Poland Auto Finance Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Structure, By Lenders, By Vehicle Type, By Financing Terms, By Consumer Demographics, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0143
- Region: Europe
- Published on: April 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Poland Auto Finance Market Outlook to 2029 - By Market Structure, By Lenders, By Vehicle Type, By Financing Terms, By Consumer Demographics, and By Region.” provides a comprehensive analysis of the auto finance industry in Poland. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of loan disbursements and financed vehicles, market segmentation; key trends and developments, regulatory landscape, consumer behavior insights, major challenges, and comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross-market comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of leading players in the Auto Finance Market. The report concludes with future market projections based on loan volumes, lending models, vehicle types, and a cause-and-effect analysis along with case studies highlighting success strategies and key risks.
Poland Auto Finance Market Overview and Size
The Poland auto finance market reached an estimated valuation of PLN 52 Billion in 2023, driven by increased vehicle ownership demand, the growth of digital financing platforms, and supportive government credit policies. The market is dominated by institutions such as mBank, Santander Consumer Bank, BNP Paribas, Getin Noble Bank, and Toyota Bank. These players are known for their competitive loan rates, fast approval systems, and expanding partnerships with automotive dealers.
In 2023, Santander Consumer Bank launched a fully digital auto loan application system that streamlined customer onboarding and reduced loan processing time to less than 48 hours. This digital-first approach is especially gaining traction in urban hubs such as Warsaw, Kraków, Wrocław, and Gdańsk, which account for the highest share of auto loans due to concentrated populations and growing middle-class demand for mobility.
Market Size for Poland Auto Finance Industry Based on Loan Disbursements in PLN, 2018–2024
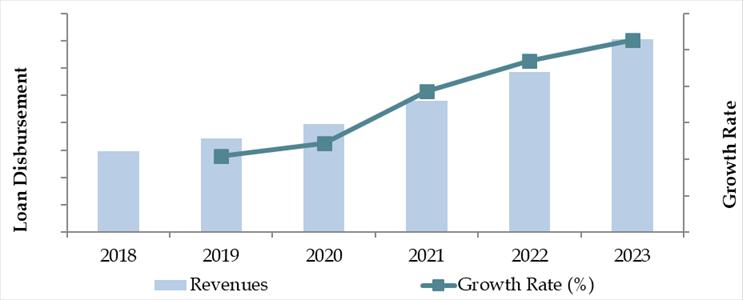
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Poland Auto Finance Market:
Economic Recovery Post-Pandemic: Poland’s steady economic recovery after the pandemic has restored consumer confidence. With improved income stability, more people are opting for car loans over outright purchases. In 2023, around 68% of new cars in Poland were financed through some form of credit or leasing scheme.
Rise in Vehicle Ownership: With increasing urban sprawl and a need for reliable transport, especially in Tier 2 cities, vehicle ownership is on the rise. Financing options such as low down payments and flexible tenures are enabling first-time buyers to enter the market.
Leasing and PCP Popularity: Financial products like personal contract purchase (PCP) and operational leasing are becoming increasingly popular, particularly among younger professionals and small business owners. These plans offer lower monthly payments and the option to upgrade vehicles every few years, enhancing affordability and convenience.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for Poland Auto Finance Market
High Interest Rates and Inflation Pressure: The persistent inflationary environment in Poland has led to higher interest rates, making auto loans less attractive for consumers. In 2023, the average interest rate for auto loans stood at 7.8%, up from 5.2% in 2021. This increase has strained affordability, particularly for new car buyers, and caused some consumers to postpone vehicle purchases or seek alternative transportation.
Credit Accessibility for Lower-Income Groups: A significant portion of Poland’s population, especially in rural regions, faces difficulty accessing credit due to stricter credit scoring norms and lack of formal income documentation. Approximately 36% of auto loan applicants in these areas were either rejected or offered suboptimal financing conditions in 2023, limiting financial inclusion in the auto market.
