Morocco Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Structure, By Type of Storage (Refrigerated Warehousing and Transportation), By Temperature Range, By End-User Industry (Pharmaceuticals, Food & Beverages, Dairy, Meat & Seafood), and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0294
- Region: North America
- Published on: September 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Morocco Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029 – By Market Structure, By Type of Storage (Refrigerated Warehousing and Transportation), By Temperature Range, By End-User Industry (Pharmaceuticals, Food & Beverages, Dairy, Meat & Seafood), and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the cold chain logistics sector in Morocco. The report includes the market's genesis and evolution, current market size in terms of revenue, segmentation by service type and end-use industries, regulatory framework, emerging trends, and key challenges. It also presents the competitive landscape with cross-comparisons and company profiles and concludes with projections up to 2029 based on industry drivers, success case studies, and growth potential.
Morocco Cold Chain Market Overview and Size
The Morocco cold chain market reached a valuation of MAD 4.3 Billion in 2023, driven by rising demand for temperature-controlled logistics in the food and pharmaceutical industries, increased export of perishables, and a growing organized retail sector. Key market players include Frigolog, Saham Logistics, STG Maroc, and SJL Group, which are recognized for their temperature-controlled warehousing infrastructure, fleet capabilities, and regulatory compliance in cold transport.
In 2023, Frigolog expanded its refrigerated warehousing capacity by 15% in the Casablanca region to cater to the growing pharmaceutical and dairy logistics demands. Casablanca and Agadir are emerging as strategic hubs for cold chain operations due to proximity to ports and high agro-industrial activity.
%2C%202018%E2%80%932023.png)
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Morocco Cold Chain Market:
Rising Export of Perishables: Morocco’s agricultural exports – especially citrus, berries, and seafood – have increased significantly, requiring efficient cold storage and transportation to maintain quality during long transit times. In 2023, over 45% of fruit exports were supported by cold chain infrastructure.
Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Demand: Growth in pharmaceutical imports and the establishment of domestic vaccine and drug distribution programs have contributed to the demand for temperature-sensitive logistics. Government initiatives in 2022 focused on strengthening medical logistics infrastructure, further boosting the sector.
Retail Modernization: The proliferation of modern trade formats (hypermarkets, supermarkets) has led to greater demand for organized cold storage and last-mile refrigerated delivery. Companies like Marjane and Carrefour are increasingly outsourcing cold logistics to third-party specialists.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for Morocco Cold Chain Market
Inadequate Infrastructure in Rural Areas: Despite advancements in urban logistics, the cold chain infrastructure in Morocco's rural and inland regions remains underdeveloped. According to a recent logistics survey, over 35% of perishable goods experience temperature deviations during transportation due to limited access to cold storage and reliable power. This directly impacts the shelf life and export potential of agricultural produce from these areas.
High Operating and Energy Costs: Cold chain operations are capital- and energy-intensive. In 2023, electricity accounted for nearly 40% of total operational costs in refrigerated warehousing. This cost burden, coupled with fluctuations in energy supply and grid reliability in certain regions, affects profitability, especially for small and mid-sized operators.
Shortage of Trained Workforce: The sector lacks adequately trained technicians and logistics staff skilled in temperature monitoring, handling of pharmaceuticals, and compliance with global standards. Industry estimates suggest that about 30% of cold chain businesses reported inefficiencies or product loss due to staff mishandling in 2022–23.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
ONSSA Food Safety Guidelines: The National Office for Food Safety (ONSSA) mandates temperature compliance and traceability for perishable goods in storage and transit. In 2023, over 60% of Morocco’s refrigerated transport operators were audited under ONSSA guidelines, signaling growing enforcement of food safety norms.
Pharmaceutical Cold Chain Compliance: The Ministry of Health has issued updated guidelines aligned with WHO GDP (Good Distribution Practices) for cold chain transportation of vaccines and temperature-sensitive drugs. In 2022, Morocco’s COVID-19 vaccination rollout helped improve pharma cold chain capabilities across Casablanca, Rabat, and Marrakesh.
Agropole and Logistics Platform Development: The Moroccan government, with support from development partners like EBRD and AFD, is investing in agro-logistics parks with cold storage infrastructure. As of 2023, facilities in Berkane and Meknès added over 20,000 pallet positions of cold storage capacity.
