Peru Copper Mining Market Outlook to 2030
By Mining Method, By Ownership/Operator Type, By Product Form, By Lifecycle Stage, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0342
- Region: Central and South America
- Published on: October 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Peru Copper Mining Market Outlook to 2030 – By Mining Method, By Ownership/Operator Type, By Product Form, By Lifecycle Stage, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the copper mining market in Peru. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer level profiling, issues and challenges, and competitive landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the copper mining market. The report concludes with future market projections based on production volumes, product mix, regions, cause-and-effect relationships, and success case studies highlighting the major opportunities and cautions.
Peru Copper Mining Market Overview and Size
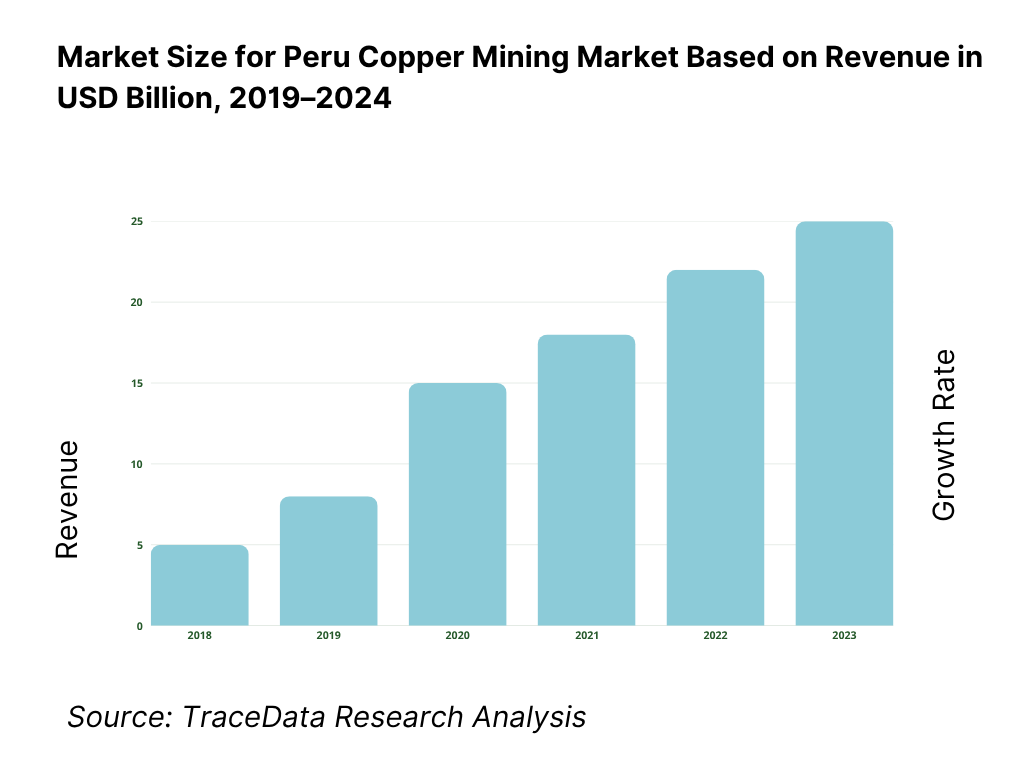
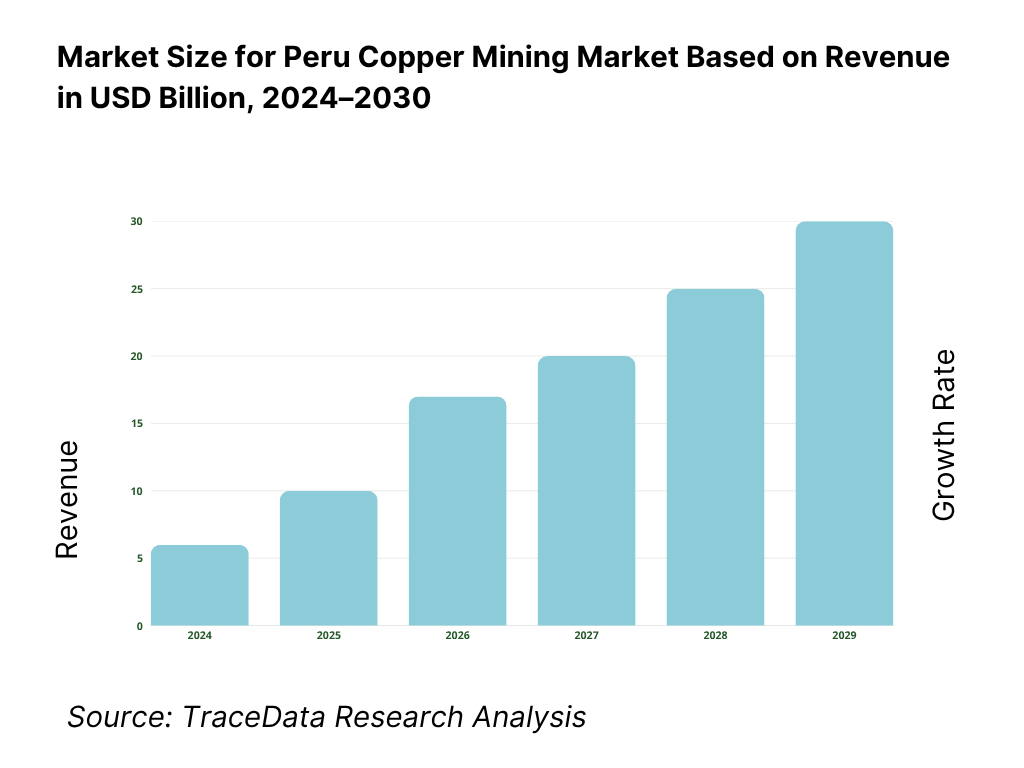
The Peru Copper Mining Market is valued at USD 19.99 billion on the basis of copper ores and concentrates export receipts, drawn from official UN Comtrade/WITS data. Export value rose to USD 20.49 billion in the following year as shipments normalized and prices stayed firm. Production printed 2.76 million tons of copper and then 2.736 million tons, reflecting strong output from Quellaveco, Cerro Verde, Antamina and Las Bambas alongside logistical frictions on the Southern Mining Corridor; pricing, offtake to Asia, and concentrate quality (As/Mo) shaped realized values.
Operational dominance clusters around Arequipa (Cerro Verde), Apurímac (Las Bambas), Moquegua (Quellaveco), Ancash (Antamina), and Tacna/Moquegua (Toquepala/Cuajone) due to tier-one porphyry endowment, established tailings and power/water infrastructure, and dependable port access at Matarani and Ilo. On the demand side, buyers are concentrated in China and Japan, with customs data showing copper ore exports of USD 15.6 billion to China and USD 1.24–1.82 billion to Japan across the comparable periods—reflecting smelting capacity scale and long-term offtake commitments.
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the Peru Copper Mining Market:
Tier-one output base and project pipeline supported by state data: Peru’s copper production reached 2,760,000 tons and subsequently 2,736,150 tons, anchored by mega-operations such as Cerro Verde, Antamina, Las Bambas, and Quellaveco reported by the energy and mines portfolio. The sector’s macro relevance is reflected in export composition tracked by the central bank and mining ministry bulletins. On the licensing front, the environmental authority reported 22 copper mining projects approved in a single calendar cycle, indicating a replenishing pipeline of brownfield debottlenecking and new pits. The combination of realized output in million-ton scale and a double-digit count of approved EIAs creates immediate room for throughput stability and incremental expansions without relying on speculative forward curves.