Complex Documentation and Loan Processing Time: Despite digital advances, some traditional lenders still require extensive paperwork and physical visits, which slows down the loan approval process. According to industry feedback, over 40% of potential borrowers abandoned their application midway due to procedural delays or confusing documentation requirements.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
KNF Oversight on Lending Practices: The Polish Financial Supervision Authority (KNF) closely monitors lending practices to ensure transparency and consumer protection. Regulatory updates in 2022 required lenders to clearly disclose the Annual Percentage Rate (APR) and all associated fees, aiming to reduce predatory lending and build consumer trust.
Support for Green Vehicle Financing: The government has launched incentives to promote financing for eco-friendly vehicles, including interest rate subsidies and VAT deductions for electric and hybrid vehicles. In 2023, green auto loans accounted for 6.2% of total new disbursements, driven by these regulatory measures.
Digital Lending Compliance Framework: New digital finance laws introduced in 2023 mandate lenders to adopt secure e-signature authentication and provide fully digital onboarding. This move is intended to boost digital adoption while safeguarding against fraud and identity theft in the auto finance ecosystem.
Poland Auto Finance Market Segmentation
By Market Structure: Traditional banks dominate the Poland auto finance landscape due to their extensive branch networks, established credibility, and competitive interest rates. These institutions cater to both new and used vehicle segments, offering fixed-rate loans, balloon financing, and leasing options. Non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) and fintech lenders are rapidly gaining ground by offering simplified digital applications, faster approvals, and personalized loan products. Their flexibility in credit assessment makes them particularly attractive to young buyers and self-employed individuals.
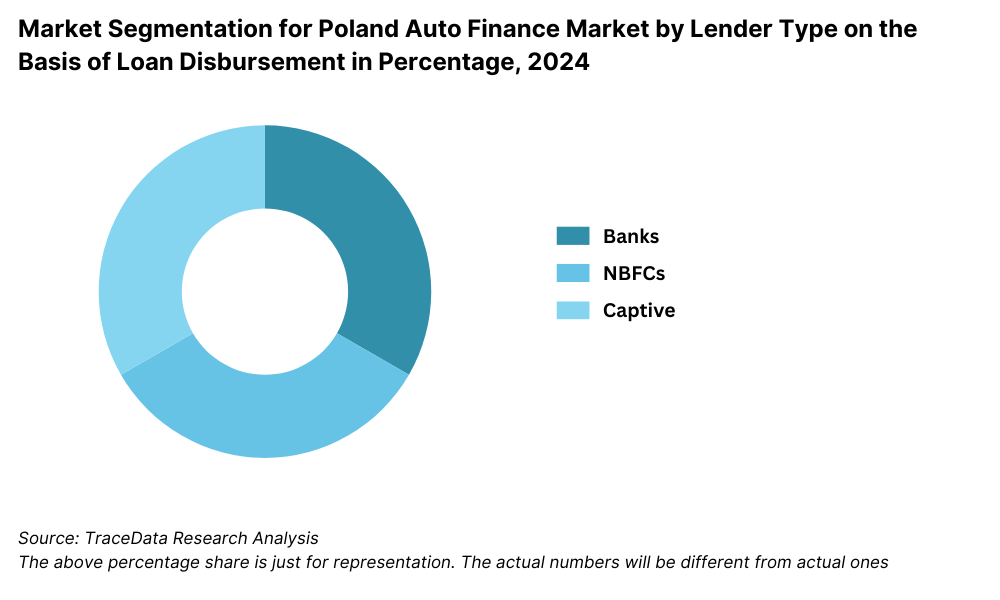
By Lender Type: Santander Consumer Bank leads the market, benefiting from strong dealer partnerships and its robust digital infrastructure. mBank and BNP Paribas follow closely, offering highly customizable auto loan packages and attractive interest rates. Fintech entrants like Autokasa and SuperAuto24 Finance are making inroads with fully online, paperless loan processing models that appeal to the tech-savvy younger generation.
