South Korea Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029
By Type of Service (Cold Storage, Cold Transportation), By Temperature Range, By End Users (F&B, Pharmaceuticals, Chemicals, Others), and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0190
- Region: Asia
- Published on: May 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “South Korea Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029 - By Type of Service (Cold Storage, Cold Transportation), By Temperature Range, By End Users (F&B, Pharmaceuticals, Chemicals, Others), and By Region.” provides a comprehensive analysis of the cold chain logistics market in South Korea. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer-level profiling, issues and challenges, and comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the Cold Chain Market. The report concludes with future market projections based on revenue by service types, end users, temperature segments, and success case studies highlighting major opportunities and cautions.
South Korea Cold Chain Market Overview and Size
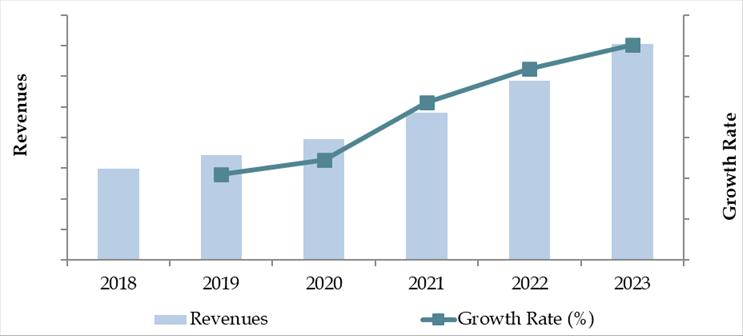
The South Korea cold chain market reached a valuation of KRW 6.2 Trillion in 2023, driven by rising demand for perishable goods, strong pharmaceutical logistics growth, and increasing export-oriented food processing activities. The market is characterized by players such as CJ Logistics, Lotte Global Logistics, Dongbu Express, Hanjin Transportation, and Hyundai Glovis. These companies are recognized for their robust logistics networks, state-of-the-art refrigerated warehouses, and investment in IoT and temperature monitoring technologies.
In 2023, CJ Logistics launched its upgraded smart cold chain platform to support real-time tracking and temperature alerts across its logistics network. Seoul, Incheon, and Busan emerged as key markets due to dense urban populations, port infrastructure, and demand from pharmaceutical and food industries.
Market Size for South Korea Cold Chain Industry on the Basis of Revenues in USD Billion, 2018-2024
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the South Korea Cold Chain Market:
Rise in E-Commerce and Quick Commerce (Q-Commerce): The expansion of online grocery and food delivery services has led to a surge in demand for temperature-controlled last-mile delivery. In 2023, over 55% of e-commerce food deliveries in Korea required some form of cold chain infrastructure, contributing significantly to the overall market growth.
Pharmaceutical and Vaccine Storage Boom: With increasing R&D and exports in biologics, South Korea's pharmaceutical sector is witnessing a heightened need for cold storage and transportation. The country saw a 25% YoY increase in pharmaceutical cold chain investments in 2023, driven by vaccine distribution and clinical trial logistics.
Government Support and Infrastructure Investment: The Ministry of Agriculture and the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety have rolled out subsidies and policy support to enhance rural cold storage capacities and streamline cold chain safety standards. In 2023, the government announced KRW 150 Billion in grants for the cold chain logistics industry to ensure national food security.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for South Korea Cold Chain Market
High Operational and Energy Costs: One of the most significant challenges faced by cold chain operators in South Korea is the high cost of electricity and fuel for refrigeration. In 2023, energy expenses accounted for nearly 30% of total operational costs in cold storage facilities. This limits scalability, especially for small and mid-sized operators, and discourages investment in rural cold chain expansion.
Limited Cold Chain Infrastructure in Rural and Remote Areas: While urban regions like Seoul and Busan are well-equipped, infrastructure gaps persist in remote and agricultural regions. According to a study by Korea Agro-Fisheries & Food Trade Corporation, nearly 40% of perishables in rural areas suffer post-harvest losses due to inadequate temperature-controlled logistics, reducing profitability for small farmers and limiting domestic sourcing.
