Morocco Logistics and warehousing Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Structure, By Types of Warehousing, By End-User Industries, By Region, By Service Types, and By Technological Adoption
- Product Code: TDR0295
- Region: North America
- Published on: September 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled "Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market Outlook to 2029 - By Market Structure, By Types of Warehousing, By End-User Industries, By Region, By Service Types, and By Technological Adoption" provides a comprehensive analysis of the logistics and warehousing market in Morocco. This report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation, trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer level profiling, issues and challenges, and comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the Logistics and Warehousing Market. The report concludes with future market projections based on sales revenue, market growth, product types, region, and success case studies highlighting major opportunities and cautions.
Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market Overview and Size
The Morocco logistics and warehousing market reached a valuation of MAD 40 billion in 2023, driven by the expanding e-commerce sector, increasing industrial activities, and Morocco's strategic geographic location as a gateway between Europe, Africa, and the Middle East. The market is supported by key players such as DB Schenker, XPO Logistics, CMA CGM, and the state-owned national logistics company, ONCF. These players have been strengthening their supply chain networks to cater to the growing demand for efficient logistics services.
The increasing demand for modern warehousing infrastructure, including temperature-controlled warehouses, has played a significant role in the market’s expansion. In 2023, the Moroccan government also launched initiatives to boost the logistics sector, including infrastructure development projects aimed at improving the road, rail, and port connectivity. Key markets such as Casablanca, Tangier, and Marrakesh have witnessed significant investments due to their proximity to major ports and high industrial activity.
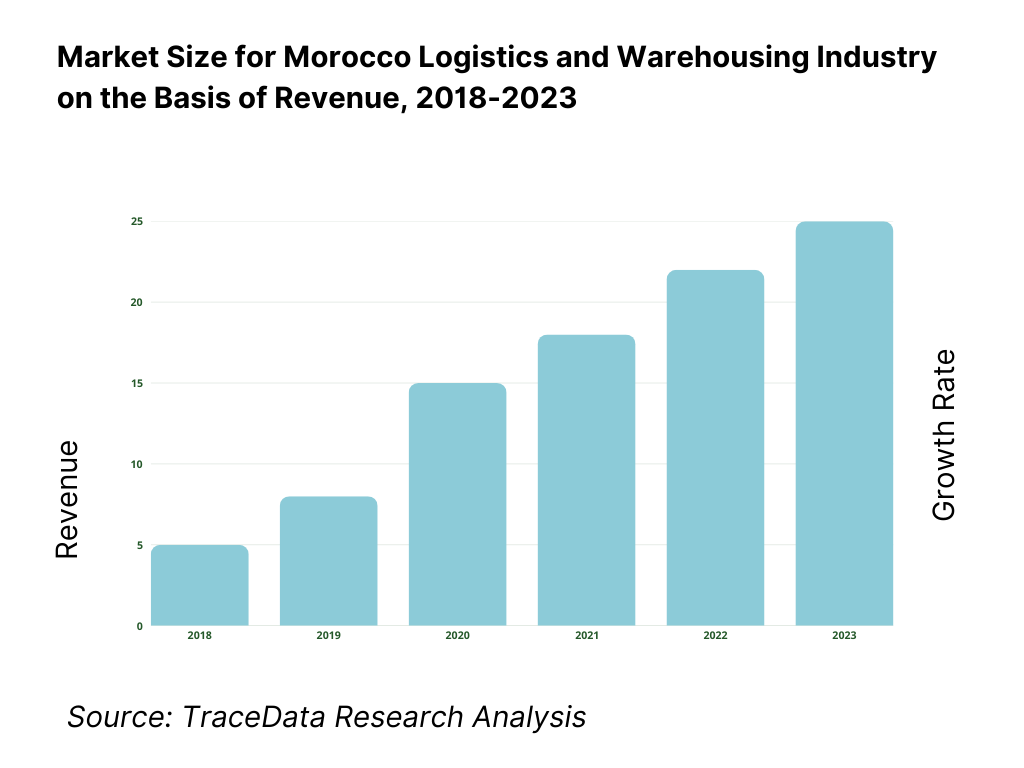
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Economic Factors: Morocco’s growing role as a regional manufacturing hub, especially in sectors like automotive, textiles, and electronics, has increased the demand for reliable logistics services. The government’s focus on boosting export capabilities is another driver, contributing to an increase in logistics demand for cross-border trade. Morocco's free trade agreements with the EU and the US have also opened up global markets, further strengthening the demand for efficient logistics and warehousing solutions.
