Oman Smart Home Devices Market Outlook to 2030
By Device Type, By Connectivity/Protocol, By Application/Dwelling Type, By Sales Channel, By Price Band, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0393
- Region: Middle East
- Published on: November 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Oman Smart Home Devices Market Outlook to 2030 - By Device Type, By Connectivity/Protocol, By Application/Dwelling Type, By Sales Channel, By Price Band, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the smart home devices market in Oman. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue and installed base, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer level profiling, issues and challenges, and competitive landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the smart home devices market. The report concludes with future market projections based on device-unit volumes, service-subscription revenues, regions, cause-and-effect relationships, and success case studies highlighting the major opportunities and cautions.
Oman Smart Home Devices Market Overview and Size
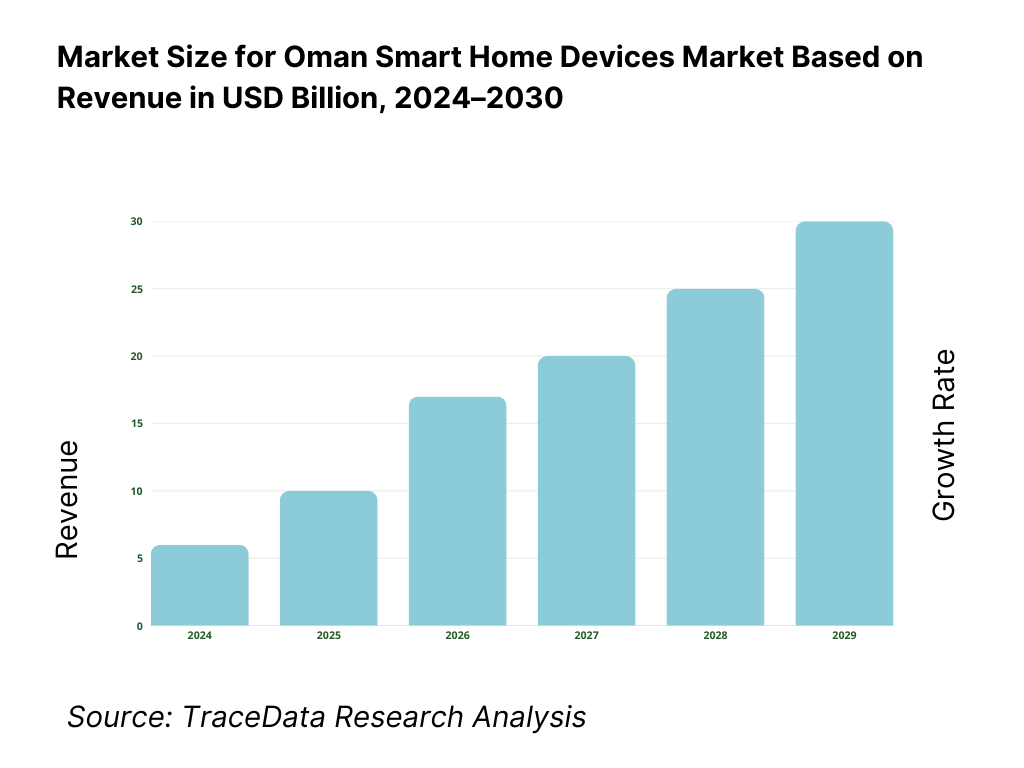
The Oman Smart Home Devices market is valued at USD 2,456.1 million, according to analysis for the Middle East & Africa region, with the Omani segment contributing a significant portion of this. Growth has been driven by rising household broadband and 5G rollout, expanding residential compound developments in Muscat and other governorates, and increasing consumer interest in home security and automation solutions. The expansion of modern trade and e-commerce channels further supports device uptake.
Key cities and regions dominating the Oman market include the Muscat metropolitan area and major residential compound developments around Al Rusayl and Seeb. These areas lead because of high disposable incomes, dense new-housing handovers, strong broadband infrastructure, and developer-led smart-home fit-outs. The influx of expatriate residents and luxury villa developments also fuels smart-home device uptake in Oman’s urban hubs.
