Qatar Logistics and warehousing Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Segments (Freight Forwarding, Warehousing, Value-Added Services), By End-Users (Retail, Oil & Gas, Manufacturing, Healthcare, E-commerce), By Mode of Transport (Road, Air, Sea), and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0304
- Region: Middle East
- Published on: September 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market Outlook to 2029 – By Market Segments (Freight Forwarding, Warehousing, Value-Added Services), By End-Users (Retail, Oil & Gas, Manufacturing, Healthcare, E-commerce), By Mode of Transport (Road, Air, Sea), and By Region.” provides a comprehensive analysis of the logistics and warehousing industry in Qatar. The report covers an overview and genesis of the sector, overall market size in terms of revenue, segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory environment, customer profiling, issues and challenges, and comparative landscape including competitive scenario, cross-comparison, key opportunities and constraints, and profiling of major logistics and warehousing players in Qatar. The report concludes with future market projections based on revenue, end-user segment, region-wise demand, value-chain dynamics, and success case studies that highlight major opportunities and market risks.
Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market Overview and Size
The Qatar logistics and warehousing market was valued at QAR 15.2 Billion in 2023, driven by the country’s strategic geographic location, continued investments in infrastructure, and growing demand from the retail and industrial sectors. Major players include GWC (Gulf Warehousing Company), Milaha, DHL Qatar, Aramex, DB Schenker, and Agility. These companies are recognized for their integrated logistics services, large-scale warehousing capabilities, and focus on cold chain and high-tech solutions.
In 2023, GWC inaugurated a new Smart Logistics Hub in Ras Bufontas Free Zone, aimed at serving e-commerce, healthcare, and re-export needs. The Doha Industrial Area and Ras Laffan are among the most active logistics zones in the country, serving both upstream and downstream demand from key sectors including oil & gas, retail, and construction.
%2C%202018-2023.png)
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market
Economic Diversification and Vision 2030: Qatar’s push toward a non-hydrocarbon economy under the National Vision 2030 is a significant driver. As a result, sectors like retail, pharmaceuticals, and food services have witnessed rising logistics demand. In 2023, non-oil sector contribution to GDP was over 61%, reflecting diversification progress.
E-commerce and Last-Mile Delivery Expansion: The boom in online shopping has pushed the need for faster, more efficient delivery networks. Qatar’s e-commerce sector grew by over 30% between 2020 and 2023, fueling demand for micro-warehousing and last-mile logistics services especially in urban centers like Doha, Al Rayyan, and Al Wakrah.
Free Zones and Infrastructure Development: Qatar Free Zones Authority (QFZA) initiatives in Ras Bufontas and Umm Alhoul have attracted global logistics players and led to the setup of advanced logistics hubs. These zones offer tax incentives, customs exemptions, and state-of-the-art facilities, contributing to rapid market development.
What Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of the Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market
High Operational Costs: One of the most pressing challenges in the Qatari logistics industry is the high cost of operations. Rising fuel prices, warehouse rental rates, and labor expenses have all contributed to increased service charges. As of 2023, it is estimated that logistics service providers in Qatar experience operational costs that are 20–25% higher than the GCC average, making it difficult for smaller players to compete and scale.
Shortage of Skilled Labor: The industry faces a persistent shortage of skilled logistics professionals, especially in areas such as supply chain analytics, customs documentation, and warehouse automation. A 2023 industry report revealed that nearly 30% of logistics companies in Qatar identified workforce skill gaps as a key operational bottleneck, impacting both service efficiency and client satisfaction.
Limited Cold Chain Infrastructure: While Qatar has made investments in warehousing, the availability of reliable cold chain storage remains insufficient to meet rising demand from the food, pharma, and e-commerce sectors. In 2023, only 18% of total warehousing capacity was temperature-controlled, restricting the country’s ability to support perishables and high-value pharma logistics.
What Are the Regulations and Initiatives Which Have Governed the Market
Qatar National Logistics Strategy (QNLS) 2023–2030: The Ministry of Transport launched QNLS to enhance Qatar’s position as a logistics hub. The strategy focuses on integrating logistics parks with port and airport zones, digitalizing customs procedures, and improving multimodal connectivity. The initiative aims to increase the contribution of the logistics sector to GDP by 30% by 2030.