E-Commerce Boom: The surge in e-commerce activities in Morocco has led to a growing need for distribution centers and last-mile delivery services. In 2023, the Moroccan e-commerce sector grew by 20%, which increased demand for warehousing solutions to store goods for faster delivery.
Technological Advancements: The adoption of advanced technologies, such as robotics, IoT, and warehouse management systems (WMS), has enhanced the efficiency and accuracy of logistics operations. The government’s support for digital transformation is expected to drive innovation in logistics and warehousing services, making them more cost-effective and reliable.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market
Quality and Capacity of Infrastructure: Despite significant investments in logistics infrastructure, Morocco faces challenges in maintaining high-quality facilities that meet the growing demand for modern warehousing solutions. A lack of sufficient temperature-controlled warehouses, for example, has created a bottleneck, particularly in the food and pharmaceuticals sectors, limiting the growth potential in these industries. Approximately 30% of logistics companies report difficulties in finding quality warehouses to meet their operational requirements.
Regulatory Complexity: Morocco’s logistics sector is governed by a combination of local and international regulations, which sometimes create compliance challenges for logistics providers. The complex customs procedures and varying standards for warehousing across different regions make it difficult for companies to standardize operations. A recent survey found that nearly 40% of logistics companies in Morocco struggle with adhering to these regulatory requirements, which delays operations and increases costs.
High Costs of Transportation and Storage: Transportation remains a critical cost driver in Morocco’s logistics sector. The high price of fuel and the cost of maintaining an efficient vehicle fleet significantly impact the bottom line of logistics companies. This has been exacerbated by the rising demand for quicker delivery times, which requires more advanced fleet management and infrastructure. In 2023, transportation costs represented approximately 45% of overall logistics expenses, creating a challenge for many companies to remain cost-effective while competing in the market.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives that Have Governed the Market
Customs and Import Regulations: The Moroccan government has enforced stringent customs regulations for goods imported through ports such as Tangier Med. These regulations have led to the establishment of more sophisticated customs management systems, but they can sometimes result in delays and additional costs for businesses. A 2023 report indicates that customs processing delays have increased by 15%, impacting supply chain timelines.
Infrastructure Development Programs: The Moroccan government has launched the National Logistics Strategy 2017-2025, which aims to improve logistics efficiency by investing in modern infrastructure, including transport corridors, ports, and rail networks. This strategy is expected to reduce logistical costs by 20% by 2025 and improve Morocco’s ranking in the World Bank's Logistics Performance Index (LPI).
Tax Incentives for Warehousing Investments: To encourage the growth of modern warehousing facilities, Morocco has introduced tax incentives for businesses that invest in energy-efficient or automated warehouses. This initiative, launched in 2022, allows logistics companies to access significant deductions on corporate taxes if they adopt green technologies in their operations. As of 2023, around 15% of new warehousing projects are utilizing these incentives to incorporate sustainable practices.
Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
By Market Structure: The Moroccan logistics and warehousing market is predominantly led by large logistics providers who have well-established networks and resources to offer a comprehensive range of services. These companies dominate the market due to their ability to handle complex supply chains, provide advanced warehousing solutions, and operate across multiple regions. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are also active in the market, though they often face challenges such as limited access to modern technology and infrastructure. The growing demand for logistics services in rural areas has led to the development of localized providers who cater to specific industries, such as agriculture and construction.
By End-User Industry: The logistics and warehousing market in Morocco is heavily influenced by industries such as automotive, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and food and beverages. The automotive sector requires extensive warehousing for spare parts and assembly components, while the electronics industry demands high-tech facilities for storing delicate components. The food and beverage sector, driven by consumer demand for fresh and processed products, fuels the growth of cold storage and temperature-controlled warehousing solutions.
By Technological Adoption: Technological advancements, such as Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), Robotics Process Automation (RPA), and Internet of Things (IoT) solutions, are becoming critical components of Morocco's logistics sector. Leading players in the market are increasingly adopting these technologies to improve inventory management, reduce operational costs, and increase warehouse efficiency. On the other hand, smaller logistics companies are in the early stages of implementing these technologies due to higher initial investments and lack of expertise.
