South Korea Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Market Outlook to 2029
By Vehicle Types, By Key Manufacturers, By Infrastructure Development, By Policy Support, and By Regional Adoption
- Product Code: TDR0102
- Region: Asia
- Published on: December 2024
- Total Pages: 80-100
Report Summary
The report titled "South Korea Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Market Outlook to 2029 - By Vehicle Types, By Key Manufacturers, By Infrastructure Development, By Policy Support, and By Regional Adoption" provides a comprehensive analysis of the hydrogen fuel cell vehicle (HFCV) market in South Korea. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue and volume, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer profiling, issues and challenges, and comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the HFCV market. The report concludes with future market projections based on adoption rates, policy influence, infrastructure development, regional adoption trends, and case studies highlighting key success factors and areas for caution.
South Korea Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Market Overview and Size
The South Korea HFCV market reached a valuation of KRW 2.5 trillion in 2023, driven by robust government support, advancements in hydrogen infrastructure, and increasing consumer and industrial demand for sustainable transportation solutions. The market is characterized by leading players such as Hyundai Motor Company, Toyota, Honda, and emerging domestic players exploring hydrogen vehicle innovation. These companies leverage South Korea’s hydrogen policies and infrastructure developments to expand their market footprint.
In 2023, Hyundai launched its next-generation hydrogen-powered NEXO with improved fuel efficiency and driving range, catering to both domestic and international markets. Key cities like Seoul, Busan, and Incheon are pivotal due to strong hydrogen refueling station networks and higher adoption rates among consumers and fleet operators.
Market Size for South Korea Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Industry on the Basis of Volume Sales in Units, 2018–2024
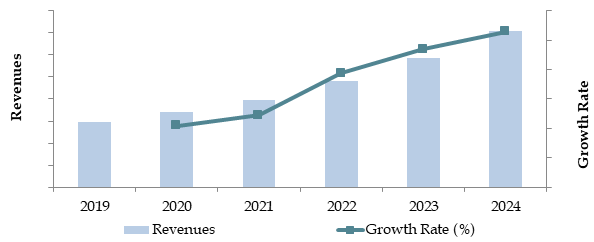
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of South Korea Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Market?
Government Initiatives and Subsidies: South Korea's Hydrogen Economy Roadmap 2040 has set ambitious targets to increase the adoption of hydrogen vehicles to 6.2 million units by 2040. Subsidies and tax incentives make HFCVs financially accessible for consumers and businesses, encouraging market growth.
Expansion of Hydrogen Refueling Infrastructure: The number of hydrogen refueling stations reached 200+ by 2023, covering key urban and intercity routes. The government aims to expand this to 310 stations by 2025, reducing range anxiety and boosting consumer confidence in HFCVs.
Environmental Regulations and Net-Zero Goals: South Korea's commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 has amplified the shift toward zero-emission vehicles. HFCVs are viewed as a critical technology to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, particularly for heavy-duty and long-distance transport.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of South Korea Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Market?
High Initial Costs: The high cost of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (HFCVs) has been a major challenge to market growth. In 2023, the average price of an HFCV in South Korea was approximately KRW 70 million, nearly double the price of conventional vehicles. This price disparity has deterred a significant segment of potential buyers, particularly middle-income consumers. While government subsidies help offset costs, they are not sufficient to drive mass adoption.
Infrastructure Limitations: The lack of sufficient hydrogen refueling stations continues to hinder market expansion. As of 2023, South Korea had approximately 220 hydrogen stations, far below the target of 310 by 2025 set by the government. Consumers are often discouraged by limited access to refueling infrastructure, especially in rural and semi-urban areas, resulting in reduced vehicle demand outside metropolitan regions.
Technological Challenges: HFCVs face challenges related to hydrogen storage, fuel cell efficiency, and durability. Despite ongoing advancements, concerns about the long-term reliability of hydrogen fuel cell systems persist. Industry data from 2023 suggests that over 15% of consumers view these technological limitations as a critical barrier to adoption.
What Regulations and Initiatives Have Governed the Market?
Hydrogen Economy Roadmap: The South Korean government launched the Hydrogen Economy Roadmap in 2019, setting ambitious goals to transition the country towards hydrogen-based energy solutions. By 2023, these initiatives had led to the production of over 15,000 hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, supported by subsidies for manufacturers and consumers. The roadmap also mandates the establishment of hydrogen production hubs and distribution networks.
