Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Structure, By Industry Segments (Fruits & Vegetables, Dairy Products, Meat & Seafood, Pharmaceuticals), By Type of Storage (Refrigerated Warehousing, Cold Transport), By End Users, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0191
- Region: Asia
- Published on: May 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029 - By Market Structure, By Industry Segments (Fruits & Vegetables, Dairy Products, Meat & Seafood, Pharmaceuticals), By Type of Storage (Refrigerated Warehousing, Cold Transport), By End Users, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the cold chain industry in Sri Lanka. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer-level profiling, issues and challenges, and comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the Cold Chain Market. The report concludes with future market projections based on sales revenue, by market, segment, region, cause and effect relationship, and success case studies highlighting the major opportunities and cautions.
Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market Overview and Size
The Sri Lanka cold chain market was valued at LKR 41 Billion in 2023, driven by the rapid expansion of organized retail, rising exports of perishable products, and a growing demand for safe pharmaceutical logistics. The market is dominated by players such as Emerald Logistics, Hayleys Advantis, Dart Global Logistics, and ColdCo Storage, who are recognized for their integrated cold storage and transport solutions, extensive infrastructure, and quality control mechanisms.
In 2023, Hayleys Advantis expanded its temperature-controlled warehousing in the Western Province to meet growing demand from the pharmaceutical and dairy sectors. Colombo and Gampaha remain the most active regions due to concentrated industrial activity, urban population, and logistics connectivity.
Market Size for Sri Lanka Cold Chain Industry on the Basis of Revenues in USD Million, 2018-2024
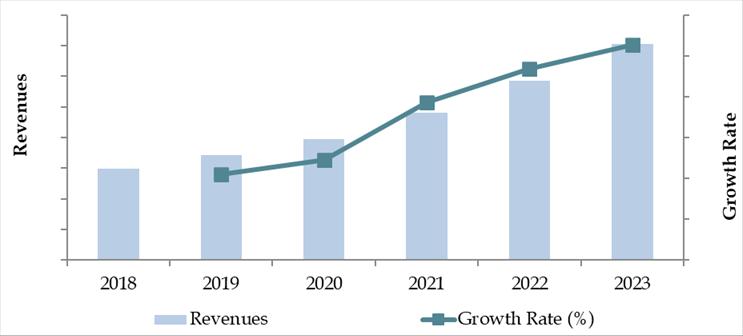
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market:
Increasing Demand for Perishable Goods: The rise in consumption of perishable products such as dairy, seafood, fruits, and vegetables has created strong demand for temperature-controlled logistics. In 2023, perishable goods contributed to nearly 60% of cold chain volume movement in Sri Lanka, as urban consumers increasingly demand fresh and safe food products throughout the year.
Pharmaceutical Sector Expansion: With the growing need for temperature-sensitive pharmaceutical storage, especially post-COVID-19, Sri Lanka has seen a 20% increase in demand for cold storage facilities serving vaccine, insulin, and diagnostic kit distribution. Regulatory compliance and the need for high-quality standards have further accelerated investments in pharma-centric cold chain infrastructure.
Government Initiatives and Export Promotion: The Sri Lankan government has prioritized food security and agricultural export promotion by offering subsidies and incentives for cold chain infrastructure development. The country aims to increase agricultural exports by 30% by 2029, pushing for better supply chain mechanisms to minimize post-harvest losses.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market
Infrastructure Limitations: A key barrier to cold chain development in Sri Lanka is the limited availability of modern cold storage and reefer transport facilities, especially outside key urban centers. As of 2023, nearly 45% of perishable goods in rural regions lack access to cold storage, resulting in significant post-harvest losses and supply chain inefficiencies.
High Operating Costs: Electricity and fuel prices in Sri Lanka have remained volatile, increasing the cost of maintaining temperature-controlled environments. On average, energy expenses contribute to over 30% of total cold chain operating costs, making it challenging for smaller operators to scale efficiently and maintain competitive pricing.
