Russia Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized), By End-User Industries (Fruits & Vegetables, Dairy Products, Pharmaceuticals, Meat & Seafood, and Others), By Transport Modes (Road, Rail, Air, and Sea), and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0308
- Region: Asia
- Published on: September 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Russia Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029 - By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized), By End-User Industries (Fruits & Vegetables, Dairy Products, Pharmaceuticals, Meat & Seafood, and Others), By Transport Modes (Road, Rail, Air, and Sea), and By Region.” provides a comprehensive analysis of the cold chain industry in Russia. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation, trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer level profiling, issues and challenges, and comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the Cold Chain Market. The report concludes with future market projections based on revenue, by segment, transport mode, region, cause and effect relationships, and success case studies highlighting major opportunities and risks.
Russia Cold Chain Market Overview and Size
The Russia cold chain market reached a valuation of RUB 280 Billion in 2023, driven by the increasing demand for temperature-sensitive goods, growth in pharmaceutical exports, and expansion in organized food retailing. The market is characterized by prominent players such as X5 Logistics, Magnit, Lineage Logistics, RZD Logistics, and Global Cold Chain. These companies are known for their strong infrastructure, integrated supply chain services, and focus on maintaining product quality across the distribution process.
In 2023, Lineage Logistics expanded its footprint by acquiring a major cold storage facility near Moscow, enhancing its capacity to cater to rising demand in the food and pharma sectors. Moscow and St. Petersburg remain key operational hubs due to their population density and industrial concentration.
%2C%202019-2024.png)
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Russia Cold Chain Market:
Growth in Pharmaceutical Sector: Increased demand for temperature-controlled logistics for vaccines, biologics, and temperature-sensitive drugs has spurred growth. In 2023, pharmaceutical cold chain services accounted for nearly 24% of total market revenue.
Expansion of Modern Retail and E-commerce: The growth of organized retail chains and online grocery platforms has increased the need for temperature-controlled warehousing and efficient last-mile delivery, especially in urban centers.
Government Initiatives: Strategic investments under Russia’s “National Project on International Cooperation and Export” have encouraged the development of logistics infrastructure including cold chain facilities to boost food exports.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for Russia Cold Chain Market
Infrastructure Gaps in Remote Areas: One of the significant barriers in Russia’s cold chain industry is the lack of reliable infrastructure in remote regions such as Siberia and the Far East. According to a 2023 logistics survey, nearly 45% of logistics firms reported difficulties in maintaining temperature integrity due to poor road connectivity and limited access to electricity, leading to spoilage risks and high operational costs.
High Operating and Energy Costs: Maintaining cold storage and refrigerated transport in Russia’s extreme climate conditions demands high energy consumption, especially during long winters. In 2023, operating costs for cold storage facilities in Russia increased by 12%, primarily due to spikes in electricity tariffs and fuel prices, negatively impacting the profitability of cold chain providers.
Lack of Skilled Workforce and Technology Adoption: Many cold chain operators continue to rely on outdated systems for inventory tracking and temperature monitoring. Additionally, there is a shortage of trained personnel to manage temperature-sensitive logistics. Data from 2023 revealed that only 28% of cold storage facilities were equipped with real-time monitoring systems, posing risks to compliance and quality assurance.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
Food Safety and Quality Control Standards: The Russian Federal Service for Surveillance on Consumer Rights Protection enforces strict food safety laws, requiring cold chain operators to maintain specific temperature thresholds throughout the supply chain. In 2023, over 3,000 inspections were conducted, and 17% of cold chain logistics companies received warnings for non-compliance with hygiene standards.
Subsidy Programs for Refrigerated Logistics: As part of the National Agro-Industrial Complex Development Program, the Russian government has offered subsidies covering up to 25% of capital expenditure for companies investing in cold chain infrastructure. In 2023, this program supported over 100 facilities focused on fruit and vegetable storage.
