Philippines Logistics and Warehousing Market Outlook to 2029
By Service Mix (Freight Forwarding, Warehousing, Courier Express & Parcel), By End User Industry (Manufacturing, Retail, FMCG, Automotive, E-commerce), By Domestic and International Logistics, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0195
- Region: Asia
- Published on: June 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Philippines Logistics and Warehousing Market Outlook to 2029 – By Service Mix (Freight Forwarding, Warehousing, Courier Express & Parcel), By End User Industry (Manufacturing, Retail, FMCG, Automotive, E-commerce), By Domestic and International Logistics, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the logistics and warehousing industry in the Philippines. The report includes an overview and genesis of the sector, overall market size in terms of revenue, segmentation of services, trends and developments, regulatory landscape, key demand drivers, challenges, comparative landscape of leading players, and profiles of major logistics and warehousing companies. The report concludes with market projections until 2029 based on key parameters, highlighting opportunities, challenges, and case studies demonstrating successful logistics strategies in the Philippines.
Philippines Logistics and Warehousing Market Overview and Size
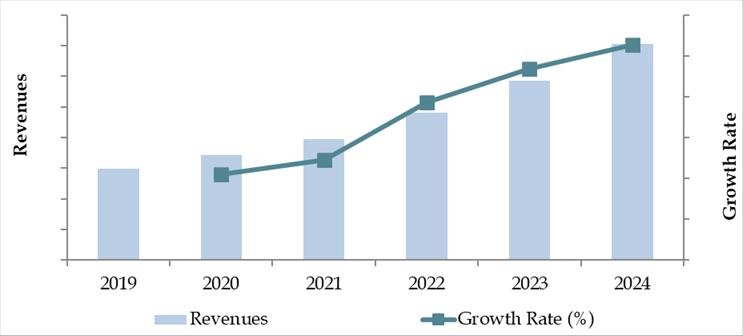
The logistics and warehousing market in the Philippines was valued at PHP 970 Billion in 2023, fueled by growing e-commerce penetration, infrastructure investments, and rising consumption in urban areas. The market features both global and local players such as LBC Express, 2GO Group, Ninja Van, DHL, FedEx, and JRS Express, which are recognized for their expansive network, integrated logistics solutions, and last-mile delivery capabilities.
Metro Manila, Cebu, and Davao are dominant logistics hubs, benefiting from their strategic geographical positioning and developed transportation ecosystems. In 2023, 2GO introduced an integrated multimodal logistics service tailored for retail and manufacturing sectors, indicating a market shift toward end-to-end logistics solutions.
Market Size for Philippines Logistics and Warehousing Industry on the Basis of Revenue in USD Billion, 2018-2024
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Philippines Logistics and Warehousing Market:
Booming E-commerce Sector: The Philippine e-commerce market grew over 20% YoY in 2023, significantly boosting demand for reliable logistics and warehousing services. E-commerce platforms such as Lazada, Shopee, and Zalora have increasingly partnered with third-party logistics (3PL) providers to manage inventory and delivery operations, especially in urban and suburban regions.
Government Infrastructure Push: The “Build, Build, Build” program has contributed to major road and port upgrades, directly enhancing the logistical efficiency across Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao. Projects like the North-South Commuter Railway and expansion of Clark International Airport have eased freight congestion and shortened delivery timelines.
Rise of Cold Chain and Value-added Warehousing: Demand for cold chain logistics is growing due to rising consumption of frozen food, pharmaceuticals, and dairy products. In 2023, cold storage capacity expanded by 18%, and this trend is expected to continue due to increased food security awareness and vaccine distribution efforts.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for Philippines Logistics and Warehousing Market
Fragmented Infrastructure and Traffic Congestion: One of the most pressing challenges in the Philippines logistics market is the poor road infrastructure and chronic congestion, especially in Metro Manila. According to a 2023 logistics performance index report, average delivery times in urban centers are 30–40% higher than regional benchmarks. These inefficiencies result in delayed shipments, increased fuel costs, and reduced service quality for logistics providers.
High Cost of Logistics: The Philippines ranks among the highest in ASEAN for logistics costs, amounting to around 27% of the cost of goods sold (COGS), compared to an average of 16% in neighboring countries. Contributing factors include port delays, fuel surcharges, and warehousing shortages. High logistics costs are particularly burdensome for small and medium enterprises (SMEs), limiting their ability to compete effectively.