Subsidy Programs for HFCVs: To boost adoption, the government offers subsidies covering up to 50% of an HFCV's cost. In 2023, the total allocation for hydrogen vehicle subsidies exceeded KRW 1 trillion, benefiting over 5,000 vehicle purchasers. These programs aim to reduce the cost burden on consumers and make HFCVs more competitive with conventional vehicles.
Refueling Infrastructure Development: The South Korean government has committed to building 310 hydrogen refueling stations by 2025 under its Hydrogen Mobility Project. In 2023, key metropolitan areas such as Seoul and Busan accounted for over 60% of the country’s hydrogen refueling infrastructure. The expansion of this network is critical to achieving broader market adoption.
South Korea Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Market Segmentation
By Market Structure: Local Manufacturers dominate the South Korean hydrogen fuel cell vehicle (HFCV) market, driven by Hyundai Motor Company’s leadership in hydrogen vehicle technology and strong government backing. Hyundai’s flagship model, NEXO, has captured the largest market share due to its cutting-edge fuel cell systems, long driving range, and established brand trust. Foreign Brands, such as Toyota and Honda, have a smaller market share but are gradually increasing their presence due to their focus on reliability and the expanding infrastructure for HFCVs in South Korea.
By Vehicle Type: Passenger Vehicles hold the majority share of the market due to rising consumer interest in eco-friendly transportation and government subsidies. In 2023, passenger vehicles, such as Hyundai’s NEXO, accounted for over 75% of HFCV sales. Commercial Vehicles, including hydrogen-powered buses and trucks, are a growing segment driven by increasing adoption for public transportation and logistics.
By Mileage: 300-500 KM Range HFCVs dominate the market due to their balance of efficiency and practicality, addressing the daily travel needs of South Korean consumers. Models offering 500+ KM range are gaining traction, particularly in urban areas, as improved hydrogen storage technology makes these vehicles more appealing to long-distance commuters.
Competitive Landscape in South Korea Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Market
The South Korea hydrogen fuel cell vehicle (HFCV) market is relatively concentrated, with a few leading companies driving innovation and adoption. Key players such as Hyundai Motor Company, Toyota, and Honda dominate the market, supported by government policies and incentives. The competitive landscape is also expanding with new entrants and collaborations aimed at advancing hydrogen technology and infrastructure.
Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
|---|---|---|
Hyundai Motor Company | 1967 | Seoul, South Korea |
Kia Corporation | 1944 | Seoul, South Korea |
Hyundai Mobis | 1977 | Seoul, South Korea |
Doosan Fuel Cell Co., Ltd. | 2014 | Seoul, South Korea |
SK E&S | 1999 | Seoul, South Korea |
POSCO Energy | 1969 | Seoul, South Korea |
Hanwha Energy | 2007 | Seoul, South Korea |
Hyosung Heavy Industries | 1962 | Seoul, South Korea |
Iljin Hysolus | 1999 | Seoul, South Korea |
Korea Gas Corporation (KOGAS) | 1983 | Daegu, South Korea |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
Hyundai Motor Company: As a market leader, Hyundai accounted for over 80% of HFCV sales in South Korea in 2023. Its flagship model, the NEXO, saw a 20% increase in sales compared to 2022, driven by extended government subsidies and advancements in hydrogen technology. Hyundai continues to invest in hydrogen infrastructure through partnerships with energy companies such as SK E&S.
Toyota: Although a smaller player in South Korea, Toyota reported a 15% growth in sales of its Mirai model in 2023. Toyota's emphasis on durability, reliability, and high resale value appeals to consumers seeking long-term sustainability. Recent collaborations with local firms have aimed to enhance their refueling station network and visibility.
Honda: Honda saw a 10% increase in HFCV sales in South Korea in 2023, with its focus on improving the affordability and efficiency of its models. The company has also invested in hydrogen research centers to localize production and meet South Korean regulations.
SK E&S: A major player in hydrogen infrastructure, SK E&S established 10 new hydrogen refueling stations in 2023, contributing to South Korea’s goal of 310 stations by 2025. Their strategic alliances with automotive manufacturers have strengthened their position as a key enabler of the hydrogen economy.
Air Liquide: As an international leader in gas technologies, Air Liquide has actively expanded its hydrogen production and distribution in South Korea. In 2023, it completed the construction of a new hydrogen liquefaction facility near Ulsan, increasing the availability of green hydrogen for vehicles.
What Lies Ahead for South Korea Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Market?
The South Korea hydrogen fuel cell vehicle (HFCV) market is projected to grow steadily by 2029, exhibiting a respectable CAGR during the forecast period. This growth is expected to be fueled by government initiatives, infrastructure expansion, and increasing consumer acceptance of sustainable transportation solutions.
