UAE Logistics Market Outlook to 2035
By Service Type, By Transport Mode, By End-Use Industry, By Contract Structure, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0496
- Region: Middle East
- Published on: January 2026
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “UAE Logistics Market Outlook to 2035 – By Service Type, By Transport Mode, By End-Use Industry, By Contract Structure, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the logistics industry in the United Arab Emirates. The report covers an overview and genesis of the market, overall market size in terms of value, detailed market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory and trade facilitation landscape, buyer-level demand profiling, key issues and challenges, and competitive landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the UAE logistics market.
The report concludes with future market projections based on trade volume growth, e-commerce penetration, industrial diversification, free-zone driven investment, infrastructure capacity expansion, regional transshipment dynamics, cause-and-effect relationships, and case-based illustrations highlighting the major opportunities and cautions shaping the market through 2035.
UAE Logistics Market Overview and Size
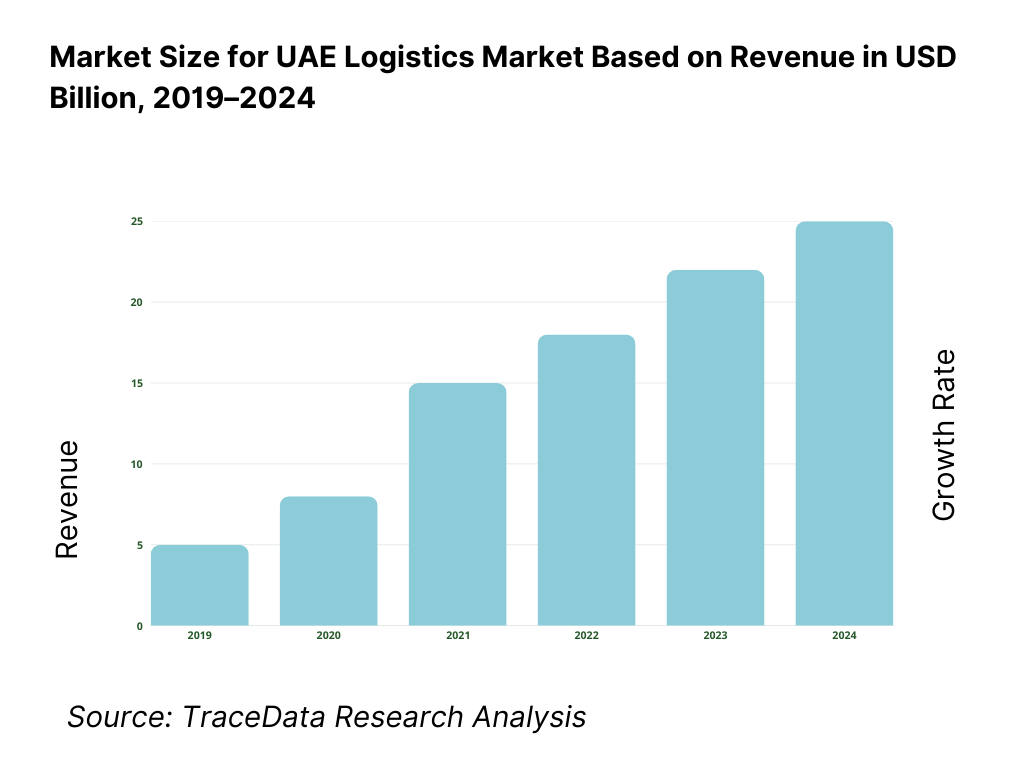
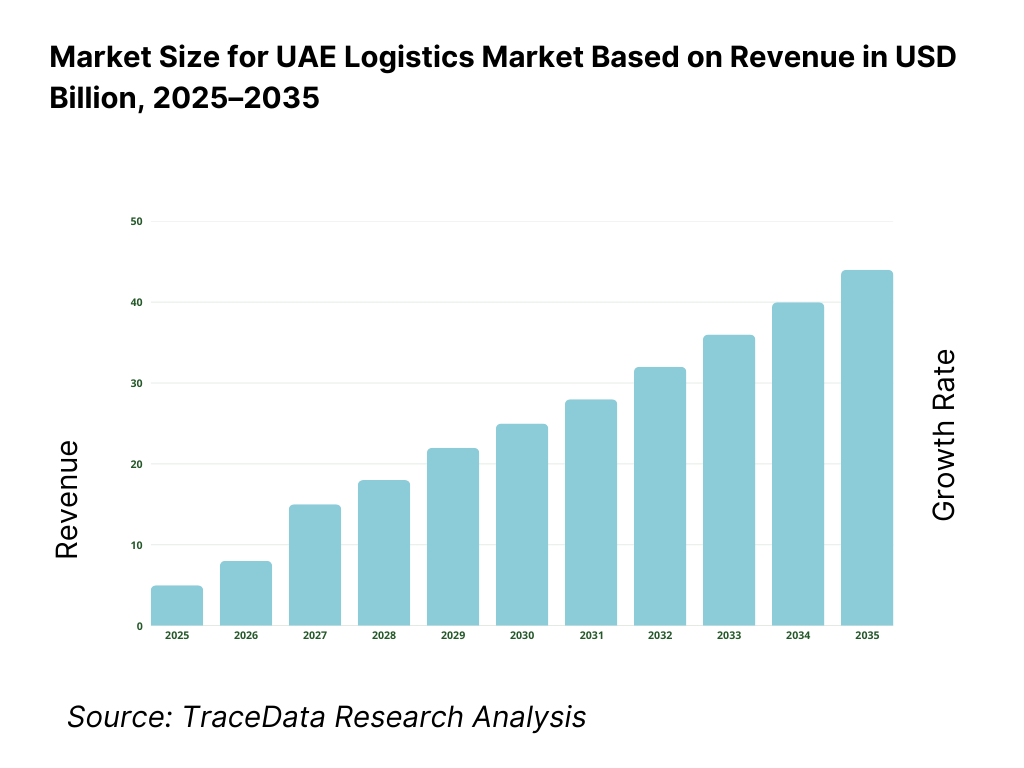
The UAE logistics market is valued at approximately ~USD ~ billion, representing the movement, storage, handling, and management of goods across domestic and international supply chains through road, sea, air, and multimodal logistics networks. The market encompasses freight forwarding, transportation, warehousing and distribution, cold chain logistics, contract logistics, value-added services, and integrated third-party logistics solutions serving both B2B and B2C customers.
The UAE’s logistics market is structurally anchored by its role as a global trade gateway linking Asia, Europe, and Africa. High port throughput, world-class airport cargo infrastructure, extensive free zone ecosystems, and strong trade facilitation frameworks position logistics as a core pillar of the country’s non-oil economy. The market benefits from sustained growth in re-exports, regional distribution activities, cross-border e-commerce, and industrial value chains serving construction, manufacturing, retail, healthcare, and energy sectors.