Fragmented Market and Low Standardization: The cold chain sector is highly fragmented, with many small unorganized players lacking standardized processes and technology adoption. According to industry estimates, nearly 60% of storage facilities do not comply with WHO-GDP or HACCP standards, hindering service reliability for sensitive sectors like pharmaceuticals and exports.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
Export-Oriented Cold Chain Support by the Government: The Sri Lankan Ministry of Agriculture and Export Development Board (EDB) has prioritized cold chain development for high-value export crops like mangoes, bananas, and seafood. Several incentive schemes, including duty waivers for cold chain equipment imports, have been rolled out under the National Export Strategy.
Pharmaceutical Compliance Standards: The National Medicines Regulatory Authority (NMRA) mandates strict adherence to Good Distribution Practices (GDP) for cold chain logistics involved in transporting vaccines, insulin, and biologicals. In 2023, 80% of licensed pharma distributors complied with temperature logging and validation procedures, a significant increase from 65% in 2021.
Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) for Infrastructure Development: The government has encouraged collaboration with private investors to develop cold storage hubs in port zones such as Colombo and Hambantota. These PPP initiatives aim to build integrated multi-temperature logistics zones to support both domestic demand and export readiness.
Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market Segmentation
By Market Structure: Organized players dominate the market due to their adherence to international cold chain standards, investment in modern infrastructure, and ability to offer integrated logistics solutions. These companies typically provide end-to-end services including real-time tracking, temperature monitoring, and compliance with pharmaceutical and food safety guidelines. Unorganized players continue to serve a significant portion of the domestic market, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas, by offering lower-cost services. However, they face challenges related to temperature control reliability, lack of automation, and limited storage capacity.
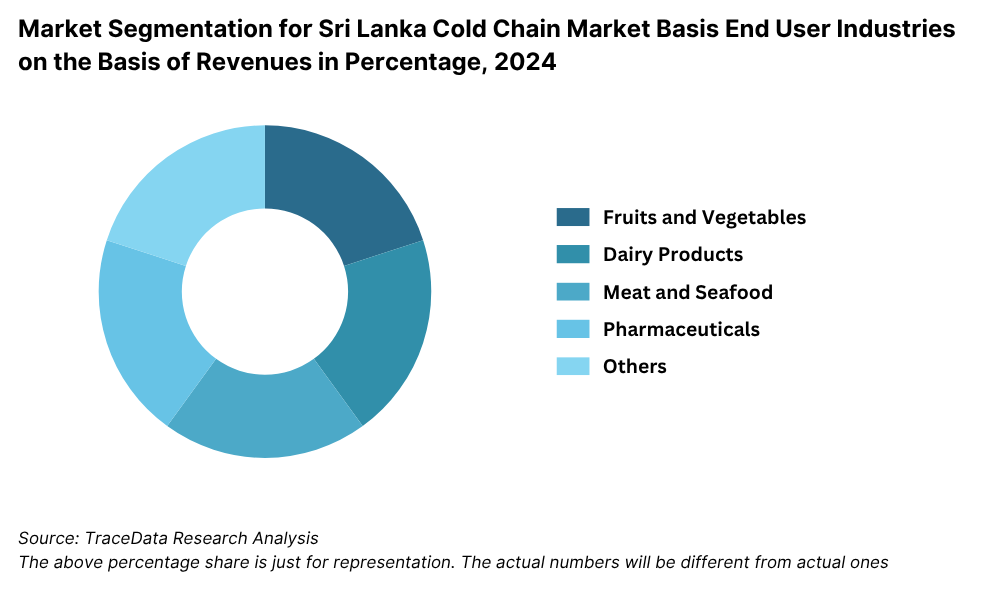
By Industry Segment: Pharmaceuticals lead the cold chain demand in Sri Lanka due to stringent temperature control requirements for vaccines, insulin, and specialty drugs. Meat and seafood follow, with a large portion being processed for export and requiring frozen storage. Dairy products contribute significantly, particularly in urban areas with growing demand for milk, cheese, and yogurt. Fruits and vegetables also play a major role as post-harvest losses remain high without proper cold storage, prompting adoption of reefer transport and pre-cooling systems.