Shortage of Skilled Workforce and Technological Readiness: The cold chain sector is increasingly reliant on IoT, real-time tracking, and automated warehouse management. However, a shortage of trained technical personnel and lagging adoption among legacy players has created operational bottlenecks. In 2023, over 45% of small-scale cold chain providers reported difficulties in managing end-to-end traceability due to lack of digital readiness.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market
Mandatory HACCP and Cold Chain Certification: The South Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety requires strict adherence to Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) protocols for food cold chain logistics. As of 2023, over 68% of cold storage and transportation companies had secured HACCP certification, improving consumer confidence but raising compliance costs for new entrants.
K-Pharma Cold Chain Guidelines: Introduced in 2022, the K-Pharma Cold Chain Guidelines govern the handling and transportation of temperature-sensitive pharmaceutical products, including biologics and vaccines. These guidelines include protocols for monitoring, calibration, and emergency response. Adoption of these standards became mandatory for all companies involved in pharmaceutical distribution from 2024 onward.
Government Infrastructure Support for Smart Cold Chain: The Korean government has initiated infrastructure grants and tax incentives under its Smart Logistics Innovation Plan 2023–2027, which includes KRW 150 billion allocated for upgrading cold chain infrastructure with IoT-based real-time monitoring systems. These incentives aim to reduce food waste by 20% and expand cold chain coverage to underdeveloped areas by 2027.
South Korea Cold Chain Market Segmentation
By Type of Service:Cold Storage holds a major share in the South Korean cold chain market, especially for food processing and pharmaceutical sectors. These facilities are critical for preserving perishable products such as dairy, meat, seafood, and vaccines. Urban centers like Seoul, Busan, and Incheon have witnessed significant investments in automated, multi-temperature warehouses.
Cold Transportation also forms a vital segment, with increasing demand from e-commerce grocery delivery, export shipments, and pharma logistics. The segment has grown with investments in refrigerated trucks, containers, and last-mile cold delivery solutions driven by rising Q-commerce and food exports.

By Temperature Range:Chilled (0°C to 10°C) storage is dominant, driven by the high consumption of dairy, fresh produce, and meal kits. This segment is heavily utilized by the food service and retail sectors. Frozen (-18°C and below) infrastructure is largely deployed for seafood, meat products, and frozen meals. The seafood industry, especially in Busan and Incheon, relies on advanced frozen storage to ensure export quality. Pharma/Ultra-Cold (-20°C to -80°C) is emerging rapidly, with growth in biologics, vaccines, and clinical trial logistics. The segment saw over 18% YoY growth in 2023 due to increased cold chain requirements from pharma exports.
By End-User Industry:Food and Beverage is the largest consumer of cold chain services in South Korea, accounting for over half the total market. Meal kit providers, processed food manufacturers, and seafood exporters form the core demand base. Pharmaceuticals are the fastest-growing segment due to rising biologics production, vaccine development, and clinical trial logistics. Others, including chemicals and cosmetics, are increasingly adopting cold chain systems to ensure compliance with temperature-sensitive storage and transport standards.

Competitive Landscape in South Korea Cold Chain Market
The South Korean cold chain market is moderately consolidated, with key players dominating through large-scale infrastructure, integrated logistics capabilities, and investments in digital cold chain technologies. However, increasing demand from pharmaceutical exports, online food delivery, and agri-exports has encouraged the entry of specialized cold logistics companies and startups offering tech-enabled solutions.
| Company Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
| CJ Logistics Corporation | 1930 | Seoul, South Korea |
| Hyundai Glovis Co., Ltd. | 2001 | Seoul, South Korea |
| Hanjin Transportation Co., Ltd. | 1945 | Seoul, South Korea |
| LX Pantos (formerly Pantos Logistics) | 1977 | Seoul, South Korea |
| Logen Co., Ltd. | 1996 | Seoul, South Korea |
| Korchina Logistics Holdings | 1994 | Seoul, South Korea |
| Daesin Logistics Co., Ltd. | 1991 | Seoul, South Korea |
| Dongbu Express Co., Ltd. | 1969 | Seoul, South Korea |
| Hansol Logistics Co., Ltd. | 1991 | Seoul, South Korea |
| Sunjin Logistics Co., Ltd. | 1990 | Incheon, South Korea |
| Seino Korea Co., Ltd. | 1993 | Seoul, South Korea |
| DHL Supply Chain Korea | 1969 (Korea: ~1980s) | Bonn, Germany |
| DB Schenker Korea Ltd. | 1872 (Korea: ~1980s) | Essen, Germany |
| Kuehne + Nagel Korea Ltd. | 1890 (Korea: ~1980s) | Schindellegi, Switzerland |
| CEVA Logistics Korea | 2006 (Korea: ~2007) | Marseille, France |
| Nippon Express Korea Co., Ltd. | 1937 (Korea: ~1980s) | Tokyo, Japan |
| FedEx Korea | 1971 (Korea: 1988) | Memphis, USA |
| UPS Korea | 1907 (Korea: 1988) | Atlanta, USA |
| Toll Group Korea | 1888 (Korea: ~2000s) | Melbourne, Australia |
| Yusen Logistics Korea | 1955 (Korea: ~1990s) | Tokyo, Japan |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
CJ Logistics: As one of the largest logistics firms in South Korea, CJ Logistics operates over 1.3 million cubic meters of cold storage space and manages a nationwide refrigerated transport network. In 2023, the company launched a smart cold chain control center for real-time temperature monitoring and route optimization, reducing delivery errors by 18%.
