Sweden Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Structure, By End-User Industries, By Temperature Type, By Mode of Transport, By Storage Infrastructure, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0326
- Region: Europe
- Published on: September 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Sweden Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029 – By Market Structure, By End-User Industries, By Temperature Type, By Mode of Transport, By Storage Infrastructure, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the cold chain logistics market in Sweden. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer-level profiling, issues and challenges, and comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the Cold Chain Market. The report concludes with future market projections based on market revenue, by application sectors, storage and transport modalities, temperature zones, and strategic case studies highlighting major opportunities and cautions.
Sweden Cold Chain Market Overview and Size
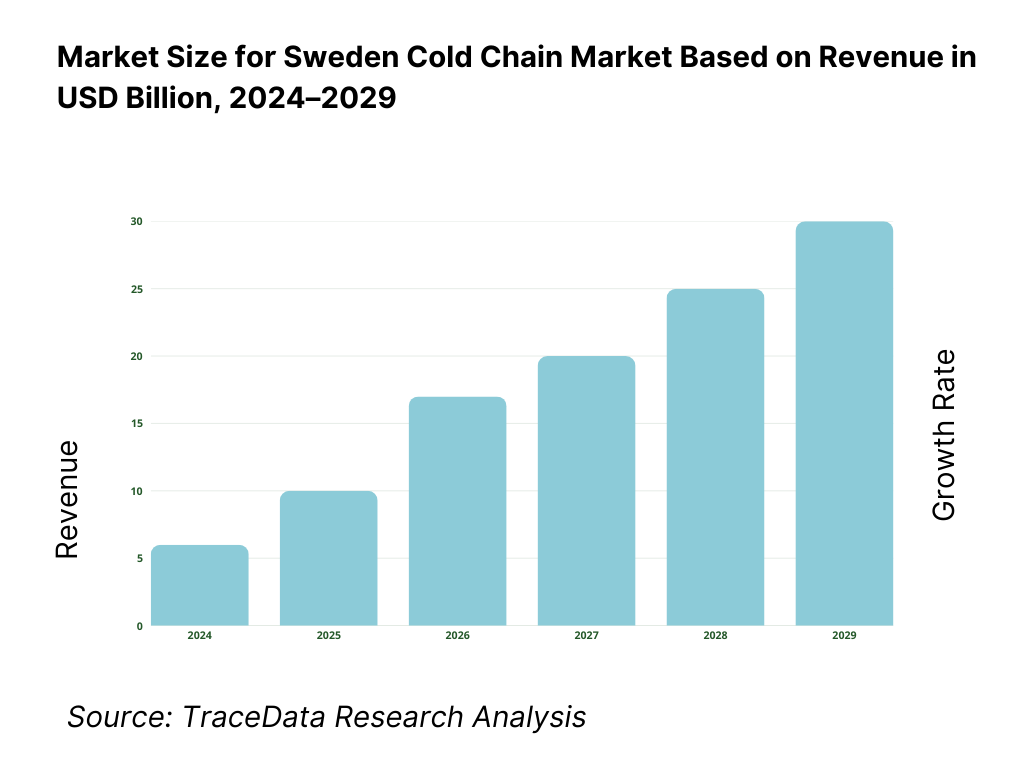
The Sweden cold chain market reached a valuation of SEK 17.5 billion in 2023, driven by increasing demand for temperature-sensitive pharmaceutical products, expanding e-commerce grocery delivery networks, and a rising emphasis on food safety regulations. The market is characterized by key players such as Bring Frigo, DHL Supply Chain, PostNord TPL, Thermo-Transit, and Kuehne + Nagel. These companies have built extensive refrigerated warehousing capacity, last-mile cold delivery networks, and integrated tracking systems to ensure real-time temperature monitoring and compliance.
In 2023, Bring Frigo inaugurated a new sustainable cold storage facility in Helsingborg to support growth in pharmaceutical and retail segments. The company aims to leverage Sweden’s strategic geographic location and highly developed logistics infrastructure to become a regional cold chain hub. Stockholm, Gothenburg, and Malmö serve as the core logistics centers due to their port connectivity, population concentration, and access to multimodal transport systems.