Proven external demand evidenced by customs-cleared shipments and buyer concentration: Trade data show copper ores and concentrates exports of USD 20,489,169,470 with consignments to China of USD 15,432,371,400 and to Japan of USD 1,824,933,990 alongside physically registered flows of 912,199,000 kg to the latter. Separate dispatch tallies recorded 2,950,000 tons exported in a single year due to sales of stockpiled material, underscoring offtake resilience even when production fluctuates. The numerical weight of consignments into Asian smelting hubs validates Peru’s role as a reliable supplier in the current cycle, supporting steady concentrator utilization and marketing plans that are contractually anchored in index-linked terms.
Grid capacity and port system throughput that can sustain mine-to-ship flows: Peru’s integrated power system generated 58,393.4 GWh over a completed year, according to operator statistics and sectoral compilations, providing the electrical backbone for comminution, flotation, and pumping across coastal-Andean operations. On the maritime side, the national port authority reports annual system cargo movement summarized on its statistical platform for 2024, with a consolidated national movement dataset available for download; this includes terminal-level tonnages for public and private ports used by bulk mineral exporters. The conjunction of five-digit GWh supply and nine-digit ton-scale cargo capability is a concrete enabler for stable mining logistics, from plant power draw to berth scheduling.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of the Peru Copper Mining Market:
Social conflict incidence documented by the Ombudsman’s Office: The Ombudsman’s monthly register listed 196 active social conflicts at year-end, of which 148 were socio-environmental, the category that most frequently involves mining corridors and project-area communities. These counts translate into recurring negotiation rounds, road-use protocols, and enforcement of haul-road safety plans across the Southern Mining Corridor. The volume of recorded cases elevates operational risk for dispatch reliability, staff mobility, and contractor scheduling, even when mines maintain production at nameplate rates. The numerical conflict base—tracked case by case—requires dedicated community relations budgets and contingency days in logistics plans for concentrate trucking and port windows.
