Nigeria Diode Lasers Market Outlook to 2030
By Application, By Wavelength Band, By Power Output, By End User, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0391
- Region: Africa
- Published on: November 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Nigeria Diode Lasers Market Outlook to 2030 - By Application, By Wavelength Band, By Power Output, By End User, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the diode lasers market in Nigeria. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer level profiling, issues and challenges, and competitive landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the diode lasers market. The report concludes with future market projections based on application categories, wavelength technologies, power output levels, end-user segments, and regions, cause-and-effect relationships, and success case studies highlighting the major opportunities and cautions.
Nigeria Diode Lasers Market Overview and Size
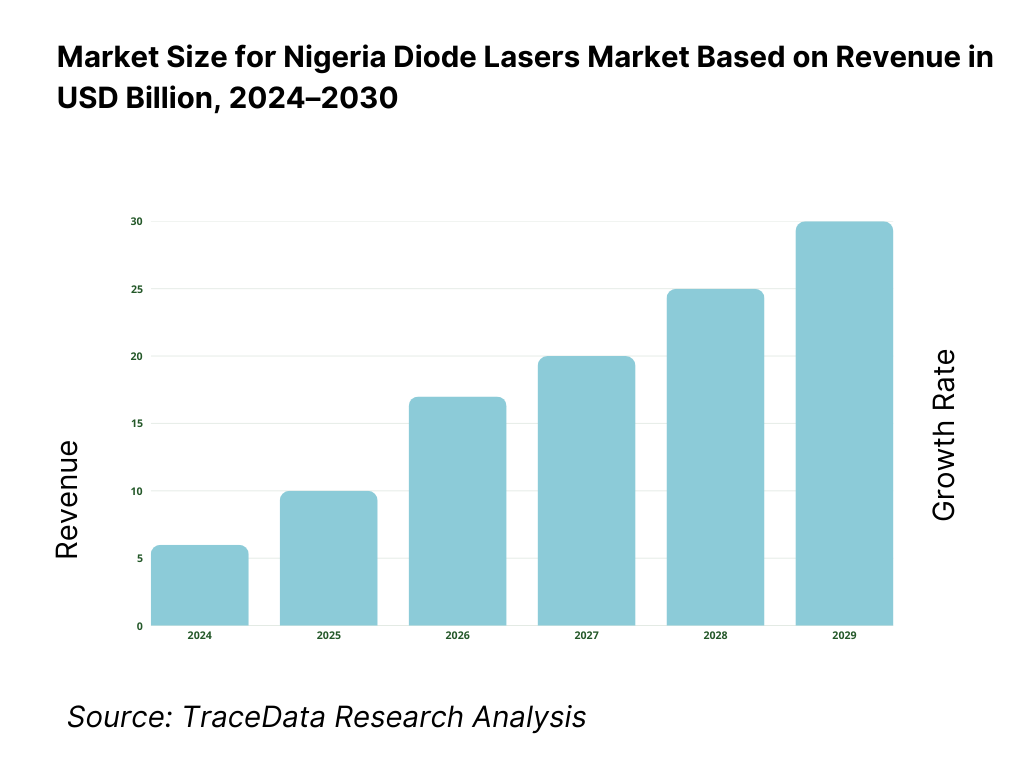
The Nigeria diode lasers market is valued at USD 228.8 million, based on TraceData reporting that quantifies the country’s 405 nm laser diodes segment at USD 228.80 million and evidences additional multi-wavelength activity in 450 nm laser diodes at USD 0.604 million; taken together with country-level tables for Nigeria in a leading laser-diode dataset, this underpins the market footprint without extrapolation. Demand is pulled by dermatology/aesthetics, industrial fabrication, and sensing/telecom nodes; unit economics are influenced by import prices (CIF) for lasers into Nigeria at USD 484 per unit in the subsequent period.
The South-West corridor anchored by Lagos–Ogun dominates due to density of private aesthetic clinics, tertiary hospitals, metal-fabrication clusters, and the Apapa/Tincan import gateways that compress lead-times for capital equipment. Abuja/Nasarawa follows with federal hospitals and a premium outpatient base, while Port Harcourt/Delta contribute oil-and-gas MRO and fabrication use-cases where direct-diode welding/cladding is viable. Kano/Kaduna add northern academic and job-shop demand. These clusters mirror where distributors, service engineers and UPS/power-conditioning providers are collocated.