Mandatory Pharmaceutical Storage Compliance: Under the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) regulations, all pharmaceutical cold chain operations in Russia must comply with GDP (Good Distribution Practice) standards. In 2023, Russia’s Ministry of Health updated guidelines to include stricter monitoring and auditing procedures, resulting in a 14% increase in compliance certifications across cold chain service providers.
Russia Cold Chain Market Segmentation
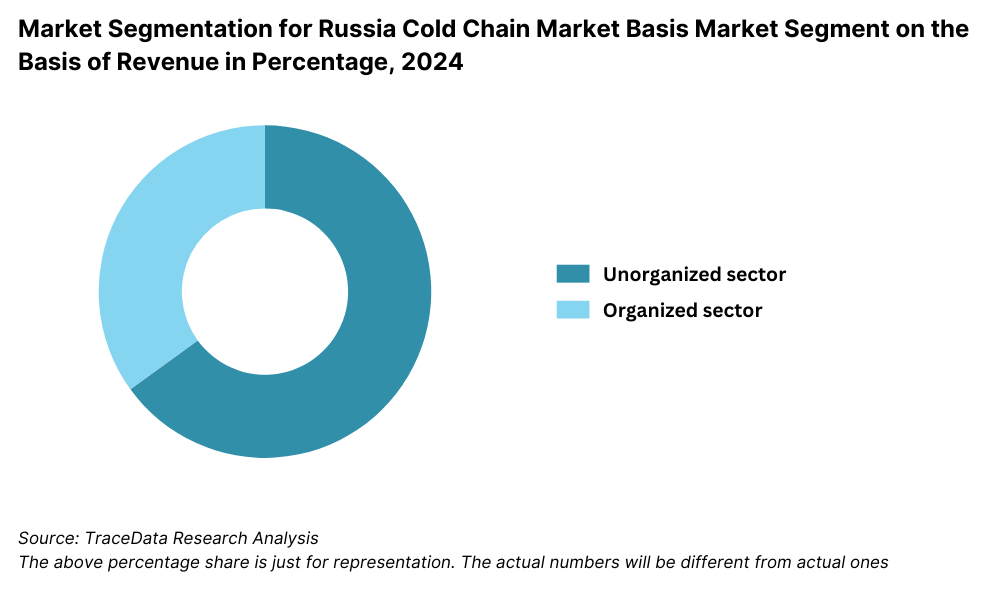
By Market Structure: The Russian cold chain industry is dominated by unorganized players, especially in Tier 2 and rural regions, where small-scale logistics operators and independent warehouse owners cater to local demand. These players often operate with limited technology and smaller storage capacities. However, organized cold chain providers are rapidly growing in urban centers like Moscow, St. Petersburg, and Yekaterinburg due to their advanced temperature monitoring systems, compliance with food and pharma safety regulations, and integration with national and international supply chains.
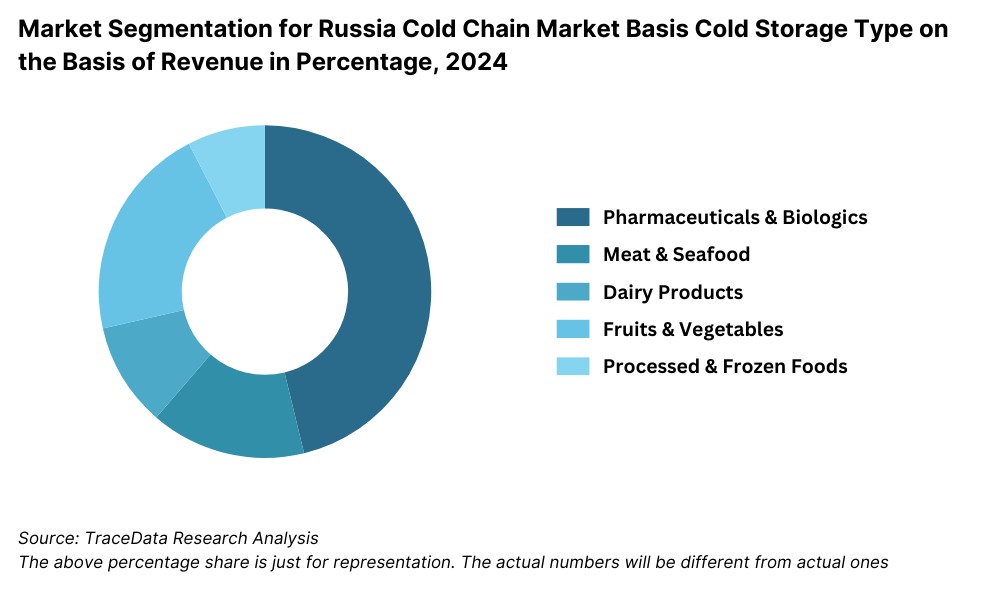
By End-User Industry: In 2023, the pharmaceutical sector emerged as a key contributor to cold chain logistics demand, driven by vaccine distribution, biologics, and other temperature-sensitive medications. The meat & seafood industry follows, especially in Russia’s coastal and