Netherlands Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029
Morocco Logistics and warehousing Market, Morocco Logistics and warehousing Industry
- Product Code: TDR0297
- Region: Europe
- Published on: September 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Netherlands Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029 - By Market Structure, By Storage and Transport Type, By End-User Industry, By Temperature Range, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the cold chain industry in the Netherlands. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation, trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer level profiling, issues and challenges, and comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the Cold Chain Market. The report concludes with future market projections based on revenue, by service type, industry verticals, region, cause and effect relationships, and success case studies highlighting major opportunities and potential risks.
Netherlands Cold Chain Market Overview and Size
The Netherlands cold chain market reached a valuation of EUR 6.3 billion in 2023, driven by the increasing demand for perishable goods, expanding food and pharmaceutical exports, and the country's strategic position as a European logistics hub. The market is characterized by key players such as Lineage Logistics, Kloosterboer, DFDS, STEF Netherlands, and NewCold, known for their advanced infrastructure, automation in warehousing, and integrated transport networks.
In 2023, Kloosterboer inaugurated a fully automated cold store facility in Rotterdam, with a capacity exceeding 60,000 pallet locations. This strategic expansion supports the rising demand from food and pharmaceutical exporters. Regions such as North Holland, South Holland, and Limburg are key markets due to their proximity to ports, agro-processing zones, and pharmaceutical clusters.
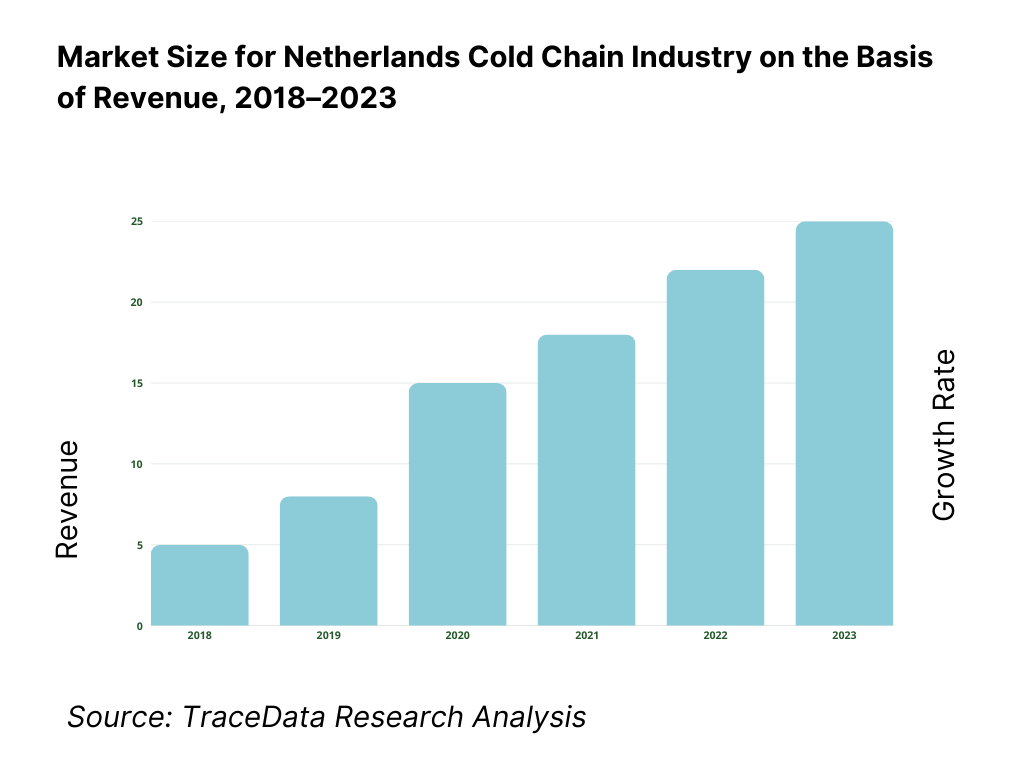
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the Netherlands Cold Chain Market:
Export-Oriented Agri and Pharma Economy: The Netherlands is the second-largest exporter of agri-food products globally and has a strong pharmaceutical manufacturing base. Cold chain solutions are critical for maintaining product integrity during export. In 2023, nearly 70% of temperature-sensitive goods exported from the Netherlands required cold chain infrastructure, thereby fuelling demand for advanced storage and transport services.