Shift Towards Commercial Hydrogen Vehicles: As the South Korean government promotes hydrogen mobility for logistics and public transportation, the adoption of hydrogen-powered buses and trucks is expected to rise. These vehicles, supported by subsidies and infrastructure expansion, will address urban pollution challenges while meeting the growing demand for eco-friendly commercial transport.
Integration of Advanced Technologies: The adoption of AI and big data analytics in fuel cell optimization and vehicle performance monitoring is anticipated to enhance vehicle efficiency and user experience. These technologies will enable better energy management, predictive maintenance, and more seamless integration with smart infrastructure networks.
Growth in Hydrogen Production Capacity: The market will benefit from increased production of green hydrogen, with South Korea investing in renewable energy-based hydrogen production facilities. This shift will ensure a more sustainable and cost-effective supply chain for HFCVs, reducing dependency on imported fossil fuels.
Focus on Policy-Driven Incentives: Government incentives, such as subsidies for vehicle purchases and tax reductions for hydrogen infrastructure investments, will continue to attract consumers and businesses. These policies are expected to lower the entry barriers and accelerate market adoption across both passenger and commercial segments.
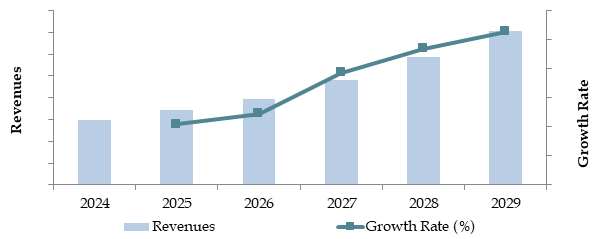
Future Outlook and Projections for South Korea Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Market on the Basis of Revenues in USD Billion, 2024-2029
South Korea Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Market Segmentation
By Market Structure:
- Passenger Vehicles
- Commercial Vehicles
- Light Commercial Vehicles
- Heavy Commercial Vehicles
- OEM-Certified Vehicles
- Aftermarket Hydrogen Conversions
By Manufacturer:
- Hyundai Motor Company
- Toyota
- Honda
- General Motors
- Kia
- BMW
- Mercedes-Benz
By Vehicle Range (KM):
- <300 KM
- 300-500 KM
- 500-700 KM
- 700 KM
By End-Use:
- Private Consumers
- Public Transportation (Buses)
- Logistics and Freight (Trucks)
- Government and Municipal Services
By Infrastructure Availability:
- Metropolitan Areas
- Suburban Areas
- Rural Areas
By Regional Adoption:
- Seoul
- Busan
- Incheon
- Daegu
- Gwangju
- Ulsan
Players Mentioned in the Report:
- Hyundai Motor Company
- Kia Corporation
- Hyundai Mobis
- Doosan Fuel Cell Co., Ltd.
- SK E&S
- POSCO Energy
- Hanwha Energy
- Hyosung Heavy Industries
- Iljin Hysolus
- Korea Gas Corporation (KOGAS)
Key Target Audience:
- Hydrogen Vehicle Manufacturers
- Hydrogen Infrastructure Developers
- Government Regulatory Bodies (e.g., Ministry of Environment, Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy)
- Logistics and Transportation Companies
- Research and Development Institutions
- Automotive Financing Companies
Time Period:
- Historical Period: 2018-2023
- Base Year: 2024
- Forecast Period: 2024-2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Value Chain Process: Role of Entities, Stakeholders and Challenges Faced
4.2. Revenue Streams for South Korea HFCV Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for South Korea HFCV Market
5.1. New Vehicle Sales in South Korea, 2018-2024
5.2. New-to-Hydrogen Vehicle Ratio in South Korea, 2018-2024
5.3. Hydrogen Refueling Infrastructure Spending in South Korea, 2024
5.4. Number of Hydrogen Refueling Stations in South Korea by Location
5.5. Cost Benefit Analysis between ICE, EV and Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle in South Korea
8. Market Size for South Korea Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Market Basis
8.1. Revenues, 2018-2024
8.2. Sales Volume, 2018-2024
9.1. By Average Vehicle Range (300 KM, 500 KM, 700 KM, above 700 KM), 2023-2024P
9.2. By Region (Seoul, Busan, Daegu, Incheon, Others), 2023-2024P
9.3. By Vehicle Type (Buses, Trucks, LCVs, Passenger Cars), 2023-2024P
9.4. By Fuel Type (Hydrogen, Methanol and Ethanol), 2023-2024P
10.1. Customer Landscape and Cohort Analysis
10.2. Customer Journey and Decision-Making
10.3. Need, Desire, and Pain Point Analysis
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11.1. Trends and Developments for South Korea HFCV Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for South Korea HFCV Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for South Korea HFCV Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges for South Korea HFCV Market
11.5. Government Regulations for South Korea HFCV Market
12.1. Market Size and Future Potential for Refueling Stations in Terms of Number of Centers, 2018-2029
12.2. Business Models and Revenue Streams
12.3. Cross-Comparison of Leading Infrastructure Developers for HFCV Basis Operational and Financial Indicators
13.1. Finance Penetration Rates and Average Costs for HFCVs, 2018-2029