Limited Cold Chain Coverage: Although demand for cold storage has surged, especially for perishable foods and pharmaceuticals, the cold chain infrastructure remains underdeveloped in secondary and rural cities. In 2023, over 40% of cold chain-dependent shipments reportedly experienced temperature-related spoilage or delays, leading to significant inventory losses for retailers and distributors.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
Ease of Doing Business Initiatives: The Philippine government has implemented various programs under the “TradeNet” platform to simplify import-export documentation and integrate agencies involved in trade processing. As of 2023, 78% of customs entries are now processed electronically, reducing manual paperwork and corruption risk.
Build Better More Infrastructure Program: Under the current administration, the "Build Better More" campaign has succeeded the previous “Build, Build, Build” program, allocating over PHP 1.2 trillion in 2023 towards logistics-related infrastructure, including airports, expressways, and inter-island transport. These projects aim to reduce transit times and expand regional connectivity by 2026.
Philippine Multimodal Transport and Logistics Roadmap: In partnership with the Department of Trade and Industry (DTI), a national roadmap was released in 2022 to improve freight logistics competitiveness by 2030. Key targets include reducing logistics costs to 20% of COGS and increasing the logistics sector’s contribution to GDP from 4.7% to 6.5%.
Philippines Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
By Market Structure: The unorganized segment, consisting of independent freight brokers, small courier companies, and local warehousing providers, currently dominates the logistics market in the Philippines. These players often cater to regional or industry-specific needs, providing cost-effective solutions for SMEs. Their agility and familiarity with local delivery challenges make them a preferred choice for last-mile and rural delivery services. The organized segment, including global 3PL providers and integrated logistics firms, is gaining ground, particularly among large-scale enterprises and e-commerce platforms seeking reliability, scale, and digital integration. These players offer multimodal transport, real-time tracking, and optimized supply chains, driving demand in urban and industrial corridors.
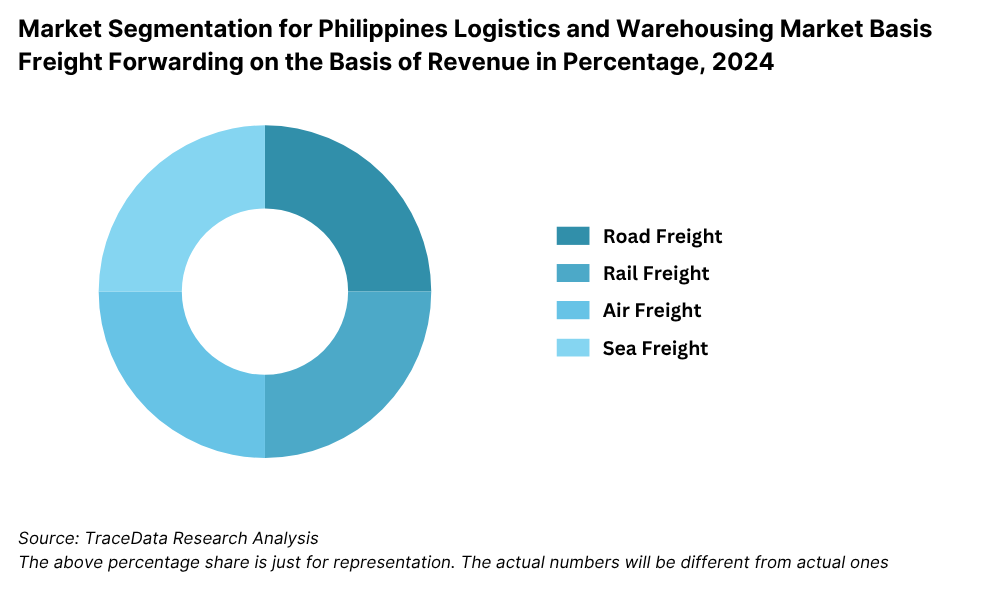
By Service Mix: Freight Forwarding remains the largest segment, driven by increased trade volumes and industrial output. It includes both air and sea freight services used by exporters and manufacturers. Warehousing accounts for a growing share as more companies seek inventory optimization, just-in-time delivery, and cold chain support.