Dubai and Abu Dhabi represent the primary logistics demand centers in the UAE. Dubai leads due to its concentration of ports, airports, free zones, regional headquarters, and e-commerce fulfillment hubs, making it the dominant transshipment and distribution node. Abu Dhabi’s logistics demand is driven by industrial clusters, energy-linked cargo, large-scale infrastructure projects, and manufacturing-oriented logistics requirements. Northern Emirates such as Sharjah and Ras Al Khaimah support cost-competitive warehousing, road-based distribution, and niche industrial logistics, while Fujairah plays a strategic role in energy logistics and east-coast maritime access outside the Strait of Hormuz.
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the UAE Logistics Market:
Expansion of trade, re-exports, and regional distribution strengthens logistics demand: The UAE continues to expand its role as a regional trade and redistribution hub, supported by bilateral trade agreements, comprehensive economic partnership agreements, and business-friendly customs regimes. A significant share of cargo handled in the UAE is destined for re-export to GCC, Africa, and South Asia, driving sustained demand for freight forwarding, bonded warehousing, consolidation, and value-added logistics services. Logistics providers benefit from high cargo velocity, repeat volumes, and the ability to offer multi-country distribution solutions from centralized UAE hubs.
Rapid growth of e-commerce and omnichannel retail accelerates warehousing and last-mile logistics: E-commerce penetration in the UAE continues to rise across retail, electronics, groceries, pharmaceuticals, and cross-border consumer goods. This growth increases demand for fulfillment centers, sortation hubs, last-mile delivery networks, and returns management capabilities. Logistics operators are investing in automation, urban distribution facilities, temperature-controlled storage, and technology-enabled delivery models to meet rising service expectations around speed, visibility, and reliability. Same-day and next-day delivery models are reshaping warehouse location strategies and transportation planning across major urban centers.
