Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Segments (Freight Forwarding, Warehousing, Courier Express and Parcel), By Mode of Transport (Road, Rail, Air, Sea), By End-User Industries (Retail, FMCG, Automotive, Manufacturing), and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0309
- Region: Asia
- Published on: September 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market Outlook to 2029 - By Market Segments (Freight Forwarding, Warehousing, Courier Express and Parcel), By Mode of Transport (Road, Rail, Air, Sea), By End-User Industries (Retail, FMCG, Automotive, Manufacturing), and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the logistics and warehousing market in Russia. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer profiling, issues and challenges, and comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross-border trade dynamics, opportunities and constraints, and company profiling of major players in the logistics and warehousing sector. The report concludes with future market projections based on industry growth drivers, segment outlooks, regional performance, cause-and-effect relationships, and case studies highlighting major trends and operational success factors.
Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market Overview and Size
The Russian logistics and warehousing market was valued at RUB 6.7 trillion in 2023, fueled by increasing domestic e-commerce, cross-border trade with CIS and Asian markets, and infrastructure development under national projects. The market is led by major players such as Delovye Linii, PEC, DPD Russia, Russian Post, and Kuehne + Nagel, which are recognized for their wide service portfolios, integrated logistics solutions, and expansive warehousing and transportation networks.
In 2023, the Russian government accelerated investments in its “International Transport Corridors” program to strengthen logistics linkages with China and Central Asia. Additionally, the surge in e-commerce has significantly boosted demand for last-mile delivery and express parcel services, especially in urban hubs like Moscow, St. Petersburg, and Kazan.
%2C%202019-2024.png)
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market:
Geopolitical Realignment & Eurasian Focus: The shift in Russia’s trade policy towards Asia and Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) countries has driven up cross-border logistics activity. China-Russia rail freight saw a 12% YoY increase in 2023, positioning Russia as a critical overland corridor for Sino-European trade.
E-Commerce Expansion: Online retail continues to surge, with a 27% growth in 2023, prompting logistics players to expand express delivery services and establish micro-fulfillment centers. Warehousing demand in urban zones has outpaced supply, especially for Grade A facilities.
Government Infrastructure Initiatives: Strategic investment in transport corridors (e.g., Moscow-Kazan high-speed rail, Northern Sea Route) and customs digitization has improved logistics efficiency. In 2023, over RUB 150 billion was allocated to freight corridor upgrades.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market
Geopolitical Sanctions and Trade Barriers: Economic sanctions from Western countries have disrupted several supply chains and limited access to international logistics technologies and services. In 2023, approximately 28% of logistics providers reported increased delays and rerouting costs due to restrictions on ports, airspace, and financial systems. These barriers have added to the cost burden and operational complexities across the sector.
Infrastructure Bottlenecks in Remote Regions: While major cities have modern infrastructure, logistics in remote or eastern parts of Russia suffers from poor connectivity and underdeveloped facilities. Industry data from 2023 shows that over 40% of logistics operators cited infrastructure gaps—particularly in Siberia and the Far East—as a key obstacle to seamless national coverage.
Volatility in Fuel Prices and Operating Costs: Due to economic uncertainty and fluctuating energy prices, logistics operators faced a 15–20% rise in operating costs in 2023. These increases particularly impacted smaller freight forwarders and regional warehousing providers, compressing margins and limiting investment in technology upgrades or fleet expansion.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market
Customs Digitization and E-Declaration System: The Russian Federal Customs Service has implemented a digital customs clearance system to improve efficiency in cross-border trade. As of 2023, more than 80% of customs declarations were processed electronically, reducing average clearance times by nearly 30%. This initiative has enhanced transparency and operational speed for freight forwarders.
National Projects for Infrastructure Development: Under the federal “Comprehensive Plan for Modernization and Expansion of Trunk Infrastructure,” the government invested over RUB 600 billion from 2021 to 2024 to modernize highways, rail hubs, and logistics corridors. This includes the Northern Sea Route and “Primorye-1” and “Primorye-2” corridors linking to China, which are improving transit capabilities.