Courier, Express & Parcel (CEP) services have expanded rapidly due to e-commerce, with demand for same-day and next-day deliveries.
Value-Added Logistics Services, such as packaging, labeling, and reverse logistics, are gaining momentum among organized players.
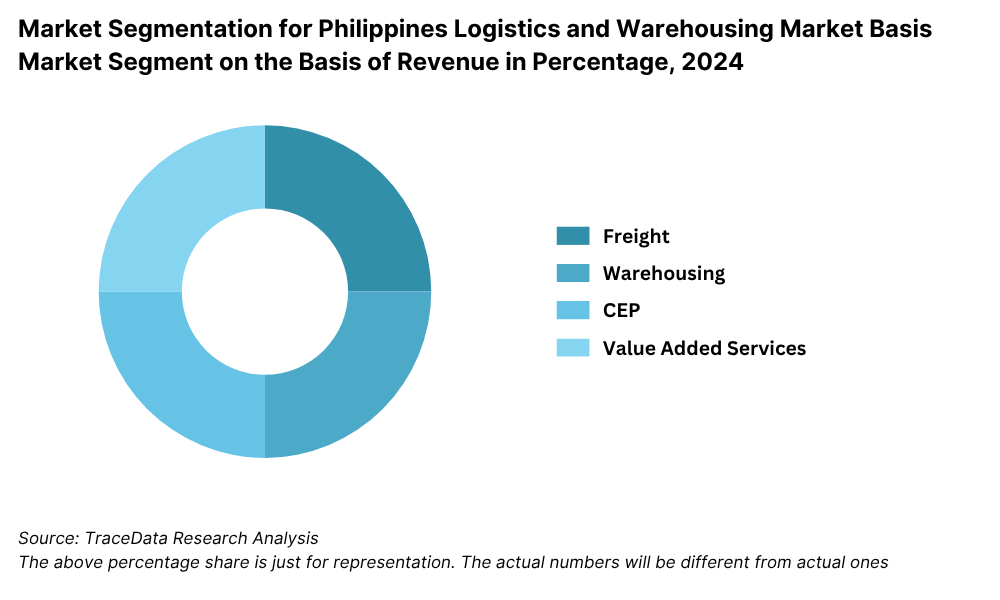
By End User Industry: The retail and e-commerce sectors are the largest contributors due to high volume and delivery frequency. Manufacturing also remains significant, especially in automotive, electronics, and garments.
FMCG and Pharmaceuticals have driven the need for efficient cold chain logistics.
The automotive and agriculture industries are also adopting warehousing and transport solutions for better distribution coverage.
Competitive Landscape in Philippines Logistics and Warehousing Market
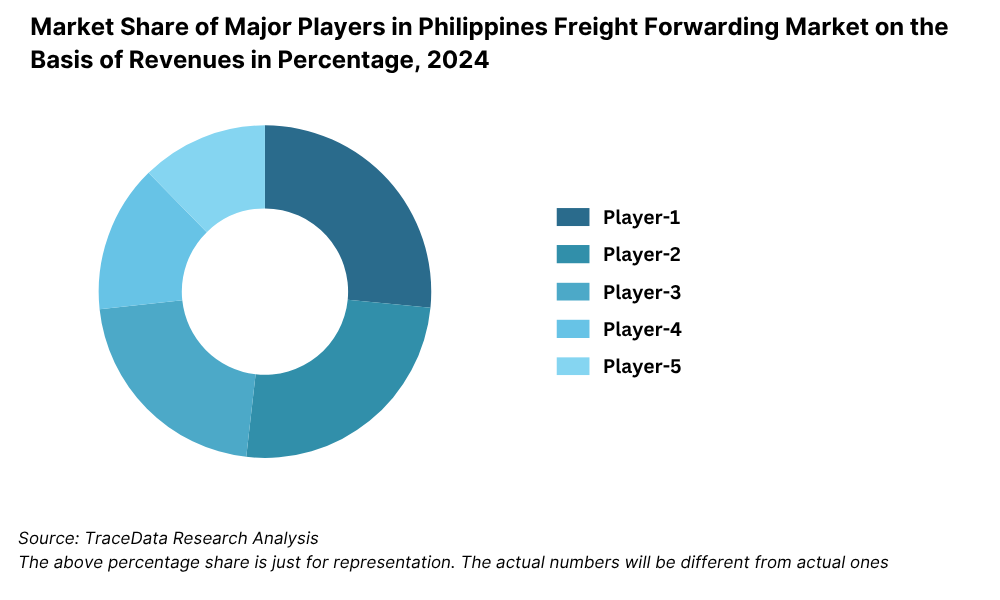
The Philippines logistics and warehousing market is moderately fragmented, with a mix of long-established companies, rising digital-first players, and regional logistics startups. The presence of both domestic operators and international logistics giants has led to competitive service offerings, ranging from express delivery to full-stack supply chain management. Major players include LBC Express, 2GO Group, JRS Express, Ninja Van, DHL, FedEx, Entrego, and Transportify.