Regulations on Foreign Ownership and Free Zones: The government has allowed 100% foreign ownership in logistics operations within designated free zones such as Ras Bufontas and Umm Alhoul. These regulatory changes have attracted major global players including DHL, Aramex, and DB Schenker, who have expanded their presence in Qatar since 2022.
Customs Modernization and Single Window System: Qatar has streamlined its customs clearance through the implementation of the "Al Nadeeb" Single Window System. In 2023, over 85% of import/export documents were processed digitally, reducing cargo clearance times by up to 40% and enhancing efficiency across the logistics chain.
Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
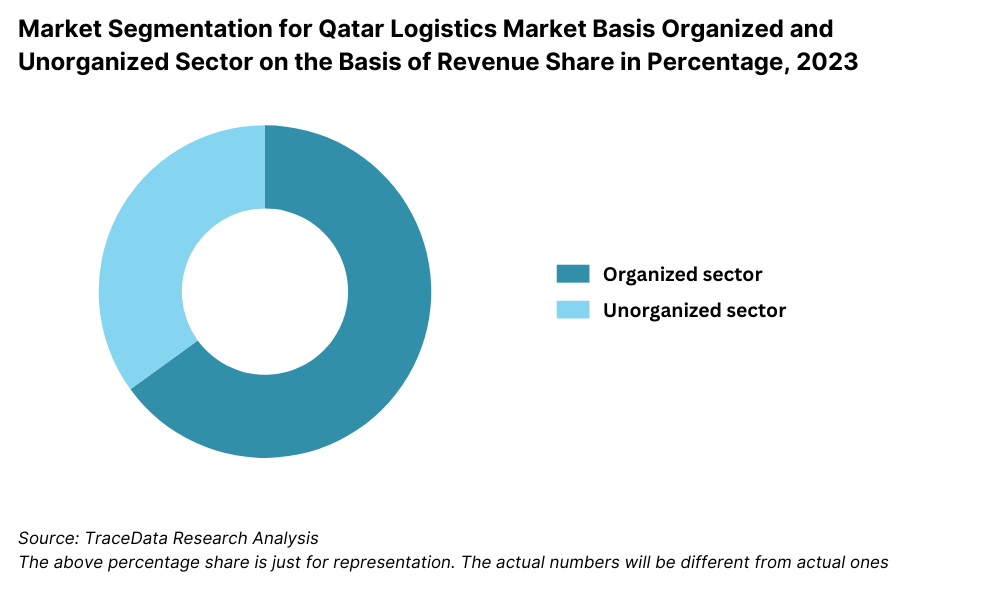
By Market Structure: The logistics sector in Qatar is increasingly dominated by organized players, particularly multinational 3PLs and government-backed logistics zones. These players benefit from access to modern infrastructure, technology integration, and compliance with global standards. However, unorganized local transporters and small warehousing providers continue to play a significant role, especially in last-mile delivery and local distribution, owing to their cost competitiveness and flexibility.