Strategic Port and Logistics Advantage: The presence of Port of Rotterdam, Europe's largest seaport, and Schiphol Airport, a major air cargo hub, has solidified the country’s role in cold chain distribution. Integrated road-rail-water connectivity has further enabled efficient multi-modal cold logistics, reducing transit times by over 30% for high-value perishables.
Increasing Stringency of Regulations: Stricter EU and national regulations regarding the storage and transportation of pharmaceuticals, vaccines, and frozen foods have mandated adherence to GDP (Good Distribution Practice) and HACCP standards. In 2023, over 85% of cold chain operators in the Netherlands were GDP-compliant, ensuring quality and safety across the logistics chain.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for Netherlands Cold Chain Market
High Energy and Operational Costs: Operating cold storage and transportation systems in the Netherlands is energy-intensive, especially due to compliance with stringent temperature requirements and the rising cost of electricity. In 2023, energy expenses accounted for nearly 35% of total operational costs in cold warehouses. As a result, smaller players struggle to maintain profitability and competitiveness, limiting industry participation.
Infrastructure Bottlenecks and Urban Congestion: The increasing demand for last-mile cold deliveries in urban areas like Amsterdam and Rotterdam has led to logistical inefficiencies due to traffic congestion and limited cold zone capacity. According to industry data, up to 18% of cold chain transport delays in 2023 were attributed to urban delivery bottlenecks, negatively affecting temperature-sensitive goods.
Shortage of Skilled Workforce: Operating and managing advanced cold chain systems requires specialized skillsets, including temperature monitoring, refrigeration handling, and regulatory compliance. However, there is a growing talent gap in the Netherlands, with over 20% of cold chain companies reporting hiring challenges for technical and logistics roles in 2023. This shortage impedes the scalability and quality assurance of services.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market
EU GDP Compliance and HACCP Guidelines: Cold chain operations handling pharmaceuticals in the Netherlands must comply with Good Distribution Practice (GDP) and Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) standards. These ensure temperature integrity, traceability, and hygiene. In 2023, more than 85% of certified facilities in the Netherlands operated under GDP protocols, indicating strong adherence to EU-level best practices.
National Sustainability Mandates for Cold Logistics: As part of the Dutch Climate Agreement, cold chain companies are required to transition toward low-emission logistics by 2030. This includes mandatory CO₂ reduction targets, energy-efficient refrigeration technologies, and investments in electric vehicle fleets. In 2023, the Dutch Ministry of Infrastructure and Water Management offered subsidies up to EUR 300,000 per project for green cold storage upgrades.
Food Safety Authority (NVWA) Oversight: The Netherlands Food and Consumer Product Safety Authority (NVWA) oversees cold chain practices related to perishable food handling. It enforces strict inspections on storage temperatures, contamination control, and traceability of products. In 2023, over 92% of audited cold chain facilities passed NVWA inspections without major non-compliance, reflecting high standards of food safety and hygiene.
Netherlands Cold Chain Market Segmentation
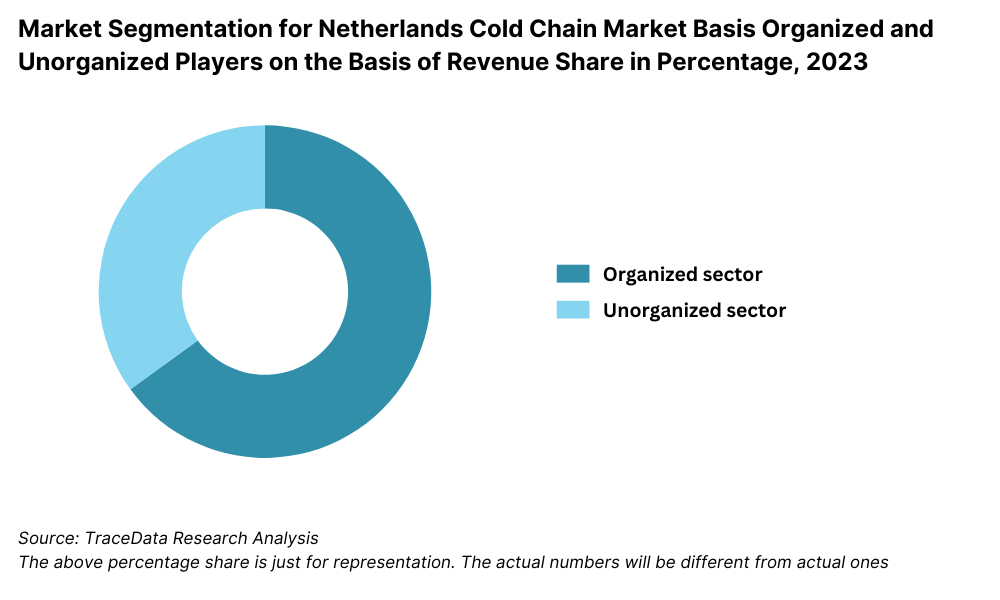
By Market Structure: The Netherlands cold chain market is largely dominated by organized players, owing to the country’s highly regulated environment and emphasis on compliance, efficiency, and sustainability. Large-scale integrated logistics companies operate sophisticated cold storage and transport networks, supported by automation, GDP certification, and carbon-reduction strategies. However, a small share is held by unorganized players, especially in rural and regional fresh produce segments, where cold infrastructure is often fragmented or reliant on small-scale operators.