| Company Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
| 2GO Group, Inc. | 1949 (as Negros Navigation) | Manila, Philippines |
| LBC Express, Inc. | 1945 | Manila, Philippines |
| JRS Express | 1960 | Manila, Philippines |
| AP Cargo Logistics Network Corp. | 1971 | Pasay, Philippines |
| Air21 (U-Freight Philippines) | 1979 | Manila, Philippines |
| Aboitiz Transport System (now part of 2GO) | 1907 | Cebu, Philippines |
| MetroPak Logistics, Inc. | 2003 | Manila, Philippines |
| Yusen Logistics Philippines, Inc. | 1955 (PH: ~1990s) | Tokyo, Japan |
| DHL Supply Chain Philippines | 1969 (PH: ~1980s) | Bonn, Germany |
| FedEx Express Philippines | 1971 (PH: 1984) | Memphis, USA |
| UPS Philippines | 1907 (PH: ~1997) | Atlanta, USA |
| Kuehne + Nagel Philippines, Inc. | 1890 (PH: ~1990s) | Schindellegi, Switzerland |
| DB Schenker Philippines | 1872 (PH: ~2000s) | Essen, Germany |
| Nippon Express Philippines Corp. | 1937 (PH: ~1970s) | Tokyo, Japan |
| Maersk Logistics Philippines | 1904 (PH: ~2000s) | Copenhagen, Denmark |
| CEVA Logistics Philippines | 2006 (PH: ~2010s) | Marseille, France |
| Agility Logistics Philippines | 1979 (PH: ~2006) | Kuwait City, Kuwait |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about major players include:
LBC Express: As one of the oldest and most trusted logistics providers in the Philippines, LBC handled over 120 million shipments in 2023. The company continues to expand its warehousing network and recently introduced enhanced cash-on-delivery options tailored for SMEs and online sellers.
2GO Group: A major logistics and transport firm under SM Investments, 2GO launched a multimodal logistics initiative in 2023, integrating sea, air, and land transport. The company recorded over PHP 18 billion in logistics revenues and invested heavily in digitizing port and freight operations.
JRS Express: Known for its wide reach and strong domestic courier services, JRS Express expanded its next-day delivery service to cover additional rural zones in 2023. It maintains over 450 branches nationwide and continues to be a key player for low-cost parcel delivery.
Ninja Van: A prominent tech-enabled logistics firm, Ninja Van delivered over 100 million parcels in the Philippines in 2023, with a strong focus on e-commerce. Its investments in route optimization and last-mile automation have improved delivery efficiency by 20% YoY.
DHL Express: Catering primarily to international shipments and B2B logistics, DHL launched its green logistics program in the Philippines in 2023, focusing on carbon-neutral warehousing and eco-packaging solutions. It remains a preferred partner for global trade and express international deliveries.
FedEx Philippines: Expanded its regional gateway in 2023 by upgrading its Clark Hub, enabling faster outbound deliveries across Southeast Asia. It also introduced AI-driven customs clearance systems, improving international delivery accuracy and speed.
Entrego: A logistics solutions provider backed by Ayala Corporation, Entrego offers fully digital warehousing, fulfillment, and last-mile delivery services. In 2023, it grew its client base among local e-commerce sellers by over 35%, focusing on same-day services.
Transportify: Focused on on-demand, intracity freight services, Transportify expanded into Visayas and Mindanao in 2023. With its app-based model, it caters to businesses needing flexible, scalable logistics, especially in urban areas with heavy traffic bottlenecks.