Logistics exposure across a long, unimodal corridor with limited redundancy: Policy notes describe the Southern Mining Corridor as a primarily road-based spine with rail only in limited stretches; the transport ministry recognizes it among 41 national logistics corridors in use. The corridor length is referenced around 485–500 km, connecting pits in Apurímac/Cusco to coastal ports such as Matarani, which constrains rerouting options during blockades or weather-related closures. National port statistics provide annual movement tables for 2024, evidencing heavy national cargo workloads that must be sequenced with mineral export windows. These numeric parameters—corridor count, corridor length in kilometers, and national cargo volumes—frame a tangible bottleneck risk.
Water licensing and hydrologic proof requirements recorded by the water authority: Mines that expand throughput must obtain hydrologic availability accreditation and subsequent licenses. Administrative files specify documentary requirements for Acreditación de Disponibilidad Hídrica and Aprovechamiento de Agua, including quantified design flows stated in liters per second and per-capita baselines such as 120 litros/día in recent district-level technical reports. The need to demonstrate source availability in cubic meters per time unit and to file multi-item dossiers increases lead-time and engineering effort for expansions, particularly in southern basins with competing agricultural and urban users. These numeric standards formalize water diligence before capacity increases.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
Environmental impact assessment decision period and written resolution: Peru’s EIA framework (Law No. 27446) establishes a formal administrative review window of 120 days for detailed environmental impact studies under the specialized evaluation service. The authority must issue a written decision, approving or rejecting the study, and may impose enforceable conditions. The fixed-day review clock and the obligation to produce a resolutive act create a predictable path for project proponents to schedule engineering freezes, contract awards, and financial close around an official timeline measured in days, rather than open-ended processes.
