Qatar CO₂ Lasers Market Outlook to 2035
By Power Rating, By Application, By End-Use Industry, By System Configuration, and By End-User Type
- Product Code: TDR0488
- Region: Middle East
- Published on: January 2026
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Qatar CO₂ Lasers Market Outlook to 2035 – By Power Rating, By Application, By End-Use Industry, By System Configuration, and By End-User Type” provides a comprehensive analysis of the CO₂ laser systems market in Qatar. The report covers an overview and genesis of the market, overall market size in terms of value, detailed market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory and compliance landscape, buyer-level demand profiling, key issues and challenges, and competitive landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players active in the Qatar CO₂ lasers market. The report concludes with future market projections based on industrial diversification initiatives, manufacturing localization, healthcare infrastructure development, precision fabrication demand, technology substitution dynamics, and cause-and-effect relationships, along with case-based illustrations highlighting the major opportunities and cautions shaping the market through 2035.
Qatar CO₂ Lasers Market Overview and Size
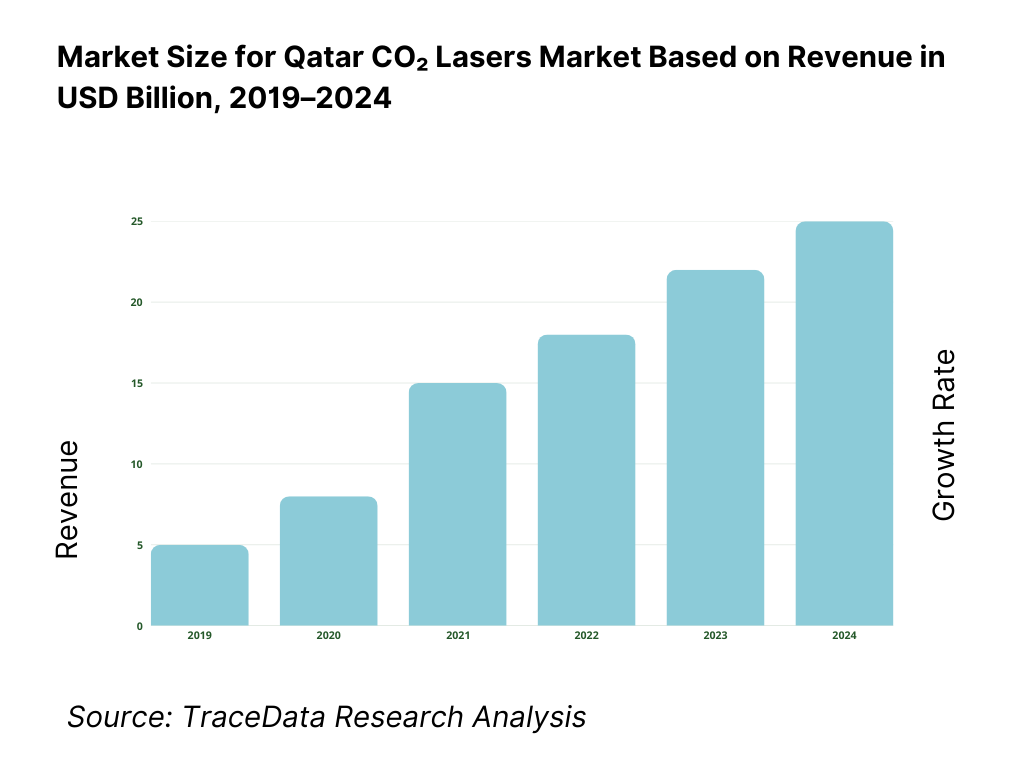
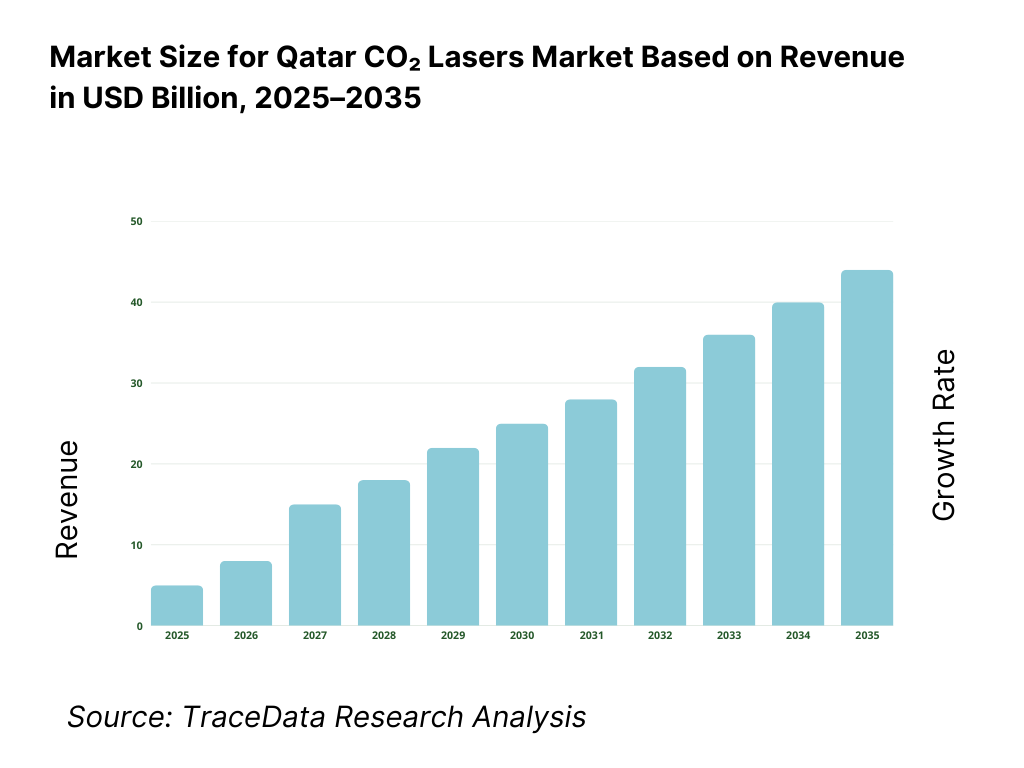
The Qatar CO₂ lasers market is valued at approximately ~USD ~ million, representing the supply of carbon dioxide laser systems used for cutting, engraving, marking, welding, surface treatment, and medical applications. CO₂ lasers operate in the infrared wavelength range and are widely used across industrial manufacturing, healthcare, packaging, textiles, electronics assembly, and signage due to their high efficiency on non-metal and certain metal materials, stable beam quality, and relatively mature technology base.
The market is anchored by Qatar’s ongoing industrial diversification under the National Vision 2030 framework, expansion of local fabrication and assembly capabilities, increasing adoption of automated and precision-based manufacturing systems, and sustained investment in healthcare infrastructure. CO₂ lasers remain a preferred solution for applications involving plastics, wood, glass, leather, rubber, ceramics, and coated metals, where fiber or solid-state lasers may not offer equivalent performance or cost efficiency.
Industrial and fabrication clusters concentrated around Doha, Ras Laffan, Mesaieed, and emerging free zones form the primary demand centers for CO₂ laser systems. These zones support fabrication workshops, EPC contractors, packaging suppliers, and industrial service providers that rely on laser-based processing for accuracy, repeatability, and productivity. The healthcare segment, including public and private hospitals, specialty clinics, and dermatology centers, contributes additional demand for medical-grade CO₂ laser systems used in soft tissue procedures, dermatology, and aesthetic treatments.
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the Qatar CO₂ Lasers Market