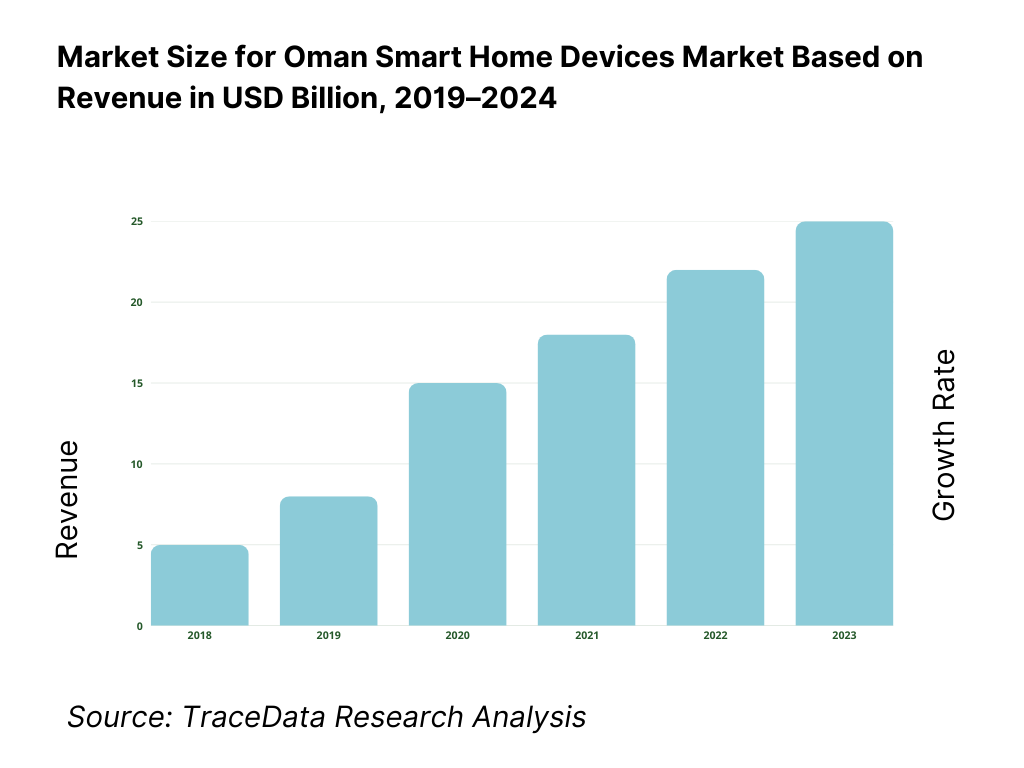
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the Oman Smart Home Devices Market:
Dense digital rails enabling device onboarding and control: Oman’s connectivity infrastructure reduces adoption friction for smart home devices by ensuring high network availability and reliability. The country has 6,350,000 mobile subscriptions, 5,340,000 mobile-broadband connections, and 582,000 fixed-broadband lines in service. Telecom sector revenues of 920,000,000 OMR highlight sustained consumer spending on connectivity that supports always-on devices such as cameras, hubs, thermostats, and energy dashboards. This strong digital foundation, reinforced by operator bundling programs, provides a scalable installed base for Wi-Fi and IP-connected smart home solutions across both urban and emerging residential centers.
Household scale, urban concentration and purchasing capacity: Oman’s growing economy and urban density drive consumer capacity for smart device adoption. The country’s economy stands at USD 105,190,000,000, while its population of 5,268,072 creates a broad addressable residential base, especially in Muscat and coastal cities. Imports of goods and services worth USD 47,411,799,185 enable a continuous inflow of electronic products, ensuring availability across retail and distribution channels. This macroeconomic and demographic structure strengthens purchasing power and supply continuity, supporting sustained demand for connected lighting, security, and energy automation devices.