Lotte Global Logistics: A major player in food and retail cold logistics, Lotte expanded its cold storage facilities by 22% YoY in 2023, focusing on multi-temperature warehousing near Seoul and Busan. It also partnered with e-commerce giants to facilitate rapid delivery of fresh and frozen goods across the country.
Dongbu Express: Dongbu has strengthened its position in the pharmaceutical cold chain space by introducing validated GDP-compliant reefer fleets and expanding its Incheon pharma logistics hub. In 2023, the company recorded a 28% increase in pharma transportation volumes.
Hyundai Glovis: Known for its global logistics footprint, Hyundai Glovis has developed containerized cold transport solutions that cater to Korea’s seafood and processed food exports. It also initiated an AI-driven warehouse temperature analytics system, reducing product spoilage by 12%.
Korea Cold Chain System (KCCS): A specialized cold logistics provider, KCCS focuses on regional food producers and SMEs. In 2023, KCCS opened its fourth regional cold hub in Jeolla province and invested in eco-friendly refrigerants for sustainable cold storage.
S.Logistics: A rising startup offering last-mile cold chain services, S.Logistics integrates mobile app-based order management and real-time delivery tracking. The company reported 55% YoY growth in refrigerated e-grocery deliveries in 2023, especially in Busan and Daegu.
What Lies Ahead for South Korea Cold Chain Market?
The South Korea cold chain market is projected to expand steadily through 2029, demonstrating a robust CAGR driven by export growth, digital transformation, and evolving consumer demands across the food and pharmaceutical sectors. The market will benefit from both domestic infrastructure upgrades and rising global demand for temperature-sensitive Korean exports.
Expansion of Biopharma and Vaccine Cold Chain Logistics: As South Korea strengthens its position as a biopharma manufacturing hub, the demand for ultra-cold storage and GDP-compliant transportation will rise. The sector is projected to contribute significantly to cold chain revenue, supported by government-led initiatives and export agreements for biologics and clinical trial materials.
Rise of Smart and Automated Cold Warehouses: With growing labor shortages and efficiency demands, cold chain providers are investing in automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) and AI-driven temperature monitoring. These smart warehouses will enhance inventory accuracy, reduce energy costs, and support predictive maintenance, thereby increasing operational resilience.
Growth of Fresh Food E-Commerce and Last-Mile Cold Delivery: South Korea’s rapidly expanding online grocery and meal kit market will continue to push the need for temperature-controlled last-mile delivery. The share of refrigerated e-commerce deliveries is expected to grow sharply, especially in urban regions, driven by changing lifestyles and consumer preference for fresh, ready-to-eat items.
Focus on Green and Sustainable Cold Chain Solutions: Environmental regulations and rising energy costs will push the market toward sustainable refrigerants, solar-powered cold storage, and EV-based refrigerated fleets. Many logistics providers are expected to adopt carbon tracking and energy-efficient designs as part of ESG mandates and consumer expectations.