Industrial diversification and fabrication capability expansion strengthens structural demand: Qatar’s strategic push to expand non-hydrocarbon industrial activity is driving the development of localized fabrication, assembly, and light manufacturing capabilities. CO₂ lasers are increasingly adopted by metal and non-metal processing workshops that serve construction, oil & gas support services, signage, furniture, and customized industrial components. These facilities prioritize precision cutting, engraving, and marking solutions that can be integrated into CNC and automated production environments. CO₂ lasers enable consistent output quality, reduced material waste, and faster turnaround times, making them well suited for project-based and small-batch industrial work common in Qatar’s market structure.
Growth of packaging, plastics, and consumer goods manufacturing supports laser adoption: Rising demand for flexible packaging, labeling, and customized consumer goods is strengthening the adoption of CO₂ lasers across packaging converters and plastics processors. CO₂ lasers are widely used for cutting films, laminates, foams, and polymer materials, as well as for high-speed marking and coding applications. As Qatar expands domestic production of packaging materials to support food security, FMCG distribution, and export-oriented manufacturing, laser-based processing offers scalability and process consistency that conventional mechanical systems struggle to achieve.
Healthcare infrastructure development and medical laser usage drive niche high-value demand: Qatar continues to invest heavily in healthcare infrastructure, specialty care centers, and advanced medical technologies. Medical CO₂ lasers are widely used in dermatology, cosmetic surgery, gynecology, ENT, and soft tissue procedures due to their precision, controlled tissue interaction, and minimal bleeding characteristics. Public healthcare expansion, rising private clinic investments, and increasing demand for aesthetic and minimally invasive procedures are contributing to steady growth in the medical CO₂ laser segment, which commands higher average selling prices and service revenues.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of the Qatar CO₂ Lasers Market:
Dependence on imported systems and long lead times impacts procurement certainty and project planning: The Qatar CO₂ lasers market is highly dependent on imported equipment sourced from Europe, East Asia, and the United States. This dependence exposes buyers to extended lead times, logistics delays, customs clearance timelines, and currency-linked pricing variability. For industrial users operating on project-based timelines—such as fabrication workshops, EPC contractors, and packaging converters—delays in system delivery can disrupt production planning and defer revenue realization. In healthcare settings, longer import cycles and regulatory approvals can postpone commissioning of medical laser systems, impacting service rollout and return-on-investment timelines.