Grid digitalization and metering infrastructure for energy use-cases: Energy management remains one of the most practical smart-home applications in Oman’s market. Under the national utilities framework, 1,130,000 electricity smart meters have been installed, laying the foundation for energy dashboards, load scheduling, and sub-metering devices. The digital grid infrastructure enables integration of household systems with real-time consumption analytics. Given Oman’s climate and high air-conditioning dependency, these systems drive energy efficiency and peak-load optimization, reinforcing the link between utility modernization and smart-home adoption across villas and managed compounds.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of the Oman Smart Home Devices Market:
Service and installation capacity outside dense corridors: While Muscat and Dhofar maintain strong retail and service coverage, remote and less-populated governorates face slower installation cycles. Out of 5,268,072 residents, only 582,000 have access to fixed broadband—indicating service disparity between dense and rural areas. This imbalance leads to longer installation response times and extended maintenance lead times for devices such as cameras, switches, and hubs. The lack of skilled technicians outside urban areas remains a barrier to scaling smart-home installations in smaller towns and peripheral regions.
Import dependence and compliance bottlenecks for connected devices: Oman’s reliance on imports poses logistical and compliance challenges for smart-home suppliers. With imported goods and services valued at USD 47,411,799,185, any delay in customs clearance or product certification disrupts retail availability. Every radio-frequency device, including Wi-Fi cameras and Zigbee hubs, must meet conformity requirements before market entry. These regulatory bottlenecks and documentation lead times often postpone new launches or promotional cycles, creating temporary gaps in product availability and affecting the competitiveness of local distributors and global OEMs.
Data-handling obligations for video and sensor workloads: Smart-home ecosystems processing video and sensor data must now comply with Oman’s Personal Data Protection Law (Royal Decree 6/2022). With 5,340,000 active mobile-broadband lines and millions of data points generated daily, ensuring compliance with consent, retention, and transfer obligations adds operational complexity. Companies must implement secure cloud storage or localized processing systems to meet privacy requirements while maintaining functionality for cameras, locks, and voice-controlled assistants. Aligning with data laws while preserving consumer convenience remains a central challenge for device manufacturers.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
Telecommunications equipment Type Approval (market access gate): All wireless and radio-enabled devices must obtain Type Approval before being imported or sold in Oman. The process ensures compliance with national standards for spectrum use, safety, and electromagnetic compatibility. It applies to categories like Wi-Fi cameras, Zigbee hubs, and Bluetooth sensors. Proper documentation and product labeling are mandatory to enter the retail or operator channels. Vendors who streamline approval documentation and testing timelines can accelerate go-to-market readiness for new smart-home devices.
Personal Data Protection Law (Royal Decree 6/2022) governing consumer data: The Personal Data Protection Law defines principles for handling personal information collected through connected devices. It mandates explicit user consent, lawful processing, data subject rights, and clear storage and transfer protocols. Smart-home ecosystems involving voice assistants, connected cameras, and mobile apps must integrate these controls into their design and operations. Compliance enhances consumer confidence in adopting connected technologies, especially those used for monitoring and security applications across villas, apartments, and compounds.
APSR-supervised advanced metering environment (grid linkage): The Authority for Public Services Regulation (APSR) supervises Oman’s advanced metering rollout, integrating household electricity data with digital energy-management systems. A total of 1,130,000 smart meters have been deployed, creating an interoperable interface between utilities and homes. This regulated infrastructure allows seamless integration of home-energy dashboards, smart plugs, and thermostats. Vendors aligning their solutions with APSR’s interoperability standards can leverage this metering ecosystem to enhance automation, efficiency, and sustainability for end consumers.