Evidenced throughput of licensing actions for copper mining projects: The environmental evaluation service publicly reported the approval of 22 copper mining projects within a completed year, representing a discrete, countable set of EIA-d approvals and modifications that passed technical scrutiny. This numeric cadence of approvals demonstrates institutional bandwidth to process multiple mine files in parallel, which reduces queue times for brownfield debottlenecking and facilitates synchronized expansions in concentrators and pits. Project developers can reference the count of approvals to benchmark likely submission windows and internal gate reviews.
Prior consultation processes recorded by the culture ministry: The prior consultation system maintains an official registry of processes and documents; public communications by the state report cumulative counts such as 108 completed or ongoing processes across sectors and project types, with mining representing a significant share. The presence of a centralized portal with process-by-process listings enables operators to plan dialogue timetables, meeting counts, and agreement tracking against state-recorded baselines. The numeric inventory of consultation cases anchors realistic schedules for early community engagement alongside EIAs.
Peru Copper Mining Market Segmentation
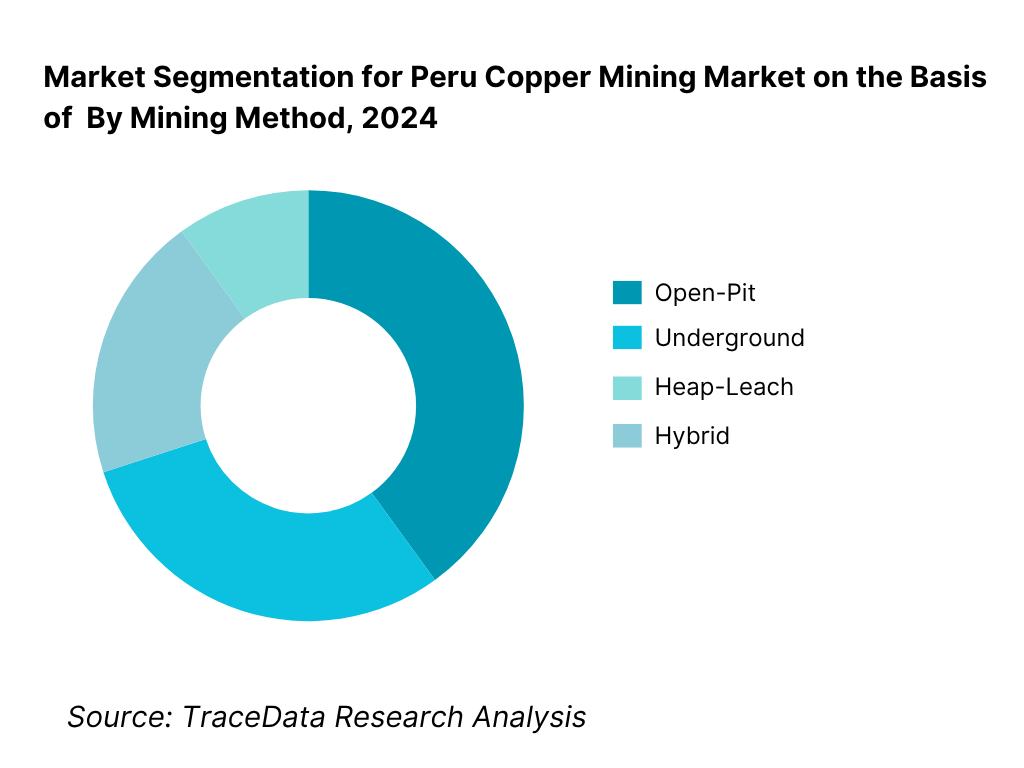
By Mining Method: Peru Copper Mining Market is segmented by mining method into open-pit, underground, heap-leach and hybrid operations. Open-pit currently holds the dominant position in Peru under this segmentation because the country’s largest porphyry systems—Cerro Verde, Antamina, Las Bambas, Toquepala, Cuajone and Quellaveco—were engineered as large-scale open pits with favorable strip ratios, wide benches, and shovel-truck or IPCC fleets that deliver high economies of scale. Process plants of 80–400 kt/d leverage conventional crushing-grinding-flotation and Mo circuits, keeping unit costs competitive versus underground alternatives while simplifying geotechnical risk management.
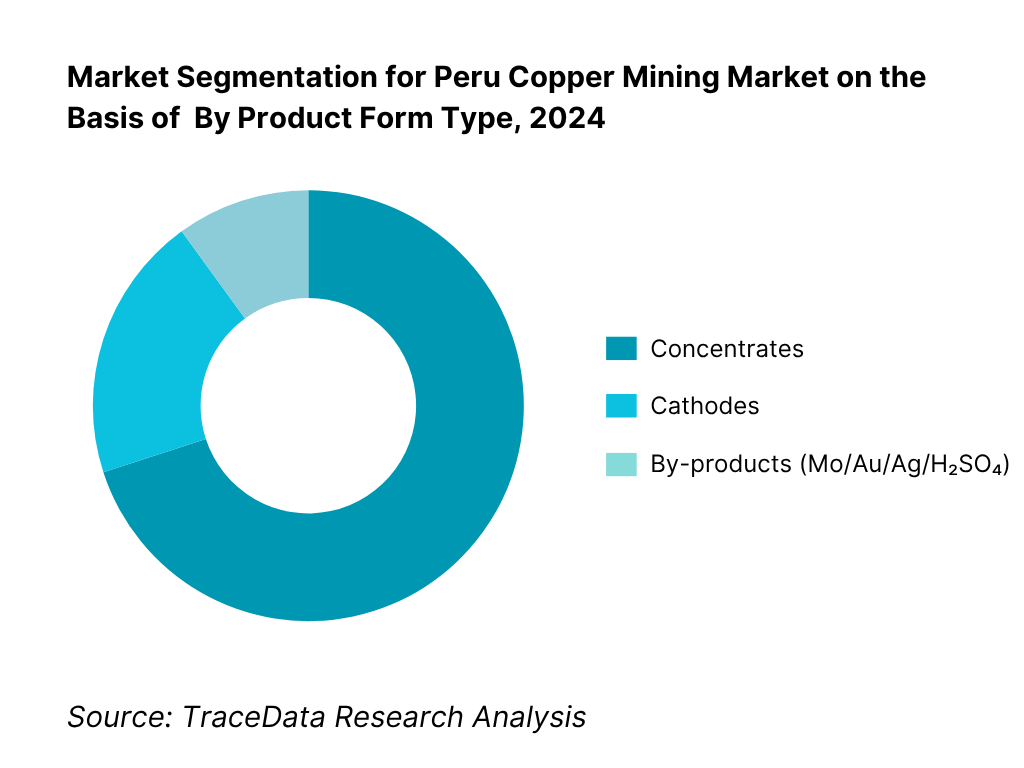
By Product Form: Peru Copper Mining Market is segmented by product form into concentrates, cathodes, and by-products. Recently, concentrates command the dominant share in Peru under this segmentation because most mega-mines are concentrate producers tied to Asian smelter offtakes. The Ilo smelter/copper refinery footprint is comparatively smaller than the mine pipeline, making ex-port concentrados the commercial norm. Concentrate logistics—bulk or containerized to Matarani/Ilo/Callao—and pricing via LME/COMEX with TC/RC terms align with traders’ preferences, reinforcing the prevalence of concentrate sales over domestic refining.