Competition from alternative laser technologies creates substitution pressure in select applications: While CO₂ lasers retain strong relevance for non-metal processing and medical applications, fiber and solid-state lasers are increasingly preferred for high-speed metal cutting and precision industrial tasks. As awareness of newer laser technologies grows among industrial buyers in Qatar, some applications that were traditionally served by CO₂ lasers are gradually shifting toward fiber-based systems. This substitution pressure limits market expansion in certain industrial segments and requires CO₂ laser suppliers to clearly articulate cost-benefit advantages, material suitability, and application-specific performance to retain relevance.
Limited availability of skilled operators and service technicians constrains effective utilization: Efficient operation and maintenance of CO₂ laser systems require trained operators, alignment specialists, and service technicians familiar with optics, gas systems, cooling units, and control software. In Qatar, reliance on expatriate technical talent and limited local skill development can create bottlenecks in system commissioning, troubleshooting, and preventive maintenance. These constraints increase downtime risk for end users and elevate dependence on distributor-led service support, influencing buyer confidence and slowing adoption among smaller workshops.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
Medical device regulations and healthcare authority approvals governing clinical laser usage: Medical CO₂ laser systems used in hospitals, specialty clinics, and aesthetic centers are subject to regulatory oversight by Qatar’s healthcare authorities. These regulations govern device registration, safety certifications, clinical usage approvals, and facility licensing requirements. Compliance with international medical device standards, radiation safety norms, and operator credentialing is mandatory prior to installation and clinical use. These regulatory processes influence procurement timelines, supplier qualification, and the pace of adoption within the medical segment.
Electrical safety, radiation control, and workplace compliance standards shaping industrial deployment: Industrial CO₂ laser systems must comply with national electrical safety standards, laser radiation exposure limits, and workplace safety regulations. Requirements related to machine guarding, emergency shutoff systems, ventilation, fume extraction, and operator protection influence system configuration and facility layout. Compliance costs and inspection requirements can vary by application and facility type, affecting overall project economics and deployment timelines.