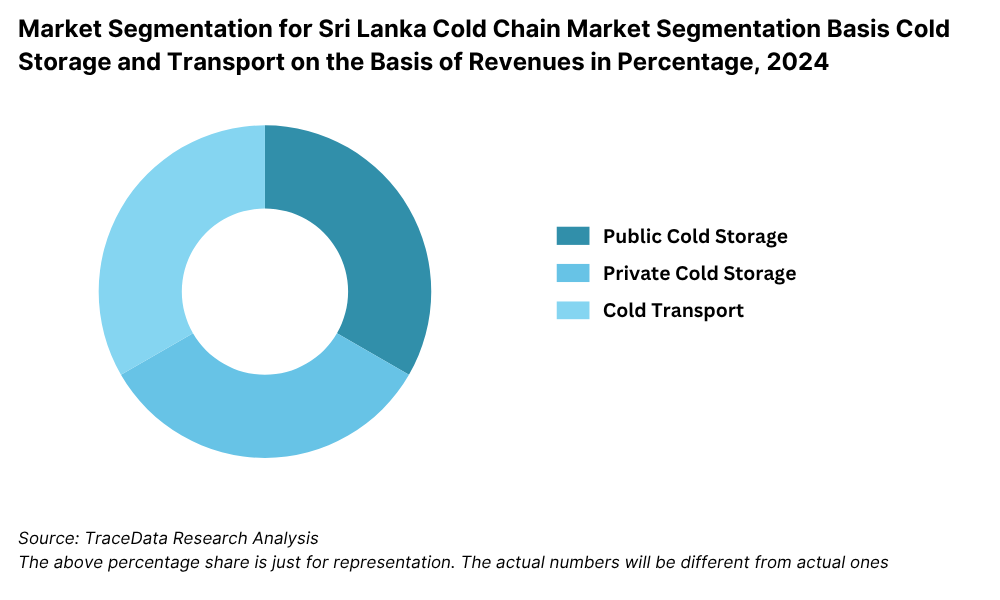
By Type of Storage: Refrigerated warehousing forms the core of the cold chain infrastructure, catering to bulk storage needs of pharmaceuticals, dairy, and seafood industries. These warehouses are typically located near industrial zones and urban centers. Cold transport is essential for first- and last-mile connectivity, especially for perishable agricultural produce and pharmaceutical logistics. In 2023, refrigerated transport saw growing traction due to increased urban consumption and expansion of e-commerce-based grocery and medicine delivery platforms.
Competitive Landscape in Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market
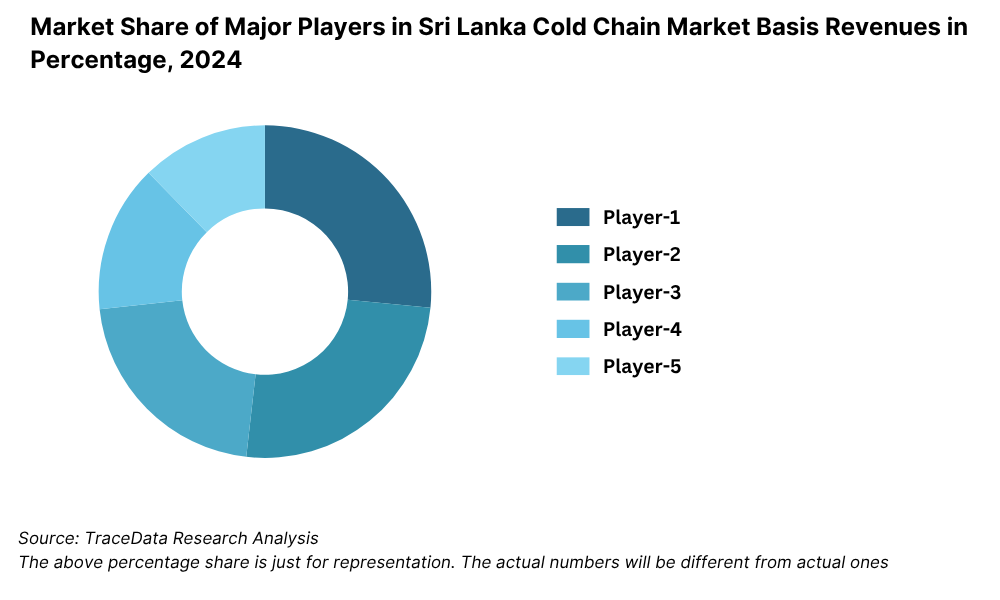
The Sri Lanka cold chain market is moderately consolidated, with a few key players operating across warehousing, transportation, and integrated logistics. However, increasing demand from pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and retail has led to the entry of new players and expansion of service offerings. Major companies like Emerald Logistics, Hayleys Advantis, Dart Global Logistics, ColdCo Storage, and EFL 3PL dominate the organized segment, offering end-to-end temperature-controlled solutions across the country.