Arctic regions, where preservation through cold chain is critical for both domestic consumption and export. Dairy and fruits & vegetables are also major segments, especially due to increasing domestic production and fresh food preferences in urban markets.
By Transport Mode: Road transport dominates cold chain logistics in Russia due to its reach and flexibility, particularly for short and medium hauls. However, rail freight is gaining traction for long-distance transportation, especially from western Russia to Siberia and the Far East. Air freight plays a critical role for pharmaceutical and high-value perishable items requiring quick delivery. Sea freight is commonly used for fish exports from port regions like Murmansk and Vladivostok.
Competitive Landscape in Russia Cold Chain Market
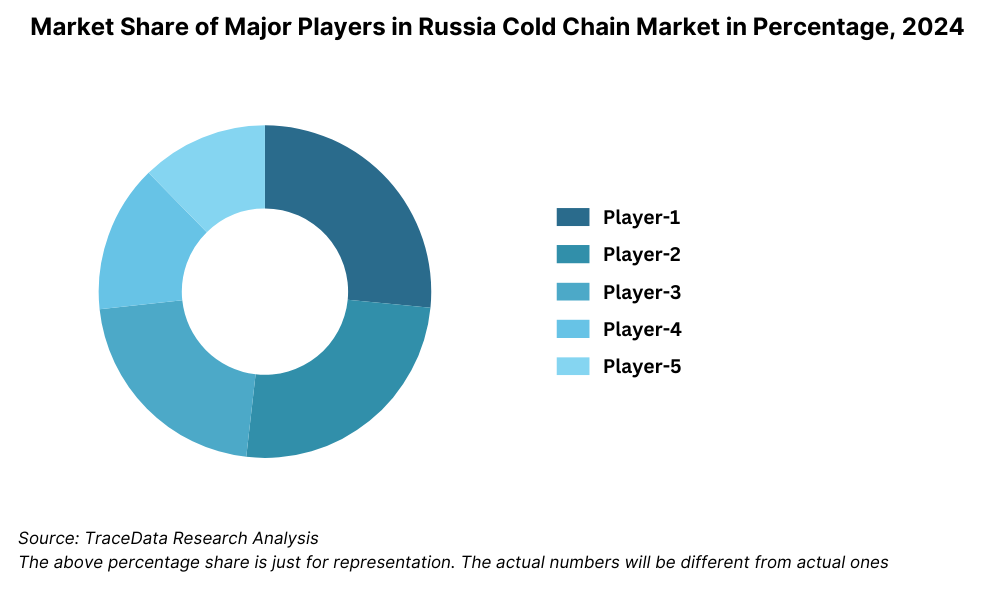
The Russia cold chain market is moderately fragmented, with a mix of domestic logistics providers, large retail-backed supply chain firms, and multinational cold storage operators. The presence of organized players is growing, especially in urban and export-focused regions, while smaller regional operators dominate in less accessible areas. Key players such as X5 Logistics, RZD Logistics, Lineage Logistics, Global Cold Chain, and Magnit Logistics are shaping the industry through investments in technology, expansion of cold storage capacity, and integration with national distribution networks.
Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
X5 Logistics | 2018 | Moscow, Russia |
RZD Logistics | 2010 | Moscow, Russia |
Lineage Logistics Russia | 2021 (Russia Entry) | Novi, Michigan, USA |
Global Cold Chain | 2012 | Moscow, Russia |
Magnit Logistics | 2006 | Krasnodar, Russia |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
X5 Logistics: The logistics arm of retail giant X5 Group, X5 Logistics manages over 40 cold storage facilities across Russia. In 2023, the company invested RUB 12 billion to modernize its temperature-controlled transport fleet, aiming to increase delivery speed and reduce spoilage for its supermarket chains Pyaterochka and Perekrestok.
RZD Logistics: A subsidiary of Russian Railways, RZD Logistics expanded its refrigerated railcar fleet by 18% in 2023, enabling long-haul cold chain solutions from western Russia to the Far East. The company also launched a pharma-dedicated cold train service between Moscow and Vladivostok.
Lineage Logistics Russia: Entering the Russian market through acquisition in 2021, Lineage has rapidly expanded its footprint by operating high-tech cold storage facilities near Moscow and St. Petersburg. In 2023, it introduced AI-based inventory management to enhance temperature compliance and reduce energy consumption.
Global Cold Chain: A homegrown player known for its strength in the food and meat segments, Global Cold Chain operates across 12 Russian cities. In 2023, it recorded a 22% YoY increase in revenue, driven by demand for fresh food storage and contract logistics for exporters.
Magnit Logistics: Supporting Russia’s second-largest grocery chain, Magnit Logistics operates an integrated cold chain spanning over 3,500 trucks and multiple regional warehouses. In 2023, the company launched a real-time temperature tracking platform, which improved compliance and helped reduce returns due to spoilage by 9%.
What Lies Ahead for Russia Cold Chain Market?
The Russia cold chain market is projected to witness steady growth by 2029, with a healthy CAGR driven by rising domestic consumption of perishables, growing pharmaceutical needs, and continued modernization of logistics infrastructure. Government-backed investments and global partnerships are expected to further strengthen cold chain capacity across the country.
Expansion of Pharmaceutical Cold Chain: With the increasing demand for biologics, vaccines, and other temperature-sensitive medications, the pharmaceutical cold chain segment is expected to expand significantly. This growth will be propelled by stricter regulations, EAEU harmonization policies, and investments in GDP-compliant infrastructure across Tier 1 and Tier 2 cities.
Technological Advancements in Cold Storage and Transport: The integration of IoT-based temperature sensors, AI-driven route optimization, and real-time monitoring systems will transform cold chain operations. These technologies will reduce spoilage rates, enhance compliance, and lower operational costs, making cold logistics more efficient and reliable.
Development of Regional Cold Chain Hubs: Strategic investments are anticipated in regional cold storage hubs, especially in Siberia, the Volga region, and the Russian Far East. These hubs will improve supply chain resilience for food exports and imports, ensuring year-round product quality in even the harshest climates.
Rising Demand from E-commerce and Quick Commerce: The boom in online grocery shopping and on-demand delivery platforms is expected to generate substantial demand for short-haul refrigerated transport and micro-fulfillment cold storage facilities, especially in urban centers.
