Oman Logistics and warehousing Market Outlook to 2029
By Mode of Freight, By Type of Warehousing, By End-User Industry, By Region, and By Service Type
- Product Code: TDR0311
- Region: Middle East
- Published on: September 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market Outlook to 2029 – By Mode of Freight, By Type of Warehousing, By End-User Industry, By Region, and By Service Type” provides a comprehensive analysis of the logistics and warehousing industry in Oman. The report includes an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation, major trends and developments, regulatory framework, customer-level profiling, key issues and challenges, and competitive landscape including cross-comparison of major players. The report concludes with market projections based on freight traffic, warehousing space, and revenue, along with success case studies, growth drivers, and bottlenecks.
Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market Overview and Size
The Oman logistics and warehousing market was valued at USD 1.00 billion in 2023, primarily driven by government-led infrastructure development under Vision 2040, the country’s strategic location along global shipping lanes, and increasing diversification of its economy. Major players such as ASYAD Group, Al Madina Logistics, DHL Oman, Aramex, and Bahwan Logistics are dominating the landscape with robust service offerings and well-integrated networks.
In 2023, ASYAD launched new cold chain logistics facilities in Sohar Freezone to support Oman’s rising demand in pharmaceuticals and perishables. Muscat and Sohar remain key logistics hubs due to their port infrastructure, proximity to trade routes, and growing industrial base.
%2C%202019-2024.png)
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market:
Strategic Geographical Position: Oman’s location at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa positions it as a natural logistics hub. Its ports (Duqm, Sohar, and Salalah) are being increasingly leveraged as alternatives to congested GCC ports. In 2023, the transshipment volume in Salalah Port grew by 8%, underscoring Oman’s potential as a regional logistics gateway.
Vision 2040 and Economic Diversification: Oman’s government has placed logistics as a key pillar in Vision 2040. The plan emphasizes reducing dependence on oil and building Oman as a global logistics hub. The government’s logistics arm, ASYAD, has invested over USD 1 billion in infrastructure and technology upgrades since 2018.
Growth of E-commerce and Retail: Rising digital penetration and demand for last-mile delivery services have boosted the demand for 3PL (third-party logistics) and warehousing services. In 2023, the e-commerce market in Oman reached USD 1.5 billion, leading to a surge in logistics demand from firms such as Aramex, Fetchr, and local e-retailers.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of the Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market
High Operational Costs: One of the major challenges in Oman’s logistics sector is the relatively high cost of transportation and warehousing. Due to fuel price fluctuations and limited domestic manufacturing, logistics firms often face increased overheads. In 2023, it was estimated that logistics operating costs in Oman were 15–20% higher compared to regional peers like UAE, significantly impacting the profit margins of local players.
Limited Skilled Workforce: The logistics industry in Oman continues to face a shortage of skilled labor, particularly in warehouse management, cold chain operations, and logistics planning. A 2023 survey revealed that around 47% of logistics firms reported difficulty in finding adequately trained professionals, which affects efficiency and delays technology adoption in the sector.
Fragmented Infrastructure and Connectivity Gaps: While major cities like Muscat, Sohar, and Salalah have seen strong logistics development, connectivity between smaller towns and remote industrial areas remains underdeveloped. This results in longer lead times and increased transportation costs. For example, inland transportation from Muscat to interior industrial zones takes up to 30% more time compared to similar distances in the UAE.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives Which Have Governed the Market
ASYAD Logistics Strategy and National Logistics Development Program (NLDP): Oman’s government, through its logistics arm ASYAD, launched the National Logistics Development Program to enhance the sector’s competitiveness and promote multimodal logistics. As of 2023, over USD 500 million was allocated for logistics infrastructure upgrades, including warehousing, rail links, and customs digitalization.