South Korea Cold Chain Market Segmentation
- By Type of Service:
o Cold Storage
o Cold Transportation
o Integrated Cold Chain Solutions - By Temperature Range:
o Chilled (0°C to 10°C)
o Frozen (-18°C and below)
o Ultra-Cold/Pharma (-20°C to -80°C) - By End-User Industry:
o Food & Beverage (Meat, Seafood, Dairy, Processed Foods, Fresh Produce)
o Pharmaceuticals & Biologics
o Chemicals & Industrial Goods
o Cosmetics & Personal Care
o E-commerce/Grocery Delivery - By Ownership Model:
o Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Providers
o In-house/Private Fleet Cold Chain
o Government-backed Infrastructure - By Region:
o Seoul Capital Area
o Incheon & Gyeonggi Province
o Busan & South Gyeongsang
o Daegu & North Gyeongsang
o Daejeon & Chungcheong
o Jeolla Province
o Jeju Island
Players Mentioned in the Report:
- CJ Logistics
- Yusen Logistics Korea
- FedEx Korea
- Dongwon Cold Storage
- Borim Logistics
- Korea Superfreeze
- HL Holdings
- Rhenus Logistics Korea
- Han Express Co. Ltd.
- Lotte Global Logistics
- Hyundai Glovis
- Ilyang Logistics
- Samil Cold Storage Co., Ltd.
- Wooyang Cold Storage
- KCTC
- SEBANG
- Pantos Logistics
- JBG Logistics
- KGL Network
- TeamFresh
Key Target Audience:
- Cold Storage & Logistics Companies
- E-commerce Grocery Platforms
- Pharmaceutical Distributors & Biotech Firms
- Food Processing and Export Firms
- Government Agencies (e.g., Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, Ministry of Agriculture)
- Real Estate & Industrial Park Developers
- Technology Providers for IoT/Automation in Cold Chain
- Logistics Investment Firms & Infrastructure Funds
Time Period:
- Historical Period: 2018–2023
- Base Year: 2024
- Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
6.1. Revenues, 2018-2024P
7.1. By Cold Storage and Cold Transport, 2023-2024P
7.2. By End-User Application (Dairy Products, Meat and Seafood, Pharmaceuticals, Fruits and Vegetables and Others), 2023-2024P
7.3. By Ownership (Owned and 3PL Cold Chain Facilities), 2023-2024P
10.1. South Korea Cold Storage Market Size
10.1.1. By Revenue, 2018-2024P
10.1.2. By Number of Pallets, 2018-2024P
10.2. South Korea Cold Storage Market Segmentation
10.2.1. By Temperature Range (Ambient, Chilled and Frozen), 2023-2024P
10.2.2. By End-User Application (Dairy Products, Meat and Seafood, Pharmaceuticals, Fruits and Vegetables and Others), 2023-2024P
10.2.3. By Major Cities, 2023-2024P
10.3. South Korea Cold Storage Market Future Outlook and Projections, 2025-2029
10.3.1. By Temperature Range (Ambient, Chilled and Frozen), 2025-2029
10.3.2. By Major Cities (Manila, Quezon, Cebu and others), 2025-2029
11.1. South Korea Cold Transport Market Size (By Revenue and Number of Reefer Trucks), 2018-2024P
11.2. South Korea Cold Transport Market Segmentation
11.2.1. By Mode of Transportation (Land, Sea and Air), 2023-2024P
11.2.2. By Location (Domestic and International), 2023-2024P
11.3. South Korea Cold Transport Market Future Outlook and Projections, 2025-2029
11.3.1. By Mode of Transport (Land, Sea and Air), 2025-2029
11.3.2. By Location (Domestic and International), 2025-2029
12.1. Trends and Developments in South Korea Cold Chain Market
12.2. Issues and Challenges in South Korea Cold Chain Market
12.3. Decision Making Parameters for End Users in South Korea Cold Chain Market
12.4. SWOT Analysis of South Korea Cold Chain Industry
12.5. Government Regulations and Associations in South Korea Cold Chain Market
12.6. Macroeconomic Factors Impacting South Korea Cold Chain Market
13.1. Parameters to be covered for Each End Users to Determine Business Potential:
13.1.1. Production Clusters
13.1.2. Market Demand, Major Products Stored, Cold Storage Companies in Guwahati catering to End Users
13.1.3. Location Preference for Each End User and their Production Plants, Preferences for Outsourcing and Captive Facility, Services Required, Facility Preferences, Decision Making Parameters
13.1.4. Cross comparison of leading end users/companies based on Headquarters, Manufacturing Plants, Products Stored, Major Products, Total Production, Cold Chain Partner, Facility Outsourced/Captive, Pallets Owned/Hired, Contact Person, Address and others
16.1. Competitive Landscape in South Korea Cold Chain Market
16.2. Competition Scenario in South Korea Cold Chain Market (Competition Stage, Major Players, Competing Parameters)
16.3. Key Metrics (Temperature Range, Pallet Position, Prices Charged, Occupancy Rate, Revenue (2023) and Employee Base) for Major Players in South Korea Cold Chain Market
16.4. Company Profiles of Major Companies in South Korea Cold Chain Market (Year of Establishment, Company Overview, Service Offered, USP, Warehousing Facilities, Warehousing Price, Cold Storage by location, Occupancy Rate, Major Clientele, Industries Catered, Employee Base, Temperature Range, Topline OPEX*, Revenue, Recent Developments, Future Strategies)
