Thailand Car Rental and Leasing Market Outlook to 2035
By Rental Duration, By Vehicle Type, By Customer Segment, By Booking & Distribution Channel, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0494
- Region: Asia
- Published on: January 2026
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Thailand Car Rental and Leasing Market Outlook to 2035 – By Rental Duration, By Vehicle Type, By Customer Segment, By Booking & Distribution Channel, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the car rental and leasing industry in Thailand. The report covers an overview and genesis of the market, overall market size in terms of value, detailed market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory and taxation landscape, customer-level demand profiling, key issues and challenges, and the competitive landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players operating in the Thailand car rental and leasing market. The report concludes with future market projections based on tourism recovery cycles, urban mobility patterns, corporate fleet outsourcing, electric vehicle (EV) adoption, infrastructure development, regional demand drivers, cause-and-effect relationships, and case-based illustrations highlighting the major opportunities and cautions shaping the market through 2035.
Thailand Car Rental and Leasing Market Overview and Size
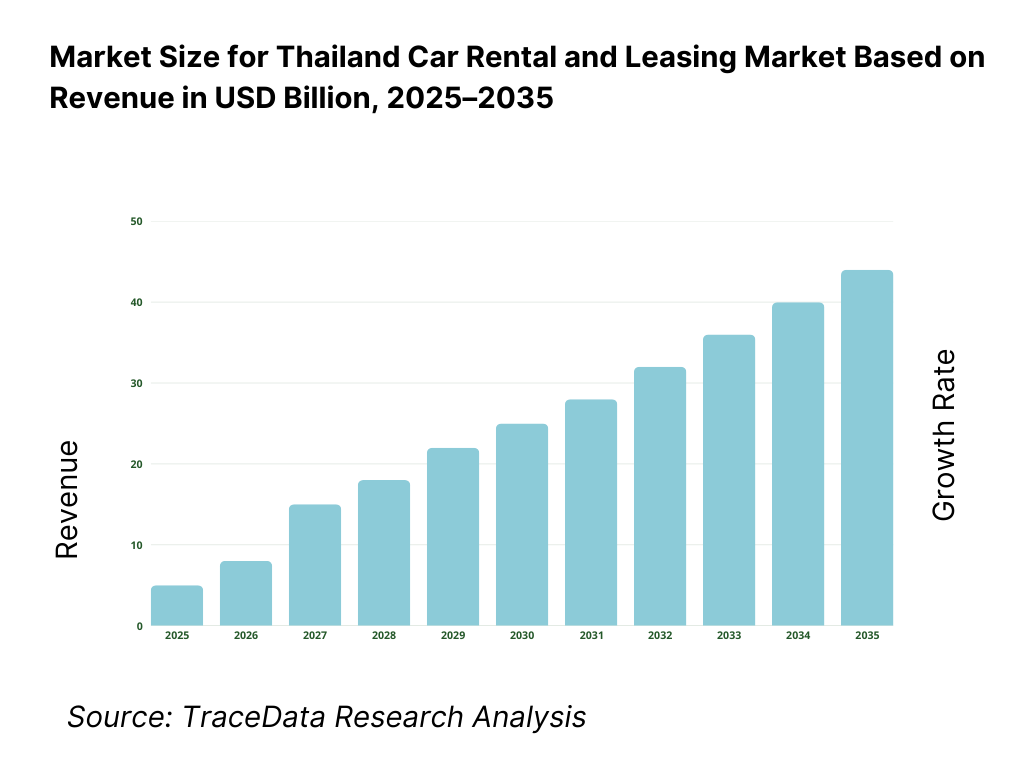
The Thailand car rental and leasing market is valued at approximately ~USD ~ billion, representing the provision of short-term rentals, long-term leasing, and fleet management services to domestic and international customers. The market includes daily and weekly self-drive rentals, chauffeur-driven services, long-term operating leases for corporates and SMEs, and specialized fleet solutions for logistics, hospitality, ride-hailing support, and government users.
The market is structurally supported by Thailand’s position as a leading tourism destination in Southeast Asia, a large urban commuter base in Bangkok and surrounding provinces, and a growing corporate preference for asset-light fleet solutions. International tourist inflows, domestic leisure travel, business travel, and event-driven mobility demand collectively sustain short-term rental volumes, while long-term leasing demand is anchored by multinational corporations, local enterprises, and public-sector entities seeking predictable mobility costs and outsourced fleet management.
Bangkok and the Eastern Economic Corridor (EEC) form the core demand hubs due to high population density, business activity, airports, and industrial estates. Key tourism regions such as Phuket, Chiang Mai, Krabi, and Pattaya drive seasonal peaks in short-term rentals, while secondary cities are witnessing gradual uptake driven by domestic tourism and regional business travel. Leasing demand is more evenly distributed, with strong penetration in industrial zones, logistics clusters, and corporate office locations.