Industrial diversification and localization initiatives supporting advanced manufacturing adoption: Qatar’s broader industrial development initiatives under national diversification programs encourage the adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies, including laser-based processing systems. Support for local fabrication, packaging production, and industrial services indirectly strengthens demand for CO₂ lasers by expanding the addressable base of precision-oriented manufacturing activities. While these initiatives do not directly mandate laser adoption, they create favorable conditions for automation, productivity enhancement, and technology-driven industrial growth.
Qatar CO₂ Lasers Market Segmentation
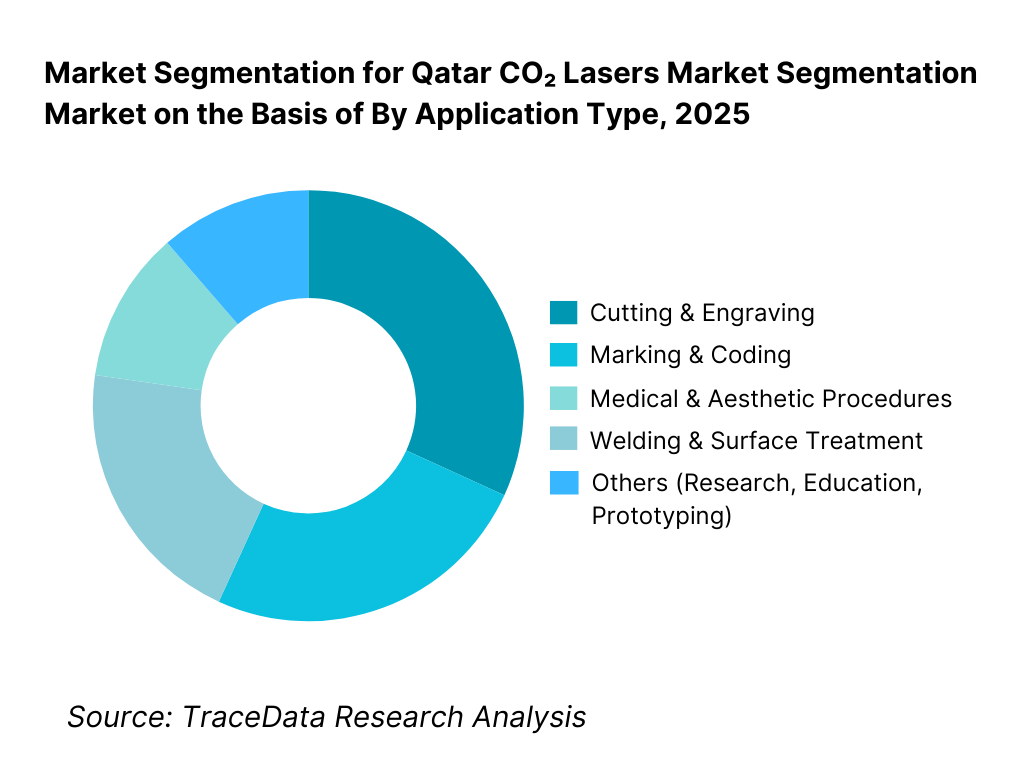
By Application Type: The cutting and engraving segment holds dominance in the Qatar CO₂ lasers market. This is because CO₂ lasers are particularly well suited for non-metal materials such as plastics, wood, acrylics, rubber, textiles, glass, and coated substrates—materials widely used across signage, packaging, interiors, and light fabrication industries in Qatar. These applications prioritize clean edges, consistent quality, and design flexibility, all of which CO₂ laser systems deliver efficiently. While medical and marking applications are growing steadily, cutting and engraving continue to benefit from workshop-level demand, customization-driven orders, and project-based industrial activity.
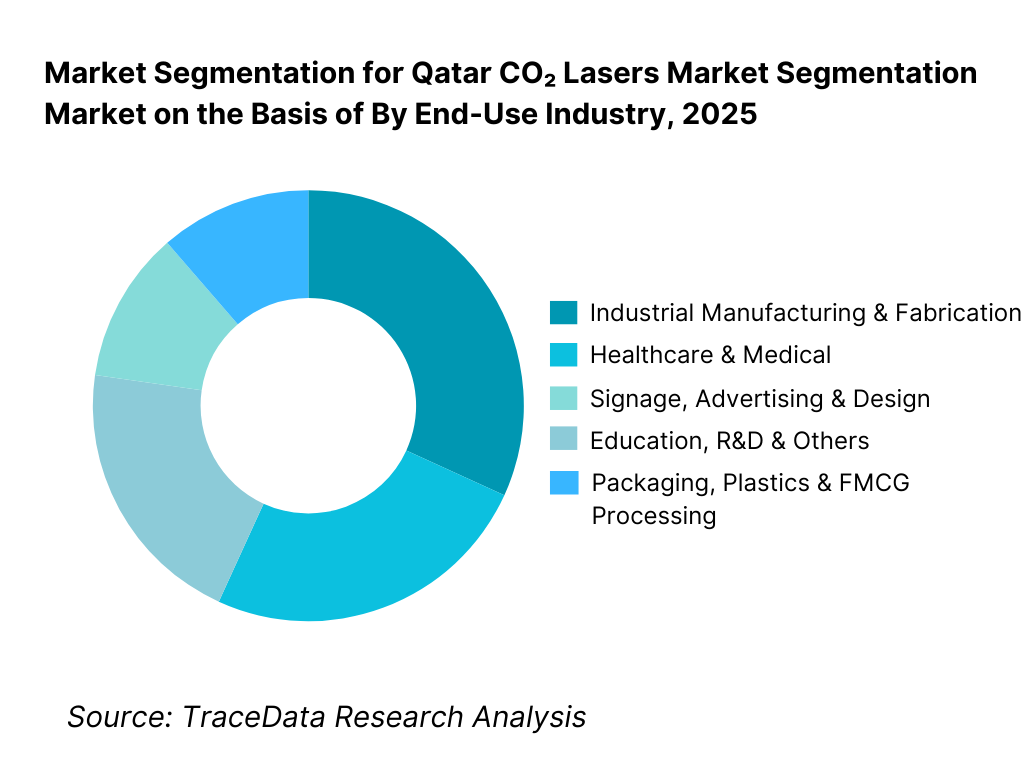
By End-Use Industry: Industrial and fabrication-related industries dominate the Qatar CO₂ lasers market. Fabrication workshops, packaging converters, signage manufacturers, and industrial service providers prioritize CO₂ lasers for their versatility, reliability, and ability to process a wide range of materials with consistent output. The healthcare segment represents a smaller but high-value share due to the higher average selling price of medical-grade CO₂ laser systems. Consumer-oriented and institutional usage remains niche but is gradually expanding as laser adoption increases in education, training, and public-sector facilities.