Morocco Cold Chain Market Segmentation
By Market Structure: The organized cold chain segment in Morocco is expanding rapidly, driven by rising compliance demands from export markets, pharmaceutical companies, and modern retail chains. Organized players offer traceability, temperature monitoring systems, and adherence to global safety standards, which are essential for high-value food and medical logistics. The unorganized segment, however, still dominates rural and semi-urban areas due to cost advantages and limited enforcement of standards, although service levels often remain inconsistent.
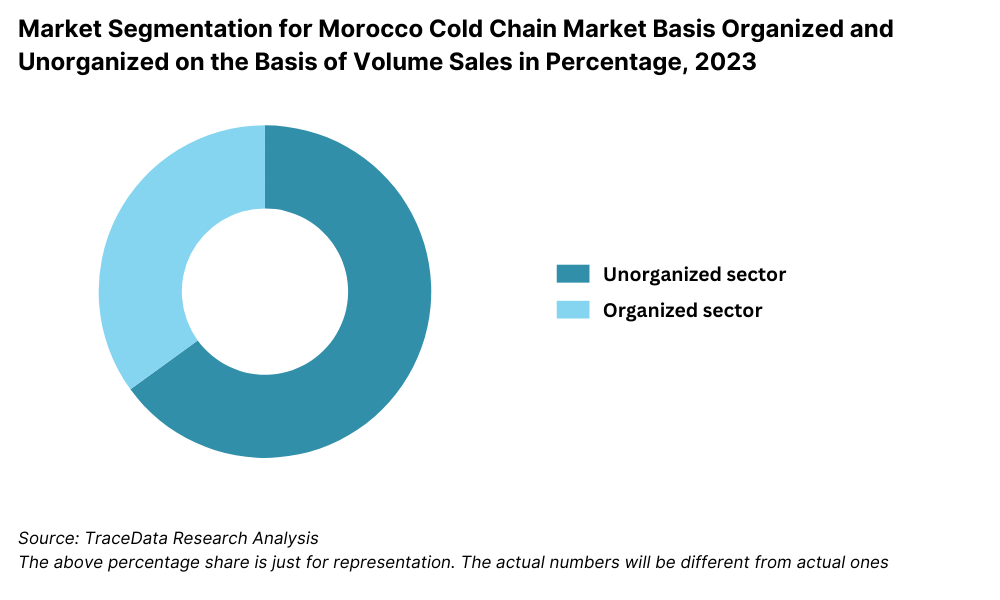
By Type of Cold Chain Service: Refrigerated transportation currently leads the segment due to the need for efficient first-mile and last-mile connectivity, especially for perishable agricultural exports. However, cold warehousing is catching up fast, particularly in urban centers like Casablanca and Tangier, driven by demand from pharmaceuticals, modern trade retailers, and seafood exporters. Multi-temperature warehousing facilities are emerging as a key differentiator in this space.
%20on%20the%20Basis%20of%20Revenue%20Share%2C%202023.png)
By Temperature Range: The market is predominantly driven by chilled storage (0°C to 5°C), which caters to fruits, dairy, and processed foods. Frozen storage (below -18°C), while smaller in share, is growing due to increasing demand from seafood exporters and quick service restaurants (QSRs). Ultra-low temperature logistics (below -25°C), used for specialty pharmaceuticals and vaccines, is a niche but growing area with significant investment interest since the COVID-19 pandemic.
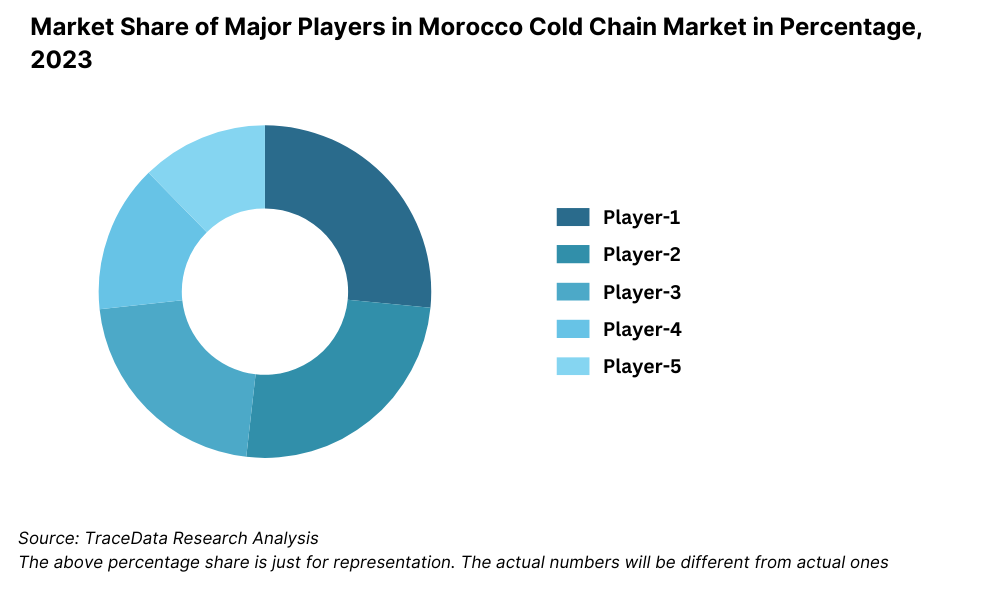
Competitive Landscape in Morocco Cold Chain Market
The Morocco cold chain market is moderately consolidated, with a mix of established logistics providers and emerging cold storage specialists. Key players include Frigolog, Saham Logistics, STG Maroc, SJL Group, and Timar, which have built significant cold storage infrastructure and operate integrated cold chain solutions. Additionally, rising interest from international logistics and private equity players is fueling investments and partnerships in this space.
Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
Frigolog | 2009 | Casablanca, Morocco |
Saham Logistics | 2005 | Casablanca, Morocco |
STG Maroc | 1999 | Tangier, Morocco |
SJL Group | 2002 | Tetouan, Morocco |
Timar | 1980 | Casablanca, Morocco |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
Frigolog: One of the largest cold logistics firms in Morocco, Frigolog expanded its cold storage footprint by 8,000 pallet positions in Casablanca in 2023. The company also introduced IoT-based temperature monitoring systems, enhancing real-time control across its refrigerated trucks.
Saham Logistics: Saham Logistics has focused on pharmaceutical logistics, securing multiple contracts with international healthcare firms in 2022–23. Its Good Distribution Practices (GDP)-compliant infrastructure has made it a preferred partner for vaccine and drug storage.
STG Maroc: STG Maroc operates extensive temperature-controlled logistics routes between Tangier, Casablanca, and key EU ports. In 2023, it added 20 new reefer trucks to its fleet and reported a 15% growth in exports of frozen seafood and processed meat.
SJL Group: Leveraging its cross-border logistics capabilities, SJL Group continues to support perishable exports to Spain and France. In 2023, the company announced plans to set up a new cold storage facility in Tetouan to support the agri-export corridor in the northern region.
Timar: A veteran player in the Moroccan logistics sector, Timar has pivoted into temperature-controlled storage over the last few years. In 2023, it launched a multi-temperature facility in Mohammedia, targeting demand from dairy and F&B clients.
What Lies Ahead for Morocco Cold Chain Market?
The Morocco cold chain market is projected to witness steady growth through 2029, driven by rising demand for food exports, expansion of the pharmaceutical and healthcare sector, and increasing investments in logistics modernization. The sector is expected to grow at a healthy CAGR, with improvements in technology, infrastructure, and regulatory alignment playing a central role.
Expansion of Agro-Exports and International Trade: As Morocco strengthens its position as a key exporter of citrus fruits, berries, seafood, and vegetables, the need for reliable cold chain logistics will continue to rise. With the EU, Middle East, and West Africa as primary trade partners, export-grade temperature control solutions will become increasingly critical.
Growth of Pharmaceutical Cold Chain: The demand for temperature-sensitive pharmaceutical products, including vaccines, insulin, and biologics, is expected to rise steadily. Regulatory alignment with WHO and EU standards, coupled with increased public and private investments, will drive the development of compliant cold storage and transport solutions, especially in Casablanca, Rabat, and Marrakesh.
Integration of IoT and Automation: Adoption of digital technologies such as IoT-based temperature sensors, real-time GPS tracking, and automated cold warehouses is expected to increase significantly. These technologies will improve operational efficiency, reduce spoilage rates, and enhance end-to-end visibility, helping Moroccan providers compete at a global standard.
Development of Cold Chain Zones and Hubs: Government-backed logistics zones like those in Agadir, Tangier Med, and Berkane will attract domestic and foreign investments. Integrated cold chain parks offering warehousing, processing, and transport in a single ecosystem will become central to regional supply chain efficiency.