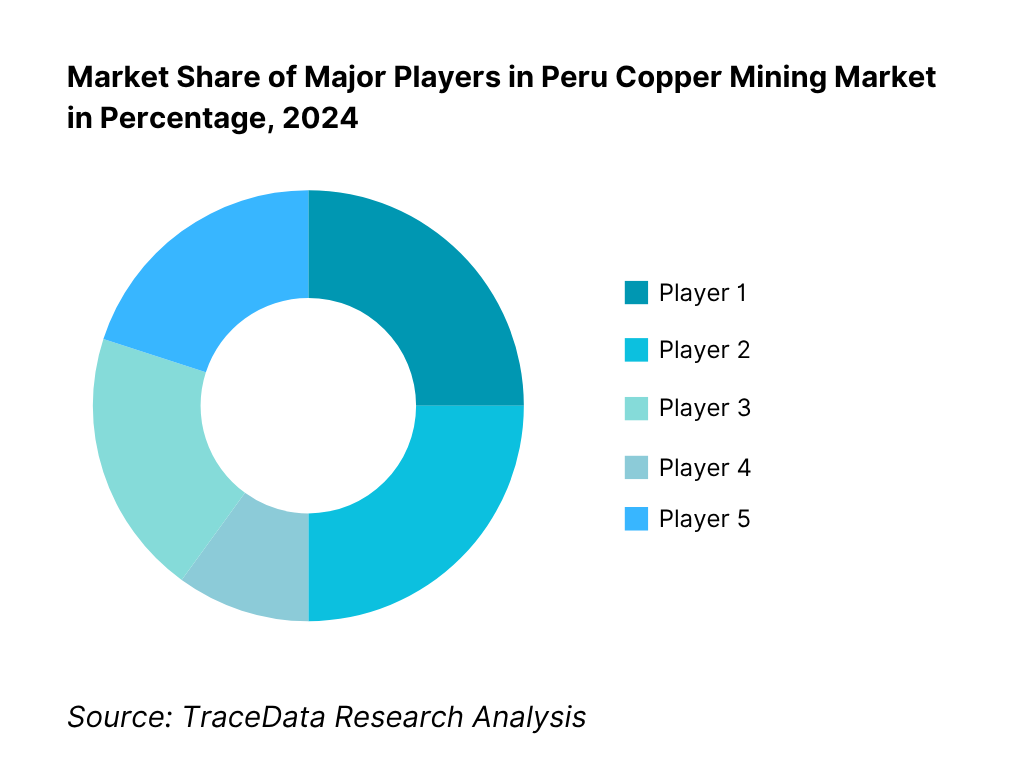
Competitive Landscape in Peru Copper Mining Market
The Peru Copper Mining Market features a tight core of tier-one operators controlling multi-decadal assets and long-term offtakes. Their influence is amplified by modernization capex (HPGR, coarse particle flotation, dry-stack tailings), renewable PPAs, and Copper Mark adoption. Strategic positions along the Southern Mining Corridor and proximity to Matarani/Ilo ports contribute to reliable export flows, reinforcing consolidation around a handful of mega-mines and high-grade districts.
Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
Southern Copper Corporation | 1952 | Mexico City, Mexico |
Compañía Minera Antamina S.A. | 1996 | Lima, Peru |
Sociedad Minera Cerro Verde S.A.A. | 1993 | Arequipa, Peru |
Minera Las Bambas S.A. | 2010 | Lima, Peru |
Minera Chinalco Perú S.A. | 2003 | Lima, Peru |
Hudbay Minerals Inc. | 1996 | Toronto, Canada |
Anglo American plc (Quellaveco) | 1917 | London, United Kingdom |
Compañía Minera Antapaccay S.A. | 1980 | Espinar (Cusco), Peru |
Marcobre S.A.C. (Mina Justa) | 2004 | Lima, Peru |
Sociedad Minera El Brocal S.A.A. | 1956 | Lima, Peru |
Compañía de Minas Buenaventura | 1953 | Lima, Peru |
Nexa Resources Perú S.A.A. | 1949 | Lima, Peru |
Compañía Minera Zafranal S.A.C. | 2011 | Lima, Peru |
First Quantum Minerals Ltd. | 1983 | Vancouver, Canada |
Minera Shouxin Perú S.A. | 2011 | Lima, Peru |
Some of the Recent Competitor Trends and Key Information About Competitors Include:
Southern Copper Corporation: As one of the largest operators in Peru, Southern Copper has advanced its Ilo smelter modernization program and expanded desalination capacity to support Toquepala and Cuajone, ensuring reliable water supply for operations and improved sustainability credentials.