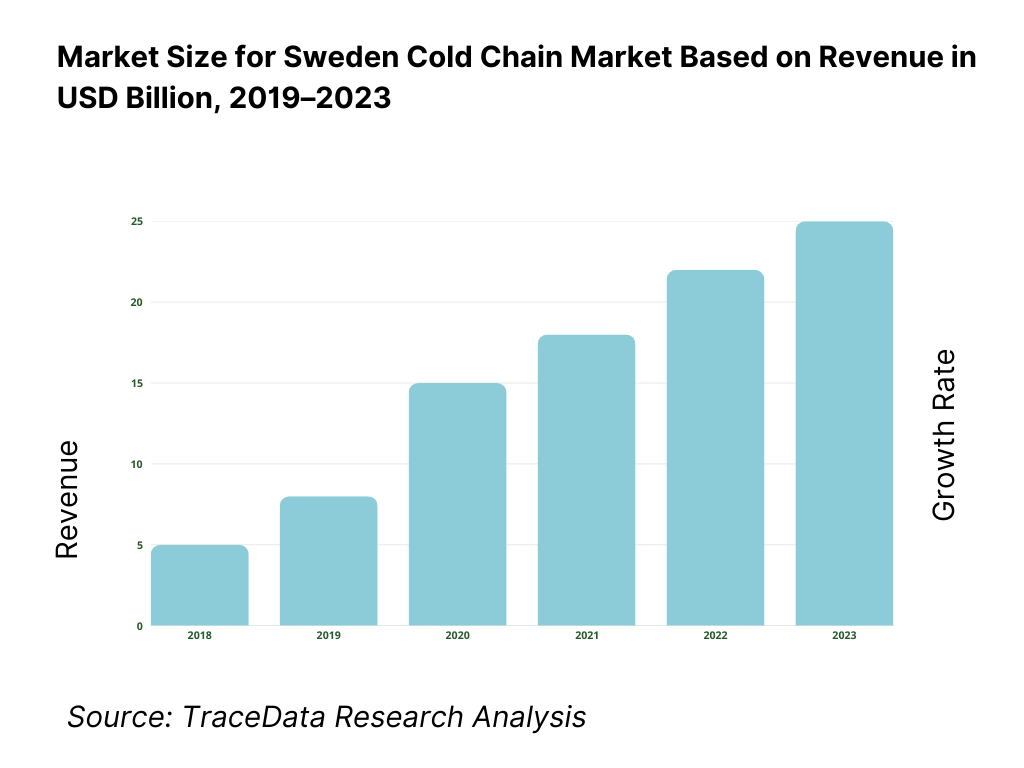
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Sweden Cold Chain Market:
Rising Demand from Pharmaceutical Sector: The pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries are among the top contributors to Sweden’s cold chain growth. In 2023, over 30% of the country’s cold chain logistics revenue was attributed to pharma-grade storage and transport, as demand for vaccines, biologics, and temperature-controlled APIs surged. Compliance with GDP (Good Distribution Practice) regulations has driven investment in validated cold chain systems and temperature-controlled warehousing.
Shift in Food Consumption Patterns: With a growing preference for organic, frozen, and ready-to-eat foods, cold chain infrastructure in Sweden is being rapidly modernized to meet evolving consumer behavior. In 2023, the frozen food segment witnessed a 9.8% YoY increase in cold chain reliance. Sweden's retail chains such as ICA, Coop, and Axfood are also expanding their refrigerated delivery models to cater to online grocery shoppers.
Technological Integration: The Swedish cold chain industry has embraced IoT-based sensors, AI-powered route optimization, and blockchain for traceability to maintain end-to-end temperature integrity. Approximately 45% of cold chain trucks and warehouses were equipped with real-time monitoring systems by 2023, significantly reducing spoilage and increasing operational transparency.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for Sweden Cold Chain Market
High Operating Costs: One of the most pressing challenges in the Swedish cold chain sector is the high cost of operations, particularly related to energy consumption and labor. According to industry estimates, refrigeration accounts for nearly 40–50% of total operational expenses in cold storage facilities. In 2023, over 30% of small and mid-sized operators reported margin pressures due to rising electricity prices and wage increases, limiting their capacity to scale operations or invest in newer technologies.
Infrastructure Gaps in Remote Areas: Despite a robust logistics network in major cities, cold chain infrastructure remains underdeveloped in rural and northern regions of Sweden. In 2023, it was estimated that over 20% of perishable goods transported to the Norrland region faced spoilage risks due to inadequate cold storage availability and longer transit times. This uneven infrastructure limits nationwide cold chain reliability and increases the risk of product loss for temperature-sensitive items.