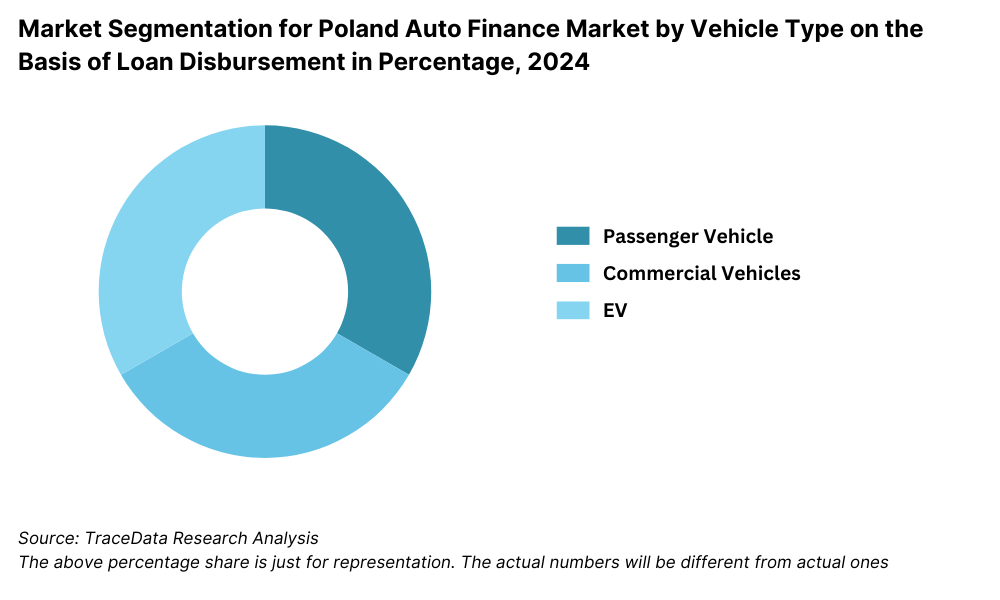
By Vehicle Type: Passenger cars dominate auto finance in Poland, particularly sedans and compact SUVs, which are popular for both personal and family use. In recent years, leasing and loans for electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrids have seen noticeable growth due to government incentives. Light commercial vehicles also represent a growing segment, driven by financing demand from small businesses and independent contractors.
Competitive Landscape in Poland Auto Finance Market
The Poland auto finance market is moderately concentrated, with a mix of established banks, specialized finance institutions, and emerging fintech firms. While traditional banks continue to dominate, the rise of digital-first lenders and auto dealership financing arms has intensified competition, offering consumers more flexible, tech-driven financing options.
| Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
| PKO Bank Polski Auto Loan | 1919 | Warsaw, Poland |
| Bank Pekao S.A. Auto Loan | 1929 | Warsaw, Poland |
| mBank Auto Loan | 1986 | Warsaw, Poland |
| Santander Consumer Bank Poland | 2006 (Poland) | Madrid, Spain |
| Alior Bank Auto Finance | 2008 | Warsaw, Poland |
| ING Bank Śląski Auto Loan | 1988 | Katowice, Poland |
| Volkswagen Financial Services Poland | 1994 | Braunschweig, Germany |
| Toyota Bank Polska | 2000 | Warsaw, Poland |
| BNP Paribas Bank Polska Auto Loan | 2008 (current form) | Paris, France |
| Getin Noble Bank Auto Finance | 2004 | Warsaw, Poland |
| Raiffeisen Leasing Polska | 2000 | Vienna, Austria |
| Peugeot Finance Polska | 2002 | Warsaw, Poland |
| BMW Financial Services Poland | 1996 | Munich, Germany |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
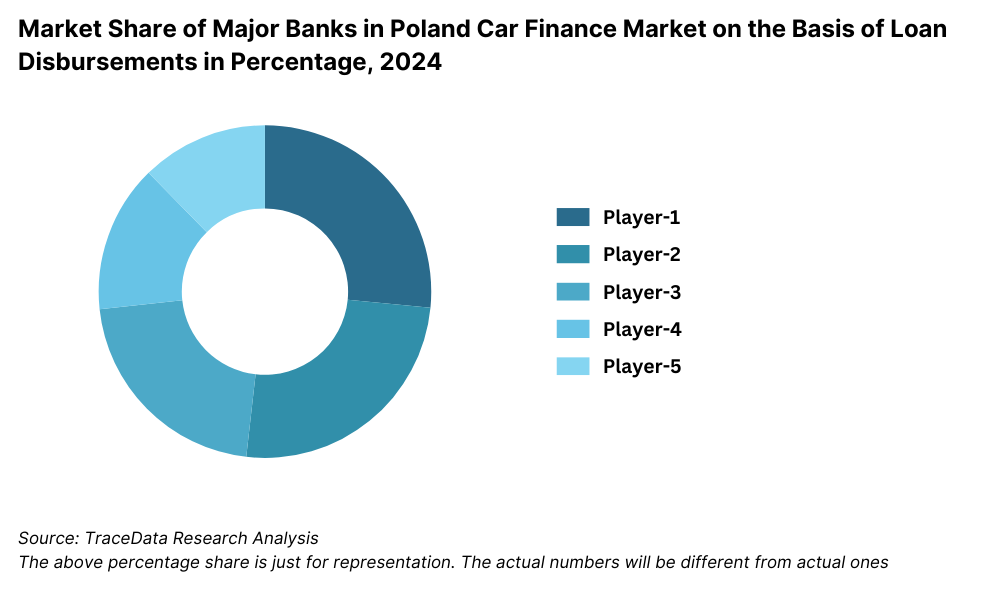
Santander Consumer Bank: One of the market leaders in Poland’s auto finance sector, Santander reported over PLN 9.5 billion in new auto loan originations in 2023. The bank continues to expand its digital ecosystem, including AI-powered loan approvals and strategic partnerships with over 500 car dealerships across the country.
mBank: Known for its strong digital capabilities, mBank has integrated car loan services directly into its mobile banking platform. In 2023, it saw a 17% YoY increase in auto loan volumes, particularly in Warsaw and Kraków. Its instant loan calculator and seamless digital journey have contributed to its popularity among tech-savvy customers.
BNP Paribas Polska: With a focus on green financing, BNP Paribas has introduced special rate packages for electric and hybrid vehicles. The bank’s auto finance portfolio grew by 12% in 2023, supported by strong dealership alliances and EV incentive tie-ins.
