Thailand Logistics and Warehousing Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Segments (Freight Forwarding, Warehousing, and Express Logistics), By End-User Industries, By Mode of Transport, By Warehousing Space, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0198
- Region: Asia
- Published on: June 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Thailand Logistics and Warehousing Market Outlook to 2029 - By Market Segments (Freight Forwarding, Warehousing, and Express Logistics), By End-User Industries, By Mode of Transport, By Warehousing Space, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the logistics and warehousing sector in Thailand. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation, trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer level profiling, issues and challenges, and comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the Thai logistics and warehousing market. The report concludes with future market projections based on industry revenue, by segment, transport mode, region, and success case studies highlighting major opportunities and key risks.
Thailand Logistics and Warehousing Market Overview and Size
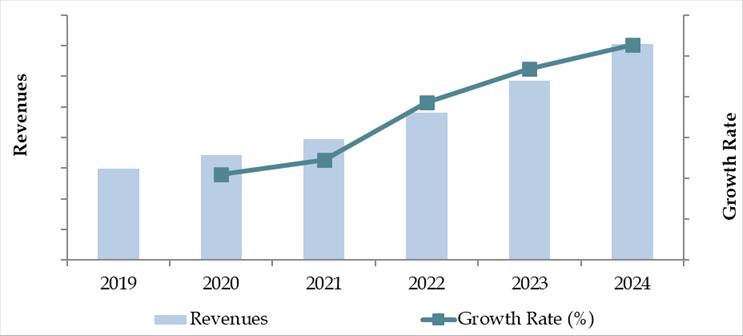
The Thailand logistics and warehousing market was valued at THB 720 Billion in 2023, propelled by the country’s role as a regional trade hub, the rise of e-commerce, and infrastructural investments under the Eastern Economic Corridor (EEC) initiative. Key players such as Kerry Express, SCG Logistics, DHL Thailand, Linfox, and Thailand Post dominate the market with their extensive networks, diversified offerings, and technology-driven solutions.
In 2023, SCG Logistics expanded its warehouse footprint in the Eastern region to cater to growing demand from manufacturing and e-commerce clients. Bangkok and Chonburi emerged as high-demand zones due to proximity to industrial estates and key seaports.
Market Size for Thailand Logistics and Warehousing Industry on the Basis of Revenue in USD Billion, 2018-2024
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Thailand Logistics and Warehousing Market:
Strategic Location and Trade Integration: Thailand’s central location in ASEAN and free trade agreements with neighboring countries have enabled it to become a logistics hub, facilitating cross-border trade and multimodal transport operations.
E-Commerce Expansion: Online retail is driving demand for last-mile delivery and real-time inventory solutions. In 2023, e-commerce shipments grew by over 20%, spurring investments in fulfillment centers and integrated logistics services.
Infrastructure Development: Ongoing projects under the EEC plan such as double-track railways, port upgrades, and smart logistics parks are enhancing connectivity and reducing lead times, making Thailand an attractive location for supply chain operations.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for Thailand Logistics and Warehousing Market
Fragmented Supply Chain and Operational Inefficiencies: A major challenge in Thailand’s logistics landscape is the fragmentation of supply chain activities, especially among small and medium enterprises (SMEs). In 2023, nearly 60% of logistics providers in Thailand operated with outdated systems, leading to poor coordination, high lead times, and increased costs. This inefficiency contributes to logistics expenses accounting for approximately 13.8% of Thailand’s GDP, which is higher than regional peers like Singapore.
Labour Shortages and Skills Gap: The logistics sector faces a notable shortage of skilled workers in areas such as inventory control, supply chain analytics, and transport optimization. Industry estimates suggest that over 25% of logistics firms reported challenges in finding qualified personnel in 2023, particularly in rural and industrial belt regions.
Infrastructure Bottlenecks: Despite heavy investments, some infrastructure projects have faced delays due to bureaucratic hurdles and land acquisition issues. For instance, Phase 2 of the double-track railway project saw a six-month delay in 2023, disrupting planned multimodal integration timelines for freight corridors linking to Laos and Cambodia.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market
Logistics Development Master Plan (2023–2027): The Thai government has implemented a national strategy to reduce logistics costs to 12% of GDP by 2027 through digitalization, enhanced multimodal transport systems, and better customs procedures. Under this initiative, over THB 200 Billion has been allocated for logistics infrastructure upgrades.
Eastern Economic Corridor (EEC) Special Zone Incentives: The EEC initiative offers tax incentives, customs exemptions, and land lease benefits to logistics operators setting up within designated industrial zones. In 2023 alone, logistics-related investment pledges in the EEC totaled THB 90 Billion, driven by demand for regional distribution hubs.
