Romania Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Structure, By Temperature Range, By Type of Product Handled, By Ownership, By End-User Industry, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0305
- Region: Europe
- Published on: September 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Romania Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029 - By Market Structure, By Temperature Range, By Type of Product Handled, By Ownership, By End-User Industry, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the cold chain logistics sector in Romania. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, detailed market segmentation, trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer level profiling, issues and challenges, and comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the Romania Cold Chain Market. The report concludes with future market projections based on revenue, by market segments, regional distribution, cause-and-effect relationships, and success case studies outlining major opportunities and risks.
Romania Cold Chain Market Overview and Size
The Romania cold chain market reached an estimated valuation of RON 2.4 Billion in 2023, driven by increasing demand for temperature-controlled logistics across sectors such as pharmaceuticals, fresh produce, frozen food, and dairy. With the rise of modern retail and e-commerce grocery delivery platforms, the demand for efficient cold storage and transport solutions has surged. Key players operating in the Romanian cold chain market include Dachser Romania, Havi Logistics, Frigo Logistic, Aquila Part Prod Com, and DSV Solutions. These companies offer integrated cold storage and refrigerated transport services, targeting urban centers like Bucharest, Cluj-Napoca, and Timisoara, which serve as primary demand hubs due to their high population density and industrial activity.
In 2023, Frigo Logistic inaugurated a new cold storage facility in Ploiești with advanced automation and real-time temperature monitoring to cater to the growing pharmaceutical and FMCG demand. Romania’s strategic geographic location and improving logistics infrastructure make it a key hub for regional cold chain distribution in Eastern Europe.
%2C%202018%E2%80%932023.png)
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Romania Cold Chain Market:
Rising Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Demand: Post-pandemic, the need for safe and reliable vaccine and biologics storage has surged. Romania’s pharmaceutical cold chain segment grew at a CAGR of 9.2% between 2020 and 2023, with increased investments in GDP-compliant temperature-controlled storage.
Growing Modern Retail and Food Exports: The expansion of supermarkets, hypermarkets, and quick-commerce platforms has significantly contributed to cold chain demand. Exports of Romanian meat and dairy to EU countries have risen by 14% YoY, necessitating robust cold transport networks.
Regulatory Push for Compliance and Safety: The Romanian government and EU authorities have introduced stricter cold chain compliance measures for food safety and pharmaceutical integrity. This has encouraged investment in modern facilities with data-logging systems, insulated fleets, and IoT-based monitoring.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of Romania Cold Chain Market
Infrastructure Gaps and High Energy Costs: One of the major bottlenecks in Romania’s cold chain sector is the limited availability of modern cold storage facilities, particularly in Tier-2 and rural regions. Nearly 35% of perishable goods losses in Romania are attributed to inadequate or outdated cold storage infrastructure. Additionally, electricity costs in Romania are among the highest in Eastern Europe, contributing to operational expenses that are 15–20% higher than in Western European countries. These factors significantly constrain cold chain scalability.
Skilled Workforce Shortage: Operating and maintaining temperature-controlled systems requires trained staff, yet there is a critical shortage of certified technicians and cold chain specialists in Romania. This issue impacts service consistency and increases the risk of product spoilage. In 2023, a survey among cold logistics firms indicated that 42% of businesses faced delays or losses due to human error in temperature monitoring or poor handling practices.
Fragmentation in the Transport Network: Romania’s cold chain transport sector is highly fragmented, with over 70% of refrigerated fleets operated by small and medium enterprises. These players often lack GPS tracking, real-time monitoring systems, and advanced vehicle insulation—leading to frequent breaches in temperature standards during transit. This fragmentation undermines service reliability and limits cross-border opportunities.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market
EU Compliance on GDP and HACCP Standards: As a member of the European Union, Romania mandates that all pharmaceutical and food cold chains comply with Good Distribution Practice (GDP) and Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) guidelines. These regulations require continuous temperature logging, tamper-proof packaging, and real-time alerts. By 2023, approximately 68% of cold storage facilities were certified under EU GDP/HACCP protocols, signaling a push towards standardization.
Romanian Ministry of Agriculture Subsidies for Cold Infrastructure: To reduce post-harvest losses and encourage agribusiness investments, the Romanian government has rolled out grant programs under the NRDP (National Rural Development Programme). These provide up to 50% co-financing for the construction of cold warehouses and acquisition of reefer vehicles for farmer cooperatives. In 2022–2023, over 120 SMEs received funding under this initiative.
