Norway Auto Finance Market Outlook to 2029
By Loan Provider Type, By Vehicle Type (New vs Used), By Type of Lenders (Bank vs NBFC vs Captive Finance), By Tenure, By Interest Rate Bracket, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0169
- Region: Europe
- Published on: May 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Norway Auto Finance Market Outlook to 2029 – By Loan Provider Type, By Vehicle Type (New vs Used), By Type of Lenders (Bank vs NBFC vs Captive Finance), By Tenure, By Interest Rate Bracket, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the auto finance market in Norway. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of credit disbursed, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer level profiling, issues and challenges, and comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the auto finance market. The report concludes with future market projections based on loan disbursed, by vehicle segment, lender type, region, and success case studies highlighting the major opportunities and cautions.
Norway Auto Finance Market Overview and Size
The Norway auto finance market reached a valuation of NOK 72 Billion in 2023, driven by high vehicle ownership rates, a strong economy, and a significant shift towards electric vehicles. The market is dominated by major players such as Santander Consumer Bank, DNB Bank, Nordea Finance, Brage Finans, and Volkswagen Møller Bilfinans. These institutions have developed extensive partnerships with dealers and manufacturers and provide attractive financing options, especially for environmentally friendly vehicles.
In 2023, DNB Bank expanded its digital auto loan platform, integrating AI-driven credit scoring to streamline application processes. Oslo and Bergen represent the highest concentration of financed vehicle purchases due to high urban vehicle density and better financial infrastructure.
Market Size for Norway Auto Finance Industry on the Basis of Loan Disbursed, 2018–2023

What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Norway Auto Finance Market:
Environmental Shift and EV Adoption: Norway's aggressive push for electric vehicle (EV) adoption—supported by tax incentives and toll exemptions—has encouraged lenders to offer special financing products for EVs. In 2023, over 80% of new vehicles financed were electric, with interest rates typically 0.5–1.0% lower for green vehicles.
Digital Financial Services Penetration: The digitalization of the banking and lending sector has simplified the auto loan process. Approximately 55% of auto finance applications were completed via online channels in 2023, with digital identity verification and e-signature capabilities increasing processing speeds and approval rates.
Consumer Behavior and Ownership Trends: With a high preference for car ownership among Norwegians and an increasing population of young urban professionals, demand for auto finance has grown steadily. Around 62% of car buyers in 2023 utilized some form of financing, with many opting for monthly installments over upfront payment due to favorable interest rates.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for Norway Auto Finance Market
Stringent Credit Requirements: Norway’s strong financial regulations and conservative banking practices often lead to stricter creditworthiness checks. Around 42% of applicants in 2023 were rejected due to insufficient credit scores or unstable income patterns, particularly affecting younger buyers and immigrants. This has reduced the potential customer base for auto loans.
High Cost of Borrowing: Due to Norway’s rising interest rate environment in recent years, average auto loan interest rates have increased to 5.2% in 2023, up from 3.8% in 2020. This upward trend has made financing less attractive for buyers, particularly for non-essential or luxury vehicles, and has delayed vehicle purchases in many cases.
Limited Financing Options for Used EVs: While demand for electric vehicles (EVs) is soaring, banks and NBFCs are hesitant to finance older or second-hand EVs due to concerns over battery lifespan and resale value. Approximately 29% of used EV buyers in 2023 reported difficulties in securing financing, limiting broader adoption among price-sensitive consumers.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market
Responsible Lending Practices: The Financial Supervisory Authority of Norway (Finanstilsynet) mandates strict income-to-debt ratios, including a 5x income borrowing cap and stress tests on interest rate hikes. These regulations, although aimed at preventing debt bubbles, limit loan eligibility for many households. In 2023, nearly 30% of rejected applications were attributed to regulatory income constraints.
Incentives for Electric Vehicle Financing: The Norwegian government continues to push green financing through interest subsidies and tax exemptions on EV loans. Auto finance companies offering green loans can access favorable regulatory treatment and lower reserve requirements. In 2023, green auto loans made up 34% of total disbursements, up from 21% in 2021.