Green Logistics and Emission Standards: Russia has begun introducing environmental regulations to align with global standards. In 2023, the government launched pilot programs to promote eco-friendly fleets, offering tax incentives for companies transitioning to electric delivery vehicles or LNG-powered trucks. Although still in early stages, adoption of green logistics practices is gaining traction among large 3PLs and urban last-mile players.
Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
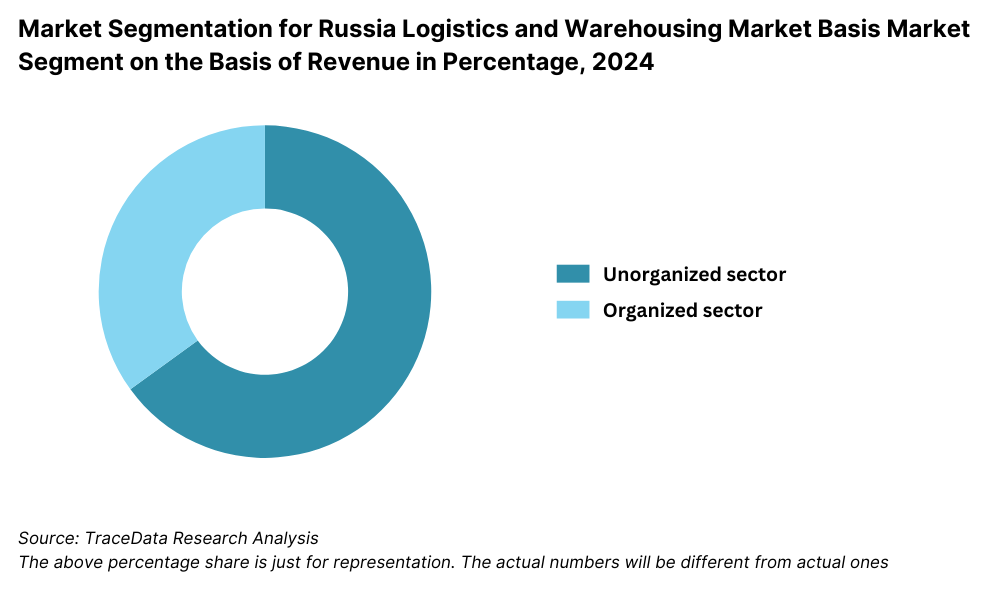
By Market Structure: The market is primarily dominated by unorganized and regional logistics players who cater to localized delivery and warehousing needs, particularly in Tier-2 and Tier-3 regions. These players offer flexibility, cost-competitive pricing, and localized route knowledge. However, organized 3PL and integrated logistics providers such as Delovye Linii, PEC, and DPD Russia are rapidly gaining market share due to investments in automation, real-time tracking, and end-to-end logistics solutions. Organized players are also better equipped to serve large corporate clients with standardized service SLAs and national reach.