Industrial diversification and manufacturing investments drive contract logistics demand: The UAE’s industrial strategy emphasizes local manufacturing, processing, and assembly across sectors such as food and beverages, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, building materials, and light engineering. These industries require integrated contract logistics solutions covering inbound raw material handling, in-plant logistics, finished goods warehousing, and outbound distribution. Logistics providers with sector-specific expertise, compliance capabilities, and scalable infrastructure are increasingly preferred partners for manufacturers seeking to optimize supply chain efficiency while maintaining regulatory adherence.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of the UAE Logistics Market:
Capacity constraints and cost volatility across warehousing, transportation, and last-mile networks impact margin stability: While the UAE offers world-class logistics infrastructure, periods of rapid demand growth—especially driven by e-commerce peaks, regional re-exports, and project cargo—can strain available warehousing capacity, trucking fleets, and last-mile delivery networks. Rental escalation in prime logistics zones, rising fuel and fleet operating costs, and competitive pressure on delivery pricing compress margins for logistics service providers. These cost dynamics can reduce pricing flexibility, particularly for long-term contracts where escalation clauses may not fully offset operational cost increases.
Dependence on expatriate labor and skill availability creates execution and scalability challenges: The logistics sector in the UAE remains heavily dependent on expatriate labor across driving, warehouse operations, customs documentation, and supervisory roles. Fluctuations in labor availability due to visa policies, wage expectations, and competition from construction and infrastructure projects can create operational bottlenecks. Shortages of skilled supervisors, fleet managers, and technology-trained warehouse staff can limit the ability of logistics providers to scale operations rapidly while maintaining service quality and compliance standards.
Operational complexity across multi-modal, multi-free-zone environments increases coordination requirements: Logistics operations in the UAE often span ports, airports, free zones, mainland facilities, and cross-border corridors. While this ecosystem enables flexibility and trade efficiency, it also introduces complexity in documentation, customs processes, intermodal coordination, and regulatory compliance. Managing cargo transfers between free zones and mainland, aligning service-level expectations across different authorities, and ensuring data consistency across systems can increase administrative overhead and execution risk, particularly for smaller or less integrated logistics operators.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
Trade facilitation frameworks, customs regulations, and free zone policies shaping logistics operations: The UAE’s logistics market operates under a combination of federal customs regulations, emirate-level authorities, and free zone-specific rules governing cargo movement, storage, and re-export activities. Customs clearance procedures, bonded warehousing regulations, duty suspension mechanisms, and documentation requirements directly influence logistics workflows and turnaround times. Free zone frameworks enable foreign ownership, tax efficiencies, and simplified trade processes, making them central to regional distribution and transshipment strategies, but they also require strict adherence to zone-specific compliance and reporting standards.
Transport, safety, and operational regulations governing road, air, and maritime logistics: Logistics providers must comply with regulations covering vehicle safety, driver licensing, load limits, hazardous goods handling, and fleet compliance across road transport operations. Air cargo logistics is governed by aviation authority requirements related to cargo security, handling procedures, and documentation, while maritime logistics follows port authority regulations, international shipping conventions, and terminal operating standards. Compliance with these frameworks affects fleet configuration, operating costs, training requirements, and insurance coverage across logistics segments.
National logistics strategies, digital initiatives, and sustainability programs influencing market direction: The UAE government actively promotes logistics sector development through national logistics strategies, digital trade platforms, and infrastructure investment programs. Initiatives focused on paperless trade, customs digitization, smart ports, and supply chain visibility aim to improve efficiency and transparency across logistics networks. At the same time, sustainability and environmental initiatives—such as emissions reduction targets, fuel efficiency standards, and green logistics incentives—are beginning to influence fleet modernization, warehouse design, and operating practices, particularly among large third-party logistics providers and multinational operators.