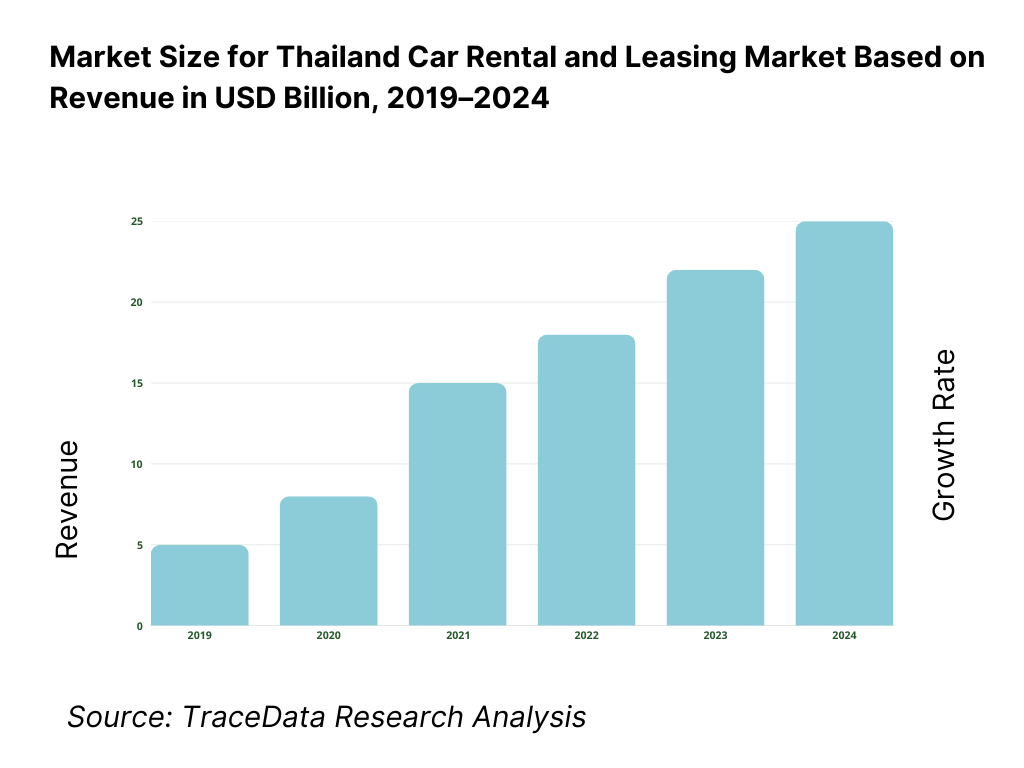
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the Thailand Car Rental and Leasing Market:
Tourism recovery and diversification of travel demand strengthen short-term rental volumes: Thailand’s tourism sector continues to recover and diversify, with growth not only from traditional international leisure travelers but also from regional tourists, digital nomads, long-stay visitors, and domestic travelers. Airports, resort destinations, and intercity travel corridors generate sustained demand for self-drive rentals and chauffeur-driven services. Car rentals offer flexibility and cost efficiency compared to taxis for multi-day travel, particularly in destinations with limited public transport connectivity. This broad-based travel demand directly supports fleet utilization and revenue stability for rental operators.
Corporate shift toward asset-light fleet management accelerates leasing adoption: Corporates in Thailand are increasingly outsourcing vehicle ownership through operating leases to reduce capital expenditure, simplify accounting, and improve fleet efficiency. Leasing solutions covering maintenance, insurance, replacement vehicles, and end-of-life management allow companies to focus on core operations while maintaining mobility. This trend is especially pronounced among multinational firms, logistics companies, sales-driven organizations, and service providers with geographically distributed teams. The predictable cost structure of leasing aligns well with tighter corporate budgeting and compliance requirements.
Urban congestion and changing mobility preferences support rental usage: Rising vehicle ownership costs, congestion in major cities, parking constraints, and regulatory measures aimed at managing traffic are reshaping mobility behavior. For urban residents and short-term users, renting a car for specific needs—such as weekend travel, business trips, or temporary assignments—can be more economical than owning a vehicle. This behavioral shift supports demand for short-duration rentals and subscription-style mobility offerings.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of the Thailand Car Rental and Leasing Market:
High vehicle acquisition costs and residual value risk affect fleet expansion decisions: Car rental and leasing operators in Thailand remain exposed to fluctuations in vehicle prices, interest rates, and depreciation trends. Rising costs of new vehicles—driven by OEM pricing, import duties on certain models, and financing costs—increase the capital intensity of fleet expansion. At the same time, uncertainty around resale values, particularly for higher-end models and electric vehicles, creates residual value risk for leasing companies. This makes operators cautious in scaling fleets aggressively, especially in periods of demand uncertainty or rapid technology transition.