| Company Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
| Elephant House (John Keells Holdings - Cold Chain) | 1866 | Colombo, Sri Lanka |
| Cargills (Ceylon) PLC (Cold Chain Operations) | 1844 | Colombo, Sri Lanka |
| Finlay Cold Storage (Finlays Colombo Ltd.) | 1893 | Colombo, Sri Lanka |
| Jaykay Marketing Services (Keells Super Cold Chain) | 1991 | Colombo, Sri Lanka |
| Hayleys Advantis (Cold Chain Logistics Division) | 2002 | Colombo, Sri Lanka |
| Emerald Foods (Cold Storage for Dairy and Ice Cream) | 1991 | Colombo, Sri Lanka |
| Pelwatte Dairy Industries Ltd. | 2006 | Buttala, Sri Lanka |
| Perera and Sons (Cold Distribution for QSR) | 1902 | Colombo, Sri Lanka |
| DHL Global Forwarding Sri Lanka (Temperature-Controlled Freight) | 1969 (SL: ~1980s) | Bonn, Germany |
| Maersk Sri Lanka (Cold Chain Logistics) | 1904 (SL: ~2000s) | Copenhagen, Denmark |
| Kuehne + Nagel Sri Lanka (Pharma and Perishables) | 1890 (SL: ~2000s) | Schindellegi, Switzerland |
| DB Schenker Sri Lanka (Cold Chain Division) | 1872 (SL: ~2000s) | Essen, Germany |
| Agility Logistics Sri Lanka (Reefer and Cold Storage) | 1979 (SL: ~2006) | Kuwait City, Kuwait |
| FedEx Sri Lanka (via Hayleys - Cold Express) | 1971 (SL: ~1990s) | Memphis, USA |
| UPS Sri Lanka (via local agent) | 1907 (SL: ~1990s) | Atlanta, USA |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
Emerald Logistics: A leading player in integrated cold chain logistics, Emerald Logistics reported a 20% increase in pharma cold storage utilization in 2023, largely driven by vaccine and biologicals distribution. The company has invested in new refrigerated facilities near Bandaranaike International Airport to enhance export preparedness.
Hayleys Advantis: Known for its large-scale warehousing capacity, Hayleys Advantis launched a state-of-the-art multi-temperature logistics hub in Western Province in 2023. The facility is designed to handle over 8,000 pallet positions and serves clients in dairy, meat, and life sciences industries.
Dart Global Logistics: Dart Global has focused on expanding reefer container services for the seafood export sector. In 2023, it reported a 15% rise in reefer cargo volume, driven by increased trade with the EU and Middle East.
ColdCo Storage: A specialized provider of cold warehousing for fruits and vegetables, ColdCo expanded its rural reach by partnering with agro-cooperatives. In 2023, the company operated more than 25 small-scale cold units across the Central and Uva provinces, reducing post-harvest losses by up to 18%.
EFL 3PL: A subsidiary of ExpoLanka Holdings, EFL 3PL has gained traction in e-commerce cold deliveries. In 2023, it piloted cold last-mile delivery services for online grocery platforms in Colombo and suburbs, leveraging GPS-enabled refrigerated vans for real-time monitoring.