UAE Logistics Market Segmentation
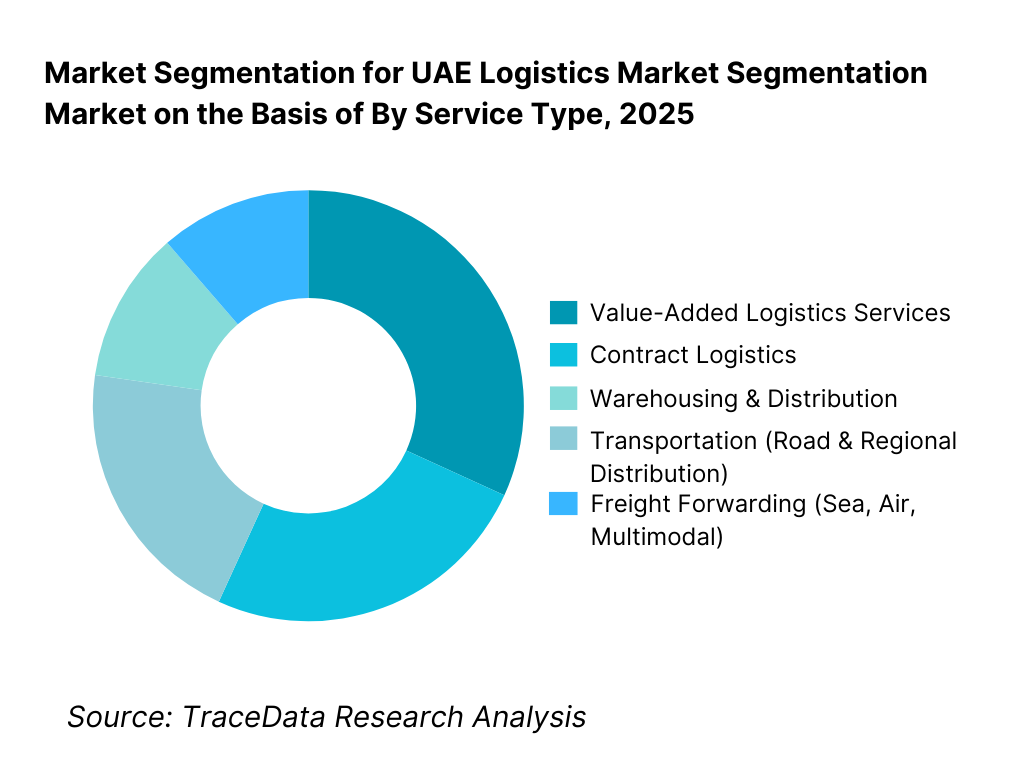
By Service Type: Freight forwarding and transportation services hold dominance. This is because the UAE functions primarily as a regional and global trade gateway, with a high proportion of cargo volumes linked to imports, exports, and re-exports. Freight forwarding—covering sea, air, and multimodal movements—forms the backbone of logistics activity, supported by strong port and airport infrastructure. Transportation services, especially road-based distribution, play a critical role in regional redistribution across the GCC and last-mile connectivity within the UAE. Warehousing and contract logistics continue to grow steadily, particularly driven by e-commerce, retail distribution, and industrial storage needs, while value-added services remain concentrated among larger integrated providers.
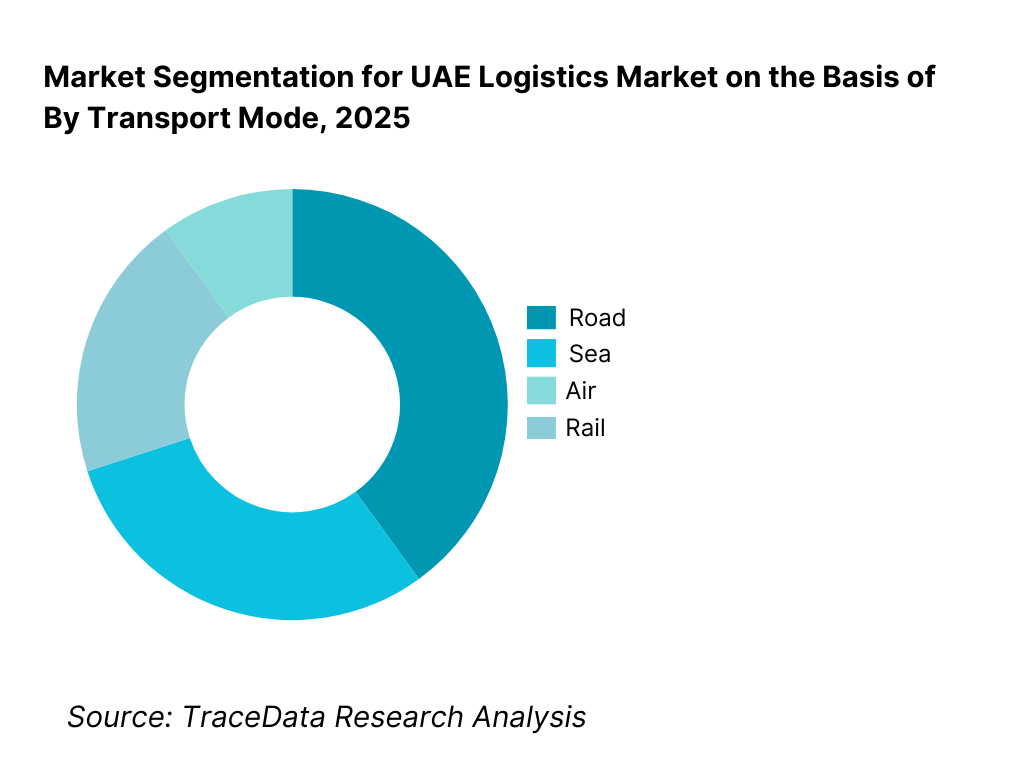
By Transport Mode: Road logistics dominate due to domestic distribution and regional connectivity. Road transport remains the most widely used mode within the UAE due to its flexibility, dense highway network, and critical role in first mile and last-mile connectivity. Sea freight is central to international trade and re-export activity, supported by high container throughput and transshipment volumes. Air cargo plays a strategic role in high-value, time-sensitive, and cross-border e-commerce shipments, while rail logistics is still emerging and expected to gain relevance over the long term as national rail connectivity expands.
Competitive Landscape in UAE Logistics Market
The UAE logistics market exhibits moderate-to-high competition, characterized by the presence of large global logistics integrators, strong regional players, and a long tail of local and niche operators. Market leadership is driven by network scale, multimodal capabilities, technology integration, free zone presence, and the ability to support complex regional distribution and re-export operations. Global players dominate large multinational accounts and contract logistics, while regional and local firms remain competitive in freight forwarding, road transport, and specialized cargo handling through cost efficiency and market familiarity.
Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
DP World | 2005 | Dubai, UAE |
Agility Logistics | 1979 | Kuwait City, Kuwait |
Aramex | 1982 | Dubai, UAE |
DHL Supply Chain | 1969 | Bonn, Germany |
Kuehne + Nagel | 1890 | Schindellegi, Switzerland |
DB Schenker | 1872 | Essen, Germany |
Ceva Logistics | 2007 | Marseille, France |
Gulf Agency Company (GAC) | 1956 | Dubai, UAE |