What Lies Ahead for Philippines Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Philippines logistics and warehousing market is projected to grow steadily through 2029, registering a healthy CAGR driven by infrastructure development, digital transformation, and increasing reliance on third-party logistics providers (3PLs). Expansion of trade, rising e-commerce penetration, and a shift toward integrated supply chain models will continue to shape the market’s trajectory.
Rise of Smart Warehousing and Automation: The logistics industry is expected to witness an increasing adoption of warehouse automation technologies, including robotics, automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS), and AI-driven inventory management. These advancements will help reduce manual errors, improve space utilization, and enhance overall operational efficiency, especially in Metro Manila and Cebu.
Growth in Cold Chain and Pharma Logistics: As demand for fresh produce, frozen food, and pharmaceutical products increases, cold chain logistics will be a high-growth segment. New investments in temperature-controlled storage facilities and refrigerated transport are expected, particularly in Mindanao and Visayas, driven by food exports and healthcare supply chains.
E-commerce as a Primary Growth Driver: With the Philippines' internet penetration exceeding 75% and the continued boom in online shopping, last-mile delivery and micro-fulfillment centers will become critical. Logistics providers will increasingly invest in hyperlocal warehousing, dark stores, and real-time delivery tracking to meet evolving consumer expectations.
Sustainability and Green Logistics: Sustainability will become a key theme, with logistics firms adopting electric delivery vehicles, solar-powered warehouses, and eco-friendly packaging. Government and private sector collaboration is expected to promote cleaner logistics, aligning with national climate goals.
Future Outlook and Projections for Philippines Logistics and Warehousing Market on the Basis of Revenues in USD Billion, 2024-2029
Philippines Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
- By Market Structure:
o Organized Sector
o Unorganized Sector
o Integrated 3PL Service Providers
o Freight Forwarders
o Courier, Express & Parcel (CEP) Providers
o Warehousing & Fulfillment Centers
o Cold Chain Logistics Companies - By Service Type:
o Freight Forwarding (Air, Sea, Land)
o Warehousing Services (Ambient, Cold Storage)
o Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
o Value-Added Services (Packaging, Labeling, Reverse Logistics) - By End User Industry:
o Retail & E-commerce
o Manufacturing
o FMCG & Pharmaceuticals
o Automotive
o Agriculture & Food Processing
o Electronics & Appliances - By Type of Transport:
o Road Freight
o Rail Freight
o Sea Freight
o Air Freight
o Intermodal/Multimodal - By Temperature Control:
o Cold Chain
o Non-Cold Chain - By Region:
o Metro Manila (NCR)
o CALABARZON
o Central Luzon
o Visayas
o Mindanao
Players Mentioned in the Report:
Freight Forwarding Companies
Vserve Ebusiness Solutions
EX-WORKS Cargo Services Inc.
Airspeed
Yello X Supply Chain Solutions
AAI Worldwide Logistics
F2 Logistics
K Line Logistics
Deutsche Post DHL Group
FedEx
UPS
Yusen Logistics
Royal Cargo
AAI Worldwide Logistics
F2 Logistics
CEVA Logistics
Ernest Logistics Corporation
K Line Logistics
DB Schenker
Kuehne + Nagel
DHL Global Forwarding
2GO
Air21
Grab Express
J&T Express
JRS Express
Lalamove
LBC Express
Ninja Van
2GO
LBC Express
JRS Express
Grab Express
Ninja Van
DHL Express
FedEx
Aramex
UPS
Warehousing Companies
E‑Commerce Logistics Companies
Express Logistics Companies
Key Target Audience:
- Logistics and Freight Companies
- E-commerce Companies
- Retail Chains and Distributors
- Cold Storage and Cold Chain Providers
- Government and Regulatory Authorities (e.g., Department of Trade and Industry, Department of Transportation)
- Investors and PE/VC Firms
- Infrastructure and Industrial Park Developers
- Warehousing Automation Companies
Time Period:
- Historical Period: 2018–2023
- Base Year: 2024
- Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Macroeconomic framework for Philippines Including GDP (2018-2024), GDP Growth (2018-2024), GDP Contribution by Sector
4.2. Logistics Sector Contribution to GDP and how the contribution has been changing in the historical assessment
4.3. Ease of Doing Business in Philippines
4.4. LPI Index of Philippines and Improvements in the last 10-15 Years