%2C%202024-2030.png)
Russia Cold Chain Market Segmentation
- By Market Structure:
o Organized Sector
o Unorganized Sector - By End-User Industry:
o Pharmaceuticals
o Meat & Seafood
o Fruits & Vegetables
o Dairy Products
o Ready-to-Eat/Processed Foods
o Others (Confectionery, Bakery, etc.) - By Mode of Transport:
o Road Transport
o Rail Transport
o Air Transport
o Sea Transport - By Type of Storage:
o Cold Storage (Chilled)
o Cold Storage (Frozen)
o Controlled Atmosphere Storage
o Refrigerated Transport Units - By Temperature Range:
o Chilled (0°C to 10°C)
o Frozen (-18°C to -25°C)
o Deep Frozen (below -25°C) - By Region:
o Central Russia (Moscow, Tula)
o Northwestern Russia (St. Petersburg, Leningrad)
o Siberia (Novosibirsk, Irkutsk)
o Ural Region (Yekaterinburg, Chelyabinsk)
o Southern Russia (Rostov, Krasnodar)
o Far East Russia (Vladivostok, Khabarovsk)
Players Mentioned in the Report:
- X5 Logistics
- RZD Logistics
- Lineage Logistics Russia
- Global Cold Chain
- Magnit Logistics
- DPD Russia (Cold Chain Division)
- ECO Resource Logistics
- Ruskhim Logistics
- Aurora Cold Chain
- Fesco Cold Chain Solutions
Key Target Audience:
- Cold Chain Logistics Companies
- Cold Storage Infrastructure Developers
- Perishable Goods Exporters
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturers and Distributors
- Quick Commerce and E-Grocery Startups
- Food Processing Companies
- Regulatory Bodies (e.g., Ministry of Industry and Trade of the Russian Federation)
- Investment Promotion Agencies
- Market Research and Consultancy Firms
Time Period:
- Historical Period: 2018–2023
- Base Year: 2024
- Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
1. Executive Summary
2. Research Methodology
3. Ecosystem of Key Stakeholders in Russia Cold Chain Market
4. Value Chain Analysis
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and Challenges They Face
4.2. Revenue Streams for Russia Cold Chain Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Russia Cold Chain Market
4.4. Cold Chain Decision-Making Process for Food and Pharma
4.5. Infrastructure and Asset Investment Decision Process
5. Market Structure
5.1. Cold Storage Capacity by Region in Russia, 2018-2024
5.2. Share of Cold Storage vs. Cold Transport, 2018-2024
5.3. Perishable Food Consumption Trends in Russia, 2024
5.4. Number of Cold Chain Warehouses by Region
6. Market Attractiveness for Russia Cold Chain Market
7. Supply-Demand Gap Analysis
8. Market Size for Russia Cold Chain Market Basis
8.1. Revenues, 2018-2024
8.2. Volume Throughput, 2018-2024
9. Market Breakdown for Russia Cold Chain Market Basis
9.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized), 2023-2024P
9.2. By End-User Industry (Pharma, Dairy, Meat & Seafood, etc.), 2023-2024P
9.3. By Storage Type (Chilled, Frozen, Controlled Atmosphere), 2023-2024P
9.4. By Transport Mode (Road, Rail, Air, Sea), 2023-2024P
9.5. By Temperature Range, 2023-2024P
9.6. By Region, 2023-2024P
10. Demand Side Analysis for Russia Cold Chain Market
10.1. End-User Landscape and Key Demand Centers
10.2. Customer Journey and Decision Criteria
10.3. Need and Pain Point Analysis
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11. Industry Analysis
11.1. Trends and Developments in Russia Cold Chain Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Russia Cold Chain Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Russia Cold Chain Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges in Russia Cold Chain Market
11.5. Government Policies and Regulatory Framework
12. Snapshot on Cold Chain in E-commerce and Online Grocery Market
12.1. Size and Growth of E-Grocery Cold Chain Segment, 2018-2029
12.2. Business Models and Partnerships
12.3. Cross Comparison of Cold Chain Use Among E-Grocery Platforms
13. Cold Chain Infrastructure Financing Landscape
13.1. Public and Private Investment Trends, 2018-2029
13.2. Cold Chain Asset Leasing and Financing Models
13.3. Government Subsidies and Grants
13.4. Average Cost of Cold Chain Setup in Russia
13.5. Cold Chain PPP Projects Overview
14. Opportunity Matrix for Russia Cold Chain Market-Presented with Radar Chart
15. PEAK Matrix Analysis for Russia Cold Chain Market
16. Competitor Analysis for Russia Cold Chain Market
16.1. Benchmarking of Key Players-Company Overview, Strength, Weakness, Infrastructure, Fleet, Clients, and Tech Adoption
16.2. SWOT and Strategic Positioning
16.3. Operating Model Analysis
16.4. Gartner Magic Quadrant Framework
16.5. Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
17. Future Market Size for Russia Cold Chain Market Basis
17.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
17.2. Volume Throughput, 2025-2029
18. Market Breakdown for Russia Cold Chain Market Basis
18.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized), 2025-2029
18.2. By End-User Industry, 2025-2029
18.3. By Storage Type, 2025-2029
18.4. By Transport Mode, 2025-2029
18.5. By Temperature Range, 2025-2029
18.6. By Region, 2025-2029
18.7. Recommendation
18.8. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all demand-side and supply-side entities relevant to the Russia Cold Chain Market. Based on this ecosystem, we shortlist 5–6 leading companies in the country using criteria such as revenue size, cold storage capacity, fleet size, and vertical integration across cold chain services.