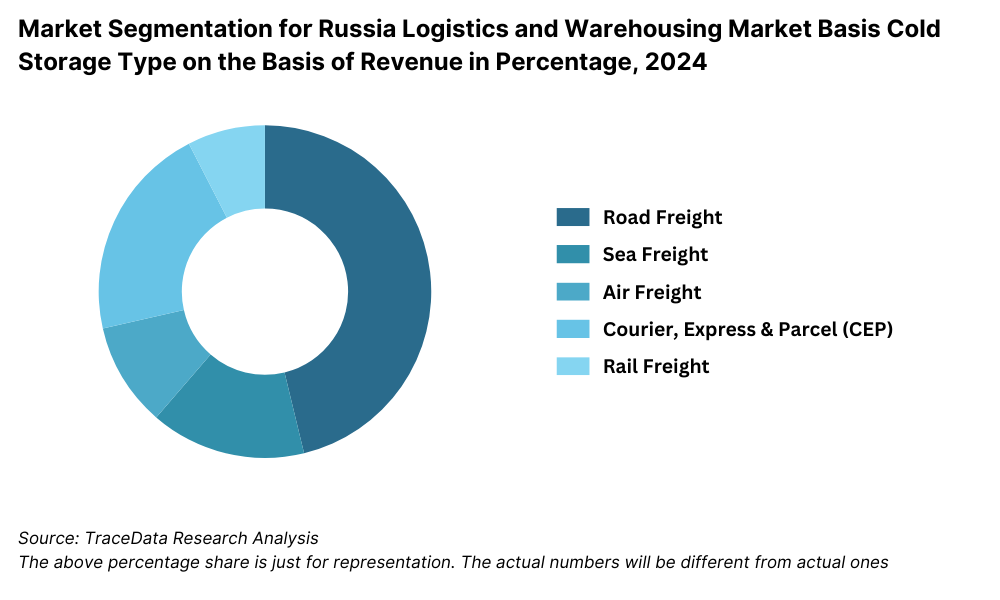
By Mode of Transport: Road freight is the dominant mode due to Russia’s vast territory and underutilized inland waterway and air logistics infrastructure. Road transport accounted for the largest revenue share in 2023, driven by intercity haulage, last-mile e-commerce delivery, and retail distribution. Rail freight follows, particularly on key corridors such as Moscow–Vladivostok and China–Russia transit, offering cost-effective long-haul solutions. Air and sea freight cater to time-sensitive and international shipments, with growing investments in the Northern Sea Route boosting the future outlook of maritime transport.
By End-User Industry: Retail and e-commerce dominate due to the rising volume of parcel deliveries and warehousing requirements, particularly in urban centers. FMCG and food logistics represent a strong share owing to demand for cold chain and last-mile delivery solutions. Automotive and manufacturing sectors are also key contributors, especially in western Russia, where several industrial clusters require inbound/outbound logistics support.
Competitive Landscape in Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market
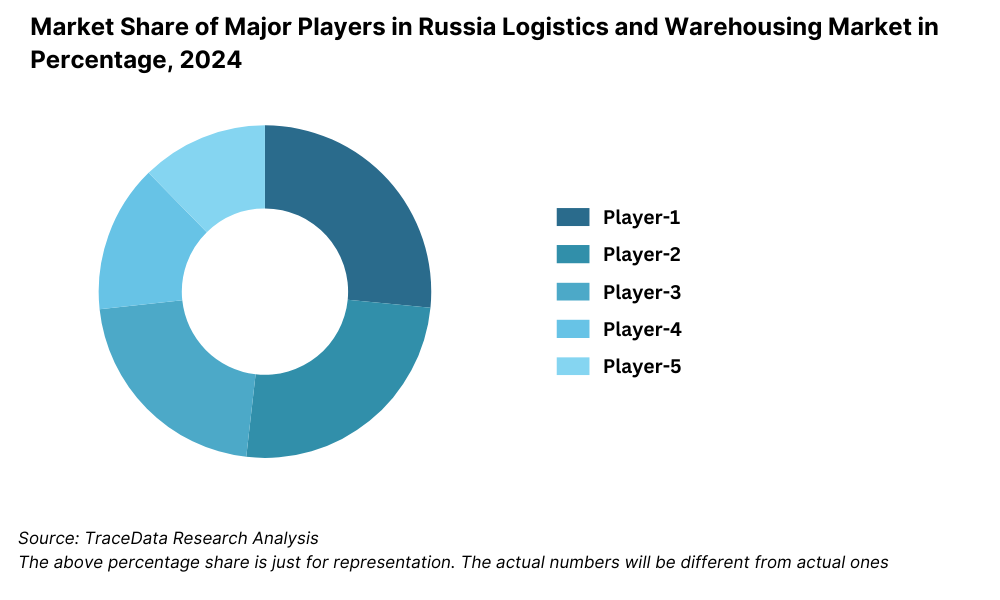
The Russian logistics and warehousing market is moderately concentrated, with a mix of domestic giants and international logistics providers. While long-standing players such as Delovye Linii and Russian Post maintain strong networks across the country, the rise of digital-first logistics firms and 3PL providers like PEC, DPD Russia, and SDEK has diversified the competitive dynamics. Innovations in express delivery, warehousing automation, and cross-border logistics services are shaping the future of competition in the market.
Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
Delovye Linii | 2001 | St. Petersburg, Russia |
PEC | 2001 | Moscow, Russia |
DPD Russia | 1991 (DPD Group) | Moscow, Russia |
Russian Post | 2002 (Reformed) | Moscow, Russia |
SDEK | 2000 | Novosibirsk, Russia |
Kuehne + Nagel | 1890 | Schindellegi, Switzerland |
C.H. Robinson | 1905 | Eden Prairie, USA |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
Delovye Linii: One of the largest domestic freight and logistics providers, Delovye Linii recorded over 4 million deliveries in 2023 across 1,000+ locations in Russia. The company has invested in smart logistics terminals and real-time cargo tracking to strengthen its position in the B2B and e-commerce segments.
PEC: Known for its strong regional coverage and affordability, PEC expanded its warehousing footprint in 2023 by launching 5 new distribution hubs across Central Russia. The firm has focused heavily on same-day and next-day delivery services in urban clusters.
DPD Russia: Backed by the DPD Group, DPD Russia emphasized cross-border delivery capabilities with Belarus and Kazakhstan. In 2023, the company reported a 22% rise in B2C deliveries, especially in the parcel segment tied to international e-commerce.
Russian Post: As a state-owned enterprise, Russian Post remains dominant in last-mile delivery, particularly in rural areas. In 2023, it processed over 1.6 billion shipments, supported by upgrades to automated sorting centers and partnerships with Chinese marketplaces.
SDEK: With a strong presence in the express courier segment, SDEK witnessed a 19% increase in international shipments in 2023. The company has also developed a network of parcel lockers and pickup points to meet growing demand from online shoppers.
Kuehne + Nagel: Although a foreign player, Kuehne + Nagel continues to serve industrial clients with specialized contract logistics and project cargo services, focusing on energy, automotive, and chemical sectors within Russia.
C.H. Robinson: Operating mainly through strategic alliances, C.H. Robinson provides supply chain optimization services, especially for high-value goods. In 2023, the company reported growth in its customs brokerage and multimodal freight solutions in Russia.
What Lies Ahead for Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Russia logistics and warehousing market is projected to witness steady growth through 2029, driven by regional trade expansion, digital transformation, and national infrastructure development initiatives. The industry is expected to record a healthy CAGR over the forecast period, supported by both domestic consumption and increasing cross-border trade with Asia and the Eurasian region.
Digitalization of Logistics Operations: The adoption of digital platforms, warehouse automation, and AI-based fleet management systems is expected to increase significantly. By 2029, a large share of logistics operators—especially 3PLs—will implement predictive analytics and IoT-enabled tracking tools to optimize routing, reduce delays, and improve overall service reliability.
Expansion of E-Commerce Fulfillment Networks: As online retail continues its upward trend, demand for last-mile delivery services and urban fulfillment centers will intensify. Logistics providers are expected to invest heavily in micro-warehousing, dark stores, and delivery drones in densely populated cities like Moscow and St. Petersburg.
Rise in Cold Chain and Pharma Logistics: With growing pharmaceutical and food safety regulations, the cold chain logistics segment is projected to expand rapidly. Demand for temperature-controlled warehousing and refrigerated transport will rise, especially in regions serving healthcare, biotechnology, and perishable goods sectors.
Strategic Role in Eurasian Supply Chains: Russia’s geographic position as a bridge between Europe and Asia will solidify further, with continued investments in rail corridors such as the Trans-Siberian and China-Europe Belt and Road railways. This will enhance its role in overland freight forwarding and multimodal logistics across Eurasia.