Seasonality and demand volatility create utilization and pricing pressure: Thailand’s car rental market is highly influenced by tourism seasonality, with peak demand during international holiday periods and significant softness during off-peak months. This uneven demand profile leads to fluctuating fleet utilization and puts pressure on pricing during low seasons. Operators must balance fleet size to avoid underutilization while still being able to serve peak demand efficiently. Smaller players are particularly vulnerable, as they have limited flexibility to redeploy vehicles across regions or customer segments.
Urban congestion, parking constraints, and regulatory controls limit usage in major cities: In cities such as Bangkok, traffic congestion, limited parking availability, and rising urban mobility restrictions reduce the attractiveness of car usage for daily commuting. For short-term rentals, this can dampen demand from urban residents who increasingly rely on public transport or ride-hailing services. For leasing clients, congestion-related productivity losses and parking costs reduce the perceived benefits of maintaining larger fleets, especially for intra-city operations.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
Vehicle registration, taxation, and insurance regulations shaping fleet economics: Car rental and leasing vehicles in Thailand are subject to specific registration requirements, annual road taxes, and mandatory insurance coverage. Differences in tax treatment between privately owned vehicles and commercially registered fleets influence operating costs and pricing strategies. Compliance with insurance mandates, including compulsory motor insurance and voluntary coverage for rental customers, adds to the overall cost structure and requires careful risk management by operators.
Tourism, transport, and consumer protection regulations influencing rental operations: Regulations related to tourism services, airport concessions, and consumer protection affect how rental companies operate, particularly in high-traffic locations such as airports and tourist hubs. Licensing requirements, contract transparency norms, and customer dispute mechanisms influence rental agreements, pricing disclosures, and service standards. While these measures enhance consumer confidence, they also increase administrative and compliance requirements for operators.
Government initiatives promoting electric vehicles and sustainable mobility: Thailand’s policy push toward electric vehicle adoption—including incentives for EV manufacturing, tax benefits, and charging infrastructure development—has indirect implications for the car rental and leasing market. Operators are encouraged to introduce EVs into their fleets, particularly for corporate leasing and urban rentals. However, uncertainty around charging availability, battery life, and resale values means adoption is gradual. Over time, these initiatives are expected to reshape fleet composition and operating models, especially as sustainability becomes a stronger procurement criterion for corporate clients.
Thailand Car Rental and Leasing Market Segmentation
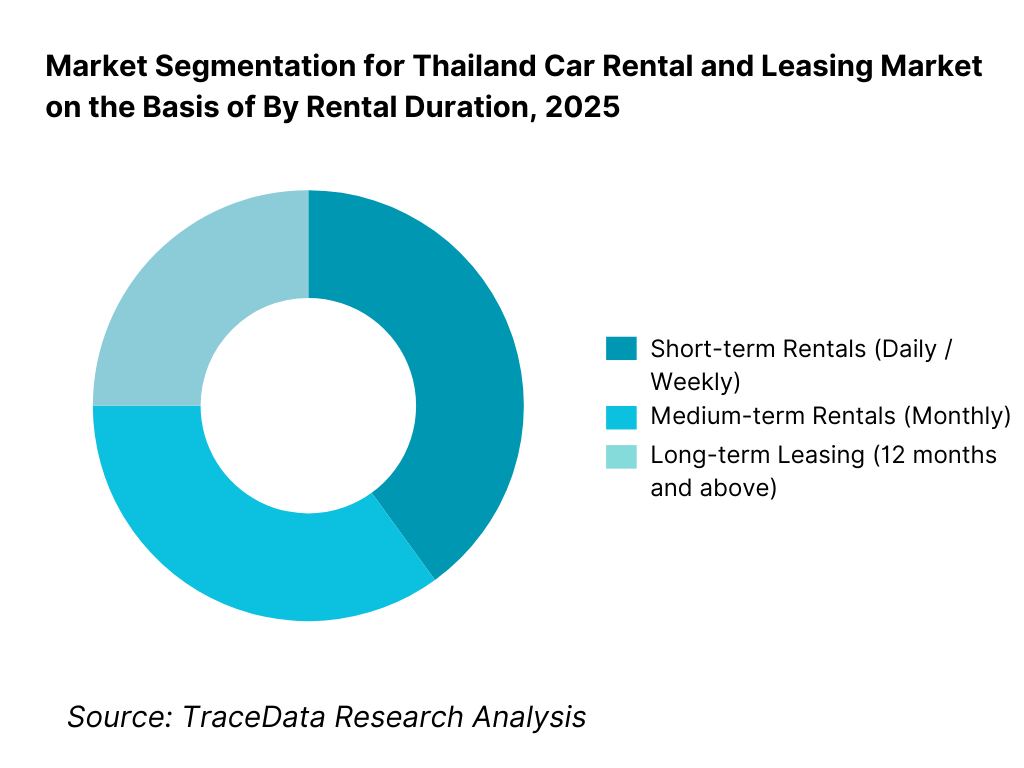
By Rental Duration: The short-term rental segment continues to hold a dominant share of the Thailand car rental and leasing market, largely driven by tourism, business travel, and temporary mobility needs. Daily and weekly rentals are strongly aligned with inbound international tourism, domestic leisure travel, and airport-based demand. However, long-term leasing is gaining structural importance as corporates, SMEs, and government entities increasingly prefer operating leases over vehicle ownership to reduce capital expenditure and administrative burden. Medium-term rentals serve as a bridge solution for expatriates, project-based employees, and temporary relocations.