Oman Smart Home Devices Market Segmentation
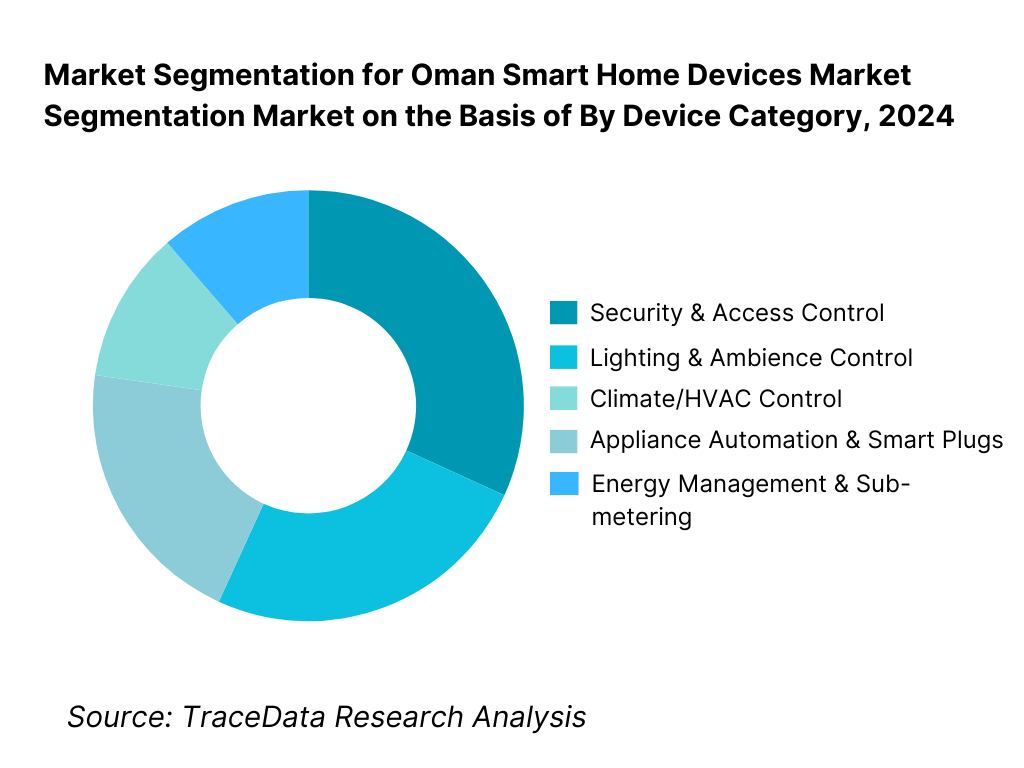
By Device Category: The Oman Smart Home Devices market is segmented by device category into: security & access control, lighting & ambience control, climate/HVAC control, appliance automation & smart plugs, energy-management & sub-metering. Among these, the security & access control sub-segment is dominating the market share this dominance is due to the strong consumer-demand for home surveillance and smart locks in villa and compound markets, a high prevalence of expatriate and rental homes seeking enhanced security, and developer-led specifications including video-doorbells and smart-locks at hand-over.
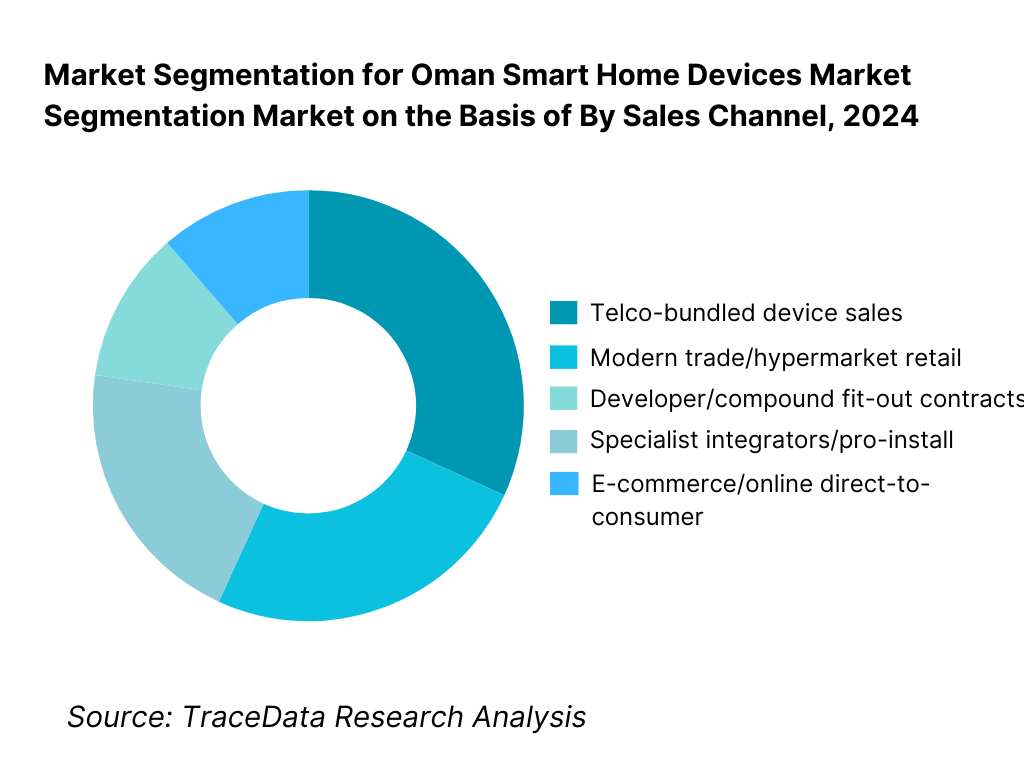
By Sales Channel: The market is also segmented by sales channel into: telco-bundled device sales, modern trade/hypermarket retail, e-commerce/online direct-to-consumer, developer/compound fit-out contracts, and specialist integrators/pro-install. The telco-bundled device sales channel is dominating this leading share reflects the strong role of major telecom operators in Oman bundling smart-home devices with broadband/5G subscriptions and post-paid plans, offering financing/EMI options, which lowers initial cost barriers for consumers.