Fragmentation of Last-Mile Delivery: The rapid growth of e-grocery and direct-to-consumer food and pharma delivery has created a bottleneck in last-mile cold chain distribution. A recent industry study highlighted that nearly 25% of temperature excursions in Sweden’s cold chain occurred during the last mile due to unstandardized delivery processes and insufficient trained workforce. Ensuring uniform temperature control during home deliveries remains a critical gap for cold chain providers.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market
EU Cold Chain Compliance Standards: Sweden adheres to stringent EU regulations on the storage and transport of perishable goods under the ATP (Agreement on the International Carriage of Perishable Foodstuffs) framework. All cold chain operators must ensure that refrigerated vehicles and storage units meet temperature uniformity and insulation standards. In 2023, over 85% of cold chain operators in Sweden were ATP-certified, reflecting strong compliance with pan-European norms.
GDP Guidelines for Pharmaceutical Logistics: To safeguard the integrity of temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals, Sweden follows Good Distribution Practice (GDP) standards mandated by the European Medicines Agency. These guidelines govern temperature monitoring, documentation, and contingency planning. In 2023, Sweden’s Medical Products Agency conducted over 200 inspections of cold chain pharma operators, with a compliance rate exceeding 92%.
Incentives for Sustainable Cold Chain Transition: To align with Sweden’s climate neutrality goals by 2045, the government has introduced incentives promoting low-carbon technologies in cold chain logistics. This includes subsidies for electric refrigerated trucks, tax rebates on solar-powered storage units, and funding for research in alternative refrigerants. In 2023 alone, over SEK 200 million was allocated under the Klimatklivet program to support sustainable cold chain infrastructure upgrades.
Sweden Cold Chain Market Segmentation
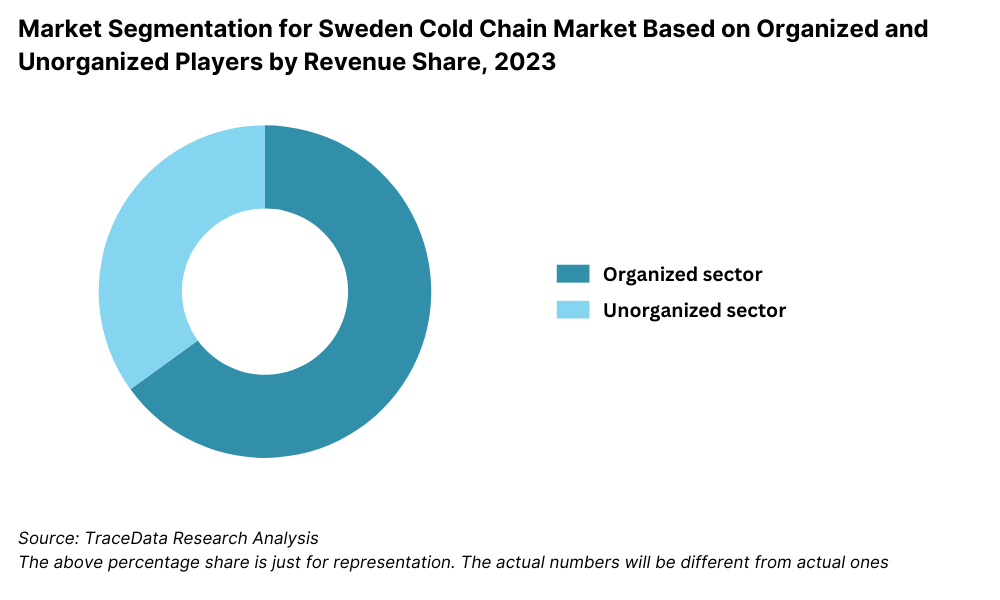
By Market Structure: The organized segment dominates Sweden’s cold chain market, primarily due to stringent compliance requirements, customer demands for traceability, and widespread adoption of digital tracking systems. Major logistics players and third-party logistics (3PL) providers such as Bring Frigo, DHL Supply Chain, and PostNord TPL operate with standardized protocols, validated temperature monitoring, and integrated storage-transport services. The unorganized segment, while relatively smaller, still operates in localized food distribution and small-scale pharma logistics—particularly in rural and underserved areas—where informal operators continue to serve local producers and retailers.