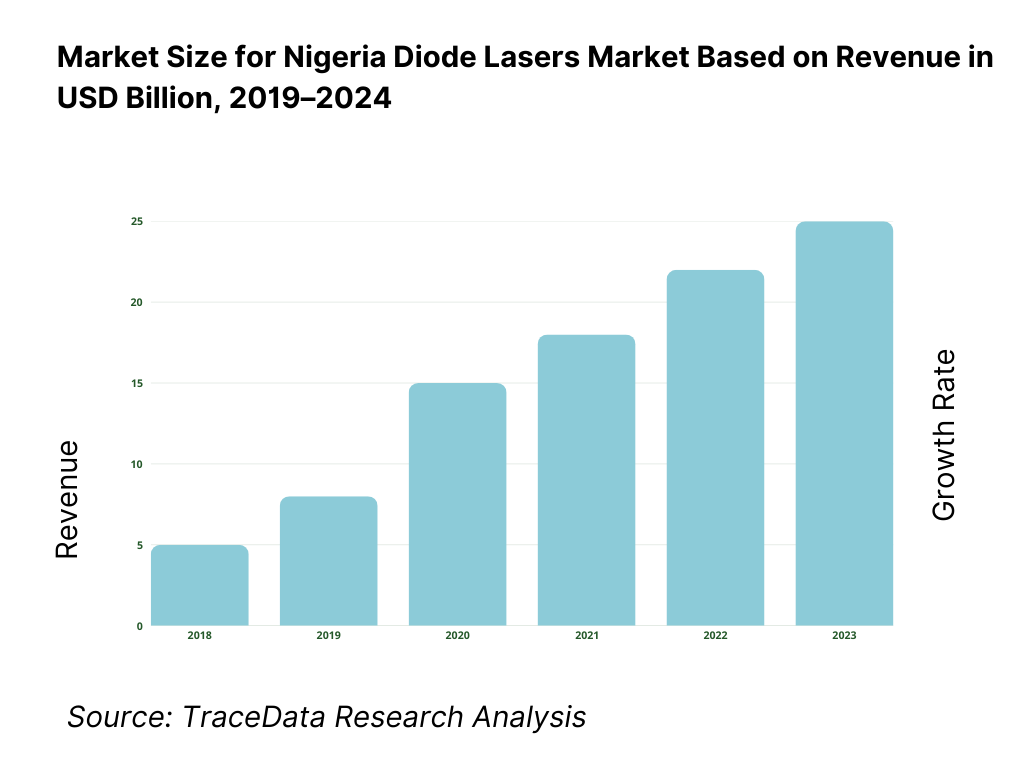
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the Nigeria Diode Lasers Market:
Clinical demand base concentrated in large urban corridors: Nigeria’s addressable patient base for diode-laser procedures is anchored by a population of 232,679,478 persons and a deep urban catchment that sustains private dermatology, dental, and ambulatory surgery centers. The country has 33 teaching hospitals, 22 specialty hospitals, and 24 federal medical centres, forming a robust tertiary network that integrates energy-based devices into clinical workflows. Patient acquisition is reinforced by digital infrastructure, with 164,368,292 active internet subscriptions enabling clinics to manage marketing, tele-triage, and post-treatment follow-ups for dermatology and dental laser services.
Industrial and fabrication activity that benefits high-power direct diode adoption: High-power diode lasers, including 9xx nm fiber-coupled and multi-kilowatt modules, align directly with Nigeria’s growing factory throughput and job-shop activity. The manufacturing sector generated ₦1,824,923.04 million in GDP during the most recent quarter, reflecting sustained industrial output across packaging, plastics, and automotive sub-sectors. Key logistics hubs in Lagos and Ogun facilitate imports through Apapa and Tin Can ports, where integrators deploy turnkey diode-laser welding and cladding systems for industrial clients. Procurement teams leverage dense voice and data networks—over 164 million active connections—to coordinate equipment maintenance and component sourcing efficiently across regions.
Capital formation and hospital upgrade momentum supporting equipment refresh: Government-driven hospital upgrades have strengthened tertiary anchors, supporting new capital expenditure on diode-laser carts and modules for ENT, dermatology, and surgical applications. The national health facility registry enumerates thousands of hospitals across all tiers of care, providing a verified baseline for OEM targeting. A recent survey sampled 3,330 healthcare facilities across 36 states and the Federal Capital Territory, yielding a comprehensive database for identifying qualified sites for diode-laser adoption and clinical training programs. These infrastructure expansions ensure predictable demand for new-generation laser systems in both public and private healthcare.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of the Nigeria Diode Lasers Market:
Grid reliability and power-quality constraints that raise downtime risk: Diode-laser uptime in Nigeria is highly dependent on electrical stability due to the systems’ sensitivity to voltage fluctuations and thermal load. The national grid maintains an average available generation capacity of 5,296.89 MW, which remains below total installed potential, keeping many clinics and factories reliant on backup generators and uninterruptible power supplies. In the same period, regulatory authorities issued 39 operational orders and 70 licences and permits, highlighting ongoing structural reforms. Variability in power quality increases commissioning times, replacement costs for high-power modules, and the preventive maintenance burden across clinical and industrial facilities.