Special Economic Zones and Customs Reforms: Oman has established Special Economic Zones (SEZs) like Duqm, Sohar, and Salalah that offer customs exemptions, tax holidays, and single-window clearance systems. These reforms have helped reduce cargo dwell time at ports by 25% between 2019 and 2023, improving efficiency for importers and exporters.
Warehousing Standards and Licensing Requirements: In 2021, Oman introduced minimum infrastructure and safety standards for licensed warehousing providers, particularly for cold chain and hazardous materials. Compliance is now mandatory for all third-party logistics providers (3PLs). As a result, about 18% of legacy warehouses either exited or upgraded their facilities in 2022–2023 to meet the new criteria.
Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
By Market Structure: Third-party logistics (3PL) providers dominate the market due to their comprehensive service offerings, integration with port and customs operations, and increasing preference among retailers and manufacturers to outsource logistics. These providers offer cost efficiency, scalability, and technology-driven services such as GPS tracking, inventory management, and route optimization. In-house logistics operations, primarily run by large industrial entities and traditional wholesalers, still maintain presence, especially in the oil and gas and construction sectors, where control over the supply chain is considered crucial.
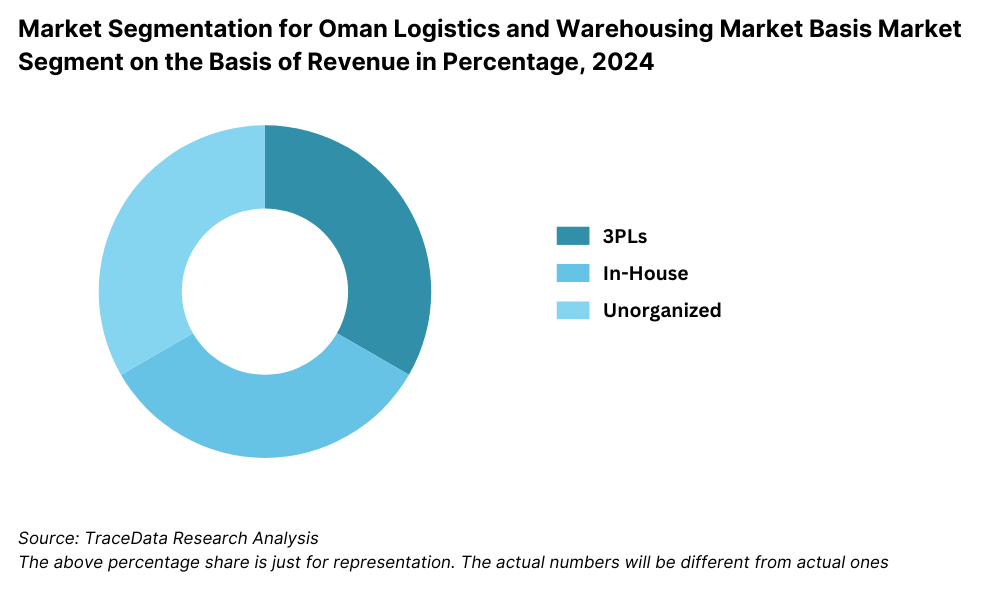
By Mode of Freight: Road freight leads the logistics sector in Oman due to the country’s well-developed highway infrastructure and connectivity between major cities such as Muscat, Sohar, and Salalah. Sea freight follows closely, supported by Oman’s strategic location and modern ports, playing a vital role in international trade and regional transshipment. Air freight, while smaller in volume, caters to urgent and high-value goods and is gradually growing with the expansion of Muscat International Airport's cargo capacity.