4.5. Custom Procedure and Custom Charges in Philippines Logistics market
5.1. Landscape of Investment Parks and Free Trade Zones in Philippines
5.2. Current Scenario for Logistics Infrastructure in Philippines
5.3. Road Infrastructure in Philippines including Road Network, Toll Charges and Toll Network, Major Goods Traded through Road, Major Flow Corridors for Road (Inbound and Outbound)
5.4. Air Infrastructure in Philippines including Total Volume Handled, FTK for Air Freight, Major Inbound and Outbound Flow Corridors, Major Goods traded through Air, Number of Commercial and passenger Airports, Air Freight Volume by Ports and other Parameters
5.5. Sea Infrastructure in Philippines including Total Volume Handled, FTK for Sea Freight, Major Inbound and Outbound Flow Corridors, Major Goods Traded through Sea, Number of Ports for Coastal and Ocean Freight, Number of Vessels, Sea Freight Volume by Ports and other Parameters
5.6. Rail Infrastructure in Philippines including Total Volume Handled, FTK for Rail Freight, Major Inbound and Outbound Flow Corridors, Major Goods Traded through Rail and others
6.1. Basis Revenues, 2018-2024P
7.1. By Segment (Freight Forwarding, Warehousing, CEP and Value-Added Services), 2018-2024P
7.2. By End User Industries, 2018-2024P
8.1. Market Overview and Genesis
8.2. Philippines Freight Forwarding Market Size by Revenues, 2018-2024P
8.3. Philippines 3PL Freight Forwarding Market Segmentation, 2018-2024P
8.3.1. By Mode of Freight Transport (Road, Sea, Air and Rail), 2018-2024P
8.3.1.1. Price per FTK for Road/Air/Sea and Rail in Philippines
8.3.1.2. Road Freight (Domestic and International Volume, FTK and Revenue; Number of Registered Vehicles)
8.3.1.3. Road Freight Domestic and International Corridors
8.3.1.4. Ocean Freight (Domestic and International Volume, FTK and Revenue; Volume by Commodity; Sea Ports Key Statistics)
8.3.1.5. Air Freight (Domestic and International Volume, FTK and Revenue)
8.3.1.6. Rail Freight (Domestic and International Volume, FTK and Revenue; Volume by Commodity and Region)
8.3.1.7. Export-Import Scenario (Value by Mode of Transport, Commodity and Country; Volume by Principal Commodities)
8.3.2. By Intercity Road Freight Corridors, 2018-2024P
8.3.3. By International Road Freight Corridors, 2018-2024P
8.3.4. By End User (Industrial, FMCG, F&B, Retail and Others), 2018-2024P
8.4. Snapshot of Freight Truck Aggregators in Philippines Including Company Overview, USP. Business Strategies, Future Plans, Business Model, Number of Fleets, Margins/Commission, Number of Booking, Major Clients, Average Booking Amount, Major Routes and others
8.5. Competitive Landscape in Philippines Freight Forwarding Market, 2021
8.5.1. Heat Map of Major Players in Philippines Freight Forwarding on the Basis of Service offering
8.5.2. Market Share of Maior Players in Philippines Freight Forwarding Market, 2023
8.5.3. Cross Comparison of Major Players in Freight Forwarding Companies on the Basis of Parameters including Volume of Road Freight, Inception Year, Number of Fleets (Owned and Subcontracted), Fleets by Type, Occupancy Rate, Number of Employees, Major Route Network, Major Clients, Revenues, Volume of Sea Freight, Volume of Air Freight, USP, Business Strategy, Technology, (2023)
8.6. Philippines 3PL Freight Forwarding Future Market Size by Revenues, 2025-2029
8.7. Philippines Freight Forwarding Market Segmentation, 2025-2029
8.7.1. Future Market Segmentation by Mode of Freight Transport (Road, Sea, Air and Rail), 2025-2029
8.7.2. Future Market Segmentation by International Road Freight Corridors (China, Thailand and Philippines), 2025-2029
8.7.3. Future Market Segmentation by End User (Industrial, FMCG, F&B, Retail and Others), 2025-2029
9.1. Market Overview and Genesis
9.2. Value Chain Analysis in Philippines Warehousing Market including entities, margins, role of each entity, process flow, challenges and other aspects
9.3. Philippines Warehousing Market Size on the Basis of Revenues and Warehousing Space, 2018-2024P
9.4. Philippines 3PL Warehousing Segmentation
9.4.1. Philippines Warehousing Revenue by Business Model (Industrial/Retail, ICD/CFS and Cold Storage), 2018-2024P
9.4.2. Philippines Warehousing By Type of Warehouse (General, Open Yard, Freezer/Chiller, Ambient and Bonded Warehouses), 2018-2024P
9.4.3. Philippines Warehousing Revenue by End User (Industrial & Construction, FMCG, Retail, Food & Beverage and Others), 2018-2024P