Sourcing is conducted through a review of industry publications, government logistics reports, trade association data, and proprietary databases to perform desk research and collate sector-wide insights.
Step 2: Desk Research
We then conduct an exhaustive desk research process leveraging multiple proprietary and public databases. This step allows for a comprehensive analysis of the market by aggregating data related to revenue estimates, player concentration, pricing trends, end-user demand, and regulatory impacts.
Additionally, company-level data such as strategic expansions, partnerships, financials, and service offerings are assessed through press releases, investor reports, public filings, and industry news. This creates a structured base for further validation.
Step 3: Primary Research
We conduct in-depth interviews with key stakeholders in the Russia Cold Chain Market including cold chain logistics providers, cold storage facility managers, pharma distributors, perishable food producers, and e-grocery operators.
These interactions are designed to validate market assumptions, refine volume and revenue estimates, and gather firsthand insight into operational challenges, value chain dynamics, pricing models, and investment outlooks.
As part of this validation, we perform disguised interviews, where the research team approaches companies as potential customers or partners. This methodology helps in validating the consistency of reported information and enriches our understanding of internal processes, customer engagement models, and service differentiation.
Step 4: Sanity Check
Top-down and bottom-up forecasting models are applied to test the reliability of data collected. These include market sizing models based on warehouse capacity, throughput volumes, average pricing, and utilization rates.
The resulting figures undergo triangulation and scenario-based stress testing to ensure data reliability, consistency across sources, and alignment with historical trends and forward-looking assumptions.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Russia Cold Chain Market?
The Russia Cold Chain Market holds strong potential, reaching a valuation of RUB 280 Billion in 2023. This growth is driven by increasing demand for temperature-sensitive goods, rising pharmaceutical and biotech logistics needs, and expanding cold storage infrastructure across key regions. Government-backed investment programs and rapid urbanization are further accelerating cold chain development.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Russia Cold Chain Market?
Key players in the Russia Cold Chain Market include X5 Logistics, RZD Logistics, Lineage Logistics Russia, Global Cold Chain, and Magnit Logistics. These companies are recognized for their extensive transport fleets, advanced storage facilities, and robust integration with retail and pharma distribution networks. Emerging players such as Aurora Cold Chain and Ruskhim Logistics are also contributing to market diversification.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Russia Cold Chain Market?
Major growth drivers include the expanding pharmaceutical sector, increased demand for fresh and frozen foods, government subsidies for cold storage infrastructure, and the rapid growth of e-commerce platforms requiring last-mile refrigerated logistics. Technological innovation in monitoring and automation is also playing a key role in optimizing efficiency and compliance.
4. What are the Challenges in the Russia Cold Chain Market?
The market faces several challenges, including high energy and operating costs, underdeveloped infrastructure in remote regions, and a shortage of skilled labor and advanced technology adoption. Regulatory compliance, especially in food and pharma logistics, also poses significant challenges for unorganized players operating without modern systems.