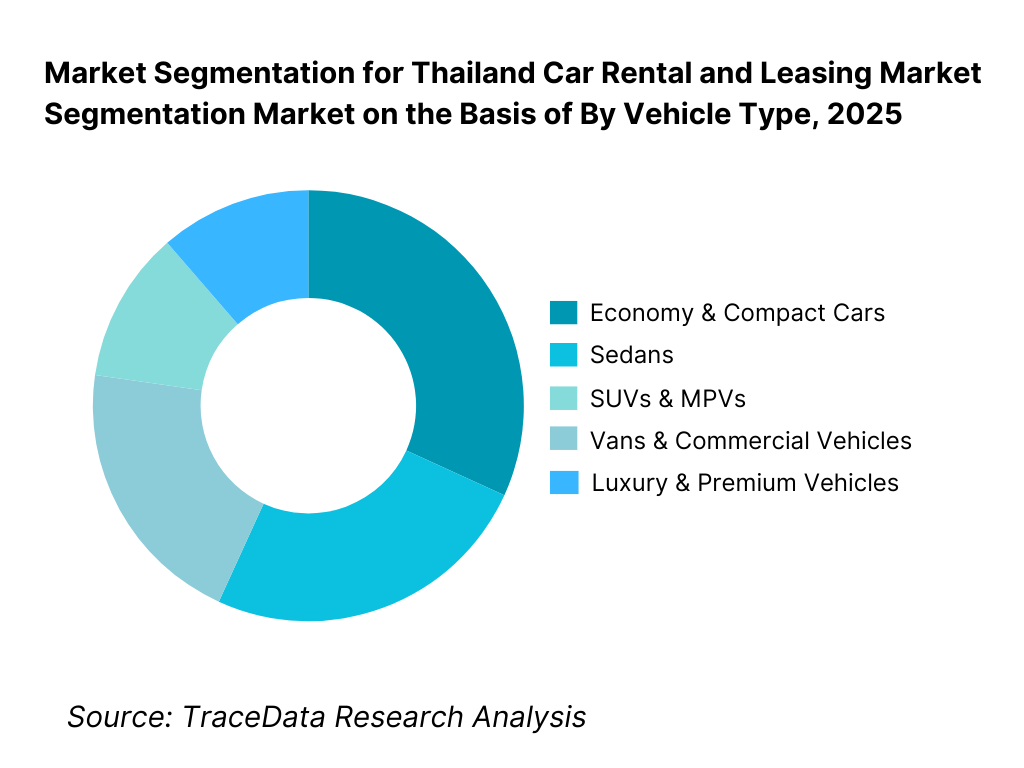
By Vehicle Type: Economy and compact cars dominate the Thailand car rental fleet due to affordability, fuel efficiency, and suitability for urban and intercity travel. SUVs and MPVs hold a growing share, particularly among family travelers, group tourists, and corporate users requiring higher seating capacity and comfort. Vans are important in tourism-heavy regions for group transport, while luxury vehicles remain a niche offering catering to premium tourists, executives, and chauffeur-driven services. Electric and hybrid vehicles are gradually being introduced, primarily in corporate leasing and urban rentals.
Competitive Landscape in Thailand Car Rental and Leasing Market
The Thailand car rental and leasing market exhibits moderate concentration, with a mix of international brands, strong domestic players, and regional operators. Market leadership is driven by fleet scale, airport presence, corporate leasing contracts, service network coverage, digital booking capability, and relationships with OEMs and insurers. Large players dominate airport and corporate segments, while local and regional operators remain competitive in city-based rentals, tourism partnerships, and flexible pricing models.
Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
Thai Rent A Car Corporation | 1978 | Bangkok, Thailand |
Avis Thailand | 1980 | Bangkok, Thailand |
Hertz Thailand | 1989 | Bangkok, Thailand |
Budget Thailand | 1997 | Bangkok, Thailand |
Sixt Thailand | 2018 | Bangkok, Thailand |
Chic Car Rent | 2004 | Bangkok, Thailand |
ASAP Car Rental & Leasing | 2016 | Bangkok, Thailand |
Drivehub (Peer-to-peer platform) | 2018 | Bangkok, Thailand |
Some of the Recent Competitor Trends and Key Information About Competitors Include:
Thai Rent A Car: As one of the largest domestic players, Thai Rent A Car benefits from extensive airport coverage, a diversified fleet, and strong corporate leasing relationships. The company’s scale allows efficient fleet rotation between tourism-heavy and business-driven regions, supporting utilization across seasons.
Avis Thailand: Avis maintains a strong position in premium short-term rentals and corporate accounts, leveraging global brand recognition and standardized service quality. Its competitive strength lies in airport locations, international traveler trust, and multinational corporate contracts.
Hertz Thailand: Hertz competes through a balanced focus on leisure rentals and long-term leasing, with emphasis on fleet quality and digital booking experience. The brand remains strong among international business travelers and higher-value customer segments.
Budget Thailand: Budget targets price-sensitive travelers and SMEs, competing on affordability and simple rental structures. Its positioning is well suited to domestic tourism and value-driven airport rentals, particularly during peak travel seasons.
ASAP Car Rental & Leasing: ASAP has emerged as a fast-growing local player with a strong focus on long-term leasing, fleet management services, and technology-enabled operations. Its leasing-centric model aligns well with corporate outsourcing trends and recurring revenue visibility.
Chic Car Rent: Chic Car Rent differentiates through partnerships with airlines, hotels, and online travel platforms. Its competitive advantage lies in high visibility across tourism channels and flexible rental offerings in key leisure destinations.
What Lies Ahead for Thailand Car Rental and Leasing Market?
The Thailand car rental and leasing market is expected to expand steadily by 2035, supported by sustained tourism inflows, continued urbanization, corporate preference for asset-light fleet models, and the increasing role of technology-led booking and fleet management. Growth momentum is further enhanced by improvements in transport infrastructure, expansion of industrial corridors (including the Eastern Economic Corridor), and evolving consumer behavior that favors flexible access over long-term ownership for specific mobility needs. As both leisure and business customers increasingly prioritize convenience, predictable pricing, and reliable service quality, rentals and operating leases will remain essential mobility solutions across Thailand through 2035.
Shift Toward Fleet-as-a-Service and Higher Penetration of Long-Term Operating Leases: The market will continue moving beyond traditional short-term rentals toward long-term operating leases bundled with maintenance, insurance, replacement vehicles, and fleet analytics. Corporate buyers will increasingly treat mobility as a managed service rather than an owned asset, particularly for sales fleets, service teams, and multi-location operations. This will strengthen demand for structured leasing products, contract-based fleet refresh cycles, and performance-linked service level agreements (SLAs), favoring operators with strong fleet management capability and nationwide service coverage.
Tourism-Led Rentals Evolve Toward Experience-Driven, Multi-Destination Mobility: Tourism will remain a primary engine of rental demand, but travel patterns are expected to evolve toward longer stays, multi-city itineraries, and higher expectations on vehicle quality and digital convenience. Operators will increasingly design fleets and packages for specific travel purposes—family travel (MPVs/SUVs), premium tourism (luxury rentals and chauffeur services), and intercity mobility with flexible drop-off options. Destinations such as Phuket, Krabi, Chiang Mai, Pattaya, and emerging secondary tourist hubs will continue driving peaks, while improved route connectivity will gradually support deeper penetration in Tier-2 locations.
Integration of EVs, Hybrids, and Sustainability Narratives in Leasing and Urban Rentals: Electric and hybrid vehicles are expected to take a larger share of new fleet additions through 2035, particularly in corporate leasing where total cost of ownership and ESG goals matter more. As charging infrastructure expands and OEM offerings become broader, EVs will increasingly be positioned as a premium-yet-efficient alternative for city driving and corporate mobility. Leasing operators with stronger partnerships across OEMs, charging providers, and service networks will be better placed to scale EV fleets while managing residual value risk and maintenance readiness.