Competitive Landscape in Oman Smart Home Devices Market
The competitive landscape in the Oman Smart Home Devices market is led by a handful of global and regional players with device, platform, service and channel capabilities, illustrating consolidation and strong brand influence.
Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
Samsung SmartThings | 2012 | Seoul, South Korea |
Xiaomi (Mi Home) | 2010 | Beijing, China |
Philips Hue (Signify) | 1891 | Amsterdam, Netherlands |
TP-Link (Tapo / Kasa) | 1996 | Shenzhen, China |
Ring (Amazon) | 2012 | Santa Monica, USA |
Aqara | 2016 | Shenzhen, China |
Arlo Technologies | 2014 | San Jose, USA |
eufy (Anker Innovations) | 2011 | Changsha, China |
Google Nest | 2010 | Mountain View, USA |
Apple Home (HomeKit) | 1976 | Cupertino, USA |
Yale (ASSA ABLOY) | 1840 | Stockholm, Sweden |
Schneider Electric (Wiser) | 1836 | Rueil-Malmaison, France |
Legrand / Netatmo | 1904 | Limoges, France |
Bosch Smart Home | 1886 | Stuttgart, Germany |
EZVIZ | 2013 | Hangzhou, China |
Some of the Recent Competitor Trends and Key Information About Competitors Include:
Samsung SmartThings: A leading player in the Omani smart home ecosystem, Samsung has expanded its Matter-enabled SmartThings ecosystem through partnerships with local distributors and retail chains. In 2024, the company strengthened its collaboration with Omantel and Ooredoo to integrate SmartThings devices with broadband packages, enhancing accessibility and bundled service adoption among households.
Xiaomi (Mi Home): Xiaomi has consolidated its dominance in the mid-range smart home device segment across Muscat and Al Batinah. The brand launched new AIoT devices—including cameras, sensors, and smart plugs—tailored for the hot climate of the Gulf region. Its strong online retail presence on Amazon Oman and Noon has contributed to a surge in e-commerce sales for plug-and-play smart products.
Philips Hue (Signify): Focusing on premium lighting and ambience solutions, Philips Hue strengthened its Oman portfolio by introducing Matter-compatible smart bulbs and localized after-sales service through GCC distribution hubs. The company also engaged in collaborative projects with luxury villa developers to supply smart lighting systems integrated with motion and voice control.
TP-Link (Tapo / Kasa): TP-Link has seen rising sales in entry-level smart plugs, cameras, and lighting devices in Oman. In 2024, the company launched an expanded Tapo app suite supporting Arabic interface, improving adoption among local users. Its products are now featured in all major modern-trade electronics stores such as Sharaf DG and Emax, with growing telco-bundle tie-ups for home monitoring kits.
Ring (Amazon): Ring continues to lead in video doorbells and security monitoring devices, gaining traction in Muscat’s residential compounds and villas. In 2023, the company rolled out new subscription-based cloud recording plans tailored for the GCC region, offering dual-storage options for enhanced privacy. Its collaboration with local system integrators has positioned Ring as a preferred brand for security automation solutions in high-income neighborhoods.
What Lies Ahead for Oman Smart Home Devices Market?