Toyota Bank Polska: Specializing in branded vehicle financing, Toyota Bank provides exclusive deals on Toyota and Lexus models. In 2023, it financed over 14,000 vehicles, representing a 20% increase compared to the previous year, driven by loyalty programs and bundled service plans.
Getin Noble Bank: Despite facing restructuring, Getin Noble continues to serve the used vehicle financing niche with competitive rate offers and extended loan tenures. It maintains strong customer retention through loyalty incentives and flexible refinancing options.
Autokasa: A rising fintech player, Autokasa enables instant vehicle financing with eKYC and paperless processing. In 2023, it facilitated over PLN 280 million in loans, primarily targeting younger consumers and gig economy workers through partnerships with ride-hailing services.
SuperAuto24 Finance: Affiliated with one of Poland’s leading online car dealerships, this lender focuses on quick financing approvals for certified used vehicles. The company experienced 22% growth in disbursed loans in 2023, attributed to its "one-click loan" integration at point-of-sale.
What Lies Ahead for Poland Auto Finance Market?
The Poland auto finance market is projected to witness consistent growth by 2029, registering a healthy CAGR over the forecast period. This growth will be driven by rising vehicle ownership, digital transformation in financial services, evolving consumer preferences, and supportive government policies promoting green and inclusive financing.
Digital Financing Acceleration: As Poland continues its digital transformation journey, a larger share of auto finance transactions will move online. The adoption of AI-based credit scoring, automated loan approvals, and integrated fintech solutions will significantly reduce processing time and enhance user experience, especially among urban and tech-savvy consumers.
Expansion of Green Auto Finance: In line with EU-wide sustainability goals, Poland is expected to see substantial growth in financing options tailored for electric and hybrid vehicles. Banks and NBFCs are likely to introduce green loan products with lower interest rates and tax incentives, further supported by government-backed EV subsidies.
Customized Loan Products for Diverse Segments: Financial institutions are anticipated to roll out more personalized loan offerings, including income-based EMI options, flexible tenure choices, and deferred payment schemes. These products will help bring previously underserved segments—such as gig workers, young professionals, and rural customers—into the formal credit ecosystem.