Al-Futtaim Logistics | 1976 | Dubai, UAE |
Some of the Recent Competitor Trends and Key Information About Competitors Include:
DP World: DP World continues to strengthen its position beyond port operations by expanding integrated logistics, inland terminals, and end-to-end supply chain services. Its competitive advantage lies in infrastructure ownership, trade corridor control, and the ability to link ports, free zones, and logistics parks into unified ecosystems supporting large-volume shippers and regional distribution models.
Aramex: Aramex maintains strong positioning in express logistics and e-commerce fulfillment, particularly across cross-border and last-mile delivery segments. The company’s focus on digital platforms, SME solutions, and regional network density supports continued relevance as e-commerce volumes expand and delivery speed expectations rise.
Agility Logistics: Agility remains a major player in contract logistics, industrial supply chains, and project logistics. Its strength lies in managing complex, asset-light logistics models across emerging markets, with particular relevance in industrial, infrastructure, and government-linked projects.
DHL Supply Chain: DHL’s competitiveness in the UAE is driven by multinational client relationships, advanced warehouse automation, and strong compliance capabilities. The company continues to expand sector-focused solutions in healthcare, technology, and consumer goods logistics where service quality and data visibility are critical.
Kuehne + Nagel: Kuehne + Nagel emphasizes freight forwarding excellence, global network integration, and technology-enabled visibility. Its position is strong in air and sea freight for high-value and time-sensitive cargo, supporting multinational supply chains operating through UAE trade hubs.
What Lies Ahead for UAE Logistics Market?
The UAE logistics market is expected to expand steadily through 2035, supported by long-term trade growth, regional re-export activity, e-commerce expansion, and sustained investment in logistics-enabling infrastructure. The country’s positioning as a global gateway between Asia, Europe, and Africa, combined with business-friendly trade policies and advanced port and airport ecosystems, will continue to anchor logistics as a strategic non-oil growth pillar. As supply chains increasingly prioritize speed, resilience, and regional hub-and-spoke distribution models, the UAE will remain a preferred base for centralized warehousing, freight forwarding, and contract logistics operations serving the wider Middle East, Africa, and South Asia.