Competitive Landscape in Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market
The Morocco logistics and warehousing market is moderately concentrated, with a few key players dominating the landscape. However, the entry of new companies and the expansion of both local and international firms have contributed to a more diversified market, providing consumers with a wider range of services.
Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
DB Schenker | 1872 | Casablanca, Morocco |
XPO Logistics | 1989 | Casablanca, Morocco |
CMA CGM | 1978 | Tangier, Morocco |
ONCF (National Railways) | 1912 | Rabat, Morocco |
Kuehne + Nagel | 1890 | Casablanca, Morocco |
Aramex | 1982 | Casablanca, Morocco |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
DB Schenker: As a global leader in logistics, DB Schenker has strengthened its presence in Morocco through investments in automated warehouses and digital supply chain solutions. The company recorded a 12% increase in revenue from its Moroccan operations in 2023, driven by the growth in e-commerce and demand for cold chain logistics.
XPO Logistics: Known for its comprehensive logistics services, including last-mile delivery and warehousing solutions, XPO Logistics reported a 20% growth in the Moroccan market in 2023. The company has expanded its footprint by investing in multi-temperature storage and enhanced transportation services, which have proven critical for industries such as pharmaceuticals and food.
CMA CGM: A significant player in Morocco’s maritime logistics sector, CMA CGM has focused on expanding its presence in both sea freight and warehousing. The company’s recent acquisition of a warehouse facility in Tangier has enhanced its ability to provide end-to-end logistics services. CMA CGM’s Moroccan operations saw a 15% increase in container throughput in 2023.
ONCF: The state-owned rail company ONCF has been a cornerstone of Morocco’s logistics infrastructure, handling a significant portion of freight transportation via rail. In 2023, ONCF expanded its rail freight services to more cities, improving distribution efficiency. The company also partnered with private logistics firms to modernize rail terminals and increase overall cargo capacity.
Kuehne + Nagel: This Swiss-based logistics giant has significantly expanded its warehousing capacity in Morocco, especially in Casablanca, to cater to the growing demand from electronics and automotive sectors. In 2023, Kuehne + Nagel launched a new warehousing facility equipped with IoT technology, which contributed to a 10% increase in its market share.
Aramex: Aramex has focused on providing express delivery and supply chain solutions for e-commerce businesses in Morocco. The company saw a 25% increase in e-commerce logistics volume in 2023, driven by its partnerships with local retailers and global e-commerce platforms. Aramex has invested in expanding its warehousing capabilities to keep up with rising demand.
What Lies Ahead for Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Morocco logistics and warehousing market is projected to grow steadily by 2029, exhibiting a robust CAGR during the forecast period. This growth is anticipated to be driven by Morocco’s strategic geographical location, infrastructure development, and the increasing demand for modern logistics services, particularly in e-commerce and cold chain logistics.
Expansion of E-commerce Logistics: The growing e-commerce sector in Morocco is expected to be a major driver of the logistics market. As more consumers turn to online shopping, the demand for efficient and timely delivery solutions, as well as last-mile delivery services, will continue to rise. Companies will need to develop more sophisticated warehousing solutions to handle increased inventory volumes and streamline distribution networks.
Cold Chain Logistics Growth: With the rising demand for perishable goods, particularly in the food and pharmaceutical sectors, cold chain logistics will experience significant growth. The increasing need for temperature-controlled warehouses and transportation networks will encourage further investment in this sector. Cold chain solutions will be critical for maintaining product integrity and meeting international standards for quality and safety.
Adoption of Automation and Technology: The integration of advanced technologies, such as Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), Robotics Process Automation (RPA), and Internet of Things (IoT), is expected to improve efficiency and reduce costs in logistics operations. Automated warehouses and smart supply chain solutions will be adopted by leading players in the market to enhance inventory management, speed up delivery times, and increase operational efficiency.
Port Expansion and Global Trade: As Morocco strengthens its position as a logistics hub connecting Europe, Africa, and the Middle East, investments in port infrastructure, especially in Tangier Med Port, will continue to grow. The expansion of Morocco’s transport corridors and logistics parks will improve connectivity and further facilitate international trade. This will lead to an increase in cross-border logistics services, particularly to Sub-Saharan Africa and Europe.