Increased Role of Dealership Financing Arms: OEMs and car dealerships will strengthen their in-house finance operations or form alliances with fintech firms to offer bundled purchase-financing packages. These integrated models will appeal to buyers looking for a seamless, one-stop car buying and financing experience.
Future Outlook and Projections for Poland Car Finance Market Size on the Basis of Loan Disbursements in USD Billion, 2024-2029
Poland Auto Finance Market Segmentation
By Market Structure:
Banks
Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)
Digital Lending Platforms (Fintechs)
OEM Captive Finance Arms
Dealership Financing
Peer-to-Peer Auto Lending
By Vehicle Type:
Passenger Cars
Light Commercial Vehicles
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Hybrid Vehicles
Used Vehicles
By Financing Terms:
Short-Term (12–24 Months)
Mid-Term (36–60 Months)
Long-Term (60+ Months)
Leasing
Balloon Financing
Personal Contract Purchase (PCP)
By Age of Consumer:
18–24
25–34
35–49
50+
By Region:
Mazowieckie (Warsaw)
Małopolskie (Kraków)
Dolnośląskie (Wrocław)
Pomorskie (Gdańsk)
Wielkopolskie (Poznań)
Śląskie (Katowice)
Players Mentioned in the Report (Banks):
- Santander Bank Polska
- mBank
- Bank Millennium
- Inbank
- Gates Investment Bank
Players Mentioned in the Report (NBFCs):
- Creamfinance
- SMEO
- Leaselink
- Wealthon
- PFR Group
Players Mentioned in the Report (Captive):
- Volkswagen Financial Services Poland
- FCA Bank Polska
- Ferrari Financial Services Poland
- Toyota Bank Polska
- PSA Finance Polska
Key Target Audience:
Commercial Banks and NBFCs
Digital Lending and Fintech Companies
Automotive Dealerships
OEM Captive Finance Arms
Regulatory Authorities (e.g., Polish Financial Supervision Authority - KNF)
Government Agencies (e.g., Ministry of Infrastructure)
Research and Economic Institutions
Investors and Venture Capital Firms in Fintech
Time Period:
Historical Period: 2018–2023
Base Year: 2024
Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and challenges they face.
4.2. Relationship and Engagement Model between Banks-Dealers, NBFCs-Dealers and Captive-Dealers-Commission Sharing Model, Flat Fee Model and Revenue streams
5.1. New Car and Used Car Sales in Poland by type of vehicle, 2018-2024
8.1. Credit Disbursed, 2018-2024
8.2. Outstanding Loan, 2018-2024
9.1. By Market Structure (Bank-Owned, Multi-Finance, and Captive Companies), 2023-2024
9.2. By Vehicle Type (Passenger, Commercial and EV), 2023-2024
9.3. By Region, 2023-2024
9.4. By Type of Vehicle (New and Used), 2023-2024
9.5. By Average Loan Tenure (0-2 years, 3-5 years, 6-8 years, above 8 years), 2023-2024
10.1. Customer Landscape and Cohort Analysis
10.2. Customer Journey and Decision-Making
10.3. Need, Desire, and Pain Point Analysis
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11.1. Trends and Developments for Poland Car Finance Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Poland Car Finance Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Poland Car Finance Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges for Poland Car Finance Market
11.5. Government Regulations for Poland Car Finance Market
12.1. Market Size and Future Potential for Online Car Financing Aggregators, 2018-2029
12.2. Business Model and Revenue Streams
12.3. Cross Comparison of Leading Digital Car Finance Companies Based on Company Overview, Revenue Streams, Loan Disbursements/Number of Leads Generated, Operating Cities, Number of Branches, and Other Variables
13.1. Finance Penetration Rate and Average Down Payment for New and Used Cars, 2018-2029
13.2. How Finance Penetration Rates are Changing Over the Years with Reasons
13.3. Type of Car Segment for which Finance Penetration is Higher
17.1. Market Share of Key Banks in Poland Car Finance Market, 2024
17.2. Market Share of Key NBFCs in Poland Car Finance Market, 2024
17.3. Market Share of Key Captive in Poland Car Finance Market, 2024
17.4. Benchmark of Key Competitors in Poland Car Finance Market, including Variables such as Company Overview, USP, Business Strategies, Strengths, Weaknesses, Business Model, Number of Branches, Product Features, Interest Rate, NPA, Loan Disbursed, Outstanding Loans, Tie-Ups and others
17.5. Strengths and Weaknesses
17.6. Operating Model Analysis Framework
17.7. Gartner Magic Quadrant
17.8. Bowmans Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
18.1. Credit Disbursed, 2025-2029
18.2. Outstanding Loan, 2025-2029
19.1. By Market Structure (Bank-Owned, Multi-Finance, and Captive Companies), 2025-2029
19.2. By Vehicle Type (Passenger, Commercial and EV), 2025-2029