Digital Transition & Smart Logistics Mandates: Under Romania’s Smart Transport 2030 vision, the government is pushing logistics players to adopt digital technologies, such as IoT-based sensors for temperature and humidity, and eCMR (electronic consignment notes) to improve traceability. Starting 2024, certain high-risk pharmaceuticals (e.g., vaccines, insulin) are required by law to be transported with blockchain-verified temperature logs, increasing investment in tech-enabled solutions.
Romania Cold Chain Market Segmentation
By Market Structure: The organized sector is gaining traction in Romania due to increasing demand from multinational retailers, pharmaceutical distributors, and food exporters that require compliance with EU standards and end-to-end visibility. These players invest in state-of-the-art infrastructure, such as GDP-compliant warehousing and GPS-enabled reefer trucks. The unorganized segment, primarily consisting of small local transporters and storage operators, still holds a notable share, particularly in regional fruit & vegetable logistics. However, limited capacity, lack of tech adoption, and fragmented operations restrict their growth in high-value sectors.
%2C%202023.png)
By Temperature Range:Chilled storage and transport (0°C to 8°C) dominate the market due to their wide application in dairy, fresh produce, bakery items, and pharmaceuticals. This segment accounts for a significant share of the cold chain network, particularly in retail and food service supply chains. Frozen logistics (below -18°C) is rapidly growing owing to increased consumption of frozen meat, seafood, and ready-to-eat meals. Growth is driven by evolving consumer lifestyles and rising exports of frozen poultry and bakery items.
%2C%202023.png)
By Type of Product Handled: The food and beverage segment holds the largest share, led by processed meat, dairy, fruits, and vegetables. Rising urbanization and modern trade expansion have increased demand for high-quality perishable foods. The pharmaceutical segment is also showing accelerated growth, driven by stringent EU regulatory requirements and increased demand for biologics and vaccines that require temperature-controlled logistics.
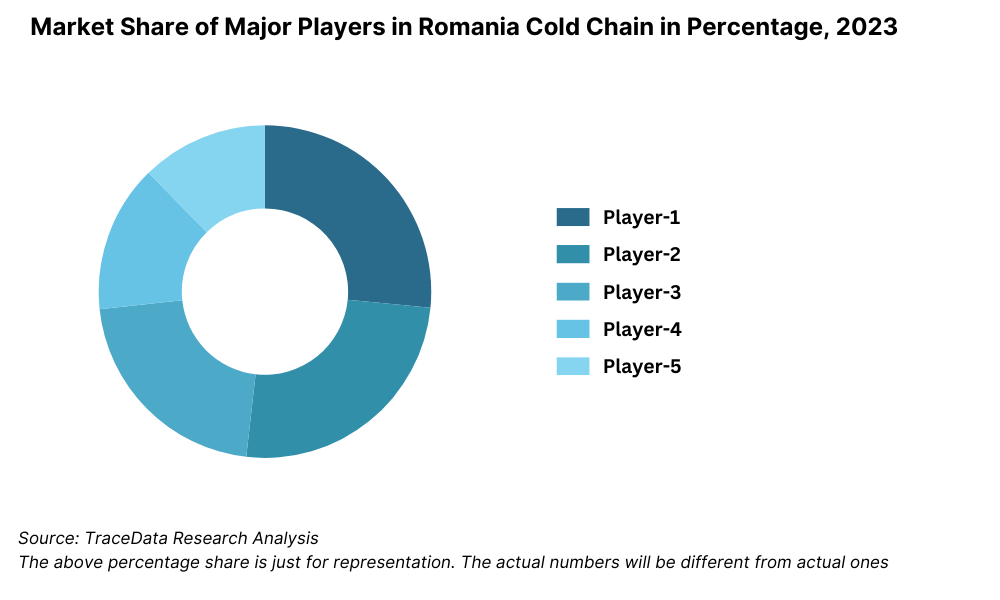
Competitive Landscape in Romania Cold Chain Market
The Romania cold chain market is moderately concentrated, with a mix of established logistics companies and emerging players specializing in temperature-controlled storage and transportation. While international 3PLs such as DSV Solutions and Dachser Romania dominate the high-compliance pharmaceutical and food export segments, domestic companies like Aquila Part Prod Com, Frigo Logistic, and Carrion Expedition are expanding their footprint with new facilities and reefer fleets. The market is also seeing growing investment from retail-linked logistics players aiming to modernize cold storage near consumption hubs.
Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
DSV Solutions | 1976 (Romania arm active since 1995) | Bucharest, Romania |
Aquila Part Prod Com | 1994 | Ploiești, Romania |
Frigo Logistic | 2001 | Cluj-Napoca, Romania |
Carrion Expedition | 2002 | Satu Mare, Romania |
Havi Logistics Romania | 2005 (local operations) | Bucharest, Romania |
Dachser Romania | 2009 | Arad, Romania |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about major players include:
DSV Solutions: DSV continues to be a dominant cold chain player in Romania, with over 30,000 sqm of temperature-controlled warehousing and integrated end-to-end pharma logistics. In 2023, DSV Romania partnered with several hospital networks for direct-to-pharmacy cold deliveries, enhancing its compliance-driven logistics portfolio.
Aquila Part Prod Com: Aquila, a leading FMCG and HoReCa logistics provider, added 40 new refrigerated trucks to its fleet in 2023. The company has expanded its reach in southern and western Romania and is investing in automation and ERP systems for better warehouse temperature regulation.
Frigo Logistic: Known for its specialized frozen goods infrastructure, Frigo Logistic opened a new -20°C warehouse facility in Cluj-Napoca in 2023. The company reported a 22% YoY growth in frozen food distribution, particularly in QSR and retail sectors.
Carrion Expedition: Carrion operates a large reefer truck fleet and is a key player in cross-border cold transport between Romania, Hungary, and Germany. In 2023, it began piloting IoT-based reefer tracking systems to improve in-transit temperature visibility and reduce spoilage.
Havi Logistics Romania: Serving multinational fast-food chains and food retailers, Havi is investing in solar-powered cold storage units to reduce energy costs. In 2023, it launched a green logistics pilot project in Bucharest with hybrid vehicles for last-mile frozen food delivery.
Dachser Romania: Dachser has expanded its pharmaceutical cold chain services, with a 2023 rollout of GDP-certified transport for biopharma clients. Its Arad facility now serves as a strategic hub for EU medical cold chain distribution.
What Lies Ahead for Romania Cold Chain Market?
The Romania cold chain market is projected to expand steadily by 2029, demonstrating a healthy CAGR over the forecast period. Growth will be fueled by increased demand across pharmaceuticals, modern retail, and food exports, coupled with improved infrastructure investments and regulatory alignment with EU standards.
Expansion of E-Grocery and Quick Commerce: As Romania’s urban population increasingly adopts online grocery and meal delivery platforms, cold chain operators will see rising demand for last-mile refrigerated logistics. Major cities like Bucharest, Cluj-Napoca, and Iasi are expected to emerge as hotspots for temperature-controlled urban delivery networks. Growth in the e-commerce grocery segment, projected to rise by 18% YoY, will drive investments in small-format cold storage hubs and multi-temperature delivery vehicles.
Surge in Pharmaceutical Cold Chain Requirements: Driven by aging population, vaccine distribution, and increased pharmaceutical exports, Romania's pharma cold chain market is poised for accelerated growth. The rollout of advanced biologics and temperature-sensitive drugs will necessitate GDP-certified storage and transit networks. By 2029, pharma cold logistics is expected to account for over 25% of total cold chain revenue.
Technology-Driven Cold Chain Evolution: Integration of IoT sensors, blockchain, and AI-based temperature analytics will enhance real-time visibility, predictive maintenance, and spoilage prevention. These innovations will also facilitate better regulatory compliance and help streamline cross-border logistics. The adoption of smart refrigeration systems and energy-efficient cooling is projected to reduce spoilage by up to 15% and lower operational costs by 10–12% by 2029.
Growth in Regional Warehousing Hubs: With EU logistics corridors expanding through Romania, regions such as Timis, Constanta, and Prahova are anticipated to become key cold storage hubs due to their proximity to border crossings, ports, and highway infrastructure. These regions are expected to attract foreign direct investment (FDI) in warehousing, logistics parks, and multi-client cold storage facilities.