Acceleration of Digital Booking, Dynamic Pricing, and Data-Driven Fleet Optimization: Technology will become a stronger competitive lever, with customers expecting seamless online booking, transparent pricing, fast onboarding, and simplified claims and support processes. Operators will increase reliance on dynamic pricing and demand forecasting to manage seasonality and improve utilization. Fleet telematics, driver behavior analytics, and automated maintenance scheduling will expand, allowing better vehicle uptime, improved customer experience, and tighter control on operating costs—especially for corporate and high-rotation rental fleets.
Thailand Car Rental and Leasing Market Segmentation
By Rental Duration
• Short-term Rentals (Daily / Weekly)
• Medium-term Rentals (Monthly)
• Long-term Leasing (12 months and above)
By Vehicle Type
• Economy & Compact Cars
• Sedans
• SUVs & MPVs
• Vans & Commercial Vehicles
• Luxury & Premium Vehicles
• Electric & Hybrid Vehicles
By Booking & Distribution Channel
• Airport Counters & Airport Partnerships
• City Branch Network / Walk-in Rentals
• Online Direct Booking (Operator Websites/Apps)
• Online Travel Agencies (OTAs) & Aggregators
• Corporate Contracts & Fleet Programs
• Dealer / OEM-Linked Leasing Channels
By Customer Segment
• Leisure & Tourism Customers
• Business Travelers
• Corporate & SME Leasing
• Government & Public Sector
• Others (Logistics, Service Fleets, Platform-linked mobility users)
By Region
• Bangkok Metropolitan Region
• Eastern Economic Corridor (EEC) & Eastern Seaboard
• Northern Thailand (e.g., Chiang Mai cluster)
• Southern Thailand (e.g., Phuket–Krabi cluster)
• Central & Western Thailand (non-Bangkok)
• Northeastern Thailand (Isan)
Players Mentioned in the Report:
• Thai Rent A Car
• Avis Thailand
• Hertz Thailand
• Budget Thailand
• Sixt Thailand
• Chic Car Rent
• ASAP Car Rental & Leasing
• Regional rental operators, local leasing firms, airport concession-linked players, and online aggregators
Key Target Audience
• Car rental operators and franchise networks
• Vehicle leasing and fleet management companies
• Corporate mobility and procurement teams
• Hotels, airlines, OTAs, and travel aggregators
• Airports and transport infrastructure operators
• OEMs, dealerships, and vehicle financiers
• Insurance providers and claims management partners
• EV charging providers and mobility infrastructure developers
• Private equity and mobility-focused investors
Time Period:
Historical Period: 2019–2024
Base Year: 2025
Forecast Period: 2025–2035
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4. 1 Delivery Model Analysis for Car Rental and Leasing including short-term rentals, long-term operating leases, chauffeur-driven services, corporate fleet outsourcing, and digital platform-based rentals with margins, preferences, strengths, and weaknesses
4. 2 Revenue Streams for Car Rental and Leasing Market including daily and weekly rentals, monthly rentals, long-term lease revenues, corporate fleet contracts, insurance add-ons, and ancillary services
4. 3 Business Model Canvas for Car Rental and Leasing Market covering fleet owners, rental operators, leasing companies, OEMs and dealers, financiers, insurers, digital platforms, and service partners
5. 1 Global Car Rental Brands vs Regional and Local Players including international brands, regional ASEAN operators, and domestic Thai rental and leasing companies
5. 2 Investment Model in Car Rental and Leasing Market including fleet acquisition models, operating lease structures, asset-light partnerships, and technology and platform investments
5. 3 Comparative Analysis of Car Rental and Leasing Distribution by Direct Booking and Aggregator or Corporate Channels including airport counters, online platforms, OTAs, and corporate contracts
5. 4 Consumer Transportation Budget Allocation comparing car rentals and leasing versus taxis, ride-hailing services, public transport, and private vehicle ownership with average spend per user per month
8. 1 Revenues from historical to present period
8. 2 Growth Analysis by rental duration and by customer segment
8. 3 Key Market Developments and Milestones including tourism recovery trends, fleet expansion initiatives, EV fleet introductions, regulatory updates, and major partnerships
9. 1 By Market Structure including global brands, regional operators, and local players
9. 2 By Rental Duration including short-term rentals, medium-term rentals, and long-term leasing
9. 3 By Vehicle Type including economy cars, sedans, SUVs and MPVs, vans, luxury vehicles, and electric or hybrid vehicles
9. 4 By Customer Segment including leisure tourists, business travelers, corporates and SMEs, government, and others
9. 5 By Consumer Demographics including age groups, income levels, and domestic versus international users
9. 6 By Booking Channel including airport counters, city branches, online direct platforms, and aggregators
9. 7 By Contract Type including on-demand rentals, subscription-based models, and corporate leasing agreements
9. 8 By Region including Bangkok Metropolitan Region, Eastern Economic Corridor, Northern, Southern, Central, and Northeastern Thailand
10. 1 Consumer Landscape and Cohort Analysis highlighting tourist-led demand, corporate mobility users, and urban versus leisure-driven usage