The Oman Smart Home Devices market is poised for continued expansion through the remainder of the decade, supported by steady economic growth, strong digital infrastructure, and policy-led modernization of residential energy systems. Oman’s nominal GDP of USD 105.19 billion provides a robust macro base for consumer technology upgrades and home automation adoption. A growing middle-income population and expanding broadband reach—5.34 million mobile broadband lines and 582,000 fixed broadband subscriptions—will sustain the ecosystem’s momentum as connectivity and lifestyle integration deepen across households and compounds.
Rise of Integrated and Hybrid Smart Living Models: The next phase of Oman’s smart home evolution will be defined by integrated hybrid ecosystems, combining connected devices, home energy management, and security automation within unified applications. With 1.13 million smart meters already deployed, households can synchronize thermostats, appliances, and lighting with grid data for real-time energy optimization. This convergence allows homes to function as intelligent energy nodes that enhance comfort, safety, and efficiency. These hybrid systems are particularly attractive for Oman’s villa-heavy housing structure, where larger properties offer greater energy-saving potential and convenience through automation.
Focus on Data Security and Localization in Device Ecosystems: Oman’s Personal Data Protection Law (Royal Decree 6/2022) is shaping how smart-home vendors manage personal and sensor data. With 6.35 million active mobile lines and millions of connected devices transmitting information, data security has become a key determinant of consumer trust. Manufacturers are increasingly emphasizing on-device AI processing, regional cloud storage, and transparent consent mechanisms to ensure compliance. These practices will strengthen confidence in categories like smart cameras, locks, and voice assistants, aligning the sector with Oman’s broader goal of digital sovereignty and secure technology adoption.
Expansion of Developer-Led Smart Communities: Real-estate growth continues to be a central driver of smart-home demand. With a population of 5.26 million and a rise in new residential permits across Muscat, Al Batinah, and Dhofar, developers are embedding smart-ready wiring, IoT-enabled access systems, and energy dashboards into new projects. These initiatives align with Oman Vision 2040, which emphasizes sustainable urban development and smart infrastructure. As developers increasingly specify pre-installed automation systems in villas and apartments, large-scale procurement from integrators and manufacturers will fuel market acceleration in the coming years.
Leveraging Artificial Intelligence and Predictive Automation: Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing Oman’s home automation landscape by enabling predictive control of climate and energy systems. With average temperatures above 30°C and air-conditioning accounting for a major share of residential power consumption, AI-based thermostats and adaptive cooling algorithms are helping households reduce load while maintaining comfort. Supported by 920 million OMR in annual telecom revenues and growing 5G penetration, AI-powered platforms integrate seamlessly with telco ecosystems, allowing real-time monitoring, diagnostics, and predictive maintenance within a single digital interface.
Growth of Sector-Specific Smart Applications: Beyond residential homes, smart technologies are expanding into commercial and institutional domains. Government agencies and large-scale operators are integrating IoT energy management and security systems in industrial zones, ports, and logistics corridors that handle more than 300 million tons of cargo annually. These developments highlight the transition from household automation to sector-specific deployments in energy, manufacturing, and logistics. As the ecosystem matures, Omani vendors and integrators are expected to extend residential innovations—such as surveillance, metering, and climate automation—into industrial and public-sector applications, broadening the market’s long-term opportunity.