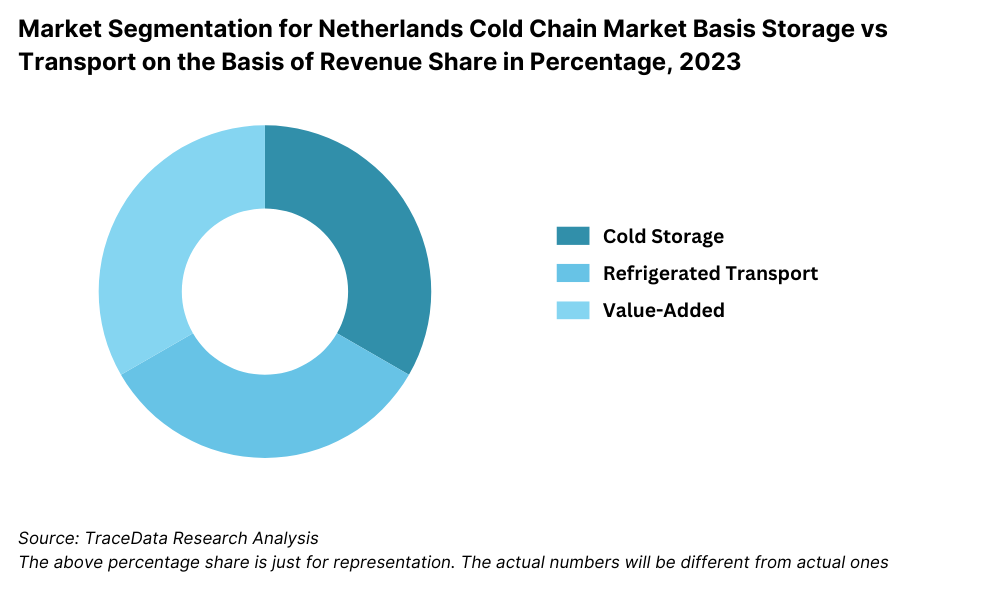
By Storage and Transport Type: Cold Storage Warehousing accounts for the largest share in the Netherlands cold chain market, driven by the growing demand from processed food, frozen seafood, and pharmaceutical sectors. These warehouses are often equipped with automated racking systems and remote temperature monitoring. On the other hand, Refrigerated Transportation – both short-haul and long-haul – is gaining traction, particularly with rising e-commerce and supermarket chains requiring temperature-controlled last-mile delivery for groceries, dairy, and meal kits.
By End-User Industry: The Food & Beverage sector is the dominant end-user of cold chain services in the Netherlands, accounting for a major share of the volume and revenue. The country’s status as a leading exporter of meat, dairy, and horticultural produce drives this demand. Pharmaceuticals and Life Sciences is the second-largest segment, supported by high-value temperature-sensitive products such as vaccines, biologics, and clinical trial materials that require GDP-compliant handling.