Mandatory Digital Customs Filing: In 2022, Thailand enforced mandatory electronic customs declarations for all importers and exporters, improving processing times and transparency. By 2023, 95% of customs filings were processed digitally, reducing average cargo clearance time by over 30%.
Thailand Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
By Market Structure: The logistics market in Thailand is largely dominated by local and regional players, particularly SMEs, due to their strong geographic penetration and competitive pricing. These operators are preferred by domestic manufacturers and retailers for their flexibility and localized knowledge. However, organized third-party logistics (3PL) and multinational providers such as DHL, CEVA Logistics, and SCG Logistics have carved out a significant share, especially in sectors like electronics, automotive, and international freight. These organized players benefit from superior infrastructure, digital tracking systems, and global networks that attract large enterprises seeking reliability and scalability.
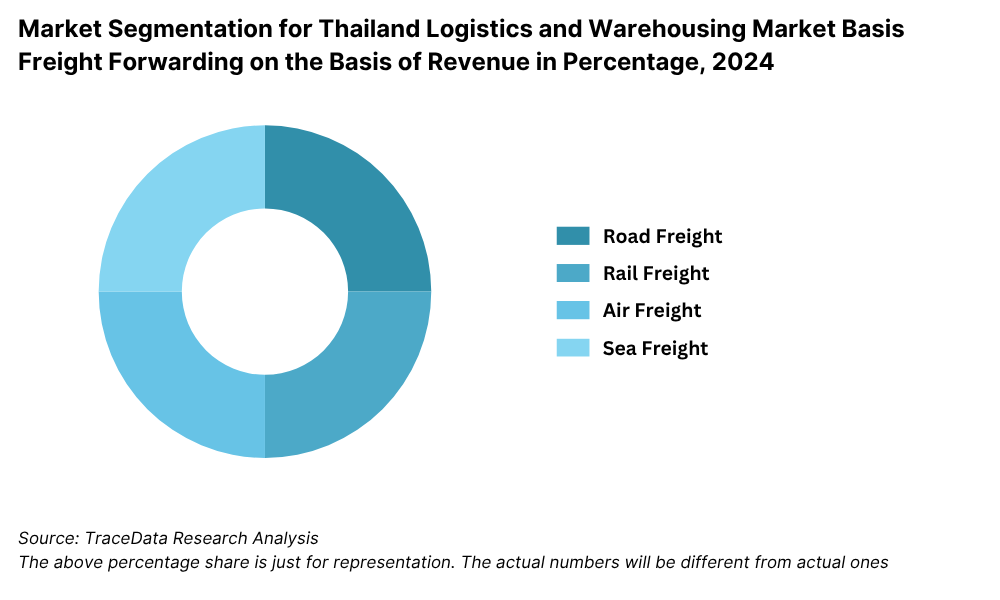
By Mode of Transport:Road transport continues to dominate the logistics landscape, accounting for the bulk of domestic movement, particularly for FMCG and retail goods, due to Thailand’s extensive road network. Rail freight is growing in importance following infrastructure developments under the EEC initiative, offering a cost-effective solution for bulk goods over longer distances. Air freight, while niche, is used extensively for high-value, time-sensitive goods such as electronics and perishables. Maritime logistics plays a critical role in international trade, with Laem Chabang Port serving as a major gateway for containerized cargo.
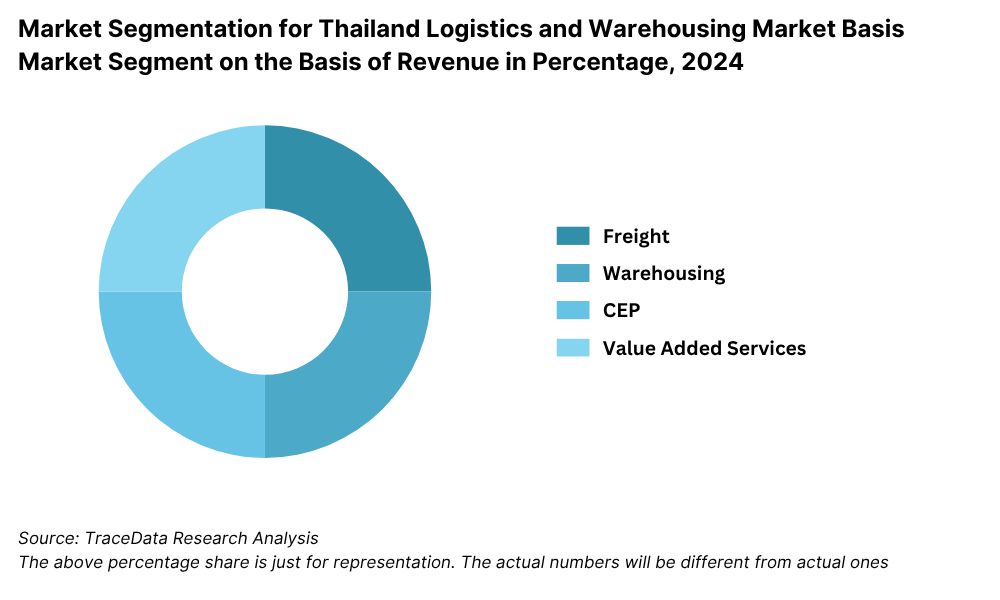
By End-User Industry:Retail and e-commerce emerged as the top end-users, driven by a surge in online sales and last-mile delivery requirements. Automotive and electronics sectors also contribute significantly due to the need for just-in-time inventory and international logistics. Healthcare and pharmaceuticals have shown notable growth in demand for temperature-controlled warehousing and fast-track distribution post-pandemic. The food & beverage industry is heavily reliant on cold storage and urban distribution networks, particularly in metropolitan areas.