Competitive Landscape in Qatar CO₂ Lasers Market
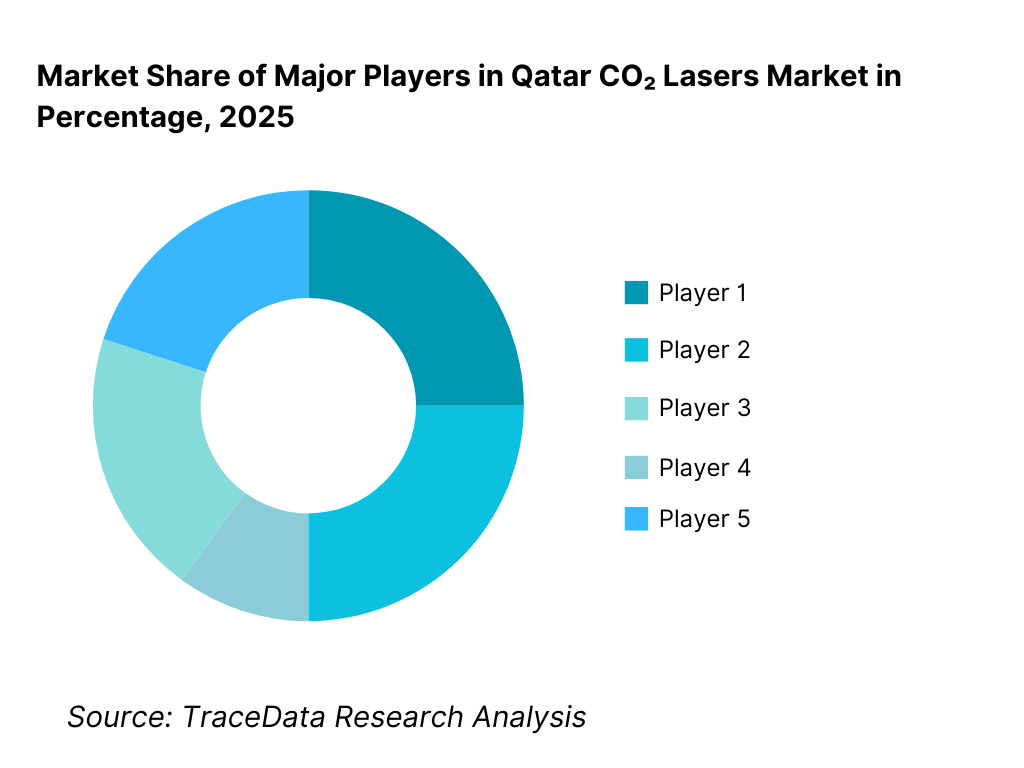
The Qatar CO₂ lasers market exhibits low-to-moderate concentration, characterized by the presence of global laser equipment manufacturers operating through authorized regional distributors and local system integrators. Market leadership is shaped by technology reliability, application breadth, after-sales service capability, spare parts availability, and regulatory compliance—particularly in the medical segment. While international brands dominate high-end industrial and medical installations, regional distributors play a critical role in system configuration, installation, operator training, and ongoing maintenance support.
Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
TRUMPF Group | 1923 | Ditzingen, Germany |
Coherent (incl. legacy Rofin) | 1966 | California, USA |
Han’s Laser Technology | 1996 | Shenzhen, China |
Trotec Laser | 1997 | Marchtrenk, Austria |
GCC LaserPro | 1989 | Taiwan |
Epilog Laser | 1988 | Colorado, USA |
Universal Laser Systems | 1988 | Arizona, USA |
Lumenis (Medical CO₂ Lasers) | 1965 | Yokneam, Israel |
Some of the Recent Competitor Trends and Key Information About Competitors Include:
TRUMPF Group: TRUMPF continues to be associated with premium industrial laser solutions, emphasizing system robustness, precision engineering, and long-term reliability. In Qatar, its competitive position is reinforced by strong distributor networks and demand from industrial users seeking proven performance for high-value fabrication and processing applications.
Coherent (including legacy Rofin platforms): Coherent maintains a strong presence in both industrial and medical CO₂ laser segments. Its broad product portfolio allows it to serve diverse applications ranging from precision cutting to advanced medical procedures. The company’s competitive strength lies in application engineering depth and global service standards.
Han’s Laser Technology: Han’s Laser competes aggressively in mid-range industrial applications by offering cost-competitive systems with broad functionality. In Qatar, it is increasingly adopted by fabrication workshops and packaging processors seeking performance at a lower capital cost, supported by regional distributors.
Trotec Laser: Trotec is strongly positioned in engraving, marking, and design-oriented applications. Its systems are widely used in signage, awards, interior décor, and customized product manufacturing. The company’s differentiation lies in ease of use, software integration, and consistent engraving quality.
Lumenis (Medical Segment): Lumenis remains a key player in medical-grade CO₂ laser systems used in dermatology, gynecology, and aesthetic procedures. Its market position in Qatar is supported by clinical credibility, regulatory compliance, and strong relationships with hospitals and specialty clinics.