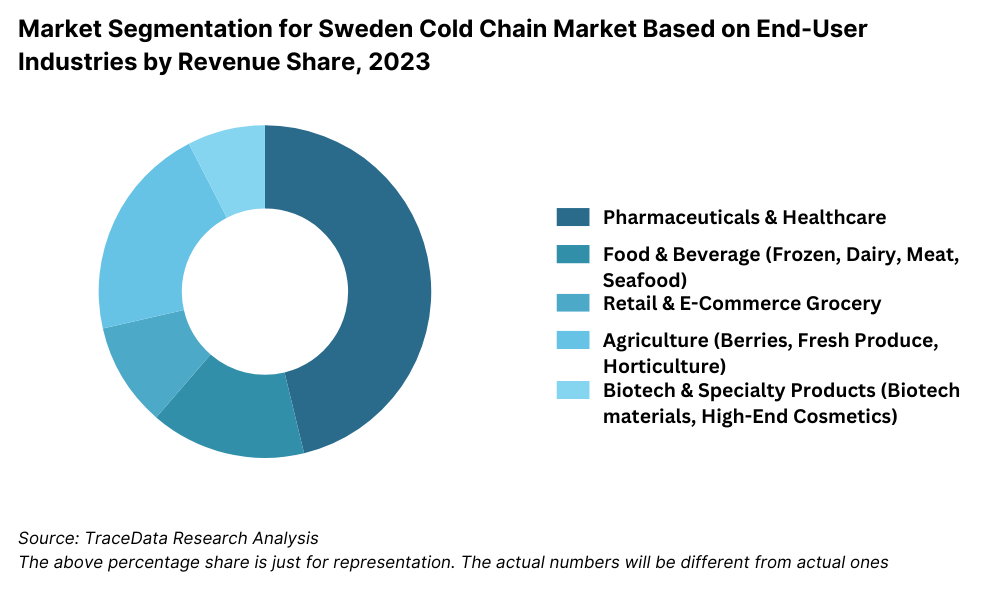
By End-User Industry: Pharmaceuticals and healthcare products account for a substantial portion of Sweden’s cold chain market due to strict GDP compliance, growth in biologics, and increasing vaccine distribution logistics. The food & beverage industry, particularly frozen food, dairy, seafood, and meat products, is also a key contributor, driven by rising consumer demand for freshness and safety. E-commerce grocery platforms and retail chains have further expanded cold chain requirements for last-mile delivery. Other segments include agriculture (e.g., berries and horticulture), biotechnology, and high-end cosmetics requiring temperature control.
By Temperature Type: The market is segmented into chilled (0–8°C), frozen (−18°C), and deep-frozen (<−20°C) categories. The chilled segment dominates due to high demand for fresh dairy, meat, and pharmaceutical products that require narrow temperature band preservation. The frozen segment is growing due to expanding consumption of frozen ready meals and seafood. The deep-frozen segment, although smaller, is relevant for specialized medical and high-value bio/pharma logistics.
Competitive Landscape in Sweden Cold Chain Market
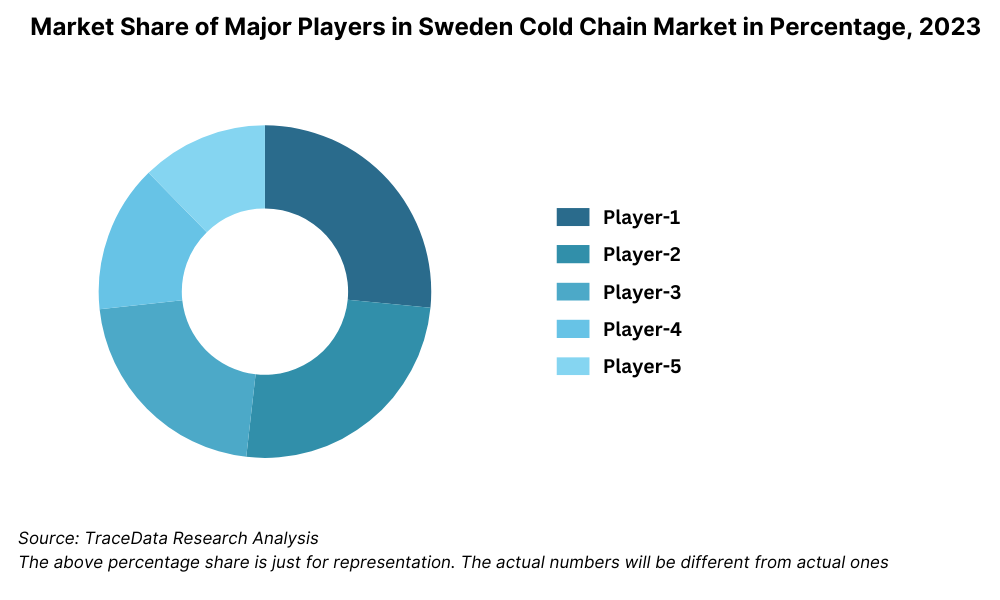
The Sweden cold chain market is moderately consolidated, with a few major logistics players leading the industry through their extensive infrastructure, regulatory compliance capabilities, and investments in green technologies. However, the landscape is gradually diversifying with the emergence of specialized cold chain startups and technology-driven service providers. Companies such as Bring Frigo, PostNord TPL, Thermo-Transit, DHL Supply Chain, and Kuehne + Nagel dominate the market by offering integrated temperature-controlled storage and transport solutions across Sweden and the broader Nordic region.
Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
Bring Frigo | 1950 | Stockholm, Sweden |
PostNord TPL | 2009 | Jönköping, Sweden |
Thermo-Transit | 1987 | Malmö, Sweden |
DHL Supply Chain | 1969 | Bonn, Germany (SE ops) |
Kuehne + Nagel | 1890 | Schindellegi, Switzerland (Swedish HQ: Gothenburg) |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
Bring Frigo: As Sweden’s largest cold chain logistics provider, Bring Frigo operates over 300,000 m² of temperature-controlled warehousing. In 2023, the company launched a carbon-neutral cold storage hub in Helsingborg and partnered with leading pharmaceutical firms for GDP-compliant last-mile delivery. Its ongoing investment in electric refrigerated trucks aligns with Sweden’s sustainability agenda.
PostNord TPL: PostNord’s third-party logistics division has expanded its cold storage footprint across key Swedish regions, including Gothenburg and Linköping. In 2023, PostNord TPL introduced AI-based warehouse automation systems for inventory accuracy and energy efficiency. It also reported a 17% YoY growth in temperature-controlled parcel deliveries for retail and healthcare clients.
Thermo-Transit: With specialization in cross-border frozen and chilled logistics between Sweden and neighboring Nordic countries, Thermo-Transit saw a 12% increase in freight volumes in 2023. The company focuses on reefer fleet expansion and has adopted real-time GPS + temperature monitoring across 90% of its vehicles.
DHL Supply Chain: DHL operates several multi-client cold storage warehouses across Sweden, serving global F&B and pharma clients. In 2023, DHL reported a 22% increase in pharmaceutical cold chain revenue due to higher biologic exports. The company also piloted solar-powered warehouse cooling systems at its Arlanda facility.
Kuehne + Nagel: One of the key players in Sweden’s international pharma logistics, Kuehne + Nagel manages end-to-end GDP-compliant supply chains. In 2023, it launched a regional control tower in Gothenburg to manage cold chain risk visibility and enhance SLA compliance for vaccine and biotech shipments.
What Lies Ahead for Sweden Cold Chain Market?
The Sweden cold chain market is projected to grow consistently through 2029, driven by expanding demand in pharmaceuticals, e-commerce grocery deliveries, and frozen food exports. With strong regulatory oversight, increasing focus on sustainability, and rapid technological adoption, the market is expected to register a healthy CAGR over the forecast period.
Acceleration of Green Cold Chain Technologies: As Sweden advances towards its 2045 net-zero emission target, the cold chain sector is expected to invest heavily in low-carbon and energy-efficient infrastructure. This includes wider adoption of solar-powered cold storage units, electric refrigerated vehicles, and natural refrigerants. In the coming years, operators prioritizing sustainability are likely to gain a competitive edge, especially in food and pharma logistics contracts.
Expansion of E-Grocery and Quick Commerce: The rise of e-commerce grocery platforms and demand for rapid delivery is reshaping last-mile cold chain dynamics. By 2029, it is expected that nearly 30% of Sweden’s perishable grocery purchases will be fulfilled through cold chain-enabled online delivery. Investment in micro-fulfillment centers and urban cold storage hubs will become critical to serving this evolving retail segment.
Growth of Biopharma and Personalized Medicine Logistics: Sweden’s prominence in biotech R&D and biologics manufacturing is projected to expand the demand for ultra-cold storage and GDP-compliant logistics. Emerging therapies like cell and gene treatments, which require precise temperature control, are expected to drive innovation in niche cold chain services over the next five years.