Oman Smart Home Devices Market Segmentation
By Device Category
Security & Access Control
Lighting & Ambience Control
Climate / HVAC Control
Appliance Automation & Smart Plugs
Energy Management & Sub-metering
By Sales Channel
Telco-Bundled Device Sales
Modern Trade / Hypermarket Retail
E-commerce / Online Direct-to-Consumer
Developer / Compound Fit-out Contracts
Specialist Integrators / Pro-Install
By Connectivity / Protocol Type
Wi-Fi
Zigbee
Thread / Matter
Z-Wave
Bluetooth / BLE Mesh
By Application / Dwelling Type
Owner-Occupied Villas
Managed Residential Compounds
Apartments / MDUs
Staff Housing / Labor Accommodation
Small Offices / Home Offices (SOHO)
By Region (Governorate)
Muscat
Dhofar / Salalah
Al Batinah (North & South)
A’Sharqiyah (North & South)
Al Dakhiliyah
Ad Dhahirah
Musandam & Al Wusta
Players Mentioned in the Report:
Samsung SmartThings
Xiaomi
Aqara
Philips Hue (Signify)
TP-Link (Tapo/Kasa)
Ring (Amazon)
Arlo
eufy (Anker)
Google Nest
Apple Home
Yale (ASSA ABLOY)
Schneider Electric (Wiser)
Legrand / Netatmo
Bosch Smart Home
EZVIZ
Key Target Audience
Device OEMs and brand managers
Telecom operators and connectivity providers (e.g., Omantel, Ooredoo)
Real-estate developers and compound managers
Residential property asset managers
Installation & system-integration firms
Energy utilities and smart-metering companies
Investments and venture-capitalist firms (smart-home / IoT startups)
Government and regulatory bodies (e.g., TRA Oman, APSR, Ministry of Housing)
Time Period:
Historical Period: 2019-2024
Base Year: 2025
Forecast Period: 2025-2030
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Delivery Model Analysis for Smart Home Devices in Oman-Retail, Telco-Bundled, Pro-Install / Installer-Led, Retrofit Self-Install-Discussion of Margins, Preference, Strengths and Weaknesses
4.2. Revenue Streams for Oman Smart Home Devices Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Oman Smart Home Devices Market
5.1. Freelance Installers vs Full-Time/Certified Installer Firms in Oman Smart Home Devices Market
5.2. Investment Model in Oman Smart Home Devices Market
5.3. Comparative Analysis of the Funnel Process by Private and Government-Led Residential Developments in Oman Smart Home Devices Market
5.4. Smart Home Devices Budget Allocation by Dwelling Type / Compound Type (Owner-occupied villa, Managed compound, Apartment) in Oman
8.1. Revenues, Historical Period
9.1. By Device Type (Hardware + Services)
9.2. By Application / Dwelling Type
9.3. By Connectivity/Protocol
9.4. By Price Band
9.5. By Sales Channel
9.6. By Region
10.1. Residential Consumer Cohorts and Segmentation
10.2. Smart Home Device Needs & Decision-Making Process
10.3. Program / Device Effectiveness & ROI Analysis
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11.1. Trends & Developments for Oman Smart Home Devices Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Oman Smart Home Devices Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Oman Smart Home Devices Market
11.4. Issues & Challenges for Oman Smart Home Devices Market
11.5. Government Regulations for Oman Smart Home Devices Market
12.1. Market Size & Future Potential for Online Channel (Hardware + Services)
12.2. Business Model & Revenue Streams for Online Smart Home Devices
12.3. Delivery Models & Types of Devices Offered Online
15.1. Market Share of Key Players by Revenue (Oman)
15.2. Benchmark of Key Competitors-Company Overview; USP; Business Strategy; Business Model; Number of Installers/Trainers; Revenues; Pricing by Device Type; Technology Used; Best-selling SKUs; Major Clients (developers/compounds); Strategic Tie-ups; Marketing Strategy; Recent Developments
15.3. Operating Model Analysis Framework-hardware vs services vs integration
15.4. Strategic Positioning Matrix-analogous to Gartner Magic Quadrant
15.5. Strategic Clock-competitive positioning and advantage (e.g., cost-leadership, differentiation, bundling)
16.1. Revenue Projections (forecast period)
16.2. Key Factors Driving Future Growth
17.1. By Device Type
17.2. By Application / Dwelling Type
17.3. By Connectivity/Protocol
17.4. By Price Band
17.5. By Sales Channel
17.6. By Region
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand-side and supply-side entities for the Oman Smart Home Devices Market. Based on this ecosystem, we will shortlist the leading 5–6 device and solution providers in the country based on their financial disclosures, regional market presence, channel coverage, and product portfolio diversity. Sourcing is conducted through industry articles, regulatory publications from TRA Oman and APSR, customs import data, as well as multiple secondary and proprietary databases to perform desk research around the market to collate industry-level information. The shortlisted entities include Samsung SmartThings, Xiaomi, TP-Link (Tapo), Ring (Amazon), Aqara, and Philips Hue (Signify), given their extensive retail footprint, telco partnerships, and developer integrations in Oman.