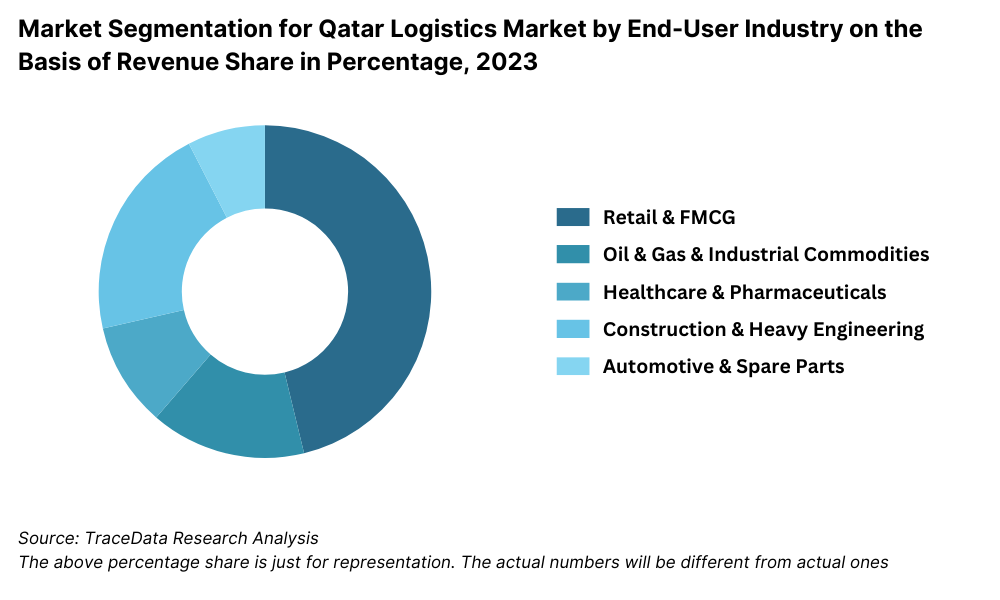
By End-User Industry: The retail and FMCG sector holds a leading share in the logistics and warehousing demand due to the rapid growth of supermarkets, hypermarkets, and e-commerce channels. Oil & Gas is the second-largest contributor, driven by the high volume of industrial shipments and requirement for specialized handling. Healthcare and Pharma are emerging segments, necessitating compliant cold chain infrastructure. Additionally, construction and heavy engineering require storage of high-value capital goods and components across project sites.
By Mode of Transport: Road transport dominates Qatar’s logistics due to well-developed highway connectivity across Doha, Al Rayyan, and key industrial zones. Sea freight contributes significantly owing to the strategic operations at Hamad Port, which handles over 70% of the country’s cargo throughput. Air freight, while limited in overall volume, plays a crucial role in high-value and time-sensitive shipments, particularly in electronics, pharma, and luxury goods.
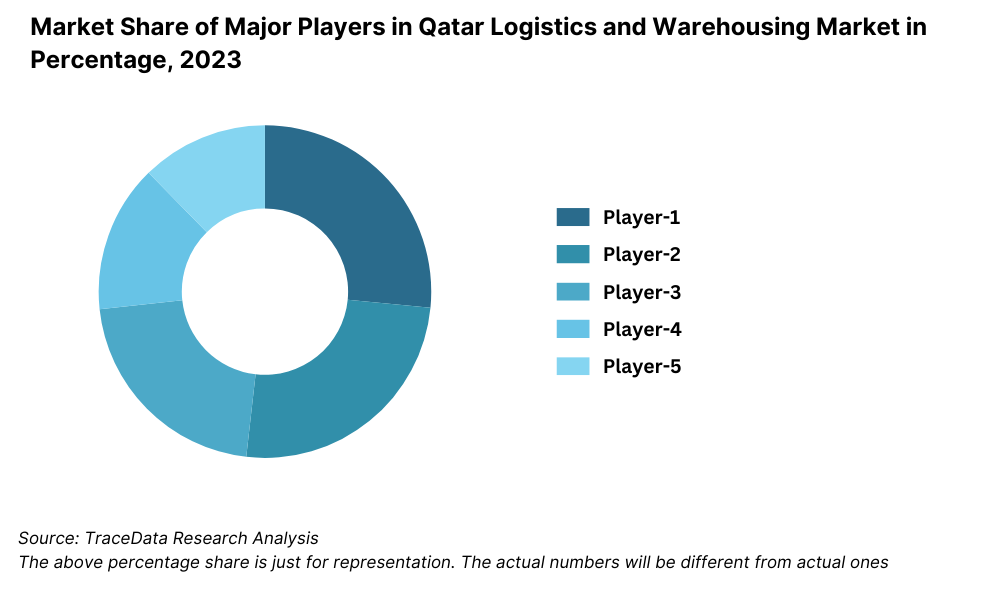
Competitive Landscape in Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market
The Qatar logistics and warehousing market is moderately consolidated, with a mix of international logistics service providers and regional players dominating key segments. The presence of global 3PLs, expansion of logistics hubs like the Qatar Free Zones (QFZ), and government-backed infrastructure initiatives have significantly enhanced the competitive intensity. Key players include DHL, GWC, Aramex, Milaha Logistics, DB Schenker, FedEx, Agility, and Qatar Post Logistics.
Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
DHL Qatar | 1971 (Global) | Doha, Qatar |
GWC | 2004 | Doha, Qatar |
Aramex Qatar | 1982 (Global) | Doha, Qatar |
Milaha Logistics | 1957 | Doha, Qatar |
DB Schenker Qatar | 1872 (Global) | Doha, Qatar |
FedEx Express Qatar | 1971 (Global) | Doha, Qatar |
Agility Logistics | 1979 (Global) | Doha, Qatar |
Qatar Post Logistics | 1950 | Doha, Qatar |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about players include:
DHL Qatar: DHL has expanded its regional footprint in Qatar Free Zones, offering end-to-end supply chain services with an emphasis on time-critical logistics. In 2023, it launched a smart warehousing facility integrated with IoT-enabled inventory management.
GWC (Gulf Warehousing Company): GWC is a leading local logistics provider with diversified services including freight forwarding, warehousing, cold chain, and industrial logistics. In 2023, GWC reported a 12% revenue increase driven by expansion in Ras Laffan and continued partnerships with oil & gas clients.
Aramex Qatar: Aramex strengthened its e-commerce logistics services by introducing automated parcel sorting and real-time delivery tracking. It handled over 2 million packages in Qatar in 2023, with a 22% YoY increase in B2C volumes.
Milaha Logistics: Known for its robust maritime and supply chain solutions, Milaha has invested in a 50,000 sq.m. logistics center in the southern logistics zone. In 2023, it signed new contracts with industrial and retail clients, expanding its non-oil client base.
DB Schenker Qatar: Focused on industrial project logistics and contract warehousing, DB Schenker established a new multi-user facility in 2023 to cater to growing demand from the manufacturing sector.
What Lies Ahead for Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Qatar logistics and warehousing market is expected to experience consistent growth through 2029, driven by rising trade volumes, strategic investments in logistics zones, diversification of the economy, and Qatar’s ambition to become a regional logistics hub. The market is projected to witness a solid CAGR over the forecast period, supported by increased demand across retail, e-commerce, and industrial sectors.
Expansion of Free Zones and Industrial Parks: Qatar’s Free Zones Authority (QFZA) is actively investing in logistics infrastructure around Hamad International Airport and Hamad Port. These zones are expected to attract multinational 3PLs and regional exporters, significantly boosting Qatar’s warehousing capacity and value-added service offerings by 2029.
Acceleration of E-commerce Fulfillment Services: The rapid growth of e-commerce in Qatar is anticipated to fuel demand for last-mile delivery, express logistics, and fulfillment centers. With online retail sales expected to rise at double-digit rates annually, logistics providers are likely to invest in automation, urban micro-fulfillment hubs, and customer-centric delivery models.
Adoption of Smart Warehousing and Automation: Warehousing in Qatar is undergoing a shift toward digitization and automation. By 2029, a significant share of new warehouse developments will incorporate WMS (Warehouse Management Systems), AI-driven inventory tracking, robotics for sorting, and energy-efficient designs. These upgrades aim to improve efficiency, reduce labor dependency, and enhance real-time visibility.
Growth in Cold Chain and Pharma Logistics: Qatar’s healthcare expansion and food security initiatives are expected to increase the need for specialized cold chain infrastructure. Government efforts to localize pharmaceutical production and import essential goods will drive demand for temperature-controlled warehousing and compliance-based distribution networks.