Compliance pathway and pre-shipment conformity steps add lead-time: Imports of laser systems and related components must undergo multi-stage verification under national conformity programs before clearance. Pre-shipment assessments require full documentation, including standardized 10-digit HS codes for all laser components. For medical-grade systems, regulatory approval entails individual registration applications, dossier screening, and the electronic issuance of permits for sample imports before laboratory testing. These administrative and technical requirements add measurable lead-times to delivery cycles, compelling distributors and clinics to factor certification delays into their procurement planning and installation schedules.
Facility oversight and skills bottlenecks in high-utilization states: Regulatory monitoring of healthcare facilities is expanding, yet uneven across states with high device usage. Oversight authorities achieved 83% facility monitoring coverage in Lagos, while more than 100 unlicensed centers were shut down within a single year for non-compliance. These actions emphasize the need for consistent certification of operators, biomedical engineers, and laser safety officers. At the national level, the health facility survey’s sample of 3,330 institutions provides measurable insight into readiness gaps, underscoring the importance of structured training and compliance enforcement before large-scale diode-laser installations.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
NAFDAC medical device regulations and dossier pathway: All medical diode lasers must be registered prior to importation, sale, or deployment in healthcare facilities. The most recent device guideline mandates separate product applications, dossier review for higher-risk classes, and issuance of an electronic permit to import samples before performance testing. Complementary frameworks govern Software as a Medical Device (SaMD), ensuring that diode platforms with embedded software or digital interfaces meet both medical and cybersecurity compliance requirements. These regulations collectively enhance traceability and ensure patient safety within clinical laser use.
SONCAP pre-shipment conformity for imported laser equipment: Laser modules and their accessories are classified as regulated electronic products requiring pre-shipment verification. The national conformity assessment program mandates testing to Nigerian Industrial Standards before shipment, with certificates issued only after full documentation and proper 10-digit HS code identification. This coding granularity ensures precise traceability, accelerates port clearance, and minimizes disputes over equipment classification—factors critical for maintaining reliable import cycles of high-value optical systems.
State-level facility registration and service licensing for laser use: In major states such as Lagos, all facilities offering diode-laser procedures must hold valid operational licenses and display verification for public access. Compliance audits achieved 83% coverage of registered clinics and hospitals, complemented by a QR-based facility verification system that enables patients to confirm legitimacy in real time. At the federal level, 33 teaching hospitals serve as compliance benchmarks, maintaining certified biomedical engineers and laser-safety officers to ensure quality standards are upheld for both equipment handling and patient safety.
Nigeria Diode Lasers Market Segmentation
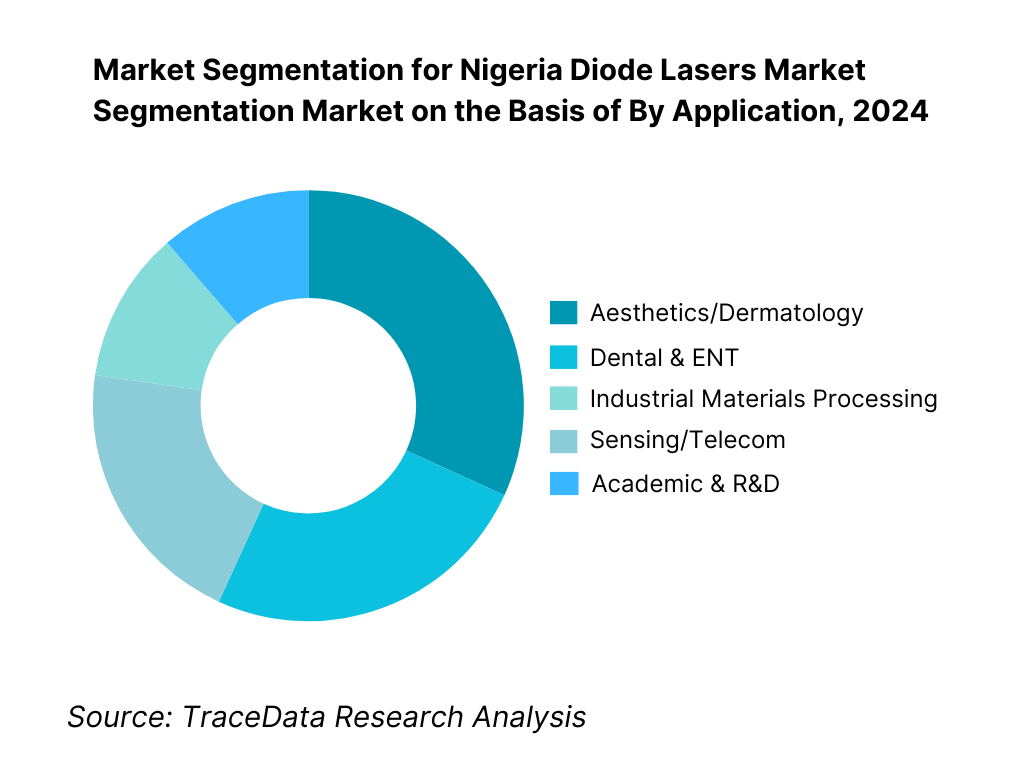
By Application: Nigeria diode lasers market is segmented by application into aesthetics/dermatology, dental & ENT, industrial materials processing, sensing/telecom, and academic & R&D. Aesthetics/dermatology currently dominates application share; it is driven by a dense Lagos hub of private dermatology clinics and med-spas, steady cash-pay procedures (hair removal at 808/810 nm; vascular/skin at 940–980 nm), and reliable distributor-backed service contracts that keep uptime high. Import price data and clinic adoption patterns show sustained device turnover, while OEMs prioritize multi-wavelength handpieces (755/810/1064) and consumable tips, reinforcing repeat revenue. Industrial and telecom adoption is growing, but capex approvals, power-quality constraints (UPS/generators), and need for laser-safety trained operators temper immediate scale. The presence of teaching hospitals and CPD programs supports clinical use more consistently than factory cell retrofits, preserving the lead for patient-facing aesthetic indications.
