o Casablanca–Settat
o Rabat–Salé–Kénitra
o Marrakech–Safi
o Fès–Meknès
o Tanger–Tétouan–Al Hoceima
o Oriental Region
o Other Interior Regions
Players Mentioned in the Report (Banks):
- Attijariwafa Bank
- Banque Centrale Populaire (BCP)
- Bank of Africa (BOA)
- Crédit Agricole du Maroc
- Société Générale Maroc
- Crédit du Maroc
- CIH Bank
- BMCI (Banque Marocaine pour le Commerce et l’Industrie)
- Al Barid Bank
Players Mentioned in the Report (NBFCs):
- Wafasalaf
- Eqdom
- Sogelease
- Taslif
- Saham Finances
- Salafin
- BMCI Leasing Auto
Players Mentioned in the Report (Captive):
- CA Auto Bank Morocco
- Mobilize Financial Services Morocco
- FCA Capital Maroc
- Volkswagen Financial Services Morocco
- Toyota Financial Services Morocco
- Mercedes-Benz Financial Services Morocco
- BMW Financial Services Morocco
Key Target Audience:
• Commercial Banks and NBFCs
• Automotive OEMs and Dealerships
• Captive Finance Arms and Leasing Companies
• Regulatory Bodies (e.g., Bank Al-Maghrib, Ministry of Economy and Finance)
• Fintech and Digital Lending Platforms
• Ride-Hailing and Mobility Startups
• Market Research and Development Agencies
Time Period:
• Historical Period: 2018–2023
• Base Year: 2024
• Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and challenges they face.
4.2. Relationship and Engagement Model between Banks-Dealers, NBFCs-Dealers and Captive-Dealers-Commission Sharing Model, Flat Fee Model and Revenue streams
5.1. New Car and Used Car Sales in Morocco by type of vehicle, 2018-2024
8.1. Credit Disbursed, 2018-2024
8.2. Outstanding Loan, 2018-2024
9.1. By Market Structure (Bank-Owned, Multi-Finance, and Captive Companies), 2023-2024
9.2. By Vehicle Type (Passenger, Commercial and EV), 2023-2024
9.3. By Region, 2023-2024
9.4. By Type of Vehicle (New and Used), 2023-2024
9.5. By Average Loan Tenure (0-2 years, 3-5 years, 6-8 years, above 8 years), 2023-2024
10.1. Customer Landscape and Cohort Analysis
10.2. Customer Journey and Decision-Making
10.3. Need, Desire, and Pain Point Analysis
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11.1. Trends and Developments for Morocco Car Finance Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Morocco Car Finance Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Morocco Car Finance Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges for Morocco Car Finance Market
11.5. Government Regulations for Morocco Car Finance Market
12.1. Market Size and Future Potential for Online Car Financing Aggregators, 2018-2029
12.2. Business Model and Revenue Streams
12.3. Cross Comparison of Leading Digital Car Finance Companies Based on Company Overview, Revenue Streams, Loan Disbursements/Number of Leads Generated, Operating Cities, Number of Branches, and Other Variables
13.1. Finance Penetration Rate and Average Down Payment for New and Used Cars, 2018-2029
13.2. How Finance Penetration Rates are Changing Over the Years with Reasons
13.3. Type of Car Segment for which Finance Penetration is Higher
17.1. Market Share of Key Banks in Morocco Car Finance Market, 2024
17.2. Market Share of Key NBFCs in Morocco Car Finance Market, 2024
17.3. Market Share of Key Captive in Morocco Car Finance Market, 2024
17.4. Benchmark of Key Competitors in Morocco Car Finance Market, including Variables such as Company Overview, USP, Business Strategies, Strengths, Weaknesses, Business Model, Number of Branches, Product Features, Interest Rate, NPA, Loan Disbursed, Outstanding Loans, Tie-Ups and others
17.5. Strengths and Weaknesses
17.6. Operating Model Analysis Framework
17.7. Gartner Magic Quadrant
17.8. Bowmans Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
18.1. Credit Disbursed, 2025-2029
18.2. Outstanding Loan, 2025-2029
19.1. By Market Structure (Bank-Owned, Multi-Finance, and Captive Companies), 2025-2029
19.2. By Vehicle Type (Passenger, Commercial and EV), 2025-2029
19.3. By Region, 2025-2029
19.4. By Type of Vehicle (New and Used), 2025-2029
19.5. By Average Loan Tenure (0-2 years, 3-5 years, 6-8 years, above 8 years), 2025-2029
19.6. Recommendations
19.7. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand side and supply side entities for Morocco Auto Finance Market. Basis this ecosystem, we will shortlist leading 5–6 financiers in the country based on their loan disbursement volumes, regional presence, borrower segments, and financing structure (bank, NBFC, or captive).
Sourcing is conducted through industry reports, government publications, financial media, and proprietary databases to perform desk research around the market and build an initial framework of stakeholders and transaction models.
Step 2: Desk Research
We subsequently engage in an exhaustive desk research process by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This includes review of annual reports, audited financial statements, central bank data, regulatory circulars, and OEM dealership financing programs.
Our team analyzes metrics such as total credit disbursed, average loan tenure, ticket sizes, customer demographics, and interest rates. This helps develop a data-driven understanding of the Morocco Auto Finance landscape and benchmark key financial indicators across market participants.
Step 3: Primary Research
We initiate a series of in-depth interviews with C-level executives, retail banking heads, loan managers, dealership financing coordinators, and end-users in the Morocco Auto Finance ecosystem. These interviews are designed to validate market estimates, understand operational bottlenecks, and collect nuanced insights into borrower behavior, risk management, and pricing dynamics.
As part of the validation approach, our team conducts disguised interviews by approaching companies as potential customers. This enables verification of key details such as turnaround time, credit criteria, documentation requirements, and fee structures, and provides an unbiased view of customer-facing processes and lender responsiveness.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- A comprehensive bottom-to-top and top-to-bottom triangulation exercise is performed to verify the accuracy of market sizing and segmentation outputs. We use modeling techniques to align projected credit disbursements, loan books, and market growth trends with vehicle sales data, macroeconomic indicators, and regional financing penetration rates.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Morocco Auto Finance Market?
The Morocco auto finance market is positioned for steady growth, reaching an estimated outstanding loan book of MAD 45 Billion in 2023. The market's potential is driven by increased vehicle demand, a growing urban middle class, and rising consumer access to structured financial products. Continued digital transformation in banking and lending services is expected to broaden market reach and support long-term scalability.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Morocco Auto Finance Market?
The Morocco Auto Finance Market includes key players such as Attijariwafa Bank, Banque Populaire, BMCE Bank of Africa, Wafasalaf, Eqdom, Maroc Leasing, and Sofac Crédit. These institutions dominate through extensive branch networks, dealership partnerships, and customized auto loan products. Captive finance and leasing solutions from OEM-aligned providers are also gaining market share.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Morocco Auto Finance Market?
Major growth drivers include Morocco's increasing vehicle ownership rate, rising disposable incomes among urban professionals, and government support for sustainable mobility. The adoption of mobile-first financial services and alternative lending models is enhancing credit access across underserved and semi-formal sectors. Additionally, green finance initiatives and preferential EV loan schemes are expected to drive future momentum.
4. What are the Challenges in the Morocco Auto Finance Market?
Key challenges include high interest rates for used vehicle loans, limited financing access in rural and semi-urban areas, and a continued reliance on traditional documentation-heavy underwriting methods. Credit penetration remains relatively low among informal sector workers due to a lack of verifiable income and credit histories. These factors constrain overall market inclusivity and growth potential.