%2C%202023-2029.png)
Romania Cold Chain Market Segmentation
• By Market Structure:
o Organized Sector
o Unorganized Sector
o Captive Logistics Providers
o 3PL Cold Chain Providers
o Local Regional Players
o Multinational Logistics Firms
• By Temperature Range:
o Chilled (0°C to 8°C)
o Frozen (Below -18°C)
o Ambient Controlled (15°C to 25°C for pharmaceuticals)
• By Type of Product Handled:
o Fruits and Vegetables
o Meat and Seafood
o Dairy Products
o Pharmaceuticals and Vaccines
o Bakery and Confectionery
o Ready-to-Eat Meals
• By Ownership:
o Captive (Owned by manufacturers/retailers)
o Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
o Leased Infrastructure
• By End-User Industry:
o Food Processing Companies
o Modern Retail Chains
o Pharmaceutical Distributors
o HoReCa (Hotels, Restaurants, Cafés)
o E-Grocery and Q-Commerce Players
o Export-Oriented Agribusiness
• By Region:
o Bucharest-Ilfov
o North-West (Cluj, Bihor)
o North-East (Iasi, Suceava)
o South-East (Constanta, Galati)
o South-Muntenia (Prahova, Dambovita)
o West (Timis, Arad)
Players Mentioned in the Report:
• DSV Solutions
• Aquila Part Prod Com
• Frigo Logistic
• Carrion Expedition
• Havi Logistics Romania
• Dachser Romania
Key Target Audience:
• Cold Chain Logistics Companies
• Pharmaceutical and Food Manufacturers
• Retail and Q-Commerce Chains
• Government & Regulatory Bodies (e.g., National Sanitary Veterinary Authority)
• Logistics Infrastructure Investors
• Technology Providers (IoT, Telematics, and Monitoring Systems)
Time Period:
• Historical Period: 2018–2023
• Base Year: 2024
• Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
1. Executive Summary
2. Research Methodology
3. Ecosystem of Key Stakeholders in Romania Cold Chain Market
4. Value Chain Analysis
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and Challenges That They Face
4.2. Revenue Streams for Romania Cold Chain Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Romania Cold Chain Market
4.4. Demand-Side Decision-Making Process
4.5. Supply-Side Decision-Making Process
5. Market Structure
5.1. Growth of Cold Chain Logistics Industry in Romania, 2018-2024
5.2. Cold Chain Infrastructure Expansion by Region, 2018-2024
5.3. Growth of Organized Retail and Q-Commerce in Romania, 2018-2024
5.4. Cold Chain Warehousing Capacity by Region, 2023-2024
6. Market Attractiveness for Romania Cold Chain Market
7. Supply-Demand Gap Analysis
8. Market Size for Romania Cold Chain Market Basis
8.1. Revenues, 2018-2024
8.2. Cold Chain Volume by Tonnes Handled, 2018-2024
9. Market Breakdown for Romania Cold Chain Market Basis
9.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized), 2023-2024P
9.2. By Ownership (3PL vs Captive), 2023-2024P
9.3. By Temperature Range (Chilled, Frozen, Ambient), 2023-2024P
9.4. By Type of Product (Fruits & Vegetables, Dairy, Meat & Seafood, Pharma, Bakery, Ready-to-Eat), 2023-2024P
9.5. By End-Use Industry (Retail, Food Processing, HoReCa, Pharma, Exporters), 2023-2024P
9.6. By Region (Bucharest, Cluj, Timis, Constanta, Prahova, Others), 2023-2024P
10. Demand Side Analysis for Romania Cold Chain Market
10.1. Customer Landscape and Segment Analysis
10.2. Customer Journey and Selection Criteria
10.3. Pain Point and Expectation Mapping
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11. Industry Analysis
11.1. Trends and Developments in Romania Cold Chain Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Romania Cold Chain Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Romania Cold Chain Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges in Romania Cold Chain Market
11.5. Government Regulations and EU Compliance Framework
12. Snapshot on Cross-Border and Export-Oriented Cold Chain Market
12.1. Volume Handled for Export Logistics, 2018-2029
12.2. Certification and Compliance for Cross-Border Trade
12.3. Comparison of Regional Cold Chain Hubs
13. Technology Landscape in Romania Cold Chain Market
13.1. Adoption of IoT, Blockchain, and Automation, 2018-2029
13.2. Cold Chain Monitoring Solutions and Fleet Telemetry
13.3. Role of Digital Platforms in Last-Mile Cold Chain
14. Opportunity Matrix for Romania Cold Chain Market-Presented with the Help of Radar Chart
15. PEAK Matrix Analysis for Romania Cold Chain Market
16. Competitor Analysis for Romania Cold Chain Market
16.1. Benchmark of Key Competitors in Romania Cold Chain Market Including Company Overview, Certifications, USP, Fleet Size, Warehousing Footprint, Key Clients, and Recent Developments
16.2. Strength and Weakness
16.3. Operating Model Analysis Framework
16.4. Gartner Magic Quadrant
16.5. Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
17. Future Market Size for Romania Cold Chain Market Basis
17.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
17.2. Volume by Tonnes Handled, 2025-2029
18. Market Breakdown for Romania Cold Chain Market Basis
18.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized), 2025-2029
18.2. By Ownership (3PL vs Captive), 2025-2029
18.3. By Temperature Range (Chilled, Frozen, Ambient), 2025-2029
18.4. By Type of Product (Fruits & Vegetables, Dairy, Meat & Seafood, Pharma, Bakery, Ready-to-Eat), 2025-2029
18.5. By End-Use Industry (Retail, Food Processing, HoReCa, Pharma, Exporters), 2025-2029
18.6. By Region (Bucharest, Cluj, Timis, Constanta, Prahova, Others), 2025-2029
18.7. Recommendation
18.8. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand side and supply side entities for Romania Cold Chain Market. Basis this ecosystem, we will shortlist leading 5-6 players in the country based upon their financial information, cold storage capacity, fleet size, and operational coverage.