Competitive Landscape in Netherlands Cold Chain Market
The Netherlands cold chain market is moderately concentrated, with several large, international players leading the industry, supported by a mix of regional logistics providers and niche service specialists. The market is defined by high infrastructure quality, automation adoption, and compliance with EU regulatory frameworks. Key players include Lineage Logistics, Kloosterboer, NewCold, DFDS, and STEF Netherlands, with increasing investment in automation, sustainability, and digital integration.
Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
Lineage Logistics | 2008 | Novi, Michigan, USA |
Kloosterboer | 1925 | IJmuiden, Netherlands |
NewCold | 2012 | Breda, Netherlands |
DFDS Logistics | 1866 | Copenhagen, Denmark |
STEF Netherlands | 1920 | Bodegraven, Netherlands |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
Lineage Logistics: One of the world’s largest temperature-controlled logistics companies, Lineage significantly expanded its footprint in the Netherlands in 2023 by upgrading its Maasvlakte II Rotterdam facility with high-density automation. This resulted in a 15% increase in throughput efficiency, catering primarily to meat and dairy exporters.
Kloosterboer: With over 90 years in cold logistics, Kloosterboer opened a fully automated deep-freeze warehouse in 2023 in Lelystad with a capacity of 60,000 pallets. The facility is designed to operate with zero-emission refrigeration systems and solar energy support, aligning with national green logistics goals.
NewCold: NewCold operates one of the largest automated cold storages in Europe, located in Breda. In 2023, it entered new contracts with several multinational food brands, expanding its capacity utilization by 25% year-on-year. Their proprietary warehouse software and energy-efficient infrastructure position them as an innovation leader.
DFDS Logistics: With strong presence in maritime and overland refrigerated transport, DFDS reported a 20% growth in cross-border cold chain movements between the Netherlands and Scandinavian markets in 2023. Investments were made into electric refrigerated trucks and digitized route optimization.
STEF Netherlands: A key player in the food logistics space, STEF focused on increasing temperature traceability and regulatory compliance in 2023. The company saw a 12% increase in demand for its pharma cold chain services, driven by biopharma exports and vaccine distribution requirements.
What Lies Ahead for Netherlands Cold Chain Market?
The Netherlands cold chain market is projected to grow steadily through 2029, with an anticipated CAGR of 5.8% during the forecast period. Growth will be driven by rising exports of perishable goods, stringent EU regulations, sustainability mandates, and technological advancements in cold logistics infrastructure.
Rise of Pharmaceutical and Biotech Cold Chain: As the Netherlands continues to position itself as a life sciences hub in Europe, demand for GDP-compliant storage and transportation of temperature-sensitive products like vaccines, cell & gene therapies, and biologics is expected to surge. By 2029, the pharmaceutical cold chain segment is forecasted to contribute nearly 25% of total cold chain revenues, up from 18% in 2023.
Expansion of Sustainable and Green Logistics: In alignment with the Dutch Climate Agreement, cold chain operators are expected to adopt low-emission refrigeration technologies, electric reefer trucks, and solar-powered warehouses. By 2029, over 60% of new cold chain facilities are expected to be built with green certifications (e.g., BREEAM), significantly reducing the industry’s carbon footprint.
Digital Twin and Predictive Monitoring Integration: The integration of IoT sensors, digital twin models, and AI-driven temperature tracking will enhance real-time visibility and reduce spoilage rates across the cold chain. These innovations will allow predictive maintenance, risk alerts, and route optimization — driving efficiency gains of up to 20% across the logistics lifecycle.
Growth of Multi-User Automated Cold Storage Facilities: There is a growing shift toward shared cold storage models, especially for SMEs and exporters with variable volumes. Multi-client automated facilities will offer flexible leasing, robotic handling, and lower per-unit costs, making cold chain services more accessible to a wider segment of the market.