9.4.4. 3PL Warehousing Space by Region, 2024P
9.5. Competitive Landscape in Philippines 3PL Warehousing Market
9.5.1. Market share of Top 10 Companies in Philippines Warehousing Market, 2023
9.5.2. Cross Comparison of Top 10 3PL Warehousing Companies on the Basis of Parameters including Company Overview, USP, Business Strategy, Future Plans, Technology, Revenues from Warehousing, Number of Warehouses, Warehousing Space, Location of Warehouses, Type of Warehouses, Occupancy Rate, Rental Rates, Clients and others, (2023)
9.6. Philippines Warehousing Future Market Size on the Basis of Revenues, 2025-2029
9.7. Philippines Warehousing Market Future Segmentation
9.7.1. Philippines Warehousing Revenue by Business Model (Industrial/Retail, ICD/CFS and Cold Storage), 2025-2029
9.7.2. Philippines Warehousing Revenue By Type of Warehouse (General, Open Yard, Freezer/Chiller, Ambient and Bonded Warehouses), 2025-2029
9.7.3. Philippines Warehousing Revenue by End User (Industrial & Construction, FMCG, Retail, Food & Beverage and Others), 2025-2029
10.1. Market Overview and Genesis
10.2. Value Chain Analysis in Philippines CEP Market including entities, margins, role of each entity, process flow, challenges and other aspects
10.3. Revenue Composition and Contribution Between First Mile/Mid Mile and Last Mile Delivery-Analysis for Domestic and International Shipments
10.4. Philippines CEP Market Size on the Basis of Revenues and Shipments, 2018-2024P
10.5. Philippines CEP Market Segmentation, 2021
10.5.1. Segmentation by Mails and Documents, E-Commerce Shipments and Express Cargo, 2023-2024P
10.5.2. Segmentation by International and Domestic Express, 2023-2024P
10.5.3. Segmentation by B2B, B2C and C2C, 2023-2024P
10.5.4. Segmentation by Period of Delivery, 2023-2024P
10.6. Competitive Landscape in 3PL Market, 2021
10.6.1. Overview and Genesis, Market Nature, Market Stage and Major Competing Parameters
10.6.2. Market Share of Companies in Philippines CEP Market on the Basis of Revenues/Number of Shipments, 2023
10.6.3. Market Share of Top 5 Companies in Philippines E-Commerce Shipment Market on the Basis of Revenues/Number of Shipments, 2023
10.6.4. Cross Comparison of Top 10 Philippines CEP Companies on the Basis of Parameters including Company Overview, USP, Business Strategy, Future Plans, Technology, Number of last Mile Delivery Shipments, Revenues, Major Clients, Number of Fleets, Number of Employees, Number of Riders, Number of Pin Code Served, Major Service Offering and others
10.7. Philippines CEP Market Size on the Basis of Revenues and Shipments, 2025-2029
10.8. Philippines CEP Market Segmentation
10.8.1. Segmentation by Mails and Documents, E-Commerce Shipments and Express Cargo, 2025-2029
10.8.2. Segmentation by International and Domestic Express, 2025-2029
10.8.3. Segmentation by B2B, B2C and C2C, 2025-2029
10.8.4. Segmentation by Period of Delivery, 2025-2029
11.1. Customer Cohort Analysis and End User Paradigm for Different Industry Verticals under Logistics Sector (Telecommunications, FMCG, Automotive, Apparel, F&B, Construction and Pharmaceuticals)
11.2. Understanding on Logistics Spend by End User, 2023-2024P
11.3. End User Preferences in terms of In-House or Outsourcing Logistics Services and Reason for Selection; Segregate this by Size of Company on the Basis of Revenues
11.4. Major Logistics Company who are Specialized in Serving Each Type of End User (Telecommunications, FMCG, Apparel, F&B, Construction and Pharmaceuticals)
11.5. Detailed Landscape of Each End Users across Parameters including Major Products Manufactured and Traded, Emerging Products, Type of Services Required, and Type of Services Outsourced, Major Companies, Contract Duration, Likelihood to Recommend, Market Orientation, Major Clusters, Type of Sourcing Preference, Pain Points, Facilities/Services Required, Future Outlook. Market Size for End User Industry Vertical with Growth Rate, 2018-2024P
12.1. Basis Revenues, 2025-2029
13.1. By Segment (Freight Forwarding, Warehousing, CEP and Value-Added Services), 2025-2029
13.2. By End User Industries, 2025-2029
13.3. Recommendation
13.4. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all demand-side and supply-side entities in the Philippines Logistics and Warehousing Market. Based on this framework, we shortlist the top 6–8 logistics providers and warehousing operators in the country, evaluating them on key parameters such as revenue, operational capacity, service portfolio, and digital infrastructure.