Transition Toward Integrated, End-to-End Logistics and Contract-Based Solutions: The future of the UAE logistics market will see a gradual shift from fragmented service offerings toward more integrated, contract-based logistics solutions. Shippers increasingly prefer single-provider models covering freight forwarding, warehousing, distribution, and value-added services to reduce coordination complexity and improve visibility. Demand is rising for customized contract logistics solutions aligned with specific industry requirements such as retail replenishment cycles, industrial supply chains, healthcare compliance, and e-commerce fulfillment. Logistics providers with the ability to design sector-specific solutions and manage long-term contracts will capture higher-value, stickier demand.
Growing Emphasis on Speed, Reliability, and Regional Distribution Efficiency: Speed-to-market and service reliability will become even more critical differentiators as regional competition intensifies. The UAE’s role as a redistribution hub will strengthen as companies centralize inventory and serve multiple markets from a single location. This will drive continued investment in high-throughput warehouses, automation, cross-docking facilities, and optimized road networks connecting ports, airports, and free zones. Providers capable of offering consistent service levels across peak and non-peak periods will gain competitive advantage, particularly in retail, FMCG, and e-commerce supply chains.
Increased Adoption of Technology, Automation, and Data-Driven Logistics Models: Digitalization will accelerate across the UAE logistics value chain, with greater adoption of warehouse management systems, transport management platforms, real-time tracking, and data analytics. Automation in warehousing—such as sortation systems, robotics, and smart inventory management—will expand to improve productivity and reduce dependence on manual labor. Customers will increasingly expect end-to-end visibility, predictive delivery timelines, and performance reporting as standard service components, favoring logistics providers with strong technology integration capabilities.
Sustainability, Fleet Modernization, and Green Logistics Practices Gain Importance: Sustainability considerations will play a growing role in logistics strategy and procurement decisions. Fleet modernization, fuel efficiency improvements, alternative fuel adoption, and energy-efficient warehouse designs will gradually influence operating models. Large shippers and multinational clients are expected to place greater emphasis on emissions reporting, sustainable transport solutions, and environmentally responsible logistics partners. While cost considerations will remain critical, sustainability narratives will increasingly shape long-term partnerships and investment decisions.
UAE Logistics Market Segmentation
By Service Type
• Freight Forwarding (Sea, Air, Multimodal)
• Transportation (Road & Regional Distribution)
• Warehousing & Distribution
• Contract Logistics
• Value-Added Logistics Services
By Transport Mode
• Road
• Sea
• Air
• Rail
By End-Use Industry
• Retail, E-commerce & Consumer Goods
• Industrial & Manufacturing
• Construction & Project Cargo
• Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals
• Others
By Contract Structure
• Transactional / Spot Logistics
• Short-Term Contract Logistics
• Long-Term Integrated Contract Logistics
By Region
• Dubai
• Abu Dhabi
• Northern Emirates (Sharjah, Ajman, Ras Al Khaimah, Umm Al Quwain)
• Fujairah
Players Mentioned in the Report:
• DP World
• Aramex
• Agility Logistics
• DHL Supply Chain
• Kuehne + Nagel
• DB Schenker
• CEVA Logistics
• Gulf Agency Company (GAC)
• Al-Futtaim Logistics
• Regional freight forwarders, transport operators, and warehousing providers
Key Target Audience
• Third-party logistics (3PL) and contract logistics providers
• Freight forwarders and multimodal transport operators
• Warehousing and distribution facility developers
• E-commerce platforms and retail supply chain managers
• Industrial and manufacturing companies
• Healthcare, pharmaceutical, and cold chain operators
• Free zone authorities and logistics park developers
• Government agencies and trade facilitation bodies
• Private equity, infrastructure, and logistics-focused investors
Time Period:
Historical Period: 2019–2024
Base Year: 2025
Forecast Period: 2025–2035
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4. 1 Service Delivery Model Analysis for Logistics including freight forwarding, transportation, warehousing, contract logistics, and value-added services with margins, preferences, strengths, and weaknesses
4. 2 Revenue Streams for Logistics Market including freight forwarding revenues, transportation revenues, warehousing rentals, contract logistics fees, and value-added service charges
4. 3 Business Model Canvas for Logistics Market covering shippers, logistics service providers, freight forwarders, transport operators, warehouse developers, free zone operators, ports and airports, and technology providers
5. 1 Global Logistics Integrators vs Regional and Local Players including multinational 3PLs, regional logistics providers, and domestic transport and warehousing operators