Increased Automation and AI-Driven Monitoring: The next phase of growth will be marked by widespread integration of AI, IoT, and predictive analytics in cold chain operations. These technologies will improve temperature tracking, route optimization, and early detection of spoilage risks. By 2029, over 70% of large operators are expected to adopt AI-based cold chain visibility platforms, boosting operational reliability and reducing wastage.
Sweden Cold Chain Market Segmentation
• By Market Structure:
o Organized Cold Chain Logistics Providers
o Unorganized / Local Cold Storage Operators
o Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Service Providers
o Integrated Storage and Transport Providers
o Pharma-Grade Cold Chain Operators
o Retail and E-Grocery Cold Delivery Networks
• By End-User Industry:
o Pharmaceuticals and Biotech
o Food & Beverage (Dairy, Meat, Seafood, Frozen Foods)
o Agriculture and Horticulture
o Cosmetics and Personal Care
o Retail and E-Commerce Grocery
o Hospitality and Food Service
• By Temperature Type:
o Chilled (0°C to 8°C)
o Frozen (−18°C)
o Deep-Frozen (Below −20°C)
o Controlled Ambient (15°C to 25°C)
• By Mode of Transport:
o Road-Based Refrigerated Transport
o Rail-Based Cold Chain
o Air Freight for Temperature-Sensitive Cargo
o Sea Freight with Reefer Containers
• By Storage Infrastructure:
o Cold Rooms
o Refrigerated Warehouses
o Blast Freezers and Deep Freezers
o Mobile Cold Storage Units
o Urban Micro Fulfillment Centers
• By Region:
o Stockholm Metropolitan Region
o Southern Sweden (Skåne, Malmö, Lund)
o Western Sweden (Gothenburg, Västra Götaland)
o Central Sweden (Örebro, Uppsala)
o Northern Sweden (Norrland, Luleå, Umeå)
Players Mentioned in the Report:
• Bring Frigo
• PostNord TPL
• Thermo-Transit
• DHL Supply Chain Sweden
• Kuehne + Nagel Sweden
• Ahola Transport
• Nagel-Group (Nordic Operations)
• Green Cargo Logistics
• DSV Cold Chain
• Frode Laursen
Key Target Audience:
• Cold Chain Logistics Companies
• Pharmaceutical and Biotech Companies
• Food Processing and Retail Firms
• E-Commerce Grocery Platforms
• Logistics and Warehouse Technology Providers
• Government Regulatory Bodies (e.g., Swedish Food Agency, MPA)
• Infrastructure Investors and REITs
• Sustainability-Focused Logistics Startups
• Market Research and Consulting Firms
Time Period:
• Historical Period: 2018–2023
• Base Year: 2024
• Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and challenges that they face
4.2. Revenue Streams for Sweden Cold Chain Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Sweden Cold Chain Market
4.4. Cold Chain Service Decision-Making Process
4.5. Infrastructure Investment and Technology Adoption Process
5.1. Cold Chain Logistics Market Size in Sweden, 2018-2024
5.2. Growth of Pharmaceutical and Biotech Cold Chain Needs, 2018-2024
5.3. E-Grocery Penetration and Demand for Last-Mile Cold Delivery, 2024
5.4. Distribution of Cold Storage and Reefer Transport Operators by Region
8.1. Revenues, 2018-2024
8.2. Storage and Transport Volume, 2018-2024
9.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized), 2023-2024P
9.2. By End-User Industry (Pharma, F&B, Agriculture, Cosmetics, Retail), 2023-2024P
9.3. By Temperature Type (Chilled, Frozen, Deep-Frozen, Controlled Ambient), 2023-2024P
9.4. By Mode of Transport (Road, Rail, Air, Sea), 2023-2024P
9.5. By Storage Infrastructure (Warehouses, Cold Rooms, Mobile Units), 2023-2024P
9.6. By Region (Stockholm, Southern Sweden, Western Sweden, etc.), 2023-2024P
10.1. End-User Needs and Service Expectations
10.2. Procurement Journey and Partner Evaluation Criteria
10.3. Service Gaps, Delays, and Pain Point Analysis
10.4. Opportunity Matrix Based on Use Case Segments
11.1. Trends and Developments for Sweden Cold Chain Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Sweden Cold Chain Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Sweden Cold Chain Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges for Sweden Cold Chain Market
11.5. Government Regulations for Sweden Cold Chain Market
12.1. Market Size and Future Potential for IoT, AI, and Blockchain Adoption in Cold Chain, 2018-2029
12.2. Business Models for Smart Cold Chain Solutions
12.3. Cross Comparison of Leading Tech-Enabled Cold Chain Providers
13.1. Government Subsidies and Green Incentives for Cold Chain Infrastructure
13.2. Private Equity, VC, and Institutional Investor Participation
13.3. Project Pipeline for Cold Warehousing and Electric Reefer Fleets, 2018-2029
13.4. Investment Trends in Green Refrigerants and Renewable Energy Adoption
16.1. Benchmark of Key Competitors in Sweden Cold Chain Market including Company Overview, Infrastructure Capacity, Services, Certifications, Sustainability Practices, Innovations, Operating Geography, and Value-Added Services
16.2. Strength and Weakness
16.3. Operating Model Analysis Framework
16.4. Gartner Magic Quadrant