Compañía Minera Antamina S.A.: Known for its scale and polymetallic profile, Antamina has implemented coarse particle flotation and advanced molybdenum recovery systems, enhancing concentrate quality while extending mine life. The company continues to invest in tailings dam safety upgrades and community infrastructure projects in Ancash.
Sociedad Minera Cerro Verde S.A.A. (Freeport-McMoRan): Cerro Verde has focused on debottlenecking its 400 kt/d concentrator and integrating high-pressure grinding rolls (HPGR) to improve throughput. The mine has also invested in a large-scale water reclamation and reuse system to reduce freshwater dependency.
MMG Las Bambas S.A.: Las Bambas has emphasized autonomous haulage trials and digital dispatch optimization, while engaging in new community road safety agreements along the Southern Mining Corridor. The company is also advancing development of the Chalcobamba pit to offset declining grades.
Anglo American Quellaveco S.A.: Quellaveco, Peru’s newest mega-project, has reached steady-state output and secured long-term renewable power purchase agreements (PPAs) to run its concentrator on 100% clean energy. The mine is also leveraging a digital twin system to optimize operations and predictive maintenance.
What Lies Ahead for Peru Copper Mining Market?
The Peru copper mining market is expected to maintain its position as a global supply cornerstone, driven by the commissioning of new projects, operational debottlenecking at existing mines, and sustained global demand for copper in renewable energy and electric mobility. Expansion of Peru’s production base, alongside infrastructure modernization and regulatory streamlining, will reinforce its role in meeting the world’s copper requirements over the coming decade.
Stabilization of New Mega-Projects: The future of the Peru copper mining market will hinge on the successful ramp-up and stabilization of projects such as Quellaveco and the planned development of Zafranal and La Granja. These projects will provide multi-decade production streams that offset declining grades at mature mines.
Emphasis on ESG and Social License: Operators will place stronger focus on achieving Copper Mark certification, reducing carbon intensity, and advancing community investment. Social conflict mitigation through continuous dialogue and transparent benefit-sharing will remain central to sustaining long-term production stability.
Technological Modernization: The market will witness deeper adoption of autonomous haulage systems, digital twin platforms, and coarse particle flotation technologies. These advances will not only boost productivity but also improve energy and water efficiency in concentrators, making Peru’s operations more competitive globally.
Renewable Energy Integration: With national generation exceeding 58,000 GWh annually, the transition to 100% renewable PPAs for major copper mines will accelerate. This will reduce operational carbon footprints and align Peruvian copper with the requirements of environmentally conscious smelters and downstream manufacturers.
Diversification into By-Products: Growing attention will be given to monetizing molybdenum, gold, silver, and sulfuric acid streams as critical contributors to revenue. This diversification strategy will improve margins and reduce exposure to pure copper price volatility, ensuring greater financial resilience.
Peru Copper Mining Market Segmentation
By Mining Method
Open-Pit Mining
Underground Mining
Heap-Leach Operations
Hybrid (Open-Pit + UG) Projects
By Product Form
Copper Concentrates
Refined Cathodes
By Lifecycle Stage
Operating Mines
Construction Stage Projects
Advanced Development
Feasibility/PFS/PEA Stage
Exploration Properties
By Region
Arequipa (Cerro Verde)
Apurímac (Las Bambas, Haquira)
Moquegua (Quellaveco, Cuajone)
Cusco (Antapaccay, Tintaya legacy pits)
Ancash (Antamina)
Tacna (Toquepala)
By Ownership/Operator Type
Multinational Majors
Joint Ventures (Antamina, Quellaveco)
Peruvian Publicly Listed Companies (Buenaventura, El Brocal)
Private Domestic Companies
Players Mentioned in the Report:
Southern Copper Corporation
Compañía Minera Antamina S.A.
Sociedad Minera Cerro Verde S.A.A. (Freeport-McMoRan)
MMG Las Bambas S.A.
Minera Chinalco Perú S.A. (Toromocho)
Hudbay Minerals Inc. (Constancia/Pampacancha)
Anglo American Quellaveco S.A.
Compañía Minera Antapaccay S.A. (Glencore)
Marcobre S.A.C. (Mina Justa)
Sociedad Minera El Brocal S.A.A.
Compañía de Minas Buenaventura S.A.A.
Nexa Resources Perú S.A.A.
Compañía Minera Zafranal S.A.C.
First Quantum Minerals Ltd. (La Granja/Haquira interests)
Minera Shouxin Perú S.A.