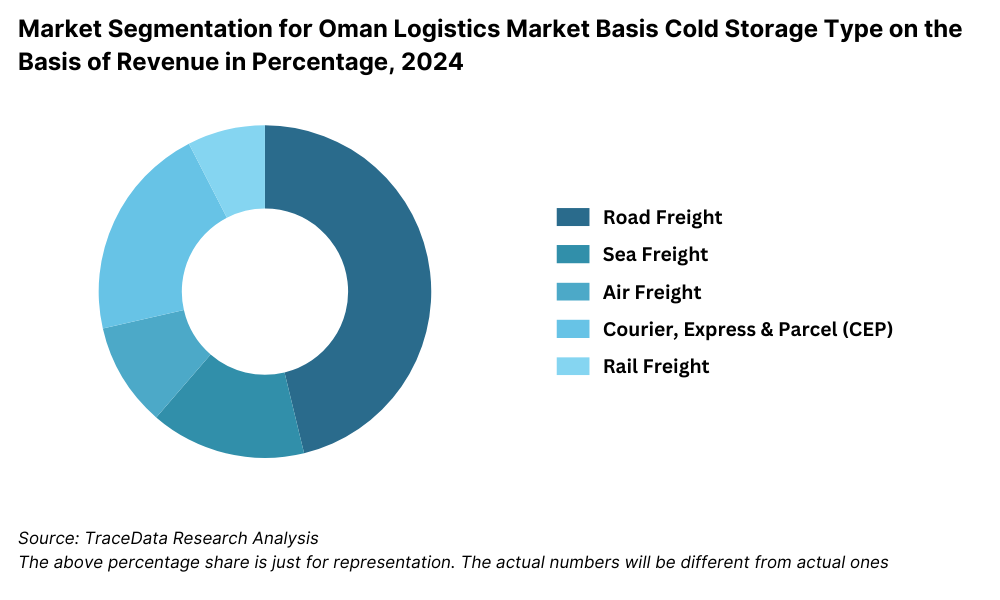
By Type of Warehousing: General warehousing dominates due to its widespread use in retail, FMCG, and industrial goods. Cold chain warehousing is rapidly expanding, driven by increasing demand from the food processing, pharmaceutical, and fisheries sectors. Bonded and customs-controlled warehousing is also gaining traction due to rising international trade and re-export activities, especially in free zones such as Sohar and Duqm.
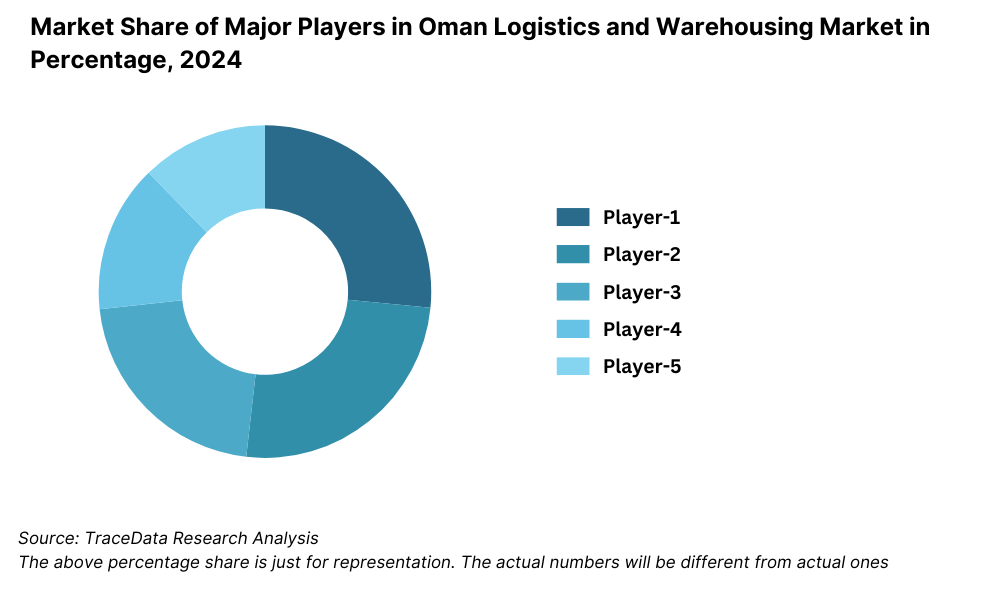
Competitive Landscape in Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market
The Oman logistics and warehousing market is moderately consolidated, with strong presence from a few dominant players supported by government initiatives, particularly through ASYAD Group. The entry of regional logistics giants and international 3PL firms such as DHL, Aramex, and DB Schenker, along with the expansion of free zones and e-commerce logistics providers, has introduced greater competition and specialization across various logistics services.
Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
ASYAD Group | 2016 | Muscat, Oman |
Al Madina Logistics | 2007 | Muscat, Oman |
Aramex Oman | 1998 (Oman ops) | Muscat, Oman |
Bahwan Logistics | 1978 | Muscat, Oman |
DHL Express Oman | 1980s | Muscat, Oman |
DB Schenker Oman | 2003 | Muscat, Oman |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
ASYAD Group: The government-backed logistics holding company has invested over USD 1 billion in infrastructure and digital transformation projects since its inception. In 2023, ASYAD expanded cold chain logistics capacity in Sohar and introduced smart warehouse management systems in key industrial zones to support demand from the pharma and fisheries sector.
Al Madina Logistics: Known for its warehousing and cold storage capabilities, the company opened a new 40,000 sq. meter facility in 2023 in Khazaen Economic City. This expansion supports growing demand in food and healthcare logistics and strengthens its 3PL service offerings.
Aramex Oman: Leveraging its pan-GCC network, Aramex reported a 20% YoY increase in cross-border e-commerce shipments in 2023. The company is focusing on last-mile delivery innovations and warehouse automation to support the retail boom in Muscat and Salalah.
Bahwan Logistics: A long-standing player with expertise in heavy haulage and project logistics, Bahwan has been involved in several major infrastructure logistics contracts in 2023, including port equipment mobilization and oilfield supply chain support.
DHL Express Oman: The firm has continued to upgrade its fleet and warehouse operations with sustainability initiatives. In 2023, DHL introduced green logistics pilots in Muscat and achieved 95% on-time performance in its time-definite delivery service.
DB Schenker Oman: Positioned as a premium service provider, DB Schenker has enhanced its Oman operations with the launch of integrated customs brokerage and bonded warehousing services. It is increasingly catering to the electronics, automotive, and industrial machinery sectors with tailored supply chain solutions.
What Lies Ahead for Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Oman logistics and warehousing market is projected to grow steadily by 2029, exhibiting a healthy CAGR during the forecast period. This growth will be driven by continued infrastructure development, regional trade expansion, and increasing reliance on integrated third-party logistics solutions.
Expansion of Multimodal Infrastructure: Oman’s continued investment in ports, roadways, and planned rail connectivity (such as the GCC railway project) is expected to significantly boost multimodal logistics capabilities. Integration of seaports like Duqm and Sohar with inland logistics corridors will reduce cargo transit times and position Oman as a transshipment and distribution hub.
Rise of E-commerce and Last-Mile Logistics: The e-commerce sector in Oman is forecasted to grow rapidly, increasing the demand for last-mile logistics solutions. Logistics players are expected to expand their urban fulfillment centers, introduce app-based delivery services, and invest in AI-powered route optimization tools to meet rising customer expectations for speed and reliability.
Cold Chain Logistics Growth: With a rising focus on healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and food safety, the cold chain segment is set to expand. Government investments and private sector interest are leading to modern, temperature-controlled warehouses, especially in economic zones like Sohar and Khazaen. This segment is projected to grow at one of the highest rates within the warehousing market.
Digital Transformation and Smart Warehousing: The integration of IoT, automation, and AI into warehousing and logistics management is expected to significantly enhance efficiency. Companies are adopting warehouse management systems (WMS), smart sensors, and robotics to reduce errors, lower costs, and increase throughput. Digitalization will be a core differentiator among logistics providers.