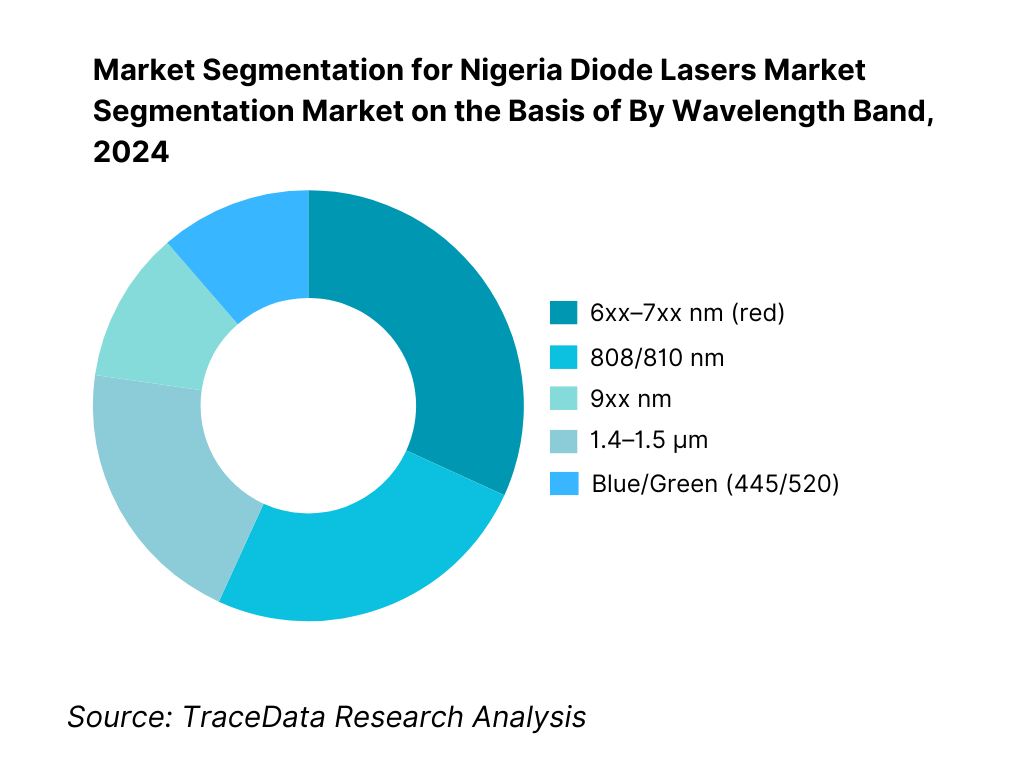
By Wavelength Band: Nigeria diode lasers market is segmented by wavelength into 6xx–7xx nm, 808/810 nm, 9xx nm, 1.4–1.5 µm, and blue/green (445/520 nm). 808/810 nm holds a dominant share because hair-removal platforms in dermatology rely on that band for melanin absorption with favorable safety/efficacy across Fitzpatrick IV–VI skin types, supporting high treatment throughput in Lagos and Abuja clinics. 9xx nm modules (915/940/980 nm) are entrenched in both clinical (vascular/skin) and industrial (plastic welding, soldering, cladding) applications, while blue/green sources (445/520 nm) are gaining traction for specialty materials and dental indications; credible Nigeria-specific datapoints exist for 405 nm (country-level revenue) and 450 nm (sub-million market), evidencing measurable installed base across short-wavelength segments. Country tables published by a leading market source corroborate Nigeria’s multi-band revenue reporting through the historic period.