%2C%202023-2029.png)
Netherlands Cold Chain Market Segmentation
• By Market Structure:
Independent Cold Storage Warehouses
Integrated Cold Chain Service Providers
Cold Chain Transport Specialists
Multimodal Cold Logistics Companies
Organized Sector
Unorganized Sector
Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Cold Chain Providers
• By Storage and Transport Type:
Frozen Storage
Chilled Storage
Controlled Ambient Storage
Refrigerated Road Transport
Refrigerated Rail Transport
Refrigerated Sea Freight
Air Cargo with Temperature Control
• By End-User Industry:
Food & Beverage (Fruits, Vegetables, Meat, Dairy, Seafood)
Pharmaceuticals and Life Sciences
Retail and E-commerce
Flowers and Horticulture
Chemicals and Specialty Materials
Hospitality and Foodservice
• By Temperature Range:
Frozen (-18°C and below)
Chilled (2°C to 8°C)
Controlled Ambient (15°C to 25°C)
• By Region:
North Holland
South Holland
Limburg
North Brabant
Gelderland
Zeeland
Players Mentioned in the Report
Lineage Logistics
Kloosterboer
NewCold
DFDS Logistics
STEF Netherlands
Bakker Logistiek
Rhenus Logistics
H&S Coldstore
Key Target Audience
Cold Chain Logistics Companies
Food and Pharmaceutical Exporters
Retail and E-Commerce Distributors
Regulatory Bodies (e.g., Netherlands Food and Consumer Product Safety Authority – NVWA)
Port and Airport Authorities
Technology Solution Providers for Cold Storage and Monitoring
Cold Storage Equipment Manufacturers
Investors and Infrastructure Funds
Research and Policy Institutions
Time Period
Historical Period: 2018–2023
Base Year: 2024
Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
1. Executive Summary
2. Research Methodology
3. Ecosystem of Key Stakeholders in Netherlands Cold Chain Market
4. Value Chain Analysis
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and Challenges They Face
4.2. Revenue Streams for Netherlands Cold Chain Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Netherlands Cold Chain Market
4.4. Cold Storage Decision-Making Process
4.5. Cold Transport Decision-Making Process
5. Market Structure
5.1. Export Dependency of Perishable Products from the Netherlands, 2018-2024
5.2. Cold Chain Penetration Rate in Key Industries, 2018-2024
5.3. Investment in Cold Chain Infrastructure, 2024
5.4. Number of Cold Chain Warehouses and Refrigerated Trucks by Region
6. Market Attractiveness for Netherlands Cold Chain Market
7. Supply-Demand Gap Analysis
8. Market Size for Netherlands Cold Chain Market Basis
8.1. Revenues, 2018-2024
8.2. Capacity (in cubic meters and pallet positions), 2018-2024
9. Market Breakdown for Netherlands Cold Chain Market Basis
9.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized), 2023-2024P
9.2. By Storage and Transport Type, 2023-2024P
9.3. By Temperature Range (Frozen, Chilled, Ambient), 2023-2024P
9.4. By End-User Industry (Food, Pharma, Floral, Retail, Others), 2023-2024P
9.5. By Region (North Holland, South Holland, Limburg, etc.), 2023-2024P
10. Demand Side Analysis for Netherlands Cold Chain Market
10.1. Customer Landscape and Industry Cohort Analysis
10.2. Logistics Planning and Cold Chain Selection Process
10.3. Customer Need, Pain Points, and Preferences
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11. Industry Analysis
11.1. Trends and Developments for Netherlands Cold Chain Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Netherlands Cold Chain Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Netherlands Cold Chain Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges for Netherlands Cold Chain Market
11.5. Government Regulations for Netherlands Cold Chain Market
12. Snapshot on Technology Integration in Cold Chain
12.1. Use of IoT, Digital Twin, and Predictive Monitoring
12.2. Automation and Robotics in Cold Storage
12.3. Green Refrigeration Technologies
13. Financing and Investment Landscape in Netherlands Cold Chain Market
13.1. Investment Trends and Green Financing Initiatives
13.2. Infrastructure Investment by Public and Private Players
13.3. Sustainability-linked Incentives and Subsidies
14. Opportunity Matrix for Netherlands Cold Chain Market-Presented with the Help of Radar Chart
15. PEAK Matrix Analysis for Netherlands Cold Chain Market
16. Competitor Analysis for Netherlands Cold Chain Market
16.1. Benchmark of Key Competitors Including Company Overview, USP, Business Strategy, Strengths, Weaknesses, Technology Adoption, Revenue Contribution, and Storage/Transport Capacity
16.2. Strength and Weakness Matrix
16.3. Operating Model Analysis Framework
16.4. Gartner Magic Quadrant Positioning
16.5. Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
17. Future Market Size for Netherlands Cold Chain Market Basis
17.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
17.2. Capacity (in cubic meters and pallet positions), 2025-2029
18. Market Breakdown for Netherlands Cold Chain Market Basis
18.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized), 2025-2029
18.2. By Storage and Transport Type, 2025-2029
18.3. By Temperature Range, 2025-2029
18.4. By End-User Industry, 2025-2029
18.5. By Region, 2025-2029
18.6. Recommendations
18.7. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
We begin by mapping the complete ecosystem and identifying all demand-side and supply-side entities for the Netherlands Cold Chain Market. This includes cold storage operators, refrigerated transport service providers, pharmaceutical and food manufacturers, exporters, e-commerce players, and regulatory agencies.