Competitive Landscape in Thailand Logistics and Warehousing Market
The Thailand logistics and warehousing market is moderately consolidated, with a few dominant players holding significant market share, particularly in organized freight forwarding and contract logistics. The rise of e-commerce and regional trade has also facilitated the entry of new-age logistics firms and tech-based aggregators, intensifying competition. Key players include Kerry Express, SCG Logistics, DHL Thailand, Linfox, Flash Express, and Best Express.
| Company Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
| Thailand Post Co., Ltd. | 2003 (origin: 1883) | Bangkok, Thailand |
| SCG Logistics Management Co., Ltd. | 2000 | Bangkok, Thailand |
| Nim See Seng Transport 1988 Co., Ltd. | 1988 | Bangkok, Thailand |
| JWD InfoLogistics Public Co., Ltd. | 1979 | Bangkok, Thailand |
| Schenker (Thai) Ltd. | 1872 (TH: ~1970s) | Essen, Germany |
| Kerry Express (Thailand) Ltd. | 2006 | Hong Kong (TH HQ: Bangkok) |
| CJ Logistics (Thailand) Co., Ltd. | 1930 (TH: ~2000s) | Seoul, South Korea |
| DHL Supply Chain (Thailand) Ltd. | 1969 (TH: ~1973) | Bonn, Germany |
| Kuehne + Nagel (Thailand) Ltd. | 1890 (TH: ~1990s) | Schindellegi, Switzerland |
| Yusen Logistics (Thailand) Co., Ltd. | 1955 (TH: ~1988) | Tokyo, Japan |
| Nippon Express (Thailand) Co., Ltd. | 1937 (TH: ~1970s) | Tokyo, Japan |
| Agility Logistics (Thailand) Ltd. | 1979 (TH: ~2005) | Kuwait City, Kuwait |
| CEVA Logistics (Thailand) Ltd. | 2006 (TH: ~2007) | Marseille, France |
| FedEx Express Thailand | 1971 (TH: ~1980s) | Memphis, USA |
| UPS Parcel Delivery Service Ltd. (Thailand) | 1907 (TH: ~1990s) | Atlanta, USA |
| Maersk Thailand Ltd. | 1904 (TH: ~1980s) | Copenhagen, Denmark |
| Siam Shipping (a division of DocShipper) | 2015 | Bangkok, Thailand / Marseille, France |
ome of the Recent Competitor Trends and Key Information Include:
Kerry Express: As a leader in last-mile delivery, Kerry Express handled over 350 million parcels in 2023. The company expanded its express delivery services to cover 99% of Thailand’s postal codes and launched eco-friendly packaging solutions to meet sustainability goals.
SCG Logistics: A key player in B2B contract logistics, SCG Logistics reported a 20% increase in warehousing demand in the Eastern Economic Corridor (EEC) zones in 2023. The company has invested in automated sorting and inventory systems to improve throughput and operational efficiency.
DHL Thailand: DHL strengthened its market presence by opening a new multi-temperature warehouse in Chachoengsao and expanding its cross-border trucking services to Laos and Cambodia. In 2023, DHL reported a 12% YoY increase in freight forwarding revenue in Thailand.
Linfox: Linfox operates large-scale warehousing and transport operations, especially in the FMCG and automotive sectors. In 2023, the company introduced an AI-powered route optimization system in Thailand, reducing fuel usage by 14%.
Flash Express: One of Thailand’s fastest-growing logistics startups, Flash Express saw parcel volumes grow by 35% in 2023. It expanded its delivery fleet and partnered with Chinese e-commerce platforms to facilitate cross-border logistics.
Best Express: Targeting Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities, Best Express has focused on regional penetration and built over 2,000 drop-off points nationwide. In 2023, it launched a same-day delivery service in Bangkok and Chiang Mai to compete with incumbents.