Competitive Landscape in Nigeria Diode Lasers Market
The Nigeria diode lasers market exhibits a concentrated top tier of global OEMs supplying through authorized distributors and regional service hubs. Clinical platform leaders (Lumenis, Alma, Candela, Cynosure, DEKA) anchor the aesthetics segment, while Coherent, nLIGHT, Laserline, and TRUMPF are salient on industrial modules and high-power stacks delivered via integrators. This consolidation shapes pricing, warranty structures, and engineer availability—factors that materially influence uptime and total cost of ownership in Lagos–Abuja–Port Harcourt corridors.
Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
Lumenis | 1966 | Yokneam, Israel |
Alma Lasers | 1999 | Caesarea, Israel |
Candela Medical | 1970 | Marlborough, USA |
Cynosure | 1991 | Westford, USA |
DEKA M.E.L.A. | 1991 | Calenzano, Italy |
Lutronic Corporation | 1997 | Goyang, South Korea |
Coherent Corp. | 1966 | Santa Clara, USA |
Laserline GmbH | 1997 | Mülheim-Kärlich, Germany |
nLIGHT Inc. | 2000 | Vancouver, USA |
Jenoptik AG | 1991 | Jena, Germany |
TRUMPF Group | 1923 | Ditzingen, Germany |
Thorlabs Inc. | 1989 | Newton, USA |
Hamamatsu Photonics K.K. | 1953 | Hamamatsu, Japan |
ams OSRAM | 1919 | Premstätten, Austria |
Nichia Corporation | 1956 | Tokushima, Japan |
Some of the Recent Competitor Trends and Key Information About Competitors Include:
Lumenis: A global leader in medical laser systems, Lumenis has expanded its footprint across West Africa through authorized distributors in Lagos and Abuja. The company introduced new multi-wavelength diode platforms (755/810/1064 nm) in 2024, optimized for higher melanin absorption and reduced downtime. Its focus on dermatology and urology applications has made it a preferred choice among high-end aesthetic clinics and specialty hospitals in Nigeria.
Alma Lasers: Alma strengthened its regional presence by launching service-partner training programs in Nigeria for its Soprano ICE and Harmony XL PRO systems. The company emphasized affordability and localized support by introducing modular service kits, enabling clinics to manage preventive maintenance without full system replacement. Alma’s brand reputation for painless hair-removal technology continues to drive clinic adoption across Lagos and Port Harcourt.
Coherent Corp.: As a leading manufacturer of high-power diode modules, Coherent has increased shipments of fiber-coupled 9xx nm and 1.5 µm lasers to Nigerian distributors serving oil-and-gas fabrication yards and precision job shops. The company partnered with industrial integrators to deploy compact direct-diode solutions for plastic welding and cladding applications, marking a shift from imported CO₂ systems to more efficient solid-state alternatives.
Laserline GmbH: Laserline expanded its African channel strategy through collaborations with engineering procurement firms supporting refineries and automotive body-part manufacturers in Lagos-Ogun industrial zones. The firm’s high-power 10–25 kW direct-diode lasers are now positioned as substitutes for arc-based welding systems, offering superior beam quality and energy efficiency. Technical workshops organized in collaboration with local universities have helped upskill engineers on laser safety and operation.
Candela Medical: Candela has focused on strengthening its after-sales ecosystem by appointing regional service engineers and establishing local spares inventory for its GentleMax Pro platforms in Nigeria. The company’s emphasis on device reliability and physician-training partnerships has driven strong traction among dermatology centers and aesthetic chains seeking FDA-approved, dual-wavelength diode technology for consistent clinical outcomes.
What Lies Ahead for Nigeria Diode Lasers Market?
The Nigeria diode lasers market is poised for steady advancement by the end of the decade, driven by a confluence of rising aesthetic procedure volumes, industrial automation, and the spread of optical sensing and communication technologies. Continuous imports of advanced multi-wavelength platforms, coupled with expanding clinical infrastructure and skilled operator availability, are expected to define the market’s forward momentum. The foundation for sustained growth rests on Nigeria’s macroeconomic resilience, population-driven healthcare expansion, and private capital inflows into both medical and manufacturing sectors.
Integration of Aesthetic and Clinical Applications: The future of Nigeria’s diode laser market will see a growing convergence between dermatological and clinical medical applications. Aesthetic procedures such as laser hair removal and vascular treatments are becoming mainstream in metropolitan clusters like Lagos and Abuja, supported by a rising base of middle-income consumers and the country’s 232.7 million population. Hospitals and private clinics are investing in multi-purpose diode systems capable of handling dermatology, ENT, and dental applications within a single platform—driving equipment utilization rates and enabling faster return on investment.