Open Banking Regulation: Norway’s implementation of PSD2 regulations has enabled greater data sharing between banks and third-party lenders, improving credit assessments and streamlining loan approvals. As of 2023, more than 60% of auto loan applicants utilized digital tools connected via open banking, boosting efficiency and customer experience across the industry.
Norway Auto Finance Market Segmentation
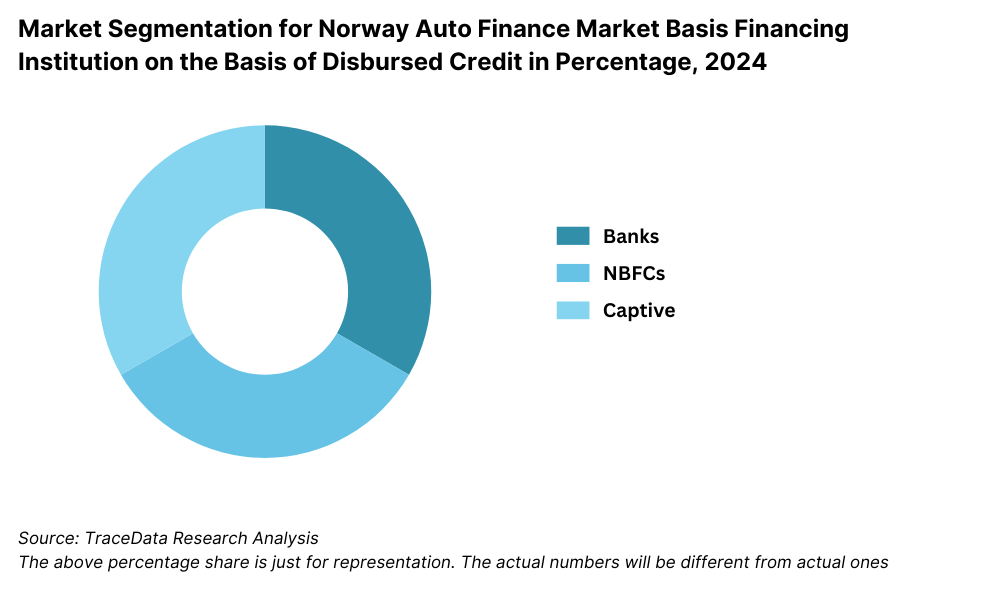
By Loan Provider Type: Banks dominate the auto finance market in Norway due to their long-standing customer relationships, low interest rate offerings, and high trust factor. Major Norwegian banks such as DNB, Nordea, and SpareBank 1 offer tailored auto loan products with flexible terms. Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) and digital-only lenders are growing in popularity, particularly among younger demographics looking for faster approvals and fully digital application experiences. Captive finance companies, such as Volkswagen Møller Bilfinans and Toyota Financial Services, maintain a significant share by offering promotional rates and brand-specific benefits at the point of sale.
By Vehicle Type (New vs Used): New car financing continues to lead in Norway due to a strong demand for electric vehicles, which are primarily sold new. In 2023, around 64% of total auto loans were for new vehicles. Used vehicle financing, although lower, is gradually increasing due to rising prices of new EVs and a maturing used EV market. Financing of used cars is particularly prominent in suburban and rural areas where affordability plays a bigger role in buyer decisions.

By Tenure of Loan: The most common auto loan tenure in Norway ranges between 3 to 5 years, accounting for a majority of loans in 2023. This range balances affordability with faster loan completion, helping consumers avoid long-term debt. However, 5–7 year loans have become more popular recently, especially among younger consumers buying electric vehicles, as longer terms reduce monthly payments.
Competitive Landscape in Norway Auto Finance Market
The Norway auto finance market is moderately concentrated, with established banks and captive finance arms of global automotive brands playing dominant roles. The market has seen increased diversification in recent years with the emergence of fintech lenders and green-focused financial platforms. Key players such as DNB Bank, Santander Consumer Bank, SpareBank 1, Nordea Finance, and Volkswagen Møller Bilfinans continue to lead, while newcomers like Aprila Bank and LeasePlan Bank are introducing flexible digital solutions.