%2C%202023-2029.png)
Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
By Market Structure:
Third-Party Logistics Providers (3PL)
Freight Forwarders
Warehouse Operators
Shipping and Port Operators
E-commerce Logistics
Cold Chain Logistics
Unorganized Sector
By Service Type:
Transportation
Warehousing
Inventory Management
Order Fulfillment
Last-Mile Delivery
Customs Clearance
By End-User Industry:
Automotive
Electronics
Pharmaceuticals
Food & Beverages
Retail & E-commerce
Textiles & Apparel
Chemicals
Agriculture
By Region:
Northern Region (Tangier, Tetouan)
Central Region (Rabat, Casablanca)
Southern Region (Agadir, Marrakesh)
Eastern Region (Oujda, Fes)
By Technological Adoption:
Advanced Technology (Automation, IoT, WMS)
Moderate Technology (RFID, Basic WMS)
Traditional Warehousing (Manual Processes)
Players Mentioned in the Report:
DB Schenker
XPO Logistics
CMA CGM
ONCF (National Railways)
Kuehne + Nagel
Aramex
DHL Supply Chain
Royal Air Maroc Cargo
Key Target Audience:
Logistics Providers
Warehouse Operators
E-commerce Companies
Cold Chain Suppliers
Freight Forwarders
Shipping and Port Operators
Regulatory Bodies (e.g., Ministry of Transport, National Port Authority)
Research and Development Institutions
Time Period:
Historical Period: 2018-2023
Base Year: 2024
Forecast Period: 2024-2029
Report Coverage
1. Executive Summary
2. Research Methodology
3. Ecosystem of Key Stakeholders in Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market
4. Value Chain Analysis
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and Challenges Faced
4.2. Revenue Streams for Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market
4.4. Buying Decision Making Process
4.5. Supply Decision Making Process
5. Market Structure
5.1. Logistics and Warehousing Market Breakdown, 2018-2024
5.2. Spend on Public Transport and Logistics Infrastructure, 2024
5.3. Key Logistics Hubs and Warehousing Facilities in Morocco
5.4. Number of Warehouses by Location in Morocco
6. Market Attractiveness for Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market
7. Supply-Demand Gap Analysis
8. Market Size for Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market Basis
8.1. Revenues, 2018-2024
8.2. Sales Volume, 2018-2024
9. Market Breakdown for Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market Basis
9.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized Market), 2023-2024P
9.2. By Transport Mode (Road, Rail, Sea, Air), 2023-2024P
9.3. By Warehousing Type (Automated, Manual, Cold Storage, Bonded), 2023-2024P
9.4. By Region, 2023-2024P
9.5. By Sector (Retail, Automotive, Manufacturing, Agriculture), 2023-2024P
9.6. By Type of Cargo (General Cargo, Perishable Goods, Heavy Goods), 2023-2024P
10. Demand Side Analysis for Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market
10.1. Customer Landscape and Cohort Analysis
10.2. Customer Journey and Decision Making
10.3. Need, Desire, and Pain Point Analysis
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11. Industry Analysis
11.1. Trends and Developments for Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges for Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market
11.5. Government Regulations for Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market
12. Snapshot on E-Commerce and Digital Transformation in Morocco Logistics Market
12.1. Market Size and Future Potential for Online Logistics and Warehousing, 2018-2029
12.2. Business Models and Revenue Streams in Digital Logistics
12.3. Cross Comparison of Leading Logistics Companies Based on Company Overview, Revenue Streams, and Operational Reach
13. Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Financing Market
13.1. Finance Penetration Rate and Average Investment for Logistics Infrastructure, 2018-2029
13.2. Types of Financing for Warehousing Operations (Private vs. Public Investments)
13.3. Financing Challenges and Opportunities for Logistics and Warehousing Companies
13.4. Warehouse Leasing Market Overview, 2023-2024P
13.5. Government Support and Subsidies for Logistics Infrastructure
14. Opportunity Matrix for Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market-Presented with the Help of Radar Chart
15. PEAK Matrix Analysis for Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market
16. Competitor Analysis for Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market
16.1. Benchmark of Key Competitors in Morocco Logistics Market including Company Overview, Business Strategies, Strengths, Weaknesses, and Global Operations
16.2. Strength and Weakness Analysis of Key Players
16.3. Operating Model Analysis Framework
16.4. Gartner Magic Quadrant for Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market
16.5. Bowman's Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage in Morocco
17. Future Market Size for Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market Basis
17.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
17.2. Sales Volume, 2025-2029
18. Market Breakdown for Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market Basis
18.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized Market), 2025-2029
18.2. By Transport Mode (Road, Rail, Sea, Air), 2025-2029
18.3. By Warehousing Type (Automated, Manual, Cold Storage, Bonded), 2025-2029
18.4. By Region, 2025-2029
18.5. By Sector (Retail, Automotive, Manufacturing, Agriculture), 2025-2029
18.6. By Type of Cargo (General Cargo, Perishable Goods, Heavy Goods), 2025-2029
18.7. Recommendation
18.8. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand-side and supply-side entities for the Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market. Based on this ecosystem, we will shortlist leading 5-6 key players in the country based on their financial information, market presence, infrastructure, and technological capabilities.