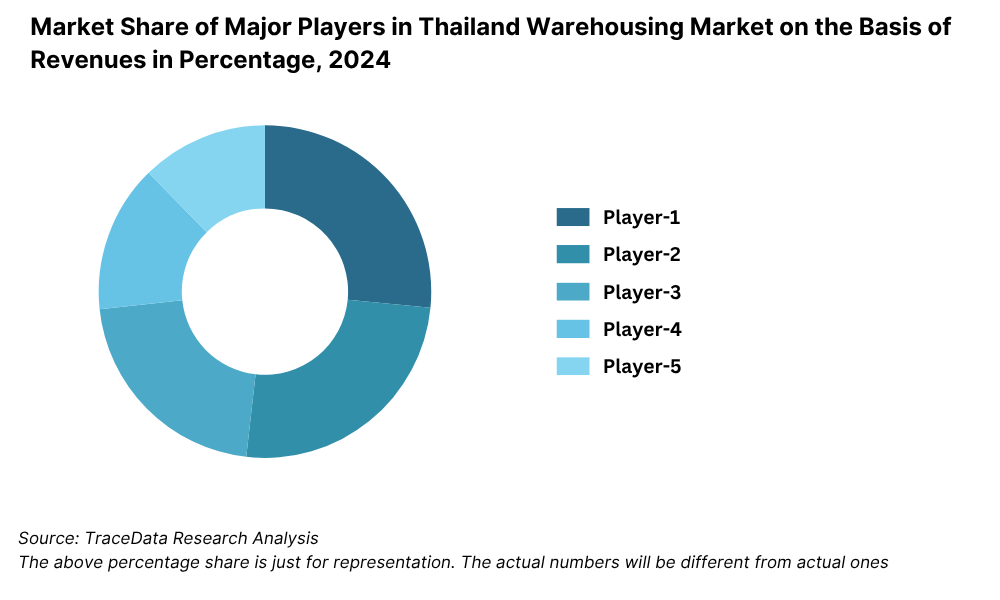
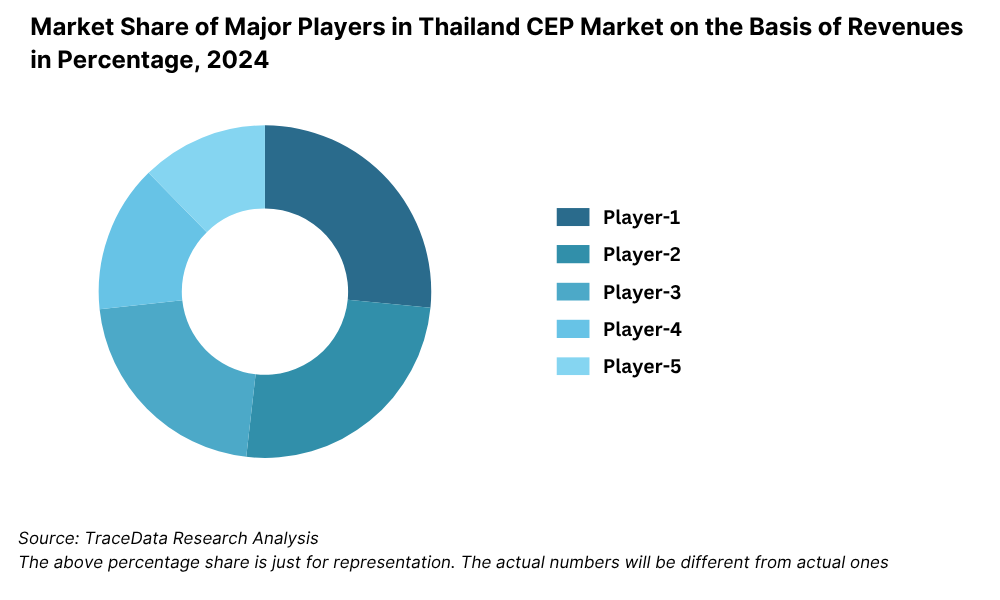
What Lies Ahead for Thailand Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Thailand logistics and warehousing market is projected to witness robust growth by 2029, driven by infrastructure upgrades, regional trade integration, and the booming e-commerce sector. The market is expected to record a healthy CAGR during the forecast period, underpinned by technological advancement and strategic policy support.
Expansion of E-Commerce and Last-Mile Delivery: The rapid growth of Thailand’s digital economy is set to further drive demand for last-mile delivery and urban warehousing. E-commerce penetration is expected to exceed 60% by 2029, with major players investing in hyperlocal fulfillment hubs and smart delivery systems to cater to evolving consumer expectations.