| Company Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
| DNB | 1822 | Oslo, Norway |
| Santander Consumer Bank | 2001 | Oslo, Norway |
| Drivalia Lease Norway | 2023 | Stabekk, Norway |
| Axo Finans | 2008 | Oslo, Norway |
| Lendo Group | 2007 | Stockholm, Sweden |
| Motty | 2020 | Oslo, Norway |
| SpareBank 1 Gruppen | 1996 | Oslo, Norway |
| Bertel O. Steen Finans | 1901 | Lørenskog, Norway |
| Bank Norwegian | 2007 | Fornebu, Norway |
| Eika Gruppen | 1997 | Oslo, Norway |
| CA Auto Finance Norge AS | 2023 | Oslo, Norway |
| DLL Group | 1969 | Eindhoven, Netherlands |
| Resurs Bank | 2001 | Helsingborg, Sweden |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
DNB Bank: As Norway's largest financial institution, DNB reported NOK 15 billion in auto loans disbursed in 2023, driven by aggressive EV financing campaigns. The bank also rolled out a mobile-first auto loan approval platform that cut processing times by 40%.
Santander Consumer Bank: Known for its strong partnerships with car dealerships and manufacturers, Santander maintained its market lead in used car financing. In 2023, it introduced green auto loan packages offering 0.5% interest rate discounts on electric vehicles.
SpareBank 1 Finans: With a focus on regional lending and personalized customer service, SpareBank 1 saw a 12% year-on-year growth in auto loan disbursement. It recently launched a loyalty program tied to insurance and banking products for auto loan customers.
Nordea Finance: Nordea introduced flexible repayment schemes and early settlement benefits in 2023, attracting urban millennials. Its auto finance portfolio expanded by 9% year-over-year, with digital channels contributing to 60% of new applications.
Volkswagen Møller Bilfinans: The captive finance arm of Volkswagen maintained a strong presence with brand-specific promotions and bundled maintenance packages. It financed over 18,000 new and used vehicles in 2023, primarily EVs and plug-in hybrids.
Aprila Bank: A rising fintech lender, Aprila Bank gained attention for offering near-instant loan approvals using AI-driven credit checks. It saw a 40% increase in customer acquisition during 2023, primarily in the used car loan segment.
LeasePlan Bank: While traditionally focused on leasing, LeasePlan expanded into private auto loans with flexible terms and subscription-like models. Its pilot programs in Oslo and Bergen showed promising uptake among younger, environmentally conscious consumers.


What Lies Ahead for Norway Auto Finance Market?
The Norway auto finance market is projected to continue its upward trajectory through 2029, supported by the country’s robust economic fundamentals, rising adoption of electric vehicles, and the digital transformation of the financial services industry. The market is expected to register a stable CAGR during the forecast period.
Acceleration of Green Financing: With Norway leading Europe in EV adoption, the auto finance sector is expected to see a rapid shift toward green loan products. Government subsidies, tax breaks, and lender-specific incentives for electric and low-emission vehicles will drive this trend, with green auto loans anticipated to surpass 50% of total disbursements by 2029.
Digital-First Lending Experience: Auto finance providers are increasingly investing in AI-driven credit assessment tools, instant digital approvals, and app-based customer interfaces. These advancements are expected to streamline the loan application process, reduce approval times, and enhance customer satisfaction, especially among digitally native consumers.
Personalized Financial Products: The market will likely witness the expansion of flexible auto loan structures, including income-linked EMIs, subscription-based ownership, and bundled insurance-finance packages. These offerings will appeal to younger consumers seeking convenience, customization, and lower financial risk.
Expansion of Used EV Financing: As the used EV market in Norway matures, financial institutions are expected to develop specific credit models and risk frameworks for pre-owned electric vehicles. Improvements in battery diagnostics and vehicle history tracking will further enable financing of older EVs, expanding access to more cost-conscious buyers.