%2C%202024-2030.png)
Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
- By Market Structure:
o Organized Logistics Providers
o Unorganized / Regional Freight Forwarders
o Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
o In-House Logistics Operations
o Contract Logistics
o Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Providers - By Mode of Transport:
o Road
o Rail
o Air
o Sea
o Multimodal - By Type of Warehousing Services:
o General Warehousing
o Cold Storage / Cold Chain
o Fulfillment Centers (E-commerce)
o Bonded Warehousing
o Automated / Smart Warehousing - By End-User Industry:
o Retail & E-commerce
o FMCG
o Automotive
o Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare
o Industrial Manufacturing
o Oil & Gas
o Agriculture and Food Processing - By Region:
o Central (Moscow, Kaluga)
o Northwestern (St. Petersburg, Leningrad)
o Southern (Rostov, Krasnodar)
o Volga (Samara, Tatarstan)
o Ural (Yekaterinburg, Chelyabinsk)
o Siberian and Far Eastern (Novosibirsk, Vladivostok)
Players Mentioned in the Report:
- Delovye Linii
- PEC
- DPD Russia
- Russian Post
- SDEK
- Kuehne + Nagel
- C.H. Robinson
Key Target Audience:
- Freight Forwarding Companies
- Warehousing and 3PL Providers
- E-commerce and Retail Companies
- Government and Regulatory Bodies (e.g., Federal Customs Service)
- Infrastructure and Logistics Park Developers
- Investment Firms and PE/VC Funds
- Industry Associations and Trade Chambers
Time Period:
- Historical Period: 2018–2023
- Base Year: 2024
- Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
1. Executive Summary
2. Research Methodology
3. Ecosystem of Key Stakeholders in Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market
4. Value Chain Analysis
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and Challenges They Face
4.2. Revenue Streams for Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market
4.4. Buying Decision Making Process (Logistics Services)
4.5. Supply Chain Decision Making Process (Warehousing & 3PL Selection)
5. Market Structure
5.1. Freight Transport Flow by Mode in Russia, 2018-2024
5.2. Domestic vs. Cross-Border Logistics Volume, 2018-2024
5.3. Share of Organized and Unorganized Logistics Providers, 2023-2024
5.4. Number of Warehousing Facilities by Region in Russia, 2023
6. Market Attractiveness for Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market
7. Supply-Demand Gap Analysis in Key Logistics Regions
8. Market Size for Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market Basis
8.1. Revenues, 2018-2024
8.2. Shipment Volume (Tons and Parcels), 2018-2024
9. Market Breakdown for Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market Basis
9.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized), 2023-2024P
9.2. By Mode of Transport (Road, Rail, Air, Sea), 2023-2024P
9.3. By Type of Warehousing Service, 2023-2024P
9.4. By End-User Industry (Retail, FMCG, Pharma, Manufacturing, Others), 2023-2024P
9.5. By Region (Central, Ural, Siberia, etc.), 2023-2024P
10. Demand Side Analysis for Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market
10.1. Customer Landscape and Use Cases
10.2. Customer Journey and Service Expectations
10.3. Needs, Desires, and Pain Points
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11. Industry Analysis
11.1. Trends and Developments in Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market
11.2. Growth Drivers
11.3. SWOT Analysis
11.4. Issues and Challenges
11.5. Regulatory Landscape and Government Initiatives
12. Snapshot on E-Commerce Fulfillment and Last-Mile Delivery Market
12.1. Market Size and Growth Potential, 2018-2029
12.2. Fulfillment Models and Revenue Streams
12.3. Cross-Comparison of Leading E-Commerce Logistics Companies in Russia
13. Russia Logistics Infrastructure Investment Landscape
13.1. Government Budget Allocations and Corridor Projects (2018-2029)
13.2. Key Infrastructure Corridors and SEZs
13.3. Private Sector Participation and PPP Models
13.4. Cold Chain and Green Warehousing Initiatives
14. Opportunity Matrix for Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market-Presented with Radar Chart
15. PEAK Matrix Analysis for Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market
16. Competitor Analysis for Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market
16.1. Benchmark of Key Competitors (Company Overview, Strategies, Revenues, Fleet Size, Warehousing Footprint, Services, Tech Capabilities, Operating Regions)
16.2. Strengths and Weaknesses
16.3. Operating Model Analysis Framework
16.4. Gartner Magic Quadrant Adaptation
16.5. Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Positioning