Sourcing is made through industry articles, multiple secondary sources, and proprietary databases to perform desk research around the market and collect industry-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
Following the ecosystem mapping, we engage in an exhaustive desk research process by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This enables us to gather a comprehensive understanding of the market by analyzing variables such as logistics services, warehouse operations, transportation costs, demand drivers, and supply chain trends.
We supplement this research with company-level data, analyzing sources like press releases, annual reports, market analysis papers, and financial statements. This foundational research serves to outline key trends, competitor strategies, and emerging opportunities within the Moroccan logistics sector.
Step 3: Primary Research
We initiate a series of in-depth interviews with C-level executives and other stakeholders representing various logistics and warehousing companies, as well as end-users across multiple industries. This interview process serves to validate market hypotheses, authenticate statistical data, and provide operational insights from industry representatives.
A bottom-up approach is adopted to evaluate market volume, considering sector-specific demand factors and supply chain logistics. The data gathered will be aggregated to form a comprehensive view of the market landscape.
To further validate our findings, we conduct disguised interviews by approaching companies as potential customers. This approach allows us to corroborate the operational and financial data shared by company executives, validate pricing models, service offerings, and market dynamics.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- A combination of bottom-up and top-down analysis, along with market size modeling exercises, is undertaken to assess the accuracy and reliability of the findings. This sanity check ensures that the data aligns with overall market trends and is internally consistent across the research process.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Morocco logistics and warehousing market is projected to grow significantly, reaching a valuation of MAD 40 Billion in 2023. The market's potential is driven by factors such as the country's strategic location as a logistics hub connecting Europe, Africa, and the Middle East, the growing demand for efficient transportation networks, and the expansion of e-commerce and manufacturing industries in the region. Furthermore, advancements in digital technologies, such as real-time tracking and automation in warehousing, are expected to drive further market growth.
2. Who are the key players in the Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Moroccan logistics and warehousing market features several key players, including multinational logistics companies such as DB Schenker, DHL, and GEFCO, along with local players like Managem and the Moroccan logistics company CTM. These companies dominate the market due to their extensive distribution networks, operational expertise, and investment in technological solutions for efficient transportation and warehousing. Additionally, regional players such as XPO Logistics and Kuehne + Nagel are also contributing to the competitive landscape.
3. What are the growth drivers for the Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The growth drivers include Morocco's geographic advantage, which positions it as a strategic gateway between Europe, Africa, and the Middle East. Other factors include the rise of e-commerce and retail sectors, increasing demand for third-party logistics (3PL) services, and the expansion of the industrial sector, particularly in automotive, textiles, and agriculture. The government’s infrastructure development initiatives, such as the expansion of ports and logistics zones, are also playing a significant role in boosting market growth. Additionally, advancements in digitalization, such as IoT and warehouse automation, are expected to enhance operational efficiency.
4. What are the challenges in the Morocco Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Despite the potential for growth, the Morocco logistics and warehousing market faces challenges such as underdeveloped infrastructure in certain regions, particularly outside major urban centers. These challenges include inadequate road networks, limited warehouse space in rural areas, and congestion in key ports and airports. Additionally, the lack of skilled workforce in logistics and warehousing, regulatory barriers related to customs and import/export regulations, and the need for improved supply chain transparency can also hinder the market's growth.