Step 2: Desk Research
Subsequently, we engage in an exhaustive desk research process by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This approach enables us to conduct a thorough analysis of the Oman Smart Home Devices Market, aggregating industry-level insights. We delve into aspects like device category revenues, import dependencies, distributor networks, protocol adoption (Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Matter), and channel distribution. We supplement this with detailed examinations of company-level data, relying on sources such as annual reports, distributor filings, TRA type-approval registries, APSR smart metering data, and developer partnership announcements. This process aims to construct a foundational understanding of both the market and the entities operating within it, defining the interplay between global OEMs, telcos, utilities, and installation ecosystems.
Step 3: Primary Research
We initiate a series of in-depth interviews with C-level executives, regional heads, distributors, telco IoT leads, and developer procurement teams representing various Oman Smart Home Devices companies and end-users. This interview process serves a multi-faceted purpose: to validate market hypotheses, authenticate secondary data, and extract valuable operational and financial insights from these industry representatives. A bottom-to-top approach is undertaken to evaluate revenue contributions for each player, aggregating to the overall market. As part of our validation strategy, our team executes disguised interviews wherein we approach each company under the guise of potential corporate or compound clients. This approach enables us to validate operational and financial information, corroborating it against secondary databases, and to understand revenue streams, value chains, pricing models, and channel margins in Oman’s retail and developer ecosystems.
Step 4: Sanity Check
A bottom-to-top and top-to-bottom analysis, along with market size modeling exercises, is undertaken to assess the sanity of the process. We reconcile household counts from NCSI Oman, broadband connectivity data from TRA Oman, and smart-meter installations from APSR with distributor sell-in volumes, e-commerce SKU counts, and telco bundle activations. This multi-tier triangulation ensures data integrity, eliminating outliers and ensuring the modeled totals are consistent with Oman’s economic, digital, and housing baselines. The final validation step confirms that all figures accurately represent the installed device base, revenue segmentation, and future scalability of the Oman Smart Home Devices Market.
FAQs
01 What is the potential for the Oman Smart Home Devices Market?
The Oman Smart Home Devices Market is poised for robust expansion, reaching a valuation of USD 2,456.1 million in 2023 according to regional data for the Middle East & Africa segment. This growth is underpinned by Oman’s steady macroeconomic fundamentals, supported by an economy valued at USD 105.19 billion, rising household incomes, and a population of 5.26 million. Increasing broadband connectivity—5.34 million mobile broadband subscriptions and 582,000 fixed-broadband connections—provides the infrastructure backbone enabling rapid adoption of connected devices across residential and commercial properties.
02 Who are the Key Players in the Oman Smart Home Devices Market?
The Oman Smart Home Devices Market features several prominent players, including Samsung SmartThings, Xiaomi (Mi Home), TP-Link (Tapo), Ring (Amazon), and Aqara, which lead due to their extensive product ecosystems, compatibility with multiple protocols (Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Matter), and established distribution networks. Other notable participants include Philips Hue (Signify), eufy (Anker), Google Nest, Apple Home, and Schneider Electric (Wiser). These companies dominate the market through local partnerships with Omantel and Ooredoo, retail presence in major electronics chains, and integration with developer-led smart housing projects.
03 What are the Growth Drivers for the Oman Smart Home Devices Market?
Key growth drivers for the Oman Smart Home Devices Market include the country’s 6.35 million active mobile lines and strong broadband penetration, which simplify remote control and device interconnectivity. The rollout of 1.13 million smart electricity meters by the national energy regulator supports energy-monitoring and automation products. Furthermore, Oman’s economy—valued at USD 105.19 billion—and growing housing stock across Muscat and Al Batinah create large addressable demand for security systems, lighting control, and climate automation in villas, compounds, and premium apartments.
04 What are the Challenges in the Oman Smart Home Devices Market?
The Oman Smart Home Devices Market faces key challenges such as limited professional installer networks beyond major cities and inconsistent after-sales service coverage. Regulatory compliance, including Type Approval for radio devices and data-protection obligations under Royal Decree 6/2022, adds procedural complexity for global OEMs. Additionally, Oman’s import dependency for electronic goods—reflected in USD 47.41 billion worth of imported goods and services—exposes suppliers to logistics costs, clearance delays, and component-availability risks, impacting product availability and pricing stability in the retail channel.