17. Future Market Size for Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market Basis
17.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
17.2. Shipment Volume, 2025-2029
18. Market Breakdown for Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market Basis
18.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized), 2025-2029
18.2. By Mode of Transport (Road, Rail, Air, Sea), 2025-2029
18.3. By Type of Warehousing (General, Cold Chain, Automated), 2025-2029
18.4. By End-User Industry, 2025-2029
18.5. By Region, 2025-2029
18.6. By E-Commerce Fulfillment vs. Traditional B2B, 2025-2029
18.7. Recommendations
18.8. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand-side and supply-side entities for the Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market. Based on this ecosystem, we shortlist leading 5–6 logistics and warehousing service providers in the country, considering their revenue size, infrastructure scale, client portfolio, and geographic presence.
Sourcing is conducted through industry publications, logistics magazines, government infrastructure updates, trade reports, and proprietary databases to perform desk research and collate industry-level insights.
Step 2: Desk Research
We conduct a comprehensive desk research process using both public and subscription-based databases. This includes the collection of data on market revenues, freight volumes, warehouse capacity, shipment modes, regional logistics hubs, and demand trends.
Detailed company-level research is also undertaken using press releases, company filings, investor presentations, customs data, and market intelligence reports. This helps build a solid foundation of operational benchmarks and competitive positioning.
Step 3: Primary Research
We conduct structured interviews with industry stakeholders such as C-level executives from logistics companies, warehouse operators, e-commerce firms, transport associations, and regulatory officials. These discussions validate hypotheses, confirm market trends, and provide insights into pricing, service quality, fleet utilization, capacity constraints, and customer preferences.
Bottom-up estimates are built by gathering operational volume and revenue data directly from players, while a disguised interview approach (posing as a prospective customer) is also employed to verify service scope, pricing models, and operational scale.
These interviews supplement secondary findings and give deeper insights into the logistics value chain, margins, technology adoption, and bottlenecks.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- A bottom-to-top and top-to-bottom triangulation approach is used to validate the final market size, segment-wise splits, and growth projections. Forecast modeling and historical backtracking are applied to ensure logical consistency across data points and assumptions.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Russia logistics and warehousing market holds substantial potential, reaching a valuation of RUB 6.7 trillion in 2023. Growth is being driven by factors such as expanding regional trade, the rise of e-commerce, and government-led infrastructure modernization projects. Russia’s strategic geographic location also positions it as a key transit hub between Europe and Asia, further enhancing its long-term market potential.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Key players in the market include Delovye Linii, PEC, DPD Russia, Russian Post, SDEK, and global operators like Kuehne + Nagel and C.H. Robinson. These companies dominate through their nationwide networks, technology-enabled services, and strong focus on integrated logistics and warehousing solutions.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Growth is primarily driven by increasing domestic e-commerce, cross-border trade with Asia, and investments in national logistics corridors. The shift toward 3PL outsourcing and adoption of digital logistics platforms are also transforming the sector. Additionally, evolving consumer behavior and demand for faster deliveries are boosting last-mile logistics and urban warehousing.
4. What are the Challenges in the Russia Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Major challenges include geopolitical sanctions, infrastructure gaps in remote regions, and volatile fuel and transport costs. Limited access to advanced logistics technologies and difficulties in modernizing outdated warehousing infrastructure also hinder rapid scalability for many players. Furthermore, regulatory complexity around customs and cross-border trade poses operational constraints for international logistics providers.