What Lies Ahead for Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market?
The Sri Lanka cold chain market is projected to witness steady growth through 2029, supported by strong demand from the pharmaceutical, agriculture, and food processing sectors. The market is expected to grow at a healthy CAGR, driven by rising export demand, investments in cold logistics infrastructure, and regulatory push for temperature compliance across sensitive sectors.
Expansion of Cold Chain Infrastructure in Rural Areas: The Sri Lankan government, along with private sector partners, is expected to focus on bridging the cold chain gap in agricultural regions. Improved road connectivity and targeted investments in pre-cooling and mobile storage units will help minimize post-harvest losses and ensure fresher produce delivery, especially in provinces like Uva, North Central, and Eastern.
Digitization and IoT Integration: The adoption of IoT-based temperature monitoring, automated warehouse systems, and GPS-enabled reefer trucks is expected to accelerate, offering real-time visibility and improved operational efficiency. These technologies will enhance traceability and ensure compliance with pharmaceutical and food safety norms.
Rise of E-Commerce-Driven Cold Deliveries: The growing popularity of online grocery and medicine delivery platforms is likely to drive the demand for cold last-mile logistics. Urban centers like Colombo, Kandy, and Galle will see increased deployment of refrigerated vans and micro-fulfillment centers to support the quick commerce ecosystem.
Increased Focus on Pharma and Vaccine Logistics: Sri Lanka's pharmaceutical cold chain segment is expected to expand significantly due to increased reliance on biologics, vaccines, and specialty drugs. Companies will invest more in WHO-GDP compliant storage and validated cold transport networks, ensuring safe and efficient movement of high-value medicines.
Future Outlook and Projections for Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market on the Basis of Revenues in USD Million, 2024-2029
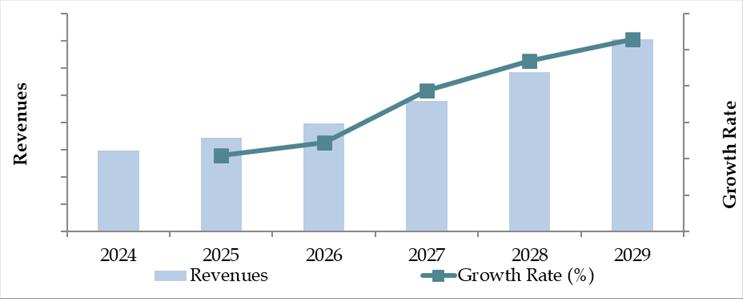
Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market Segmentation
• By Market Structure:
o Organized Sector
o Unorganized Sector
o Integrated Cold Chain Providers
o Standalone Cold Storage Providers
o Cold Transport Operators
o Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Cold Chain Services
• By Industry Segment:
o Pharmaceuticals
o Fruits & Vegetables
o Meat & Seafood
o Dairy Products
o Processed Food
o Quick Service Restaurants (QSRs) & Retail Chains
• By Type of Storage:
o Refrigerated Warehousing
o Cold Transport (Reefer Trucks)
o Multi-temperature Facilities
o Portable Cold Rooms
• By Temperature Range:
o Frozen (-18°C and below)
o Chilled (0°C to 8°C)
o Controlled Ambient (15°C to 25°C)
• By End Users:
o Exporters
o Food Processors
o Pharmaceutical Companies
o Retailers & Supermarkets
o E-commerce & Online Grocery Platforms
o Government & Health Departments
• By Region:
o Western Province (Colombo, Gampaha, Kalutara)
o Central Province (Kandy, Matale, Nuwara Eliya)
o Southern Province
o Northern & Eastern Provinces
o Uva & Sabaragamuwa Provinces
Players Mentioned in the Report:
- Lineage Logistics
- Yusen Logistics Sri Lanka
- Transcargo (Private) Limited
- Aitken Spence Logistics
- Finlay Cold Storage
- Expolanka Freight (EFL)
- Spectra Logistics
- Logicare
- McLarens Logistics Group
- Abans Logistics (Pvt) Ltd
- Kerry Logistics Lanka (Pvt) Ltd
- Omni Logistics Sri Lanka
- LAUGFS Holdings
Key Target Audience:
• Cold Chain Logistics Companies
• Food & Agriculture Exporters
• Pharmaceutical Distributors
• Retail Chains & QSR Operators
• E-commerce Grocery Platforms
• Government & Policy Makers
• Cold Chain Equipment Suppliers
• Investors and Infrastructure Funds
Time Period:
• Historical Period: 2018–2023
• Base Year: 2024
• Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
6.1. Revenues, 2018-2024P
7.1. By Cold Storage and Cold Transport, 2023-2024P
7.2. By End-User Application (Dairy Products, Meat and Seafood, Pharmaceuticals, Fruits and Vegetables and Others), 2023-2024P
7.3. By Ownership (Owned and 3PL Cold Chain Facilities), 2023-2024P