%2C%202024-2030.png)
Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
• By Market Structure:
o Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Providers
o In-house Logistics Providers
o Contract Logistics Providers
o Freight Forwarders
o Express Delivery Services
o Full-Service Integrated Logistics Players
• By Mode of Freight:
o Road Freight
o Sea Freight
o Air Freight
o Rail Freight (Proposed/Planned)
• By Type of Warehousing:
o General Warehousing
o Cold Chain Warehousing
o Bonded Warehousing
o Container Freight Stations (CFS)
o E-commerce Fulfillment Centers
o Multi-client Warehouses
o Dedicated Warehouses
• By End-User Industry:
o Retail and E-commerce
o Oil and Gas
o FMCG
o Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
o Automotive
o Manufacturing and Industrial Goods
o Agriculture and Food Processing
• By Region:
o Muscat
o Sohar
o Salalah
o Duqm
o Nizwa and Interior Regions
Players Mentioned in the Report:
• ASYAD Group
• Al Madina Logistics
• Aramex Oman
• Bahwan Logistics
• DHL Express Oman
• DB Schenker Oman
• Khimji Ramdas Logistics
• GAC Oman
Key Target Audience:
• Logistics and Warehousing Companies
• E-commerce and Retail Companies
• Cold Chain Logistics Providers
• Freight Forwarders and 3PL Operators
• Special Economic Zone Developers
• Government and Regulatory Bodies (e.g., ASYAD, Ministry of Transport)
• Industrial and Real Estate Developers
• Market Research and Consulting Firms
Time Period:
• Historical Period: 2018–2023
• Base Year: 2024
• Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
1. Executive Summary
2. Research Methodology
3. Ecosystem of Key Stakeholders in Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market
4. Value Chain Analysis
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and challenges that they face
4.2. Revenue Streams for Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market
4.4. Customer Decision-Making Process
4.5. Service Provider Selection Process
5. Market Structure
5.1. Freight Movement Trends in Oman, 2018-2024
5.2. Modal Split of Logistics (Road, Sea, Air), 2018-2024
5.3. Spend on Logistics Services by End-User Industry, 2024
5.4. Number of Warehousing Facilities by Type and Region, 2024
6. Market Attractiveness for Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market
7. Supply-Demand Gap Analysis
8. Market Size for Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market Basis
8.1. Revenues, 2018-2024
8.2. Freight Volume and Warehousing Capacity, 2018-2024
9. Market Breakdown for Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market Basis
9.1. By Market Structure (3PL, In-house, Contract Logistics), 2023-2024P
9.2. By Mode of Freight (Road, Sea, Air), 2023-2024P
9.3. By Type of Warehousing (General, Cold Chain, Bonded), 2023-2024P
9.4. By Region (Muscat, Sohar, Salalah, Duqm, Interior), 2023-2024P
9.5. By End-User Industry (Retail, FMCG, Oil & Gas, Pharma, Automotive, Manufacturing), 2023-2024P
10. Demand Side Analysis for Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market
10.1. Customer Landscape and Industry-wise Logistics Spend
10.2. Client Journey and Service Selection
10.3. Need, Preference, and Gap Analysis
10.4. Contracting Criteria and Pain Point Analysis
11. Industry Analysis
11.1. Trends and Developments in Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges for Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market
11.5. Government Regulations and Initiatives
12. Snapshot on E-commerce and Express Logistics
12.1. Market Size and Future Potential for Express and Last-Mile Delivery, 2018-2029
12.2. Business Models and Revenue Streams
12.3. Cross-Comparison of Key E-commerce Logistics Players by Overview, Cities Served, Fleet Size, Delivery Time, and Pricing Model
13. Snapshot on Cold Chain Logistics
13.1. Temperature Controlled Warehousing and Transportation Capacity, 2018-2029
13.2. Growth of Cold Chain Logistics in Pharma, Food, and Agri-Sector
13.3. Technology and Compliance in Cold Chain Operations
14. Opportunity Matrix for Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market-Presented with the help of Radar Chart
15. PEAK Matrix Analysis for Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market
16. Competitor Analysis for Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market
16.1. Benchmark of Key Competitors in Oman Logistics Market including Company Overview, Services, Strength, Weakness, USP, Warehouse Area, Fleet Size, Clients, Recent Developments
16.2. Strength and Weakness Analysis
16.3. Operating Model Comparison
16.4. Gartner Magic Quadrant
16.5. Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
17. Future Market Size for Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market Basis
17.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
17.2. Freight Volume and Warehousing Capacity, 2025-2029
18. Market Breakdown for Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market Basis
18.1. By Market Structure, 2025-2029
18.2. By Mode of Freight, 2025-2029
18.3. By Type of Warehousing, 2025-2029
18.4. By Region, 2025-2029
18.5. By End-User Industry, 2025-2029
18.6. Recommendation
18.7. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand side and supply side entities for Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market. Basis this ecosystem, we will shortlist leading 5-6 logistics service providers in the country based upon their financial information, warehousing capacity, fleet size, and operational footprint.