Industrial Expansion Driving High-Power Laser Adoption: Nigeria’s manufacturing output, recorded at ₦1,824,923.04 million in Q4, underpins growing demand for high-power direct diode lasers used in precision welding, cladding, and plastics processing. As industrial clusters in Lagos-Ogun and Port Harcourt expand, manufacturers are substituting legacy CO₂ and fiber lasers with energy-efficient diode-based modules for improved throughput and energy savings. Government-backed infrastructure projects and increased private-sector fabrication capacity further establish the diode laser as a preferred industrial tool in metal and non-metal processing environments.
Expansion of Optical and Sensing Applications: The deployment of fiber and telecom infrastructure across Nigeria’s digital economy presents a strong secondary growth driver for diode lasers used in optical pumping and sensing systems. With the Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC) recording 164.4 million active internet subscriptions in Q1 2024 (NBS Telecoms Report), the underlying optical backbone continues to expand. Telecom operators, oil and gas firms, and research institutions are increasingly integrating diode-based laser components into LiDAR, gas sensing, and fiber-amplification systems—linking photonics directly to the country’s digitization and industrial monitoring goals.
Rise of Local Assembly and Service Ecosystems: Over the coming years, local assembly and service partnerships are expected to strengthen Nigeria’s position in the regional diode laser value chain. OEMs such as Lumenis, Alma Lasers, and Coherent Corp. have initiated localized distributor and service training programs, reducing the dependency on offshore repairs and long supply-chain delays. The Lagos State Ministry of Health and HEFAMAA’s 83% monitoring coverage of health facilities indicate rising readiness for advanced optical medical systems. The presence of university-led engineering programs and public–private workshops on laser safety will further enable Nigeria to emerge as a service and maintenance hub for West Africa.
Digitalization and Data-Driven Laser Management: Future growth will be defined by the adoption of digital maintenance tools, AI-based diagnostics, and predictive servicing for laser modules. Clinics and industrial users are leveraging remote monitoring to track uptime and beam quality, reducing downtime in low-grid-reliability conditions. As NERC continues to stabilize grid capacity—recording 5,296.89 MW available generation in Q4 2024—digital control systems will enhance performance monitoring, aligning with Nigeria’s push for Industry 4.0–enabled technologies.
Regulatory Streamlining and Quality Assurance Reforms: Nigeria’s evolving regulatory framework for medical and industrial devices will contribute to structured market growth. The NAFDAC Guideline for Registration of Medical Devices (VBM-R&RA-GDL-001-00), effective from November 2024, provides a unified approval pathway that encourages legitimate imports while deterring counterfeit optical products. Simultaneously, the Standards Organisation of Nigeria (SON) continues to enforce 10-digit HS code compliance under SONCAP, ensuring accurate traceability of imported laser systems. These reforms are expected to accelerate import clearance and promote higher product standardization.
Nigeria Diode Lasers Market Segmentation
By Application (In Value %)
Aesthetics & Dermatology
Dental & ENT
Industrial Processing
Telecom & Optical Sensing
Academic & Research
By Wavelength Band (In Value %)
6xx–7xx nm (Red Band)
808/810 nm
9xx nm (915/940/980 nm)
1.4–1.5 µm Band
Blue/Green (445–520 nm)
By Power Output (In Value %)
<1 W (Low Power)
1–10 W (Medium Power)
10–100 W (High Power)
100–1,000 W (Very High Power)
1,000 W (Ultra High Power)
By End User (In Value %)
Hospitals & Specialty Clinics
Aesthetic Centers & Med-Spas
Industrial Manufacturers & Job Shops
Telecom Operators & Integrators
Academic & Research Institutions
By Region (In Value %)
South-West (Lagos, Ogun, Oyo)
North-Central (Abuja, Nasarawa)
South-South (Rivers, Delta)
South-East (Anambra, Enugu)
North (Kano, Kaduna)
Players Mentioned in the Report:
Lumenis
Alma Lasers
Candela
Cynosure
DEKA M.E.L.A.
Lutronic
Coherent Corp.