5. 2 Investment Model in Logistics Market including asset-heavy warehousing models, asset-light freight forwarding models, fleet ownership versus outsourcing, and infrastructure-linked investments
5. 3 Comparative Analysis of Logistics Service Delivery by Integrated Contract Logistics and Transactional / Spot Service Models including long-term contracts and ad-hoc shipments
5. 4 Shipper Logistics Spend Allocation comparing outsourced logistics services versus in-house logistics operations with average spend by industry
8. 1 Revenues from historical to present period
8. 2 Growth Analysis by service type and by transport mode
8. 3 Key Market Developments and Milestones including port expansions, logistics park developments, digital trade initiatives, and regulatory updates
9. 1 By Market Structure including global logistics providers, regional players, and local operators
9. 2 By Service Type including freight forwarding, transportation, warehousing, contract logistics, and value-added services
9. 3 By Transport Mode including road, sea, air, and rail
9. 4 By End-Use Industry including retail and e-commerce, industrial and manufacturing, construction and project cargo, healthcare and pharmaceuticals, and others
9. 5 By Contract Structure including spot logistics, short-term contracts, and long-term integrated logistics
9. 6 By Shipment Type including domestic, import, export, and re-export
9. 7 By Customer Type including SMEs, large enterprises, and multinational corporations
9. 8 By Region including Dubai, Abu Dhabi, Northern Emirates, and Fujairah
10. 1 Shipper Landscape and Industry Segmentation highlighting retail, industrial, and e-commerce demand clusters
10. 2 Logistics Service Provider Selection and Purchase Decision Making influenced by cost, reliability, network coverage, and technology capability
10. 3 Service Performance and ROI Analysis measuring turnaround times, service reliability, cost efficiency, and contract renewals
10. 4 Gap Analysis Framework addressing capacity shortages, service differentiation gaps, and technology adoption challenges
11. 1 Trends and Developments including growth of contract logistics, automation in warehousing, digital freight platforms, and sustainability initiatives
11. 2 Growth Drivers including trade expansion, e-commerce growth, infrastructure investment, and outsourcing of logistics functions
11. 3 SWOT Analysis comparing global logistics scale versus regional agility and local cost competitiveness
11. 4 Issues and Challenges including margin pressure, labor dependency, capacity constraints, and regulatory complexity
11. 5 Government Regulations covering customs frameworks, transport safety regulations, free zone policies, and trade facilitation initiatives in the UAE
12. 1 Market Size and Future Potential of e-commerce-driven logistics and last-mile delivery services
12. 2 Business Models including platform-led delivery, third-party last-mile partnerships, and in-house fulfillment models
12. 3 Service Delivery Models and Type of Solutions including same-day delivery, next-day delivery, and cross-border e-commerce logistics
15. 1 Market Share of Key Players by revenues and service mix
15. 2 Benchmark of 15 Key Competitors including global integrators, regional logistics firms, and leading domestic operators
15. 3 Operating Model Analysis Framework comparing asset-heavy, asset-light, and hybrid logistics models
15. 4 Gartner Magic Quadrant positioning global leaders and regional challengers in logistics and supply chain services
15. 5 Bowman’s Strategic Clock analyzing competitive advantage through service differentiation versus cost-led logistics strategies
16. 1 Revenues with projections
17. 1 By Market Structure including global, regional, and local logistics providers
17. 2 By Service Type including freight forwarding, transportation, warehousing, and contract logistics
17. 3 By Transport Mode including road, sea, air, and rail
17. 4 By End-Use Industry including retail, industrial, construction, and healthcare
17. 5 By Contract Structure including spot, short-term, and long-term contracts
17. 6 By Shipment Type including domestic and cross-border logistics
17. 7 By Customer Type including SMEs and large enterprises
17. 8 By Region including Dubai, Abu Dhabi, Northern Emirates, and Fujairah
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
We begin by mapping the complete ecosystem of the UAE Logistics Market across demand-side and supply-side entities. On the demand side, entities include retailers and e-commerce platforms, FMCG distributors, industrial and manufacturing companies, construction and project cargo owners, healthcare and pharmaceutical companies, energy sector players, and government and public-sector agencies involved in trade and infrastructure development. Demand is further segmented by logistics requirement (freight forwarding, transportation, warehousing, contract logistics), shipment type (domestic, import, export, re-export), service complexity (standard vs value-added), and contract structure (spot, short-term, long-term integrated contracts).