Sourcing is made through industry articles, multiple secondary, and proprietary databases to perform desk research around the market to collate industry-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
Subsequently, we engage in an exhaustive desk research process by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This approach enables us to conduct a thorough analysis of the market, aggregating industry-level insights. We delve into aspects like total logistics revenue, freight volumes, number of service providers, types of warehousing, demand by sector, and other variables.
We supplement this with detailed examinations of company-level data, relying on sources like press releases, annual reports, port authority data, financial statements, and similar documents. This process aims to construct a foundational understanding of both the market and the entities operating within it.
Step 3: Primary Research
We initiate a series of in-depth interviews with C-level executives and other stakeholders representing various Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market companies and end-users. This interview process serves a multi-faceted purpose: to validate market hypotheses, authenticate statistical data, and extract valuable operational and financial insights from these industry representatives. Bottom to top approach is undertaken to evaluate freight movement and warehousing capacity for each player thereby aggregating to the overall market.
As part of our validation strategy, our team executes disguised interviews wherein we approach each company under the guise of potential customers. This approach enables us to validate the operational and financial information shared by company executives, corroborating this data against what is available in secondary databases. These interactions also provide us with a comprehensive understanding of service offerings, value chain, pricing models, and other key market drivers.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- Bottom to top and top to bottom analysis along with market size modeling exercises is undertaken to assess sanity check process.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Oman logistics and warehousing market holds significant growth potential, reaching a valuation of USD 1.00 billion in 2023. The market is poised for expansion, driven by Oman’s strategic geographic location, government-led infrastructure development under Vision 2040, and growing demand from sectors such as e-commerce, retail, and pharmaceuticals. The development of key logistics hubs like Sohar, Salalah, and Duqm, combined with increasing international trade, positions Oman as an emerging logistics gateway in the region.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market is led by major players such as ASYAD Group, Al Madina Logistics, and Aramex Oman. These companies have a strong national presence, advanced infrastructure, and integrated supply chain solutions. Other notable players include Bahwan Logistics, DHL Express Oman, and DB Schenker Oman, all of whom are expanding their operations through technology integration and specialized warehousing services.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Key growth drivers include Oman’s strategic investments in port and road infrastructure, the rise of e-commerce and last-mile delivery demand, increasing adoption of cold chain solutions, and supportive government policies aimed at positioning Oman as a regional logistics hub. Additionally, the growing presence of free zones and special economic areas facilitates trade and warehousing expansion.
4. What are the Challenges in the Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Challenges in the Oman Logistics and Warehousing Market include high operational costs, limited availability of skilled logistics professionals, and infrastructure gaps in remote regions. Fragmented service offerings and a lack of advanced digital adoption among smaller logistics players also pose challenges. Furthermore, competition from more mature regional logistics hubs like the UAE can impact Oman’s efforts to attract global logistics demand.