Key Target Audience
Mining majors & project developers (asset owners, Peru strategies)
Investments and venture capitalist firms (mining-tech, services, and streaming/royalty opportunities)
Government and regulatory bodies (MINEM, SENACE, OEFA, ANA, OSINERGMIN, SUNAT)
International smelters & traders (China, Japan, Korea, Europe procurement desks)
EPC/EPCM & mining contractors (drill-blast, haulage, plant upgrades)
OEMs & consumables suppliers (mining fleets, mill liners, reagents, explosives, filtration, tailings tech)
Banks & export credit agencies (project finance, offtake prepayments)
Logistics & port operators
Time Period:
Historical Period: 2019-2024
Base Year: 2025
Forecast Period: 2025-2030
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Delivery Model Analysis for Copper Mining-Open-Pit, Underground, Heap-Leach, Smelting & Refining (Margins, Productivity KPIs, Strengths & Weaknesses)
4.2. Revenue Streams for Peru Copper Mining Market (Concentrates, Cathodes, By-products: Molybdenum, Gold, Silver, Sulfuric Acid, Tolling, Offtake Agreements)
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Peru Copper Mining Market (Cost Structure, Revenue Streams, Key Partners, Community Agreements, Environmental Commitments)
5.1. Freelance/Contractor Mining Services vs In-House Workforce (drilling, hauling, maintenance; wage vs contractor costs, productivity impact)
5.2. Investment Model in Peru Copper Mining Market (Greenfield, Brownfield Expansion, Streaming/Royalties, JV Partnerships, State Contracts)
5.3. Comparative Analysis of Project Approval Funnel-Private vs Government-backed Mines (EIA timelines, consulta previa, social agreements, financing models)
5.4. Copper Mining Capex & Opex Allocation by Project Stage (Exploration, Construction, Operations, Closure)
8.1. Revenues (USD Bn), Historical-Production × Copper Prices
9.1. By Market Structure (In-House vs Outsourced Mining Operations)
9.2. By Mining Method (Open-Pit, Underground, Heap-Leach, Hybrid)
9.3. By Lifecycle Stage (Operating, Construction, Advanced Development, Feasibility/Exploration)
9.4. By Product Form (Concentrates, Cathodes, By-products)
9.5. By Ownership Type (Multinational, JV, Peruvian Public, Private)
9.6. By Region (Arequipa, Apurímac, Moquegua, Cusco, Ancash, Tacna)
9.7. By Logistics Mode (Road, Rail, Pipeline, Port Access)
10.1. End-User Landscape-China, Japan, Europe, U.S. smelters/traders
10.2. Copper Buyer Needs & Procurement Decision-Making Process (TC/RC terms, concentrate quality, arsenic penalties, LME/COMEX exposure)
10.3. ROI Analysis of Copper Mining Projects (NPV, IRR, payback period)
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework (mine output vs global electrification demand)
11.1. Trends & Developments (automation, digital twins, renewable PPAs, seawater desalination, dry-stack tailings, social license models)
11.2. Growth Drivers (global EV adoption, renewable energy expansion, high-grade porphyry reserves, infrastructure investments)
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Peru Copper Mining Market
11.4. Issues & Challenges (community conflicts, logistics bottlenecks, permitting delays, water scarcity, declining grades)
11.5. Government Regulations (royalty structure, special mining tax, EIA approvals, consulta previa obligations, stability agreements)
12.1. Peru’s Share in Global Copper Output & Export Markets
12.2. Smelting/Refining Gaps & Concentrate Dependence
12.3. Future Global Copper Deficit & Peru’s Expansion Pipeline
15.1. Market Share of Key Players in Peru Copper Mining Market (by Output & Revenue)
15.2. Benchmark of Key Competitors-Company Overview, USP, Mine Portfolio, Production Volumes, Revenues, Cash Costs, Technology Used, Best Performing Mines, Community Agreements, Strategic Partnerships, Recent Developments
15.3. Operating Model Analysis Framework (Integrated vs pure-play, smelting/refining linkages, contractor reliance)
15.4. Gartner Magic Quadrant-Positioning of Peru’s Copper Producers
15.5. Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
16.1. Revenues (USD Bn), Forecast
17.1. By Market Structure (In-House vs Outsourced Mining Operations)
17.2. By Mining Method (Open-Pit, Underground, Heap-Leach, Hybrid)
17.3. By Lifecycle Stage (Operating, Development, Exploration)
17.4. By Product Form (Concentrates, Cathodes, By-products)
17.5. By Ownership Type (Multinational, JV, Public, Private)
17.6. By Region (Arequipa, Apurímac, Moquegua, Cusco, Ancash, Tacna)
17.7. By Logistics Mode (Road, Rail, Pipeline, Port Access)
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand-side and supply-side entities for the Peru Copper Mining Market. On the supply side, this includes mining majors, EPC/EPCM contractors, equipment OEMs, reagent suppliers, logistics providers, and port operators. On the demand side, it encompasses international smelters, commodity traders, and downstream manufacturers in Asia, Europe, and North America. Based on this mapping, we shortlist 5–6 leading copper mining operators in Peru (e.g., Southern Copper, Antamina, Cerro Verde, Las Bambas, Quellaveco, Hudbay) using financial disclosures, production statistics, and export footprint. Sourcing is conducted through government bulletins (MINEM, BCRP), industry articles, and proprietary trade databases to collate industry-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
An exhaustive desk research process is carried out by referencing secondary and proprietary databases. This enables a thorough analysis of the Peru Copper Mining Market, aggregating insights on production volumes, port throughput, workforce data, mine lifecycles, and demand structures. We also examine regulatory filings and environmental approvals. Company-level data—such as annual reports, community investment disclosures, Copper Mark certifications, and sustainability statements—are analyzed to understand financial stability, operational efficiency, and social license practices. This process builds a robust foundation for understanding the sectoral value chain and the entities that shape market dynamics.