13.2. Trends in Financing for Commercial and Private Segments
13.3. Average Financing Tenure for HFCVs in South Korea
13.4. Financing Disbursement Trends, 2018-2024P
16.1. Market Share of Major Players in South Korea Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Market Basis Volume Sales, 2024
16.2. Benchmark of Key Competitors in South Korea Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Market Basis Operational and Financial Parameters
16.3. Operating Model Analysis Framework
16.4. SWOT Analysis of Key Competitors
16.5. Strategic Positioning Using Framework
16.6. Operating Model Analysis Framework
16.7. Gartner Magic Quadrant for Market Positioning
16.8. Bowman's Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
17.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
17.2. Sales Volume, 2025-2029
18.1. By Average Vehicle Range (300 KM, 500 KM, 700 KM, above 700 KM), 2025-2029
18.2. By Region (Seoul, Busan, Daegu, Incheon, Others), 2025-2029
18.3. By Vehicle Type (Buses, Trucks, LCVs, Passenger Cars), 2025-2029
18.4. By Fuel Type (Hydrogen, Methanol and Ethanol), 2025-2029
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Mapping the Ecosystem: Map the ecosystem to identify all demand-side and supply-side entities within the South Korea Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle (HFCV) market. This process includes key manufacturers, infrastructure providers, regulatory bodies, and end-users. Leading players, such as Hyundai Motor Company and infrastructure developers like SK E&S, are shortlisted based on financial performance, production capacity, and volume.
Data Sourcing: Sources include industry reports, secondary research, and proprietary databases to collate comprehensive information about the HFCV market. This stage focuses on understanding production levels, policy impacts, and demand trends.
Step 2: Desk Research
Conduct thorough desk research using diverse secondary sources, including annual reports, press releases, financial statements, and market studies.
Collect market-level data such as sales revenues, market share, pricing trends, and infrastructure investments.
Analyze company-level performance to understand operational dynamics, competitive positioning, and technological advancements.
Step 3: Primary Research
Interviews with Key Stakeholders: Engage in interviews with executives, government officials, infrastructure providers, and end-users. These interviews validate market hypotheses, authenticate statistical data, and uncover operational insights.
Disguised Validation: Employ disguised interviews with companies, posing as potential customers to cross-verify operational and financial details provided during interviews against secondary sources.
Collect data on hydrogen production costs, refueling infrastructure development, and customer adoption patterns through these interactions.
Step 4: Sanity Check
Conduct bottom-to-top and top-to-bottom analyses to verify data accuracy.
Perform market size modeling to ensure consistency across all data points.
- Reassess assumptions and cross-validate findings with industry benchmarks and government reports.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the South Korea Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Market?
The South Korea HFCV market is expected to grow significantly, reaching a valuation of KRW 8 trillion by 2029. This growth is fueled by strong government support, technological advancements, and the expansion of hydrogen infrastructure. Increasing consumer and commercial adoption of HFCVs will further enhance the market's potential.
2. Who are the Key Players in the South Korea Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Market?
Key players include Hyundai Motor Company, Toyota, Honda, SK E&S, and Air Liquide. Hyundai leads the market due to its advanced technology and government-backed initiatives. Other notable players include POSCO Energy and Hanwha Solutions, which are heavily involved in infrastructure and hydrogen production.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the South Korea Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Market?
The primary growth drivers include robust government policies, infrastructure development, and advancements in hydrogen technology. Increasing adoption of eco-friendly vehicles for both personal and commercial use and the shift towards green hydrogen production are also significant contributors.
4. What are the Challenges in the South Korea Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Market?
The market faces several challenges, including high initial vehicle costs, limited refueling infrastructure, and stringent regulatory requirements. Additionally, technological limitations in hydrogen storage and distribution pose significant hurdles to broader market adoption.