Future Outlook and Projections for Norway Car Finance Market Size on the Basis of Loan Disbursements in USD Billion, 2024-2029

Norway Auto Finance Market Segmentation
• By Loan Provider Type:
o Banks
o Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)
o Captive Finance Companies
o Online/Fintech Lenders
• By Vehicle Type:
o New Vehicles
o Used Vehicles
o Electric Vehicles (EVs)
o Hybrid Vehicles
o Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles
• By Loan Tenure:
o Less than 2 years
o 2–3 years
o 3–5 years
o 5–7 years
• By Interest Rate Bracket:
o Below 3%
o 3%–5%
o 5%–7%
o Above 7%
• By Age of Vehicle:
o Less than 2 years
o 2–4 years
o 5–7 years
o Over 7 years
• By Age of Consumer:
o 18–29 years
o 30–44 years
o 45–59 years
o 60+ years
• By Region:
o Eastern Norway (Oslo, Viken)
o Western Norway (Bergen, Stavanger)
o Central Norway (Trøndelag)
o Northern Norway (Troms og Finnmark)
o Southern Norway (Agder, Vestfold og Telemark)
Players Mentioned in the Report (Banks):
- DNB Bank
- Nordea Bank Norge
- Handelsbanken Norway
- SpareBank 1 SR-Bank
- SpareBank 1 Østlandet
- Storebrand Bank
- BN Bank
- Sbanken
- Santander Consumer Bank
- Bank Norwegian
Players Mentioned in the Report (NBFCs):
- Axo Finans
- Lendo Group
- Motty
- Instabank
- yA Bank
- Svea Finans
- Klarna
- Qred
- Anyfin
- Froda
Players Mentioned in the Report (Captive):
- Toyota Kreditbank
- Volkswagen Financial Services
- BMW Financial Services
- Mercedes-Benz Financial Services
- Ford Credit
- GMAC Bank
- Scania Finans
- Hyundai Capital
- Nissan Finance
- Stellantis Financial Services
Key Target Audience:
• Auto Finance Companies
• Commercial Banks and NBFCs
• Online Lending Platforms
• Automobile Manufacturers and Dealerships
• Regulatory Bodies (e.g., Finanstilsynet – Financial Supervisory Authority of Norway)
• Market Research and Consulting Firms
Time Period:
• Historical Period: 2018–2023
• Base Year: 2024
• Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and challenges they face.
4.2. Relationship and Engagement Model between Banks-Dealers, NBFCs-Dealers and Captive-Dealers-Commission Sharing Model, Flat Fee Model and Revenue streams
5.1. New Car and Used Car Sales in Norway by type of vehicle, 2018-2024
8.1. Credit Disbursed, 2018-2024
8.2. Outstanding Loan, 2018-2024
9.1. By Market Structure (Bank-Owned, Multi-Finance, and Captive Companies), 2023-2024
9.2. By Vehicle Type (Passenger, Commercial and EV), 2023-2024
9.3. By Region, 2023-2024
9.4. By Type of Vehicle (New and Used), 2023-2024
9.5. By Average Loan Tenure (0-2 years, 3-5 years, 6-8 years, above 8 years), 2023-2024
10.1. Customer Landscape and Cohort Analysis
10.2. Customer Journey and Decision-Making
10.3. Need, Desire, and Pain Point Analysis
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11.1. Trends and Developments for Norway Car Finance Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Norway Car Finance Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Norway Car Finance Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges for Norway Car Finance Market
11.5. Government Regulations for Norway Car Finance Market
12.1. Market Size and Future Potential for Online Car Financing Aggregators, 2018-2029
12.2. Business Model and Revenue Streams
12.3. Cross Comparison of Leading Digital Car Finance Companies Based on Company Overview, Revenue Streams, Loan Disbursements/Number of Leads Generated, Operating Cities, Number of Branches, and Other Variables
13.1. Finance Penetration Rate and Average Down Payment for New and Used Cars, 2018-2029
13.2. How Finance Penetration Rates are Changing Over the Years with Reasons
13.3. Type of Car Segment for which Finance Penetration is Higher
17.1. Market Share of Key Banks in Norway Car Finance Market, 2024
17.2. Market Share of Key NBFCs in Norway Car Finance Market, 2024
17.3. Market Share of Key Captive in Norway Car Finance Market, 2024
17.4. Benchmark of Key Competitors in Norway Car Finance Market, including Variables such as Company Overview, USP, Business Strategies, Strengths, Weaknesses, Business Model, Number of Branches, Product Features, Interest Rate, NPA, Loan Disbursed, Outstanding Loans, Tie-Ups and others
17.5. Strengths and Weaknesses
17.6. Operating Model Analysis Framework
17.7. Gartner Magic Quadrant
17.8. Bowmans Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
18.1. Credit Disbursed, 2025-2029
18.2. Outstanding Loan, 2025-2029
19.1. By Market Structure (Bank-Owned, Multi-Finance, and Captive Companies), 2025-2029
19.2. By Vehicle Type (Passenger, Commercial and EV), 2025-2029
19.3. By Region, 2025-2029
19.4. By Type of Vehicle (New and Used), 2025-2029
19.5. By Average Loan Tenure (0-2 years, 3-5 years, 6-8 years, above 8 years), 2025-2029
19.6. Recommendations
19.7. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand side and supply side entities for the Norway Auto Finance Market. Based on this ecosystem, we shortlisted 5–6 leading financial institutions and auto loan providers in the country, selected using criteria such as financial performance, loan disbursement volume, market share, and digital penetration.