Initial sourcing is conducted through industry articles, trade association reports (e.g., PSB, DTI), government publications, logistics newsletters, and proprietary databases to perform comprehensive desk research and compile sector-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
An extensive secondary research process is undertaken, using credible proprietary databases and publicly available sources. These include government trade data, customs reports, industry whitepapers, annual reports, press releases, and market intelligence reports.
This helps us build a foundational understanding of key metrics such as market size (in PHP Billion), freight volume handled (in metric tons), warehouse capacity (in million sq. ft.), industry segmentation by service type, pricing trends, and regional presence.
Company-level data is deeply reviewed using public filings and third-party financial portals to evaluate their service offerings, operating models, and investments in digital and cold chain logistics.
Step 3: Primary Research
We conduct a series of in-depth interviews with CXOs, senior logistics managers, warehouse operators, e-commerce stakeholders, and transport association representatives across the Philippines. These conversations validate hypotheses generated during desk research and offer firsthand insights into market dynamics.
A bottom-up approach is employed to assess service-wise and region-wise revenue for each major player. Disguised interviews are also undertaken under the pretext of potential clients to cross-check pricing, service SLAs, warehousing capabilities, and transit timelines.
These interviews reveal critical insights into technology adoption, margin structures, fulfillment rates, and customer expectations from logistics partners.
Step 4: Sanity Check
The final market sizing is verified through a top-down and bottom-up triangulation approach. Market models are cross-validated using primary estimates, third-party projections, and historical performance indicators to ensure consistency.
Sensitivity analyses are conducted on key assumptions (e.g., average freight cost per km, warehouse rental rates, parcel volume per capita) to ensure robustness of projections through 2029.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Philippines Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Philippines logistics and warehousing market is projected to experience robust growth, reaching an estimated valuation of PHP 1.3 trillion by 2029. This growth is supported by expanding e-commerce activity, infrastructure investments, rising demand for cold chain logistics, and increased regional trade integration. The market's potential is further enhanced by digital transformation and the emergence of tech-driven logistics startups offering real-time tracking and last-mile delivery optimization.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Philippines Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The key players include established logistics companies such as LBC Express, 2GO Group, JRS Express, Ninja Van, and international players like DHL Express and FedEx Philippines. New-age logistics platforms such as Entrego and Transportify are also gaining traction due to their focus on digital innovation and urban delivery efficiency.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Philippines Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Major growth drivers include the rapid rise of e-commerce, increasing demand for fast and reliable last-mile delivery, and government infrastructure development under programs like “Build Better More.” The need for cold chain logistics in the food and pharmaceutical industries and integration with regional trade frameworks (e.g., RCEP) are further propelling the market forward.
4. What are the Challenges in the Philippines Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Key challenges include high logistics costs (up to 27% of COGS), poor infrastructure in certain regions, traffic congestion in urban centers, and inconsistent customs processing times. The limited reach of cold chain logistics and fragmented warehousing capacity outside major hubs also pose significant barriers to growth. Regulatory bottlenecks and land acquisition delays add to operational inefficiencies.