10. 2 Rental and Leasing Provider Selection and Purchase Decision Making influenced by pricing, vehicle availability, insurance coverage, brand trust, and digital convenience
10. 3 Utilization and ROI Analysis measuring fleet utilization rates, average revenue per vehicle, seasonality impact, and customer lifetime value
10. 4 Gap Analysis Framework addressing fleet mix gaps, pricing volatility, service quality consistency, and digital experience shortcomings
11. 1 Trends and Developments including growth of long-term leasing, EV fleet adoption, subscription mobility models, and digital booking platforms
11. 2 Growth Drivers including tourism recovery, corporate fleet outsourcing, urban mobility challenges, and infrastructure expansion
11. 3 SWOT Analysis comparing global brand scale versus local market agility and cost competitiveness
11. 4 Issues and Challenges including seasonality, fleet financing costs, residual value risk, regulatory compliance, and margin pressure
11. 5 Government Regulations covering vehicle registration, taxation, insurance norms, airport concession policies, and EV-related incentives in Thailand
12. 1 Market Size and Future Potential of electric and hybrid vehicles in rental and leasing fleets
12. 2 Business Models including EV leasing, corporate green fleet programs, and mixed ICE-EV fleet strategies
12. 3 Delivery Models and Type of Solutions including charging partnerships, telematics, and energy management solutions
15. 1 Market Share of Key Players by revenues and by fleet size
15. 2 Benchmark of 15 Key Competitors including international rental brands, regional players, domestic Thai operators, and digital platforms
15. 3 Operating Model Analysis Framework comparing global rental models, leasing-led fleet management models, and platform-driven aggregation models
15. 4 Gartner Magic Quadrant positioning global leaders and regional challengers in car rental and leasing services
15. 5 Bowman’s Strategic Clock analyzing competitive advantage through service differentiation versus price-led mass rental strategies
16. 1 Revenues with projections
17. 1 By Market Structure including global brands, regional operators, and local players
17. 2 By Rental Duration including short-term rentals, medium-term rentals, and long-term leasing
17. 3 By Vehicle Type including economy, SUV/MPV, luxury, and electric vehicles
17. 4 By Customer Segment including tourists, corporates, and government users
17. 5 By Consumer Demographics including age and income groups
17. 6 By Booking Channel including direct, aggregator, and corporate channels
17. 7 By Contract Type including on-demand, subscription-based, and long-term lease agreements
17. 8 By Region including Bangkok, EEC, Northern, Southern, Central, and Northeastern Thailand
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
We begin by mapping the complete ecosystem of the Thailand Car Rental and Leasing Market across demand-side and supply-side entities. On the demand side, entities include international and domestic tourists, business travelers, corporates (MNCs and local enterprises), SMEs, government and public-sector users, hotels and travel operators with mobility tie-ups, logistics and service companies requiring fleets, and event-driven mobility users. Demand is further segmented by use case (leisure travel, airport transfers, intercity travel, corporate mobility, last-mile service fleets), rental duration (daily/weekly, monthly, multi-year operating leases), and procurement model (walk-in/airport counter, online booking, OTA/aggregator, corporate contract, tender-based procurement).
On the supply side, the ecosystem includes national car rental brands, domestic leasing and fleet management companies, regional rental operators, airport concession partners, online platforms and aggregators, dealerships and OEM-linked leasing channels, financiers and vehicle lenders, insurance companies and claims partners, maintenance/repair networks, telematics and fleet tracking providers, and charging infrastructure partners for EV fleets. From this mapped ecosystem, we shortlist 6–10 leading rental and leasing players and a representative set of regional operators based on fleet size, airport presence, corporate portfolio depth, service network coverage, technology capability, and penetration across key tourism and industrial corridors. This step establishes how value is created and captured across fleet procurement, financing, utilization management, distribution, customer onboarding, servicing, and vehicle remarketing.
Step 2: Desk Research
An exhaustive desk research process is undertaken to analyze the Thailand market structure, demand drivers, and segment behavior. This includes reviewing tourism and travel patterns, airport passenger flows, domestic intercity movement trends, corporate fleet outsourcing adoption, and industrial corridor expansion that influences leasing demand. We assess customer preferences around convenience, vehicle type, insurance packages, deposit norms, driver requirements, and the role of digital booking and pricing transparency. Company-level analysis includes review of fleet mix, branch and airport coverage, booking channel strategy, corporate contract models, maintenance and replacement policies, and ancillary revenue models (insurance upsell, add-ons, cross-border packages where applicable).