Sourcing is made through industry articles, multiple secondary, and proprietary databases to perform desk research around the market to collate industry-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
Subsequently, we engage in an exhaustive desk research process by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This approach enables us to conduct a thorough analysis of the market, aggregating industry-level insights. We delve into aspects like the revenue generation, number of active market players, capacity utilization, compliance levels, pricing trends, and other variables. We supplement this with detailed examinations of company-level data, relying on sources like press releases, annual reports, financial statements, and similar documents. This process aims to construct a foundational understanding of both the market and the entities operating within it.
Step 3: Primary Research
We initiate a series of in-depth interviews with C-level executives and other stakeholders representing various Romania Cold Chain Market companies and end-users. This interview process serves a multi-faceted purpose: to validate market hypotheses, authenticate statistical data, and extract valuable operational and financial insights from these industry representatives. Bottom to top approach is undertaken to evaluate revenue contribution and capacity for each player thereby aggregating to the overall market.
As part of our validation strategy, our team executes disguised interviews wherein we approach each company under the guise of potential customers. This approach enables us to validate the operational and financial information shared by company executives, corroborating this data against what is available in secondary databases. These interactions also provide us with a comprehensive understanding of revenue streams, value chain, process, pricing, and other factors.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- Bottom to top and top to bottom analysis along with market size modeling exercises is undertaken to assess sanity check process.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Romania Cold Chain Market?
The Romania Cold Chain Market is poised for substantial growth, reaching an estimated valuation of RON 2.4 Billion in 2023. This growth is driven by increasing demand across sectors such as pharmaceuticals, processed foods, dairy, and fresh produce. Romania’s strategic location within the EU, rising food exports, and expanding retail infrastructure further enhance the market’s long-term potential. The growing focus on compliance, digitalization, and last-mile delivery is expected to accelerate cold chain investments across the country.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Romania Cold Chain Market?
The Romania Cold Chain Market features several key players, including DSV Solutions, Aquila Part Prod Com, and Frigo Logistic. These companies dominate the market due to their extensive fleet operations, temperature-controlled warehousing, and strong presence in both domestic and cross-border logistics. Other notable players include Carrion Expedition, Havi Logistics Romania, and Dachser Romania.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Romania Cold Chain Market?
Primary growth drivers include rising demand from the pharmaceutical and food export sectors, expansion of modern retail formats, and the increasing penetration of e-grocery and quick commerce platforms. Additionally, government subsidies for cold infrastructure development and compliance with EU GDP and HACCP standards are encouraging further investment. Technological advancements such as IoT-enabled reefer trucks and temperature-monitoring systems are also contributing to the market’s robust growth.
4. What are the Challenges in the Romania Cold Chain Market?
The Romania Cold Chain Market faces several challenges, including limited cold storage capacity in rural areas, high energy costs, and a shortage of skilled technicians to manage sensitive logistics operations. Market fragmentation—particularly among small-scale transporters—can lead to inefficiencies and gaps in temperature control. Moreover, compliance with EU regulatory frameworks demands significant investment in infrastructure and training, which can pose barriers for smaller firms.