%2C%202023-2029.png)
Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
By Market Structure:
Freight Forwarding Companies
Express Logistics Providers
Last-Mile Delivery Players
Contract Logistics and 3PL Companies
Government-Backed Logistics Zones (e.g., QFZ, Manateq)
Organized Logistics Service Providers
Unorganized and Local Transporters
Cold Chain Logistics Providers
By End-User Industry:
Retail & FMCG
Oil & Gas
E-commerce
Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare
Automotive
Manufacturing & Industrial
Food & Beverage
Construction Materials
By Mode of Transport:
Road
Sea
Air
Multimodal Transport
By Type of Warehousing:
General Storage Warehouses
Cold Storage Warehouses
Bonded Warehouses
Distribution Centers
Fulfillment Centers
By Region:
Doha
Al Rayyan
Al Wakrah
Ras Laffan Industrial City
Qatar Free Zones (Umm Alhoul, Ras Bufontas)
Players Mentioned in the Report:
GWC (Gulf Warehousing Company)
DHL Express Qatar
Aramex Qatar
Milaha Logistics
DB Schenker Qatar
Agility Logistics
Qatar Post Logistics
FedEx Express Qatar
Maersk Logistics Qatar
Kuehne + Nagel Qatar
Key Target Audience:
3PL and 4PL Service Providers
Industrial and Retail Companies
E-commerce Platforms and Sellers
Cold Chain & Pharma Logistics Firms
Government Agencies (e.g., MOT, QFZA, QDB)
Trade & Logistics Zone Authorities (e.g., Manateq, QFZ)
Supply Chain Technology Providers
Warehousing Infrastructure Developers
Transport Aggregators and Fleet Operators
Time Period:
Historical Period: 2018–2023
Base Year: 2024
Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
1. Executive Summary
2. Research Methodology
3. Ecosystem of Key Stakeholders in Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market
4. Value Chain Analysis
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and Challenges They Face
4.2. Revenue Streams for Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market
4.4. Buyer Decision-Making Process (B2B & Government Procurement)
4.5. Supply-Side Decision-Making Framework
5. Market Structure
5.1. Import and Export Trends for Qatar, 2018-2024
5.2. Logistics Contribution to Qatar’s GDP, 2018-2024
5.3. Container Traffic and Cargo Throughput (Hamad Port and HIA), 2018-2024
5.4. Number of Warehousing and Logistics Players by Region
6. Market Attractiveness for Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market
7. Supply-Demand Gap Analysis for Logistics & Storage Capacity
8. Market Size for Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market Basis
8.1. Revenues, 2018-2024
8.2. Tonnage Volume Moved / Warehouse Space Utilized, 2018-2024
9. Market Breakdown for Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market Basis
9.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized Sector), 2023-2024P
9.2. By Mode of Transport (Road, Sea, Air), 2023-2024P
9.3. By Type of Warehousing (General, Cold Storage, Bonded, Fulfillment), 2023-2024P
9.4. By End-User Industry (Retail, Oil & Gas, Pharma, etc.), 2023-2024P
9.5. By Region (Doha, Ras Laffan, QFZ, Others), 2023-2024P
9.6. By Value-Added Services (Sorting, Labeling, Customs, Reverse Logistics), 2023-2024P
10. Demand Side Analysis for Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market
10.1. Key Industry Clusters Driving Demand
10.2. Buyer Journey and Logistics Decision Drivers
10.3. Industry-Specific Logistics Needs (Retail, FMCG, Healthcare)
10.4. Pain Points and Service Gaps
11. Industry Analysis
11.1. Trends and Developments in Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis
11.4. Issues and Challenges
11.5. Government Regulations and Strategic Initiatives
12. Snapshot on E-Commerce Logistics Market
12.1. Market Size and Future Potential, 2018-2029
12.2. Fulfillment Models (Last-Mile, Micro-Fulfillment, Express)
12.3. Cross-Comparison of Key Players: Facilities, Coverage, Business Model
13. Qatar Cold Chain and Pharma Logistics Market
13.1. Cold Storage Demand by Sector (Pharma, F&B, Dairy, etc.)
13.2. Regulatory Compliance Needs (GCC, WHO Standards)
13.3. Key Operators in the Cold Chain Segment
13.4. Facility Gaps and Investment Opportunities
14. Opportunity Matrix for Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market-Presented with Radar Chart
15. PEAK Matrix Analysis for Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Providers
16. Competitor Analysis for Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market
16.1. Benchmark of Key Competitors by Services, Strength, Coverage, Technology
16.2. Strengths and Weaknesses
16.3. Operating Model Analysis Framework
16.4. Gartner Magic Quadrant Positioning
16.5. Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
17. Future Market Size for Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market Basis
17.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
17.2. Volume (Freight Moved / Area Leased), 2025-2029
18. Market Breakdown for Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market Basis
18.1. By Market Structure (Organized vs Unorganized), 2025-2029
18.2. By Mode of Transport, 2025-2029
18.3. By Warehouse Type, 2025-2029
18.4. By Region, 2025-2029
18.5. By End-User Industry, 2025-2029
18.6. By Value-Added Services, 2025-2029
18.7. Recommendation
18.8. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the entire ecosystem and identify all demand-side and supply-side entities relevant to the Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market. This includes 3PL companies, freight forwarders, warehouse operators, industrial clients, e-commerce players, and regulatory authorities.
Based on this mapped ecosystem, we shortlist 5–6 leading logistics service providers in Qatar based on operational scale, financial performance, warehouse footprint, and modal coverage.
Sourcing is performed through extensive secondary research from industry publications, logistics trade portals, government reports, regulatory filings, and proprietary databases to construct a comprehensive market outline.
Step 2: Desk Research
Conduct thorough desk research using a wide array of secondary sources and proprietary data. This allows us to establish a detailed understanding of market parameters such as logistics volumes (freight tonnage), warehouse occupancy rates, pricing benchmarks, market shares, modal split, and regional distribution.
In-depth company-level analysis is performed using annual reports, investor presentations, press releases, Ministry of Transport reports, and official free zone disclosures to analyze business models, expansion plans, and financial health of key players.
Step 3: Primary Research
Carry out detailed in-depth interviews with senior executives and operations managers across logistics providers, e-commerce platforms, warehousing firms, and regulatory authorities. These interactions serve to validate key hypotheses, cross-check volume and revenue estimates, and gather qualitative insights on service gaps and growth drivers.
A bottom-up approach is applied to estimate warehouse space utilization, freight volumes handled, and revenue contribution per segment for each major player. These figures are then aggregated to calculate the overall market size.
Disguised interviews are also conducted with logistics operators under the pretext of potential clients to validate commercial terms, service capabilities, pricing structures, and operational capacities — ensuring a 360-degree verification of all secondary inputs.
Step 4: Sanity Check
A combination of bottom-up and top-down modeling is used to conduct a sanity check of all findings. This includes triangulation between revenue estimates, warehouse area capacity, freight volumes, and sectoral consumption patterns.
Internal benchmarking with other GCC logistics markets (e.g., UAE, KSA, Oman) is undertaken to ensure realistic projections and contextually accurate forecasting.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Qatar logistics and warehousing market is expected to witness robust growth through 2029, fueled by infrastructure development, increased trade activity, and diversification of the economy under Qatar National Vision 2030. With rising demand from sectors such as retail, oil & gas, e-commerce, and pharmaceuticals, the market offers high potential for both domestic and international logistics service providers. Strategic government initiatives, like the Qatar Free Zones and logistics parks near Hamad Port and Airport, further amplify this potential.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Major players in the Qatar logistics and warehousing industry include GWC (Gulf Warehousing Company), DHL Qatar, Aramex, Milaha Logistics, DB Schenker, FedEx Express, Agility Logistics, and Qatar Post Logistics. These companies are recognized for their advanced warehousing infrastructure, integrated service offerings, and strong regional logistics networks.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Key growth drivers include Qatar’s strategic location as a regional logistics hub, increased investments in free zones and multimodal transport infrastructure, and a surge in e-commerce and cold chain logistics demand. Additionally, regulatory reforms, digital transformation in customs clearance, and government support for private sector logistics initiatives are enabling rapid market expansion.
4. What are the Challenges in the Qatar Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The market faces several challenges including high operational costs, limited availability of skilled logistics workforce, and underdeveloped cold storage infrastructure. Additionally, dependency on imported labor and regulatory complexities for cross-border logistics pose operational constraints. Addressing these issues through technology adoption, workforce development, and policy support remains crucial for sustainable growth.