We also examine the regulatory and operating environment shaping rentals and leases, including vehicle registration and tax treatment for fleets, insurance requirements, airport concession rules, and policy initiatives supporting EV adoption. The outcome of this stage is a comprehensive industry foundation that defines the segmentation logic and creates the assumptions needed for market estimation and future outlook modeling.
Step 3: Primary Research
We conduct structured interviews with car rental companies, vehicle leasing and fleet management firms, airport counter operators, OTA/aggregator partners, corporate procurement and admin managers, hotel/travel partners, vehicle dealers, insurers, and maintenance network stakeholders. The objectives are threefold: (a) validate assumptions around demand concentration by region and channel, seasonality patterns, and customer mix, (b) authenticate segment splits by rental duration, vehicle type, customer segment, and booking/distribution channel, and (c) gather qualitative insights on pricing behavior, utilization thresholds, fleet renewal cycles, accident and claims trends, customer pain points, and the operational constraints related to vehicles, staffing, and servicing.
A bottom-to-top approach is applied by estimating active fleet counts, average revenue per vehicle by segment, and utilization rates across peak and off-peak periods, which are aggregated to develop the overall market view. In selected cases, disguised buyer-style interactions are conducted with operators and aggregators to validate field-level realities such as deposit policies, insurance inclusions/exclusions, hidden add-ons, peak-season pricing spikes, and typical customer friction points at pickup and return.
Step 4: Sanity Check
The final stage integrates bottom-to-top and top-to-down approaches to cross-validate the market view, segmentation splits, and forecast assumptions. Demand estimates are reconciled with macro indicators such as tourism recovery trajectories, airport throughput, GDP and service-sector growth, corporate hiring and mobility budgets, industrial corridor development, and vehicle financing conditions. Assumptions around utilization, fleet acquisition costs, residual value behavior, and insurance/claims costs are stress-tested to understand their impact on profitability and fleet expansion.
Sensitivity analysis is conducted across key variables including inbound tourism growth intensity, fuel price trends, EV adoption pace, financing rate changes, and competitive pricing pressure from aggregators and regional operators. Market models are refined until alignment is achieved between fleet supply expansion capacity, channel throughput, and demand-side travel and corporate mobility pipelines, ensuring internal consistency and robust directional forecasting through 2035.
FAQs
01 What is the potential for the Thailand Car Rental and Leasing Market?
The Thailand car rental and leasing market holds strong potential, supported by sustained inbound and domestic tourism, increasing preference for flexible mobility solutions, and the steady shift of corporates toward operating leases and outsourced fleet management. Rentals remain a key mobility option for tourism-heavy regions and airport-driven demand, while leasing is expected to expand faster in value as companies prioritize predictable mobility costs, bundled maintenance, and administrative simplicity. As EV penetration rises and digital booking becomes the default purchase behavior, higher-value fleet solutions and service-driven differentiation are expected to strengthen market expansion through 2035.
02 Who are the Key Players in the Thailand Car Rental and Leasing Market?
The market features a combination of international rental brands, strong domestic car rental companies, and established leasing and fleet management providers. Competition is shaped by fleet scale, airport and tourism corridor presence, corporate contract strength, service network coverage, technology-enabled booking and fleet optimization, and the ability to manage claims, maintenance, and remarketing effectively. Aggregators and digital platforms increasingly influence customer acquisition and pricing dynamics, especially for short-term rentals.
03 What are the Growth Drivers for the Thailand Car Rental and Leasing Market?
Key growth drivers include tourism normalization and diversification, rising corporate adoption of asset-light fleet models, greater intercity travel and leisure mobility demand, and increasing customer reliance on online booking platforms. Additional growth momentum comes from improvements in transport infrastructure, expansion of industrial zones and business corridors, and growing corporate focus on ESG—supporting gradual EV integration into lease fleets. The ability of leading operators to deliver predictable service quality, transparent pricing, and efficient fleet availability continues to reinforce adoption across customer segments.
04 What are the Challenges in the Thailand Car Rental and Leasing Market?
Challenges include demand seasonality and off-peak utilization pressure, rising vehicle acquisition and financing costs, residual value risk (especially for newer technology vehicles), and operational friction related to insurance, deposits, and claims handling. Competitive pricing pressure from digital aggregators can compress margins, particularly for short-term rentals. In major cities, congestion and parking constraints can limit certain urban use cases, while in tourist corridors, service consistency and risk management become critical to protect brand reputation and profitability.