16.5. Strength and Weakness
16.6. Operating Model Analysis Framework
16.7. Gartner Magic Quadrant
16.8. Bowmans Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
17.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
18.1. By Cold Storage and Cold Transport, 2025-2029
18.2. By End-User Application (Dairy Products, Meat and Seafood, Pharmaceuticals, Fruits and Vegetables and Others), 2025-2029
18.3. By Ownership (Owned and 3PL Cold Chain Facilities), 2025-2029
18.4. Recommendation
18.5. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand side and supply side entities for South Korea Cold Chain Market. Basis this ecosystem, we will shortlist leading 5-6 service providers in the country based upon their financial information, cold storage and transportation capacity, technology capabilities, and customer base.
Sourcing is made through industry articles, multiple secondary, and proprietary databases to perform desk research around the market to collate industry-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
Subsequently, we engage in an exhaustive desk research process by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This approach enables us to conduct a thorough analysis of the market, aggregating industry-level insights. We delve into aspects like the market size in KRW, number of operational facilities, capacity utilization, regional penetration, temperature range distribution, and other variables. We supplement this with detailed examinations of company-level data, relying on sources like press releases, annual reports, financial statements, and similar documents. This process aims to construct a foundational understanding of both the market and the entities operating within it.
Step 3: Primary Research
We initiate a series of in-depth interviews with C-level executives and other stakeholders representing various South Korea Cold Chain Market companies and end-users. This interview process serves a multi-faceted purpose: to validate market hypotheses, authenticate statistical data, and extract valuable operational and financial insights from these industry representatives. Bottom to top approach is undertaken to evaluate storage and transportation volumes for each player thereby aggregating to the overall market.
As part of our validation strategy, our team executes disguised interviews wherein we approach each company under the guise of potential customers. This approach enables us to validate the operational and financial information shared by company executives, corroborating this data against what is available in secondary databases. These interactions also provide us with a comprehensive understanding of service offerings, pricing structure, process flows, technology integration, and cold chain reliability.
Step 4: Sanity Check
- Bottom to top and top to bottom analysis along with market size modeling exercises is undertaken to assess sanity check process.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the South Korea Cold Chain Market?
The South Korea cold chain market is poised for substantial growth, reaching a valuation of KRW 6.2 Trillion in 2023. This growth is driven by rising demand for temperature-sensitive logistics in the food, pharmaceutical, and chemical sectors. The market's potential is further supported by government investment in infrastructure, expanding biopharma exports, and the increasing role of technology in supply chain visibility and efficiency.
2. Who are the Key Players in the South Korea Cold Chain Market?
The South Korea Cold Chain Market features several key players, including CJ Logistics, Lotte Global Logistics, and Dongbu Express. These companies dominate the market due to their extensive cold storage infrastructure, nationwide transportation networks, and technology-enabled services. Other notable players include Hyundai Glovis, Korea Cold Chain System (KCCS), and S.Logistics.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the South Korea Cold Chain Market?
The primary growth drivers include the surge in e-commerce grocery and meal kit delivery, growing pharmaceutical exports requiring cold chain compliance, and government-led logistics modernization plans. Additionally, rising health consciousness among consumers and increasing demand for food safety and quality are driving the need for more reliable cold storage and transportation systems.
4. What are the Challenges in the South Korea Cold Chain Market?
The South Korea Cold Chain Market faces several challenges, including high operational costs related to energy usage, limited infrastructure in rural regions, and a shortage of skilled professionals for managing cold chain technologies. Regulatory compliance related to HACCP, GDP, and temperature monitoring also poses a challenge for small and medium operators seeking to scale.