Development of Integrated Logistics Parks: The government’s continued investment under the Eastern Economic Corridor (EEC) will accelerate the development of integrated logistics zones. These hubs will support multimodal transport, facilitate cross-border trade, and offer plug-and-play infrastructure to logistics operators—particularly in Chonburi, Rayong, and Chachoengsao.
Adoption of Automation and AI: Logistics firms in Thailand are expected to increasingly adopt automation, robotics, and AI-driven route optimization to boost efficiency. By 2029, it is estimated that over 50% of modern warehouses will be semi- or fully automated, reducing operational costs and enhancing inventory accuracy.
Rise of Green and Sustainable Logistics: Sustainability is becoming a core focus, with companies expected to adopt electric delivery vehicles, solar-powered warehouses, and carbon tracking systems. Thailand’s commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 will drive regulatory support and incentivize green logistics practices.
Future Outlook and Projections for Thailand Logistics and Warehousing Market on the Basis of Revenues in USD Billion, 2024-2029
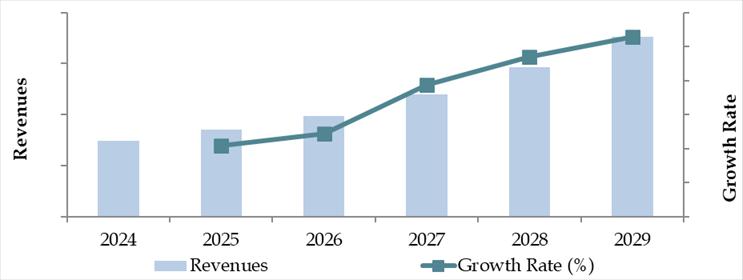
Thailand Logistics and Warehousing Market Segmentation
By Market Structure:
Freight Forwarding Companies
Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Providers
Fourth-Party Logistics (4PL) Providers
Express Delivery Services
Contract Logistics Providers
Organized Sector
Unorganized/Traditional Operators
Cold Chain Logistics Providers
By Mode of Transport:
Road Transport
Rail Transport
Air Freight
Sea Freight / Maritime Logistics
Multimodal Transport
By End-User Industry:
E-commerce and Retail
Automotive
Food & Beverage
Electronics and Electricals
Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
Industrial Manufacturing
Agriculture and Perishables
By Type of Warehousing Space:
Grade A Warehouses
Grade B & C Warehouses
Cold Storage Facilities
E-commerce Fulfillment Centers
Built-to-Suit (BTS) Warehouses
By Region:
Central Thailand (incl. Bangkok)
Eastern Thailand (incl. EEC)
Northern Thailand
Southern Thailand
Northeastern Thailand
Players Mentioned in the Report:
Freight Forwarding Companies
Dynamic Air Cargo
Transpo Logistics
World Air Logistics
Triple i Logistics
NRS Logistics
Eagles Air & Sea
Pilot Air Cargo
Embassy Freight (Thailand)
MOL Logistics
Rhenus Thailand
Warehousing Companies
DB Schenker (Thailand)
Kuehne + Nagel (Thailand)
Rhenus Thailand
Integrated Logistics Services (ILS)
SCGJWD Logistics
E‑Commerce Logistics Companies
SIAM Shipping / DocShipper
Pakman Fulfillment
Sokochan
Aden (Ascend Group)
JWD InfoLogistics (Fuze Post cold‑chain express)
Express Logistics Companies
DHL Express
FedEx
UPS
SF Express
J&T Express
Key Target Audience:
Logistics and Warehousing Companies
E-commerce Companies and Aggregators
Industrial Estate Developers
Government and Regulatory Authorities (e.g., Ministry of Transport, BOI)
Technology Providers for Logistics Automation
Private Equity and Infrastructure Investors
Research and Consulting Firms
Time Period:
Historical Period: 2018–2023
Base Year: 2024
Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4.1. Macroeconomic framework for Thailand Including GDP (2018-2024), GDP Growth (2018-2024), GDP Contribution by Sector
4.2. Logistics Sector Contribution to GDP and how the contribution has been changing in the historical assessment
4.3. Ease of Doing Business in Thailand
4.4. LPI Index of Thailand and Improvements in the last 10-15 Years
4.5. Custom Procedure and Custom Charges in Thailand Logistics market
5.1. Landscape of Investment Parks and Free Trade Zones in Thailand
5.2. Current Scenario for Logistics Infrastructure in Thailand
5.3. Road Infrastructure in Thailand including Road Network, Toll Charges and Toll Network, Major Goods Traded through Road, Major Flow Corridors for Road (Inbound and Outbound)
5.4. Air Infrastructure in Thailand including Total Volume Handled, FTK for Air Freight, Major Inbound and Outbound Flow Corridors, Major Goods traded through Air, Number of Commercial and passenger Airports, Air Freight Volume by Ports and other Parameters