%2C%202023-2029.png)
Morocco Cold Chain Market Segmentation
• By Market Structure:
o Organized Cold Chain Operators
o Unorganized Cold Chain Operators
o Integrated 3PL Providers
o Standalone Cold Storage Providers
o Refrigerated Transporters
o Public-Private Partnership (PPP) Infrastructure
• By Type of Service:
o Cold Storage
o Refrigerated Transportation
o Integrated Cold Chain Solutions
o Last-Mile Temperature-Controlled Delivery
• By Temperature Range:
o Chilled (0°C to 5°C)
o Frozen (-18°C and below)
o Ultra-Low Temperature (-25°C and below)
o Controlled Atmosphere Storage
• By End-User Industry:
o Fruits & Vegetables
o Meat & Seafood
o Dairy Products
o Pharmaceuticals & Vaccines
o Bakery & Confectionery
o Foodservice & QSR
o Retail & Supermarkets
• By Region:
o Casablanca-Settat
o Rabat-Salé-Kénitra
o Tanger-Tétouan-Al Hoceïma
o Souss-Massa
o Oriental
o Fès-Meknès
Players Mentioned in the Report:
• Frigolog
• Saham Logistics
• STG Maroc
• SJL Group
• Timar
• Dislog Group
• Maersk Morocco (Cold Chain Division)
• Tibbett Logistics Morocco
Key Target Audience:
• Cold Chain Logistics Providers
• Agro Exporters and Food Processors
• Pharmaceutical Distributors and Manufacturers
• Supermarket Chains & QSR Brands
• Regulatory Bodies (e.g., ONSSA, Ministry of Agriculture, Ministry of Health)
• Development Organizations (e.g., EBRD, USAID)
• Cold Chain Technology Providers
Time Period:
• Historical Period: 2018–2023
• Base Year: 2024
• Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
1. Executive Summary
2. Research Methodology
3. Ecosystem of Key Stakeholders in Morocco Cold Chain Market
4. Value Chain Analysis
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and Challenges Faced
4.2. Revenue Streams for Morocco Cold Chain Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Morocco Cold Chain Market
4.4. Logistics Procurement & Storage Decision-Making Process
4.5. End-User Procurement Decision-Making Process
5. Market Structure
5.1. Cold Chain Logistics Penetration in Key Industries (F&B, Pharma, Dairy), 2018-2024
5.2. Share of Organized vs. Unorganized Cold Chain Providers, 2018-2024
5.3. Power and Fuel Cost Trends for Cold Storage Operations in Morocco, 2023-2024
5.4. Number of Cold Chain Operators in Morocco by Region
6. Market Attractiveness for Morocco Cold Chain Market
7. Supply-Demand Gap Analysis for Temperature-Controlled Logistics
8. Market Size for Morocco Cold Chain Market Basis
8.1. Revenues (in MAD Billion), 2018-2024
8.2. Cold Storage Capacity (in pallet positions), 2018-2024
8.3. Refrigerated Transport Fleet Size, 2018-2024
9. Market Breakdown for Morocco Cold Chain Market Basis
9.1. By Market Structure (Organized vs. Unorganized), 2023-2024P
9.2. By Type of Service (Storage vs. Transportation vs. Integrated), 2023-2024P
9.3. By Temperature Range (Chilled, Frozen, Ultra-Low), 2023-2024P
9.4. By End-User Industry (Fruits & Vegetables, Meat, Dairy, Pharma), 2023-2024P
9.5. By Region (Casablanca-Settat, Rabat-Salé-Kénitra, Souss-Massa, etc.), 2023-2024P
10. Demand Side Analysis for Morocco Cold Chain Market
10.1. Customer Segmentation and Procurement Preferences
10.2. Buying Journey and Vendor Evaluation Process
10.3. Pain Points, Expectations, and Service Gaps
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11. Industry Analysis
11.1. Trends and Developments in Morocco Cold Chain Market
11.2. Growth Drivers
11.3. SWOT Analysis
11.4. Challenges in Cold Chain Infrastructure Development
11.5. Government Regulations and Incentives
12. Snapshot on Technology and Digitalization in Cold Chain
12.1. IoT and Real-Time Monitoring Integration
12.2. Energy-Efficient Cooling Technologies
12.3. Automation in Warehousing and Fleet Management
13. Morocco Cold Chain Financing and Investment Trends
13.1. Funding Support and Investment Initiatives (EBRD, AFD, USAID)
13.2. Investment Trends by Domestic and International Players
13.3. Payback Period and Return on Investment for Cold Storage Projects
13.4. PPP and Government-Backed Projects
14. Opportunity Matrix for Morocco Cold Chain Market-Radar Chart
15. PEAK Matrix Analysis for Morocco Cold Chain Providers
16. Competitor Analysis for Morocco Cold Chain Market
16.1. Benchmarking of Key Players-Infrastructure, Services, Capabilities
16.2. Company Strengths and Weaknesses
16.3. Business and Operating Model Comparison
16.4. Competitive Positioning using Bowman’s Strategic Clock
17. Future Market Size for Morocco Cold Chain Market Basis
17.1. Revenues (in MAD Billion), 2025-2029
17.2. Cold Storage Capacity and Transport Fleet Size, 2025-2029
18. Market Breakdown for Morocco Cold Chain Market Basis
18.1. By Market Structure (Organized vs. Unorganized), 2025-2029
18.2. By Type of Service (Storage, Transport, Integrated), 2025-2029
18.3. By Temperature Range, 2025-2029
18.4. By End-User Industry, 2025-2029
18.5. By Region, 2025-2029
18.6. Recommendation
18.7. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
We began by mapping the ecosystem and identifying all demand-side and supply-side entities relevant to the Morocco Cold Chain Market. This included cold storage operators, refrigerated transporters, agro-exporters, pharmaceutical distributors, government bodies, and logistics integrators. Based on this ecosystem, we shortlisted 5–6 leading players in Morocco by evaluating their infrastructure scale, service capabilities, client base, and financial performance.