Sourcing was conducted using industry whitepapers, regulatory publications, financial databases, company websites, and relevant Nordic market reports to perform desk research and compile macro and micro-level industry insights.
Step 2: Desk Research
We then conducted an extensive desk research process using various secondary and proprietary databases. This included a deep dive into market sizing, consumer behavior, loan tenures, interest rate trends, regional penetration, and EV-specific financing. We analyzed company financials, published loan books, investor presentations, news releases, and official industry data published by Statistics Norway, Finanstilsynet (FSA), and automotive industry groups.
This step enabled us to build a robust knowledge base of the current state of the auto finance industry and its major players, incorporating both demand-side dynamics and supply-side structures.
Step 3: Primary Research
A series of direct interviews were conducted with executives from leading banks, NBFCs, fintech lenders, auto dealerships, and green loan providers in the Norway Auto Finance Market. These discussions validated our hypotheses and filled data gaps left by desk research. Stakeholders included product managers, credit analysts, regional heads, and EV loan specialists.
To ensure data authenticity and uncover insights not publicly available, disguised interviews were also performed—wherein researchers approached organizations as potential customers. This enabled us to gather granular data on pricing structures, eligibility criteria, sales conversion metrics, and digital adoption in loan processing.
A bottom-up approach was used to estimate market size by aggregating data from individual institutions. This was cross-validated using a top-down approach based on total vehicle registrations and car purchase financing rates.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- Market triangulation techniques were applied by comparing internal calculations with external benchmarks and third-party data. Both bottom-to-top and top-to-bottom methods were utilized to ensure consistency across market sizing and forecasting models. Multiple scenario analyses were also run to project the Norway Auto Finance Market under different macroeconomic and policy conditions.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Norway Auto Finance Market?
The Norway Auto Finance Market is positioned for steady growth through 2029, driven by the country's strong economic fundamentals, increasing adoption of electric vehicles, and a digitally savvy population. The market reached a valuation of approximately NOK 80 billion in total loan disbursement in 2023, with future growth expected to be supported by green financing initiatives, digital lending platforms, and evolving consumer behavior towards flexible and sustainable car ownership models.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Norway Auto Finance Market?
Key players in the Norway Auto Finance Market include major financial institutions such as DNB Bank, Santander Consumer Bank, Nordea Finance, and SpareBank 1 Finans. Additionally, captive finance arms like Volkswagen Møller Bilfinans and new-age players like Aprila Bank and LeasePlan Bank are gaining traction, especially in the digital and EV-focused financing space.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Norway Auto Finance Market?
Significant growth drivers include the government’s strong push for electric vehicle adoption, favorable interest rates for green auto loans, and the increasing integration of fintech in lending operations. The digital transformation of banking services, combined with consumer demand for convenience, is accelerating the shift towards online loan applications, automated approvals, and personalized financing solutions.
4. What are the Challenges in the Norway Auto Finance Market?
The market faces several challenges such as stringent creditworthiness checks, which can restrict access for younger and low-income consumers. Rising interest rates in recent years have also increased the cost of borrowing, discouraging some from financing vehicle purchases. Additionally, the limited availability of financing options for older or used electric vehicles presents a barrier to widespread adoption in the secondary EV market.