What Lies Ahead for Qatar CO₂ Lasers Market?
The Qatar CO₂ lasers market is expected to expand steadily through 2035, supported by ongoing industrial diversification, gradual localization of fabrication and packaging activities, expansion of healthcare infrastructure, and sustained demand for precision-based material processing solutions. Growth momentum is reinforced by increasing automation in industrial workshops, rising adoption of laser-based medical and aesthetic procedures, and the continued relevance of CO₂ lasers in non-metal and soft-tissue applications. As end users prioritize reliability, application versatility, and predictable operating performance, CO₂ lasers are expected to remain an essential technology across multiple sectors in Qatar.
Continued Relevance of CO₂ Lasers in Non-Metal Processing and Medical Applications: While alternative laser technologies continue to gain traction in certain metal-cutting applications, CO₂ lasers are expected to maintain a strong position in non-metal processing, packaging, signage, plastics, textiles, and medical procedures. These applications benefit from the wavelength characteristics, material interaction efficiency, and proven performance of CO₂ lasers. Through 2035, demand will increasingly be driven by application-specific suitability rather than technology novelty, reinforcing the role of CO₂ lasers where they offer clear functional and economic advantages.
Gradual Shift Toward Higher-Power and Application-Specific System Configurations: The future market will see a gradual shift from basic entry-level systems toward higher-power and application-optimized CO₂ laser configurations. Industrial users are increasingly seeking systems designed around specific operational requirements such as higher throughput, improved beam stability, integrated automation, and compatibility with CNC and digital control platforms. In healthcare, demand will shift toward advanced medical-grade systems offering enhanced precision, safety features, and procedure-specific configurations. Suppliers offering tailored solutions rather than generic platforms are expected to capture higher-value demand.
Increasing Importance of After-Sales Support, Training, and Local Service Capability: As CO₂ laser installations increase across industrial and medical facilities, buyers will place greater emphasis on reliable after-sales service, preventive maintenance, and operator training. Given Qatar’s reliance on imported systems, local distributor capability in installation support, spare parts availability, and response time will become a critical differentiator. Through 2035, suppliers and distributors with strong local technical teams and service infrastructure will be better positioned to build long-term customer relationships and recurring service revenues.
Integration with Automation, Digital Controls, and Industry 4.0 Workflows: CO₂ laser systems in Qatar are expected to increasingly integrate with digital control systems, automation platforms, and data-driven production workflows. Industrial users will demand improved software interfaces, remote diagnostics, and compatibility with broader factory automation initiatives. While full-scale smart manufacturing adoption may remain gradual, incremental digital integration will enhance productivity, reduce downtime, and improve process consistency, strengthening the value proposition of advanced CO₂ laser systems.
Qatar CO₂ Lasers Market Segmentation
By Application Type
• Cutting & Engraving
• Marking & Coding
• Medical & Aesthetic Procedures
• Welding & Surface Treatment
• Research, Education & Others
By Power Rating
• Low Power (Below 100W)
• Medium Power (100W–500W)
• High Power (Above 500W)
By End-Use Industry
• Industrial Manufacturing & Fabrication
• Packaging, Plastics & FMCG Processing
• Healthcare & Medical
• Signage, Advertising & Design
• Education, R&D & Others
By System Configuration
• Standalone CO₂ Laser Systems
• Integrated CNC / Automated Systems
• Tabletop / Benchtop Systems
• Medical-Grade Clinical Systems
By End-User Type
• Industrial Workshops and Fabricators
• Packaging and Converting Companies
• Hospitals and Specialty Clinics
• Signage and Design Studios
• Educational and Research Institutions
Players Mentioned in the Report:
• TRUMPF Group
• Coherent (including legacy Rofin platforms)
• Han’s Laser Technology
• Trotec Laser
• GCC LaserPro
• Epilog Laser
• Universal Laser Systems
• Lumenis (Medical CO₂ Lasers)
• Regional distributors, system integrators, and service providers in Qatar
Key Target Audience
• CO₂ laser manufacturers and technology providers
• Authorized distributors and system integrators
• Industrial fabrication workshops and manufacturers
• Packaging, plastics, and FMCG processors
• Hospitals, specialty clinics, and aesthetic centers
• Signage, advertising, and design companies
• Education and research institutions
• Industrial automation and equipment investors
Time Period:
Historical Period: 2019–2024
Base Year: 2025
Forecast Period: 2025–2035
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4. 1 Delivery Model Analysis for CO₂ Lasers including direct OEM sales, authorized distributor-led sales, system integrator-led delivery, and turnkey installation models with margins, preferences, strengths, and weaknesses
4. 2 Revenue Streams for CO₂ Lasers Market including equipment sales, installation and commissioning revenues, maintenance and service contracts, spare parts and consumables, and training services