Sourcing for this phase was executed through industry whitepapers, market intelligence platforms, government reports, and proprietary databases to collate structured market information and define the market framework.
Step 2: Desk Research
We conducted exhaustive desk research using a combination of secondary sources and proprietary intelligence tools. The objective was to derive a consolidated industry view, capturing variables such as total warehousing capacity (in pallet positions), number of refrigerated trucks, major end-user segments, average pricing per pallet/ton-km, and key growth drivers.
Additionally, detailed company profiling was carried out through press releases, investor presentations, regulatory filings, and media coverage. This allowed for the identification of company-level strengths, cold chain solutions, regional focus areas, and expansion trends.
Step 3: Primary Research
Our research team conducted in-depth interviews with decision-makers across Morocco's cold chain ecosystem, including logistics managers, facility operators, exporters, pharma distributors, and government stakeholders. These interviews validated hypotheses derived from secondary research and helped refine estimates for market sizing and segment-wise contribution.
A bottom-up approach was used to estimate market size—evaluating warehousing capacities, utilization levels, vehicle fleet strength, and average pricing across providers—then aggregated at the industry level.
As part of our validation process, disguised interviews were conducted by posing as potential clients. This enabled us to cross-check operational data, pricing models, service offerings, and infrastructure metrics with actual market behavior and public data points.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- A sanity check was performed through both top-down (demand-side export volume, retail infrastructure, pharmaceutical demand modeling) and bottom-up (company-level aggregation) approaches. Market triangulation and iterative data modeling were used to ensure consistency, alignment, and validity of the final market size and forecasts presented.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Morocco Cold Chain Market?
The Morocco Cold Chain Market holds strong growth potential, with the market reaching a valuation of MAD 4.3 Billion in 2023. This growth is being fueled by the increasing need for temperature-controlled logistics in key sectors such as agro-exports, pharmaceuticals, dairy, and retail. Government investments in logistics zones and rising global demand for Moroccan perishables further underscore the future scalability of this sector. With enhanced regulatory frameworks and the integration of digital solutions, the market is expected to grow at a steady pace through 2029.
• Who are the Key Players in the Morocco Cold Chain Market?
The Morocco Cold Chain Market is led by prominent players such as Frigolog, Saham Logistics, STG Maroc, SJL Group, and Timar. These companies offer services ranging from cold storage and refrigerated transportation to integrated end-to-end solutions. International logistics providers and regional agri-exporters are also entering the market through partnerships and investments, contributing to a more competitive and diversified landscape.
• What are the Growth Drivers for the Morocco Cold Chain Market?
Key growth drivers include Morocco’s increasing agro-export volumes (especially citrus, berries, and seafood), expansion of pharmaceutical cold chain needs, and modernization of retail and QSR supply chains. Government initiatives supporting cold logistics infrastructure, compliance with EU food safety and pharma standards, and growing consumer demand for fresh and safe food products are also playing a pivotal role in driving market expansion.
• What are the Challenges in the Morocco Cold Chain Market?
The Morocco Cold Chain Market faces several challenges, such as inadequate infrastructure in rural regions, high energy and maintenance costs, and a shortage of trained cold chain professionals. Fragmentation of service providers and lack of standardization impact the overall quality and reliability of services. Moreover, ensuring consistent compliance with international cold chain standards remains a critical challenge, especially for exporters targeting developed markets.