10.1. Sri Lanka Cold Storage Market Size
10.1.1. By Revenue, 2018-2024P
10.1.2. By Number of Pallets, 2018-2024P
10.2. Sri Lanka Cold Storage Market Segmentation
10.2.1. By Temperature Range (Ambient, Chilled and Frozen), 2023-2024P
10.2.2. By End-User Application (Dairy Products, Meat and Seafood, Pharmaceuticals, Fruits and Vegetables and Others), 2023-2024P
10.2.3. By Major Cities By Major Cities (Colombo, Gampaha, Kalutara, Kandy, Galle, Kurunegala, Anuradhapura, Jaffna and Others), 2023-2024P
10.3. Sri Lanka Cold Storage Market Future Outlook and Projections, 2025-2029
10.3.1. By Temperature Range (Ambient, Chilled and Frozen), 2025-2029
10.3.2. By Major Cities, 2025-2029
11.1. Sri Lanka Cold Transport Market Size (By Revenue and Number of Reefer Trucks), 2018-2024P
11.2. Sri Lanka Cold Transport Market Segmentation
11.2.1. By Mode of Transportation (Land, Sea and Air), 2023-2024P
11.2.2. By Location (Domestic and International), 2023-2024P
11.3. Sri Lanka Cold Transport Market Future Outlook and Projections, 2025-2029
11.3.1. By Mode of Transport (Land, Sea and Air), 2025-2029
11.3.2. By Location (Domestic and International), 2025-2029
12.1. Trends and Developments in Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market
12.2. Issues and Challenges in Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market
12.3. Decision Making Parameters for End Users in Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market
12.4. SWOT Analysis of Sri Lanka Cold Chain Industry
12.5. Government Regulations and Associations in Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market
12.6. Macroeconomic Factors Impacting Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market
13. Detailed End User Analysis to Determine Cold Storage Potential in Sri Lanka for Segments including Fruits and Vegetables, QSR, Confectionary, Bakery, Pharmaceuticals, Dairy, Meat and Seafood
13.1.1. Production Clusters
13.1.2. Market Demand, Major Products Stored, Cold Storage Companies in Sri lanka catering to End Users
13.1.3. Location Preference for Each End User and their Production Plants, Preferences for Outsourcing and Captive Facility, Services Required, Facility Preferences, Decision Making Parameters
13.1.4. Cross comparison of leading end users/companies based on Headquarters, Manufacturing Plants, Products Stored, Major Products, Total Production, Cold Chain Partner, Facility Outsourced/Captive, Pallets Owned/Hired, Contact Person, Address and others
16.1. Competitive Landscape in Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market
16.2. Competition Scenario in Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market (Competition Stage, Major Players, Competing Parameters)
16.3. Key Metrics (Temperature Range, Pallet Position, Prices Charged, Occupancy Rate, Revenue (2023) and Employee Base) for Major Players in Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market
16.4. Company Profiles of Major Companies in Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market (Year of Establishment, Company Overview, Service Offered, USP, Warehousing Facilities, Warehousing Price, Cold Storage by location, Occupancy Rate, Major Clientele, Industries Catered, Employee Base, Temperature Range, Topline OPEX*, Revenue, Recent Developments, Future Strategies)
16.5. Strength and Weakness
16.6. Operating Model Analysis Framework
16.7. Gartner Magic Quadrant
16.8. Bowmans Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
17.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
18.1. By Cold Storage and Cold Transport, 2025-2029
18.2. By End-User Application (Dairy Products, Meat and Seafood, Pharmaceuticals, Fruits and Vegetables and Others), 2025-2029
18.3. By Ownership (Owned and 3PL Cold Chain Facilities), 2025-2029
18.4. Recommendation
18.5. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand side and supply side entities for Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market. Basis this ecosystem, we will shortlist leading 5–6 service providers in the country based upon their financial information, infrastructure capacity, segmental focus (pharma, food, dairy), and logistics coverage.