4. 3 Business Model Canvas for CO₂ Lasers Market covering laser OEMs, distributors, system integrators, component suppliers, healthcare providers, industrial end users, and service partners
5. 1 Global CO₂ Laser Manufacturers vs Regional and Local Distributors including TRUMPF, Coherent, Han’s Laser, Trotec, GCC LaserPro, Epilog Laser, and other regional or local suppliers
5. 2 Investment Model in CO₂ Lasers Market including R&D investments, technology upgrades, distributor network expansion, and after-sales service infrastructure investments
5. 3 Comparative Analysis of CO₂ Laser Distribution by Direct-to-End-User and Distributor or System Integrator Channels including industrial and medical segments
5. 4 End-User Capital Equipment Budget Allocation comparing CO₂ laser investments versus alternative laser technologies and conventional processing equipment
8. 1 Revenues from historical to present period
8. 2 Growth Analysis by application type and by end-use industry
8. 3 Key Market Developments and Milestones including technology upgrades, distributor partnerships, regulatory approvals, and major industrial or healthcare installations
9. 1 By Market Structure including global OEMs, regional distributors, and local integrators
9. 2 By Application Type including cutting and engraving, marking and coding, medical and aesthetic procedures, welding, and surface treatment
9. 3 By Power Rating including low power, medium power, and high power CO₂ lasers
9. 4 By End-Use Industry including industrial fabrication, packaging and plastics, healthcare, signage and design, and education or RD
9. 5 By End-User Type including industrial workshops, packaging converters, hospitals and clinics, signage companies, and research institutions
9. 6 By System Configuration including standalone systems, integrated CNC or automated systems, tabletop systems, and medical-grade systems
9. 7 By Purchase Type including new installations, upgrades, and replacements
9. 8 By Region including Doha, Al Rayyan, Al Wakrah, Al Khor, and other industrial or commercial zones of Qatar
10. 1 End-User Landscape and Cohort Analysis highlighting industrial versus medical demand clusters
10. 2 CO₂ Laser System Selection and Purchase Decision Making influenced by application fit, price, service support, and regulatory compliance
10. 3 Utilization and ROI Analysis measuring operating hours, productivity gains, and payback periods
10. 4 Gap Analysis Framework addressing skill availability, service responsiveness, and technology awareness
11. 1 Trends and Developments including automation integration, higher-power systems, medical laser adoption, and digital controls
11. 2 Growth Drivers including industrial diversification, healthcare expansion, demand for precision processing, and technology localization
11. 3 SWOT Analysis comparing CO₂ laser maturity versus emerging laser technologies
11. 4 Issues and Challenges including import dependence, skilled manpower constraints, capital cost sensitivity, and competitive substitution
11. 5 Government Regulations covering medical device approvals, radiation safety standards, electrical compliance, and import regulations in Qatar
12. 1 Market Size and Future Potential of medical and aesthetic CO₂ laser applications
12. 2 Business Models including hospital procurement, private clinic investments, and distributor-led supply models
12. 3 Delivery Models and Type of Solutions including clinical systems, portable platforms, and procedure-specific configurations
15. 1 Market Share of Key Players by revenues and installed base
15. 2 Benchmark of 15 Key Competitors including TRUMPF, Coherent, Han’s Laser, Trotec, GCC LaserPro, Epilog Laser, Universal Laser Systems, Lumenis, and other global, regional, and local players
15. 3 Operating Model Analysis Framework comparing global OEM-led models, distributor-driven models, and system integrator-led approaches
15. 4 Gartner Magic Quadrant positioning global laser technology leaders and regional challengers in the CO₂ lasers market
15. 5 Bowman’s Strategic Clock analyzing competitive advantage through technology differentiation versus cost-led positioning
16. 1 Revenues with projections
17. 1 By Market Structure including global OEMs, regional distributors, and local integrators
17. 2 By Application Type including cutting, engraving, medical, and marking applications
17. 3 By Power Rating including low, medium, and high power systems
17. 4 By End-Use Industry including industrial, healthcare, and commercial segments
17. 5 By End-User Type including workshops, hospitals, clinics, and converters
17. 6 By System Configuration including standalone and integrated systems
17. 7 By Purchase Type including new, upgrade, and replacement demand
17. 8 By Region including Doha and other key industrial and commercial zones of Qatar
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
We begin by mapping the complete ecosystem of the Qatar CO₂ Lasers Market across demand-side and supply-side entities. On the demand side, entities include industrial fabrication workshops, packaging and plastics converters, signage and advertising firms, medical and aesthetic clinics, hospitals, research institutions, and specialized service providers using laser-based processing. Demand is further segmented by application type (cutting, engraving, marking, medical procedures), system configuration (standalone, integrated CNC, medical-grade systems), and purchase intent (new installation, capacity upgrade, replacement).