5.5. Sea Infrastructure in Thailand including Total Volume Handled, FTK for Sea Freight, Major Inbound and Outbound Flow Corridors, Major Goods Traded through Sea, Number of Ports for Coastal and Ocean Freight, Number of Vessels, Sea Freight Volume by Ports and other Parameters
5.6. Rail Infrastructure in Thailand including Total Volume Handled, FTK for Rail Freight, Major Inbound and Outbound Flow Corridors, Major Goods Traded through Rail and others
6.1. Basis Revenues, 2018-2024P
7.1. By Segment (Freight Forwarding, Warehousing, CEP and Value-Added Services), 2018-2024P
7.2. By End User Industries, 2018-2024P
8.1. Market Overview and Genesis
8.2. Thailand Freight Forwarding Market Size by Revenues, 2018-2024P
8.3. Thailand 3PL Freight Forwarding Market Segmentation, 2018-2024P
8.3.1. By Mode of Freight Transport (Road, Sea, Air and Rail), 2018-2024P
8.3.1.1. Price per FTK for Road/Air/Sea and Rail in Thailand
8.3.1.2. Road Freight (Domestic and International Volume, FTK and Revenue; Number of Registered Vehicles)
8.3.1.3. Road Freight Domestic and International Corridors
8.3.1.4. Ocean Freight (Domestic and International Volume, FTK and Revenue; Volume by Commodity; Sea Ports Key Statistics)
8.3.1.5. Air Freight (Domestic and International Volume, FTK and Revenue)
8.3.1.6. Rail Freight (Domestic and International Volume, FTK and Revenue; Volume by Commodity and Region)
8.3.1.7. Export-Import Scenario (Value by Mode of Transport, Commodity and Country; Volume by Principal Commodities)
8.3.2. By Intercity Road Freight Corridors, 2018-2024P
8.3.3. By International Road Freight Corridors, 2018-2024P
8.3.4. By End User (Industrial, FMCG, F&B, Retail and Others), 2018-2024P
8.4. Snapshot of Freight Truck Aggregators in Thailand Including Company Overview, USP. Business Strategies, Future Plans, Business Model, Number of Fleets, Margins/Commission, Number of Booking, Major Clients, Average Booking Amount, Major Routes and others
8.5. Competitive Landscape in Thailand Freight Forwarding Market, 2021
8.5.1. Heat Map of Major Players in Thailand Freight Forwarding on the Basis of Service offering
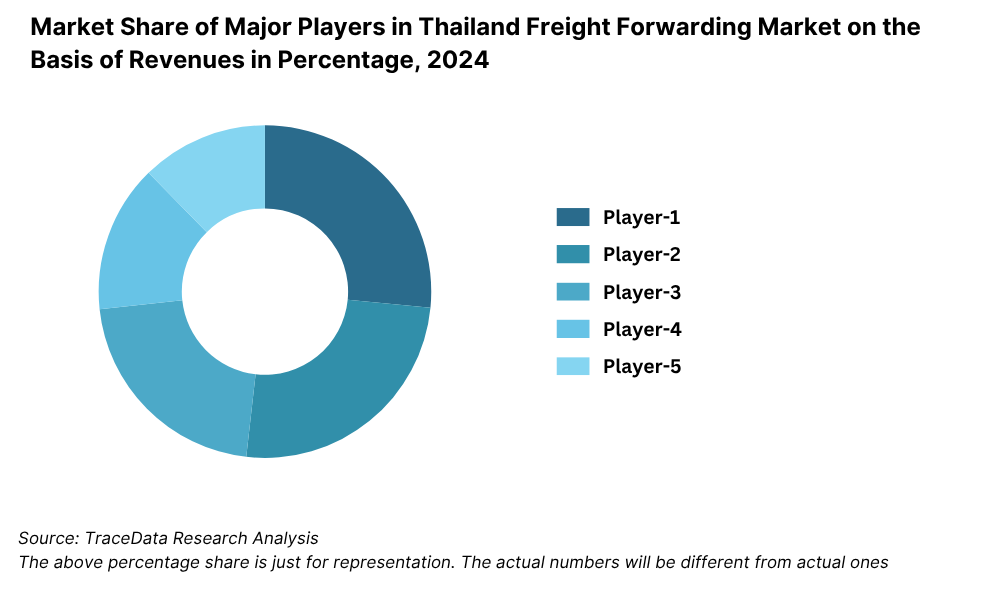
8.5.2. Market Share of Maior Players in Thailand Freight Forwarding Market, 2023
8.5.3. Cross Comparison of Major Players in Freight Forwarding Companies on the Basis of Parameters including Volume of Road Freight, Inception Year, Number of Fleets (Owned and Subcontracted), Fleets by Type, Occupancy Rate, Number of Employees, Major Route Network, Major Clients, Revenues, Volume of Sea Freight, Volume of Air Freight, USP, Business Strategy, Technology, (2023)
8.6. Thailand 3PL Freight Forwarding Future Market Size by Revenues, 2025-2029
8.7. Thailand Freight Forwarding Market Segmentation, 2025-2029
8.7.1. Future Market Segmentation by Mode of Freight Transport (Road, Sea, Air and Rail), 2025-2029
8.7.2. Future Market Segmentation by International Road Freight Corridors (China, Thailand and Thailand), 2025-2029
8.7.3. Future Market Segmentation by End User (Industrial, FMCG, F&B, Retail and Others), 2025-2029
9.1. Market Overview and Genesis
9.2. Value Chain Analysis in Thailand Warehousing Market including entities, margins, role of each entity, process flow, challenges and other aspects
9.3. Thailand Warehousing Market Size on the Basis of Revenues and Warehousing Space, 2018-2024P
9.4. Thailand 3PL Warehousing Segmentation
9.4.1. Thailand Warehousing Revenue by Business Model (Industrial/Retail, ICD/CFS and Cold Storage), 2018-2024P
9.4.2. Thailand Warehousing By Type of Warehouse (General, Open Yard, Freezer/Chiller, Ambient and Bonded Warehouses), 2018-2024P
9.4.3. Thailand Warehousing Revenue by End User (Industrial & Construction, FMCG, Retail, Food & Beverage and Others), 2018-2024P
9.4.4. 3PL Warehousing Space by Region, 2024P
9.5. Competitive Landscape in Thailand 3PL Warehousing Market
9.5.1. Market share of Top 10 Companies in Thailand Warehousing Market, 2023