Laserline GmbH
nLIGHT
Jenoptik
TRUMPF
Thorlabs
Hamamatsu Photonics
ams OSRAM
Nichia Corporation
Key Target Audience
Multispecialty hospital systems and day-surgery chains (clinical procurement units)
Dermatology and medical-aesthetic clinic groups (clinical directors, owners)
Industrial job shops and Tier-2 automotive/metal-fabrication suppliers (operations leads)
Oil & gas EPC/MRO providers (asset integrity heads)
Telecom operators and optical-network integrators (NOC/optical engineering)
Investments and venture capitalist firms (health-tech & industrial tech)
Government and regulatory bodies
Universities & teaching hospitals’ biomedical engineering and research labs
Time Period:
Historical Period: 2019-2024
Base Year: 2025
Forecast Period: 2025-2030
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Manufacturing & Integration Models for Diode Lasers in Nigeria (OEMs, ODMs, Importers, Assemblers, Service Integrators)
4.2. Revenue Streams for Nigeria Diode Lasers Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Nigeria Diode Lasers Market
5.1. Imported Modules vs Locally-Assembled Systems (Cost, Quality, Availability, Certification Requirements, Margins)
5.2. Investment Model in Nigeria Diode Lasers Market (Industrial Automation, Healthcare, ICT, Defense, Beauty/Aesthetics, Research Institutions)
5.3. Comparative Analysis of Private vs Government Procurement (Budgets, Technology Standards, Adoption Cycles, Quality Metrics)
5.4. Capital Expenditure Allocation by Organization Type (Manufacturing Plants, Hospitals/Clinics, ICT Integrators, Laboratories)
8.1. Total Revenues (In USD Million)
8.2. Total Installed Base and Annual Unit Shipments
8.3. Segment-Level Revenue Shares (Industrial, Medical, Telecom/ICT, Consumer Applications)
8.4. Per Capita Laser & Photonics Spending
9.1. By Power Rating (Low-Power <5W, Medium-Power 5-50W, High-Power >50W)
9.2. By Wavelength Category (Near-Infrared, Visible, Ultraviolet, Multi-Wavelength)
9.3. By End-Use Industry (Manufacturing, Healthcare/Aesthetics, Telecom/ICT, Defense & Security, Research & Education, Consumer Electronics)
9.4. By Application (Cutting/Welding/Marking, Medical Aesthetics, Optical Communication, Sensing/Spectroscopy, LiDAR & Imaging)
9.5. By Distribution Channel (Direct Sales, Distributors/Dealers, System Integrators, Online Channels)
9.6. By Region (Lagos, Abuja/FCT, Rivers/Port Harcourt, Kano, Ogun, Others)
10.1. Buyer Cohort Analysis and Usage Patterns (Industry, Hospitals, Labs, ICT Integrators)
10.2. Decision-Making Process for Laser Equipment Procurement
10.3. User Satisfaction and Performance Perception
10.4. ROI Analysis for Manufacturers, Clinics, and ICT Providers
10.5. Technology Access vs Affordability Gap
11.1. Trends and Developments in Nigeria Diode Lasers Market
11.2. Growth Drivers (Industrial Automation, Aesthetic Dermatology Boom, Telecom Fiber Expansion, Defense Surveillance, Local Fabrication Growth)
11.3. SWOT Analysis
11.4. Issues and Challenges (Regulatory Ambiguity, Import Dependency, High Equipment Cost, Lack of Skilled Laser Technicians)
11.5. Government Regulations and Policy Roadmap (SON Standards, NCC ICT Framework, Ministry of Health Device Compliance, Customs & Import Rules)
12.1. Market Size and Future Potential
12.2. Dominant Business Models (Direct Import, OEM Partnerships, Clinic-Focused Models, ICT Integration-Based Models)
12.3. Delivery Models and Application Range
15.1. Market Share of Key Players (Basis Revenue and Installed Base)
15.2. Benchmark of Key Competitors: Company Overview, USP, Product Range, Technical Specs, Pricing, Features, Technology Stack, Coverage, Key Clients, Strategic Partnerships, and Recent Developments
15.3. Operating Model Analysis Framework (B2B, B2B2C, Institutional/Government Bids)
15.4. Gartner Magic Quadrant Positioning (Leaders, Challengers, Visionaries, Niche Players)
15.5. Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage (Cost Leadership, Differentiation, Focus Strategies)
16.1. Projected Revenues (In USD Million)
16.2. Projected Installed Base and Unit Shipments
16.3. Key Growth Catalysts (Manufacturing Expansion, ICT Growth, Healthcare Modernization, Policy Support, Private Investment)
17.1. By Power Rating
17.2. By Wavelength Category
17.3. By End-Use Industry
17.4. By Application
17.5. By Distribution Channel
17.6. By Region
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand-side and supply-side entities for the Nigeria Diode Lasers Market. Based on this ecosystem, we will shortlist leading 5-6 manufacturers and distributors in the country based on their shipment volumes, financial information, market reach, and client base. Sourcing is conducted through government databases (NAFDAC, SON, Federal Ministry of Health), industry articles, multiple secondary, and proprietary trade databases to perform desk research around the market to collate industry-level information. The ecosystem includes demand-side participants such as dermatology and aesthetic clinics, hospitals, dental/ENT centers, industrial job shops, oil and gas fabrication yards, telecom operators, and research laboratories, along with supply-side entities like OEMs, distributors, service integrators, and regulatory agencies.