On the supply side, the ecosystem includes global CO₂ laser manufacturers, regional distributors, authorized local agents, system integrators, automation solution providers, optics and component suppliers, software providers, installation and commissioning partners, service and maintenance contractors, and regulatory bodies governing medical devices and radiation safety. From this mapped ecosystem, we shortlist 6–10 leading CO₂ laser manufacturers and a representative set of regional distributors based on product range, application depth, installed base in Qatar, service capability, regulatory compliance track record, and presence across industrial and medical segments. This step establishes how value is created and captured across equipment supply, integration, commissioning, training, and after-sales service.
Step 2: Desk Research
An exhaustive desk research process is undertaken to analyze the Qatar CO₂ lasers market structure, demand drivers, and application-level behavior. This includes reviewing industrial diversification initiatives, manufacturing and packaging capacity additions, healthcare infrastructure investments, and adoption trends for laser-based processing technologies. We assess buyer preferences around system reliability, application suitability, total cost of ownership, and local service availability.
Company-level analysis includes review of manufacturer product portfolios, distributor presence, pricing positioning, service models, and typical end-use applications. We also examine regulatory and compliance dynamics governing industrial and medical laser deployment, including import requirements, radiation safety norms, and medical device approvals. The outcome of this stage is a comprehensive industry foundation that defines segmentation logic and establishes the assumptions required for market sizing and long-term outlook modeling.
Step 3: Primary Research
We conduct structured interviews with CO₂ laser manufacturers, regional distributors, system integrators, industrial workshop owners, packaging processors, signage companies, and healthcare professionals using medical-grade laser systems. The objectives are threefold:
(a) validate assumptions around demand concentration, application mix, and buyer decision criteria,
(b) authenticate segmentation splits by application, power rating, end-use industry, and system configuration, and
(c) gather qualitative insights on pricing behavior, lead times, service expectations, training requirements, and system performance in local operating conditions.
A bottom-to-top approach is applied by estimating installed base, replacement cycles, and average system values across key segments, which are aggregated to develop the overall market view. In selected cases, disguised buyer-style interactions are conducted with distributors and service providers to validate field-level realities such as quotation timelines, service response, spare parts availability, and typical barriers faced during system commissioning.
Step 4: Sanity Check
The final stage integrates bottom-to-top and top-to-down approaches to cross-validate market estimates, segmentation splits, and forecast assumptions. Demand projections are reconciled with macro indicators such as industrial activity growth, healthcare spending trends, packaging and plastics output, and capital equipment import patterns. Assumptions around technology substitution, regulatory approvals, service capability, and skill availability are stress-tested to understand their impact on adoption rates. Sensitivity analysis is conducted across key variables including industrial automation intensity, healthcare investment momentum, and competitive pressure from alternative laser technologies. Market models are refined until alignment is achieved between supplier capacity, distributor throughput, and end-user demand, ensuring internal consistency and robust directional forecasting through 2035.
FAQs
01 What is the potential for the Qatar CO₂ Lasers Market?
The Qatar CO₂ lasers market holds steady growth potential, supported by industrial diversification, increasing adoption of precision fabrication technologies, expansion of packaging and plastics processing, and sustained investment in healthcare and aesthetic services. CO₂ lasers remain highly relevant for non-metal processing and medical applications where their wavelength characteristics and operational reliability deliver strong performance. As demand shifts toward application-specific and higher-performance systems, the market is expected to capture incremental value through 2035.
02 Who are the Key Players in the Qatar CO₂ Lasers Market?
The market is characterized by the presence of global laser equipment manufacturers operating through authorized regional distributors and local system integrators. Competition is shaped by product reliability, application breadth, regulatory compliance, after-sales service capability, and local technical support. Medical-grade CO₂ laser suppliers operate under stricter regulatory oversight and often maintain closer relationships with healthcare institutions and distributors with clinical expertise.
03 What are the Growth Drivers for the Qatar CO₂ Lasers Market?
Key growth drivers include expansion of fabrication and packaging activities, rising demand for customized and precision-based manufacturing, continued investment in healthcare infrastructure, and growing adoption of laser-based medical and aesthetic procedures. Additional momentum comes from gradual automation of industrial workshops and increased preference for non-contact, high-precision processing technologies that reduce waste and improve consistency.
04 What are the Challenges in the Qatar CO₂ Lasers Market?
Challenges include reliance on imported systems with associated lead times, competition from alternative laser technologies in select applications, limited availability of skilled operators and service technicians, and high upfront capital costs for advanced systems. Regulatory approval requirements, particularly in the medical segment, can also extend procurement cycles and influence purchasing decisions.