Based on this ecosystem, we shortlist 5–6 leading players across the value chain, evaluating them based on parameters such as revenue, infrastructure capacity (e.g., pallet space, reefer fleet size), regional presence, and technological capabilities.
Sourcing for this stage is done via multiple secondary and proprietary sources such as industry associations, logistics publications, government databases (e.g., CBS, NVWA), and internal research archives.
Step 2: Desk Research
An extensive desk research process is conducted referencing secondary and proprietary databases, industry publications, and regulatory reports. This step allows us to aggregate critical market-level data including total cold chain capacity, historical revenue performance, pricing structures, number of players, and service breakdowns.
We also analyze individual company data by reviewing annual reports, sustainability disclosures, investor presentations, press releases, and case studies to build comprehensive profiles and benchmark their competitive positioning.
Step 3: Primary Research
We conduct a series of in-depth interviews with cold chain logistics providers, exporters (food, pharma, and chemicals), port and airport authorities, warehouse automation vendors, and other stakeholders. These interviews serve to validate market size estimates, test our hypotheses, and collect operational insights such as asset utilization rates, capacity expansion plans, and bottlenecks.
A bottom-up approach is applied to calculate volume capacity and revenue contributions by each player, aggregating them to arrive at the total market size.
We also implement disguised interviews, where our team approaches companies as potential partners or customers to verify storage costs, service levels, and technology deployments. This helps validate claims made in public disclosures and ensures a robust triangulation of data.
Step 4: Sanity Check
A dual-layered bottom-to-top and top-to-bottom validation model is applied using multiple reference points (e.g., installed cold storage capacity in cubic meters, revenue per pallet/month, reefer transport volume, export volumes of perishables). This ensures our market size models are consistent, credible, and reflect realistic growth expectations based on ground-level inputs and macroeconomic indicators.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Netherlands Cold Chain Market?
The Netherlands cold chain market is expected to witness robust growth, reaching a valuation of approximately EUR 9.5 Billion by 2029. This growth is driven by the country's strong export-oriented agri-food and pharmaceutical sectors, increasing demand for temperature-controlled logistics, and a strategic geographic position as a European distribution hub. The market’s potential is further amplified by rising sustainability mandates, advancements in automation, and increased investment in cold infrastructure.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Netherlands Cold Chain Market?
The Netherlands Cold Chain Market is led by major logistics and cold storage players including Lineage Logistics, Kloosterboer, NewCold, DFDS Logistics, and STEF Netherlands. These companies dominate the landscape through their extensive warehousing capacity, advanced temperature-monitoring systems, and integrated multimodal transportation networks. Regional players such as Bakker Logistiek and Rhenus Logistics also play significant roles, particularly in niche sectors like floral exports and temperature-sensitive retail goods.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Netherlands Cold Chain Market?
Key growth drivers include the country’s role as a gateway for perishable goods in Europe, driven by the Port of Rotterdam and Schiphol Airport. The expanding pharmaceutical and life sciences industry, coupled with strict EU regulations (GDP, HACCP), also fuels the demand for temperature-controlled storage and transport. Additionally, sustainability-focused investments (e.g., energy-efficient warehouses, electric reefer fleets) and adoption of automation and predictive technologies are accelerating operational efficiency and market growth.
4. What are the Challenges in the Netherlands Cold Chain Market?
The Netherlands Cold Chain Market faces several challenges, including high energy and infrastructure costs, which impact profitability, especially for smaller players. Urban congestion and delivery delays in high-density regions create last-mile inefficiencies. There is also a shortage of skilled technical workforce, particularly in warehouse automation, refrigeration systems, and regulatory compliance. Finally, aligning with evolving sustainability targets and CO₂ regulations requires significant capital investment, posing entry and scalability barriers for new players.