9.5.2. Cross Comparison of Top 10 3PL Warehousing Companies on the Basis of Parameters including Company Overview, USP, Business Strategy, Future Plans, Technology, Revenues from Warehousing, Number of Warehouses, Warehousing Space, Location of Warehouses, Type of Warehouses, Occupancy Rate, Rental Rates, Clients and others, (2023)
9.6. Thailand Warehousing Future Market Size on the Basis of Revenues, 2025-2029
9.7. Thailand Warehousing Market Future Segmentation
9.7.1. Thailand Warehousing Revenue by Business Model (Industrial/Retail, ICD/CFS and Cold Storage), 2025-2029
9.7.2. Thailand Warehousing Revenue By Type of Warehouse (General, Open Yard, Freezer/Chiller, Ambient and Bonded Warehouses), 2025-2029
9.7.3. Thailand Warehousing Revenue by End User (Industrial & Construction, FMCG, Retail, Food & Beverage and Others), 2025-2029
10.1. Market Overview and Genesis
10.2. Value Chain Analysis in Thailand CEP Market including entities, margins, role of each entity, process flow, challenges and other aspects
10.3. Revenue Composition and Contribution Between First Mile/Mid Mile and Last Mile Delivery-Analysis for Domestic and International Shipments
10.4. Thailand CEP Market Size on the Basis of Revenues and Shipments, 2018-2024P
10.5. Thailand CEP Market Segmentation, 2021
10.5.1. Segmentation by Mails and Documents, E-Commerce Shipments and Express Cargo, 2023-2024P
10.5.2. Segmentation by International and Domestic Express, 2023-2024P
10.5.3. Segmentation by B2B, B2C and C2C, 2023-2024P
10.5.4. Segmentation by Period of Delivery, 2023-2024P
10.6. Competitive Landscape in 3PL Market, 2021
10.6.1. Overview and Genesis, Market Nature, Market Stage and Major Competing Parameters
10.6.2. Market Share of Companies in Thailand CEP Market on the Basis of Revenues/Number of Shipments, 2023
10.6.3. Market Share of Top 5 Companies in Thailand E-Commerce Shipment Market on the Basis of Revenues/Number of Shipments, 2023
10.6.4. Cross Comparison of Top 10 Thailand CEP Companies on the Basis of Parameters including Company Overview, USP, Business Strategy, Future Plans, Technology, Number of last Mile Delivery Shipments, Revenues, Major Clients, Number of Fleets, Number of Employees, Number of Riders, Number of Pin Code Served, Major Service Offering and others
10.7. Thailand CEP Market Size on the Basis of Revenues and Shipments, 2025-2029
10.8. Thailand CEP Market Segmentation
10.8.1. Segmentation by Mails and Documents, E-Commerce Shipments and Express Cargo, 2025-2029
10.8.2. Segmentation by International and Domestic Express, 2025-2029
10.8.3. Segmentation by B2B, B2C and C2C, 2025-2029
10.8.4. Segmentation by Period of Delivery, 2025-2029
11.1. Customer Cohort Analysis and End User Paradigm for Different Industry Verticals under Logistics Sector (Telecommunications, FMCG, Automotive, Apparel, F&B, Construction and Pharmaceuticals)
11.2. Understanding on Logistics Spend by End User, 2023-2024P
11.3. End User Preferences in terms of In-House or Outsourcing Logistics Services and Reason for Selection; Segregate this by Size of Company on the Basis of Revenues
11.4. Major Logistics Company who are Specialized in Serving Each Type of End User (Telecommunications, FMCG, Apparel, F&B, Construction and Pharmaceuticals)
11.5. Detailed Landscape of Each End Users across Parameters including Major Products Manufactured and Traded, Emerging Products, Type of Services Required, and Type of Services Outsourced, Major Companies, Contract Duration, Likelihood to Recommend, Market Orientation, Major Clusters, Type of Sourcing Preference, Pain Points, Facilities/Services Required, Future Outlook. Market Size for End User Industry Vertical with Growth Rate, 2018-2024P
12.1. Basis Revenues, 2025-2029
13.1. By Segment (Freight Forwarding, Warehousing, CEP and Value-Added Services), 2025-2029
13.2. By End User Industries, 2025-2029
13.3. Recommendation
13.4. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand-side (e.g., e-commerce, retail, manufacturing, FMCG, pharma) and supply-side (e.g., 3PLs, freight forwarders, warehousing providers, last-mile delivery firms) entities within the Thailand Logistics and Warehousing Market.