Step 3: Primary Research
We conduct in-depth interviews with senior executives and technical managers across Peru’s copper mining industry, as well as with smelters, traders, and local regulatory officials. These interviews validate market hypotheses, authenticate production and export data, and provide operational insights such as plant recovery rates, logistics challenges, and community engagement models. A bottom-to-top approach is applied to evaluate the revenue contributions and output volumes of each operator, which are then aggregated into a national market picture. As part of validation, our team also undertakes disguised interviews by approaching companies as prospective buyers or partners. This method enables verification of operational and financial details, while also clarifying revenue streams, pricing structures, and contractual arrangements with offtakers.
Step 4: Sanity Check
A combined bottom-to-top and top-to-bottom validation is carried out using market size modeling and reconciliation with customs-cleared export values and official mine production data. This step ensures consistency between reported production volumes, export receipts, and company-level financials. Any variances are analyzed against historical trends, operational disruptions, or community conflict events. This dual approach ensures the credibility and accuracy of the final market analysis for the Peru Copper Mining Market.
FAQs
01 What is the potential for the Peru Copper Mining Market?
The Peru Copper Mining Market holds substantial potential, with production reaching 2.736 million tons of copper supported by mega-mines such as Antamina, Cerro Verde, Las Bambas, and Quellaveco. Export receipts exceeded USD 20.4 billion, underscoring the sector’s importance in global supply chains. The market’s potential is further reinforced by Peru’s position as the world’s second-largest copper producer, a growing pipeline of projects like Zafranal and La Granja, and the increasing global demand for copper in renewable energy, electric vehicles, and grid infrastructure.
02 Who are the Key Players in the Peru Copper Mining Market?
The Peru Copper Mining Market features several key players, including Southern Copper Corporation, Compañía Minera Antamina S.A., Sociedad Minera Cerro Verde S.A.A., MMG Las Bambas S.A., and Anglo American Quellaveco S.A. These companies dominate the market due to their multi-decade reserves, large-scale concentrators, and robust offtake agreements with Asian smelters. Other notable participants include Minera Chinalco Perú S.A., Hudbay Minerals Inc., Compañía Minera Antapaccay S.A., Marcobre S.A.C., and Sociedad Minera El Brocal S.A.A., all of which contribute significantly to national production and exports.
03 What are the Growth Drivers for the Peru Copper Mining Market?
The primary growth drivers include the global demand for copper fueled by renewable energy capacity additions, with over 58,393 GWh of national electricity generation supporting power-intensive concentrator operations. Export data confirm strong external demand, with 912,199,000 kg of copper ore exported to Japan alone and more than USD 15 billion in shipments to China, highlighting stable offtake. Additionally, Peru’s regulatory framework has enabled the approval of 22 copper mining projects within a year, strengthening the pipeline of future output and ensuring continuity in supply for global markets.
04 What are the Challenges in the Peru Copper Mining Market?
The Peru Copper Mining Market faces several challenges, including social conflicts, with the Ombudsman’s Office reporting 196 active disputes, of which 148 are socio-environmental and frequently tied to mining corridors. Logistics limitations along the 485 km Southern Mining Corridor constrain trucking efficiency and make concentrate exports vulnerable to disruptions. Water licensing requirements also create hurdles, as technical approvals require quantified flow data in liters per second and extensive documentation before expansion. These challenges combine to pose significant barriers to stable operations, even as global demand continues to rise.