Sourcing is made through industry articles, multiple secondary, and proprietary databases to perform desk research around the market to collate industry-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
Subsequently, we engage in an exhaustive desk research process by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This approach enables us to conduct a thorough analysis of the market, aggregating industry-level insights. We delve into aspects like storage capacity (in pallet positions), fleet strength of refrigerated vehicles, pricing trends, temperature range capabilities, and sectoral end-use demand.
We supplement this with detailed examinations of company-level data, relying on sources like press releases, annual reports, infrastructure blueprints, tender announcements, and similar documents. This process aims to construct a foundational understanding of both the market and the entities operating within it.
Step 3: Primary Research
We initiate a series of in-depth interviews with C-level executives and other stakeholders representing various Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market companies and end-users including pharma distributors, F&B exporters, retail chains, and logistics service providers.
This interview process serves a multi-faceted purpose: to validate market hypotheses, authenticate statistical data, and extract valuable operational and financial insights from these industry representatives. Bottom to top approach is undertaken to evaluate capacity utilization, storage throughput, and fleet deployment per player thereby aggregating to the overall market.
As part of our validation strategy, our team executes disguised interviews wherein we approach each company under the guise of potential clients or business partners. This approach enables us to validate the operational and financial information shared by company executives, corroborating this data against what is available in secondary databases. These interactions also provide us with a comprehensive understanding of pricing models, revenue streams, facility specifications, delivery capabilities, and sector-specific challenges.
Step 4: Sanity Check
Bottom to top and top to bottom analysis along with market size modeling exercises is undertaken to assess sanity check process. This involves triangulation of total market volume and value across segments and cross-verification with macroeconomic indicators, trade data, and logistics trends.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market?
The Sri Lanka cold chain market is poised for robust growth, with the market reaching a valuation of LKR 41 Billion in 2023. This growth is fueled by increasing demand for temperature-controlled logistics across pharmaceuticals, dairy, seafood, and fresh produce segments. The government’s export-oriented policies, rising health consciousness, and the expansion of modern retail and e-commerce platforms are further accelerating the market’s long-term potential.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market?
The Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market features several key players, including Emerald Logistics, Hayleys Advantis, and Dart Global Logistics. These companies lead the market due to their end-to-end integrated services, cold storage infrastructure, and nationwide transportation capabilities. Other prominent players include ColdCo Storage and EFL 3PL, who are increasingly focusing on innovation and regional expansion.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market?
The primary growth drivers include increased demand for pharmaceutical-grade logistics, the rise of organized food retail, and the need to reduce post-harvest agricultural losses. Additionally, public-private partnerships, government subsidies for export logistics, and the integration of digital technologies like IoT and GPS tracking are significantly contributing to the growth of the Sri Lanka cold chain market.
4. What are the Challenges in the Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market?
The Sri Lanka Cold Chain Market faces several challenges, including infrastructure limitations in rural regions, high energy and operational costs, and a shortage of trained cold chain professionals. Fragmentation in service quality and lack of standardization among unorganized players also hinder market scalability. Additionally, rising fuel prices and limited local manufacturing of cold chain equipment increase cost pressures on service providers.