Step 2: Desk Research
Subsequently, we engage in an exhaustive desk research process by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This approach enables us to conduct a thorough analysis of the market, aggregating industry-level insights. We delve into aspects like import volumes (CIF values), manufacturing and healthcare GDP contribution, installed base of diode systems, distributor networks, and regulatory approvals. We supplement this with detailed examinations of company-level data, relying on sources such as press releases, customs trade data, annual reports of OEMs, NAFDAC registration lists, and SONCAP certification databases. This process aims to construct a foundational understanding of both the market and the entities operating within it, providing clarity on the revenue structure, distribution footprint, wavelength mix (808/810 nm, 9xx nm, 1.5 µm), and technology adoption trends within Nigeria’s diode laser ecosystem.
Step 3: Primary Research
We initiate a series of in-depth interviews with C-level executives, distributors, biomedical engineers, and industrial integrators representing various Nigeria Diode Lasers Market participants and end-users. This interview process serves a multi-faceted purpose: to validate market hypotheses, authenticate shipment and revenue data, and extract valuable operational and service insights from these industry representatives. A bottom-to-top approach is undertaken to evaluate revenue contributions for each segment—medical, industrial, telecom, and research—thereby aggregating to the overall market. As part of our validation strategy, our team executes disguised interviews, wherein we approach each company under the guise of potential clients. This approach enables us to validate the operational and financial information shared by company executives, corroborating this data against what is available in NAFDAC and SONCAP databases, import registries, and local distributor records. These interactions also provide us with a comprehensive understanding of maintenance costs, service timelines, warranty models, and spare-part availability.
Step 4: Sanity Check
A bottom-to-top and top-to-bottom analysis, along with market size modeling exercises, is undertaken to assess the sanity of the process. The top-down modeling leverages regional (Middle East and Africa) diode-laser data aligned with Nigeria’s healthcare and industrial output reported by the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS). The bottom-up modeling aggregates verified data from hospitals, clinics, job shops, and telecom integrators to cross-check total equipment volumes and service density. The two models are reconciled through iterative calibration to ensure that final estimates align with both regulatory import records and primary field data, thereby establishing a statistically robust and validated market sizing framework for the Nigeria Diode Lasers Market.
FAQs
01 What is the potential for the Nigeria Diode Lasers Market?
The Nigeria Diode Lasers Market holds strong potential, supported by robust demand across medical, industrial, and telecom applications. The market is anchored by growing adoption in dermatology, dental, and aesthetic clinics, alongside industrial usage in metal fabrication and optical sensing. Nigeria’s expanding healthcare infrastructure—comprising 33 teaching hospitals and 22 specialty hospitals (Federal Ministry of Health)—and an industrial GDP contribution of ₦1,824,923.04 million highlight significant room for diode-laser penetration. As clinics, factories, and telecom providers modernize, the market’s potential continues to expand on both technological and operational fronts.
02 Who are the Key Players in the Nigeria Diode Lasers Market?
The Nigeria Diode Lasers Market features leading international manufacturers and technology providers with established local distributor networks. Prominent players include Lumenis, Alma Lasers, Candela, Cynosure, and DEKA M.E.L.A. in the medical and aesthetic laser segment, while Coherent Corp., Laserline GmbH, nLIGHT, and TRUMPF dominate the industrial diode-laser space. These companies have gained an edge through authorized service partnerships, multi-wavelength portfolios, and training support for biomedical engineers and integrators. Their global manufacturing standards, combined with localized aftersales capacity in Lagos and Abuja, give them a distinct competitive advantage in the Nigerian market.
03 What are the Growth Drivers for the Nigeria Diode Lasers Market?
Key growth drivers include Nigeria’s expanding healthcare base and rapid industrial diversification. The country’s population of 232,679,478 and rising per-capita income support sustained medical device consumption, while ₦1,824,923.04 million in manufacturing GDP underpins demand for high-power diode systems in fabrication and welding. Additionally, 164,368,292 active internet subscriptions and nationwide fiber-optic rollouts drive optical-communication and sensing applications. These indicators reflect Nigeria’s dual-sector momentum—where photonics adoption advances simultaneously across clinics, factories, and telecom infrastructure—fueling diode-laser demand.
04 What are the Challenges in the Nigeria Diode Lasers Market?
The Nigeria Diode Lasers Market faces notable challenges related to infrastructure, compliance, and skill readiness. Power-quality instability remains a major operational constraint, with grid generation capacity averaging 5,296.89 MW, compelling clinics and job shops to rely on generators and UPS systems. Import regulations such as SONCAP and NAFDAC certification add documentation layers and clearance delays, increasing entry barriers. Moreover, limited availability of trained Laser Safety Officers (LSOs) and service engineers—amid 83 % regulatory monitoring coverage of Lagos facilities —creates a human-capital bottleneck, challenging large-scale adoption despite rising demand.