16.5. Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
17.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
17.2. Storage and Transport Volume, 2025-2029
18.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized), 2025-2029
18.2. By End-User Industry, 2025-2029
18.3. By Temperature Type, 2025-2029
18.4. By Mode of Transport, 2025-2029
18.5. By Storage Infrastructure Type, 2025-2029
18.6. By Region, 2025-2029
18.7. Recommendation
18.8. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand side and supply side entities for Sweden Cold Chain Market. Basis this ecosystem, we will shortlist leading 5–6 service providers in the country based upon their financial information, warehousing capacity, fleet size, and market presence.
Sourcing is made through industry articles, multiple secondary, and proprietary databases to perform desk research around the market to collate industry-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
Subsequently, we engage in an exhaustive desk research process by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This approach enables us to conduct a thorough analysis of the market, aggregating industry-level insights. We delve into aspects like the total warehousing footprint, cold transport penetration, number of organized/unorganized players, price benchmarks, and regulatory compliance rates.
We supplement this with detailed examinations of company-level data, relying on sources like press releases, annual reports, financial statements, sustainability disclosures, and similar documents. This process aims to construct a foundational understanding of both the market and the entities operating within it.
Step 3: Primary Research
We initiate a series of in-depth interviews with C-level executives and other stakeholders representing various Sweden Cold Chain Market companies and end-users. This interview process serves a multi-faceted purpose: to validate market hypotheses, authenticate statistical data, and extract valuable operational and financial insights from these industry representatives. Bottom to top approach is undertaken to evaluate cold storage and transport capacity for each player thereby aggregating to the overall market.
As part of our validation strategy, our team executes disguised interviews wherein we approach each company under the guise of potential customers. This approach enables us to validate the operational and financial information shared by company executives, corroborating this data against what is available in secondary databases. These interactions also provide us with a comprehensive understanding of service pricing, utilization rates, value chain integration, and compliance processes.
Step 4: Sanity Check
Bottom to top and top to bottom analysis along with market size modeling exercises is undertaken to assess sanity check process.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Sweden Cold Chain Market?
The Sweden cold chain market is poised for sustained growth, reaching a valuation of SEK 17.5 Billion in 2023. This growth is driven by rising demand in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors, increasing reliance on e-commerce grocery deliveries, and the country’s strong commitment to food safety and sustainability. The market’s potential is further amplified by Sweden’s advanced logistics infrastructure and regulatory alignment with EU cold chain standards.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Sweden Cold Chain Market?
The Sweden Cold Chain Market features several key players, including Bring Frigo, PostNord TPL, and Thermo-Transit. These companies dominate the market due to their extensive temperature-controlled warehousing, reliable refrigerated transport networks, and compliance with GDP and ATP regulations. Other notable players include DHL Supply Chain Sweden and Kuehne + Nagel Sweden.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Sweden Cold Chain Market?
The primary growth drivers include increased demand for temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals, growth in frozen and ready-to-eat food consumption, and the expansion of e-commerce grocery and last-mile delivery services. Technological advancements such as IoT-enabled tracking, automation, and real-time temperature monitoring systems are also enhancing operational efficiency and reliability, further driving market growth.
4. What are the Challenges in the Sweden Cold Chain Market?
The Sweden Cold Chain Market faces several challenges, including high operational costs driven by energy usage and labor shortages. Infrastructure limitations in remote regions can impact product integrity during long-distance transport. Additionally, the fragmentation of last-mile cold delivery services and the need for standardized compliance across all operators present barriers to market efficiency and expansion.