19.3. By Region, 2025-2029
19.4. By Type of Vehicle (New and Used), 2025-2029
19.5. By Average Loan Tenure (0-2 years, 3-5 years, 6-8 years, above 8 years), 2025-2029
19.6. Recommendations
19.7. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand side and supply side entities for Poland Auto Finance Market. Basis this ecosystem, we will shortlist leading 5-6 lenders in the country based upon their financial information, loan disbursement volume, and market presence.
Sourcing is made through industry articles, multiple secondary, and proprietary databases to perform desk research around the market to collate industry-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
Subsequently, we engage in an exhaustive desk research process by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This approach enables us to conduct a thorough analysis of the market, aggregating industry-level insights. We delve into aspects like the loan disbursement volumes, number of market players, interest rate trends, consumer profiles, and other variables. We supplement this with detailed examinations of company-level data, relying on sources like press releases, annual reports, financial statements, and similar documents. This process aims to construct a foundational understanding of both the market and the entities operating within it.
Step 3: Primary Research
We initiate a series of in-depth interviews with C-level executives and other stakeholders representing various Poland Auto Finance Market companies and end-users. This interview process serves a multi-faceted purpose: to validate market hypotheses, authenticate statistical data, and extract valuable operational and financial insights from these industry representatives. Bottom to top approach is undertaken to evaluate loan disbursement volume for each player thereby aggregating to the overall market.
As part of our validation strategy, our team executes disguised interviews wherein we approach each company under the guise of potential customers. This approach enables us to validate the operational and financial information shared by company executives, corroborating this data against what is available in secondary databases. These interactions also provide us with a comprehensive understanding of revenue streams, value chain, process, pricing, and other factors.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- Bottom to top and top to bottom analysis along with market size modeling exercises is undertaken to assess sanity check process.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Poland Auto Finance Market?
The Poland auto finance market holds significant growth potential, reaching a valuation of PLN 52 Billion in 2023. Growth is being fueled by rising car ownership, increasing consumer access to credit, and the rapid expansion of digital lending platforms. The market is also supported by favorable economic conditions and government incentives for eco-friendly vehicle financing, positioning Poland as a strong performer within the Central and Eastern European auto finance landscape.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Poland Auto Finance Market?
Key players in the Poland Auto Finance Market include Santander Consumer Bank, mBank, BNP Paribas Polska, Toyota Bank Polska, and Getin Noble Bank. These institutions dominate due to their well-established lending infrastructure, wide dealership networks, and competitive interest rate offerings. Emerging fintech players such as Autokasa and SuperAuto24 Finance are also making notable contributions through their digital-first, customer-centric financing models.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Poland Auto Finance Market?
Major growth drivers include the increasing demand for personal mobility, the growing popularity of electric and hybrid vehicles, and the digital transformation of banking and financial services. Flexible loan products, rising consumer confidence, and the expanding availability of credit across different income segments are further accelerating the growth of auto finance in Poland.
4. What are the Challenges in the Poland Auto Finance Market?
The Poland Auto Finance Market faces several challenges, including high interest rates driven by inflationary pressure, limited credit access for low-income or rural populations, and complex documentation processes in traditional lending. Additionally, the underdevelopment of used car financing and the lack of financial literacy among certain demographics present hurdles to broader market penetration.