Based on this ecosystem, we shortlist 6–8 leading logistics and warehousing companies in Thailand, selected using parameters such as revenue size, warehouse capacity, fleet size, service integration, and digital adoption.
Sourcing is carried out using industry articles, news portals, investor presentations, and proprietary databases to conduct desk research and compile relevant industry-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
A rigorous secondary research process is undertaken to gather insights from public and private domain sources including Ministry of Transport (Thailand), BOI publications, World Bank Logistics Performance Index, trade associations (e.g., Thai Logistics Association), and commercial reports.
Key variables studied include total logistics market size, segmentation by transport and warehousing, infrastructure investments, cost structures, and pricing trends.
We complement this with detailed analysis of company-level data through annual reports, press releases, case studies, and third-party research to build a comprehensive industry landscape.
Step 3: Primary Research
We conduct in-depth interviews with senior executives from leading logistics firms, industry consultants, supply chain heads of large corporates, and government-affiliated stakeholders.
These interviews help validate desk research insights, uncover strategic priorities, and gather ground-level perspectives on infrastructure gaps, technology adoption, and competitive dynamics.
To validate volume and capacity information, we conduct disguised interviews with logistics operators as mystery clients, inquiring about fleet size, warehousing footprint, service costs, and technology usage.
A bottom-up approach is used to build market estimates by aggregating revenue and volume data across segments and regions. This is further cross-validated using a top-down triangulation method.
Step 4: Sanity Check
Final outputs are validated using top-down and bottom-up modeling techniques, market ratio analyses, and macroeconomic alignment.
We also conduct peer benchmarking across ASEAN countries and apply historical growth trends and policy-driven forecasts to ensure data accuracy and reliability.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Thailand Logistics and Warehousing Market?
The Thailand logistics and warehousing market is expected to witness substantial growth, reaching a projected valuation of THB 1,200 Billion by 2029. This growth is supported by the country's strategic geographic location, robust infrastructure development under the Eastern Economic Corridor (EEC), and booming e-commerce and export sectors. The increasing demand for integrated logistics solutions and smart warehousing is set to further unlock market potential.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Thailand Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Key players in the Thailand logistics and warehousing industry include Kerry Express, SCG Logistics, DHL Thailand, Flash Express, Linfox, and Best Express. These companies are leading due to their expansive service networks, investments in digital infrastructure, and sector-specific logistics capabilities across automotive, retail, FMCG, and healthcare.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Thailand Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Major growth drivers include increased cross-border trade within ASEAN, rapid e-commerce adoption, rising demand for cold chain and last-mile logistics, and government-led infrastructure investments. Additionally, digital transformation in logistics operations—such as automation, AI, and real-time tracking—are improving service quality and scalability across the supply chain.
4. What are the Challenges in the Thailand Logistics and Warehousing Market?
Key challenges include a fragmented market structure with many small, unorganized players, infrastructure delays, and a shortage of skilled logistics professionals. Regulatory complexity, fluctuating fuel prices, and rising environmental standards also pose operational challenges. Moreover, ensuring supply chain resilience and cold storage capacity in remote regions remains a pressing concern.