On the supply side, the ecosystem includes global logistics integrators, regional third-party logistics providers, freight forwarders, road transport operators, warehousing and logistics park operators, port and airport authorities, free zone operators, customs and trade facilitation bodies, technology solution providers, and last-mile delivery platforms. From this mapped ecosystem, we shortlist 8–12 leading logistics service providers and a representative set of regional and local operators based on network scale, service breadth, sector focus, free zone presence, technology adoption, and client portfolio. This step establishes how value is created and captured across freight movement, storage, distribution, and value-added logistics services.
Step 2: Desk Research
An exhaustive desk research process is undertaken to analyze the UAE logistics market structure, demand drivers, and segment behavior. This includes reviewing trade and re-export trends, port and airport cargo throughput, e-commerce growth patterns, industrial diversification initiatives, and logistics infrastructure expansion. We assess buyer preferences around service reliability, turnaround time, network coverage, pricing models, and technology-enabled visibility.
Company-level analysis includes review of logistics service portfolios, geographic coverage, warehousing footprints, transport fleet strategies, sector specialization, and contract structures. We also examine regulatory and policy frameworks governing customs clearance, free zone operations, transport safety, and cross-border trade facilitation. The outcome of this stage is a comprehensive industry foundation that defines the segmentation logic and creates the assumptions needed for market estimation and long-term outlook modeling.
Step 3: Primary Research
We conduct structured interviews with logistics service providers, freight forwarders, warehouse operators, transport fleet managers, e-commerce supply chain heads, industrial shippers, and trade experts. The objectives are threefold: (a) validate assumptions around demand concentration, outsourcing intensity, and service mix evolution, (b) authenticate segment splits by service type, transport mode, end-use industry, and contract structure, and (c) gather qualitative insights on pricing behavior, capacity utilization, margin pressures, technology adoption, and customer expectations around service levels and visibility.
A bottom-to-top approach is applied by estimating cargo volumes, warehouse capacity utilization, and average service pricing across key segments and regions, which are aggregated to develop the overall market view. In selected cases, disguised buyer-style interactions are conducted with freight forwarders and transport operators to validate field-level realities such as rate negotiations, peak season constraints, service differentiation, and execution challenges.
Step 4: Sanity Check
The final stage integrates bottom-to-top and top-to-down approaches to cross-validate the market view, segmentation splits, and forecast assumptions. Demand estimates are reconciled with macro indicators such as trade growth, e-commerce penetration, industrial output, infrastructure capacity expansion, and government-led logistics initiatives. Assumptions around capacity availability, cost inflation, labor dependency, and regulatory changes are stress-tested to understand their impact on market growth and service adoption.
Sensitivity analysis is conducted across key variables including trade volume growth intensity, pace of contract logistics adoption, technology penetration, sustainability-related cost implications, and infrastructure utilization rates. Market models are refined until alignment is achieved between service provider capacity, customer demand patterns, and logistics infrastructure throughput, ensuring internal consistency and robust directional forecasting through 2035.
FAQs
01 What is the potential for the UAE Logistics Market?
The UAE Logistics Market holds strong long-term potential, supported by its role as a global trade and re-export hub, sustained growth in e-commerce and retail distribution, and continued investment in logistics-enabling infrastructure. The market benefits from high cargo velocity, regional distribution demand, and increasing outsourcing of supply chain functions. As companies prioritize speed, reliability, and centralized regional logistics models, the UAE is expected to remain a preferred base for logistics operations serving the Middle East, Africa, and South Asia through 2035.
02 Who are the Key Players in the UAE Logistics Market?
The market features a mix of global logistics integrators, strong regional players, and specialized local operators. Competition is shaped by network scale, multimodal capabilities, free zone access, technology integration, and sector-specific expertise. Large players dominate integrated contract logistics and multinational accounts, while regional and local firms remain competitive in freight forwarding, road transport, and niche service segments through cost efficiency and market familiarity.
03 What are the Growth Drivers for the UAE Logistics Market?
Key growth drivers include expansion of trade and re-export activity, rapid growth of e-commerce and omnichannel retail, industrial diversification initiatives, and continuous investment in ports, airports, and logistics parks. Additional momentum comes from increasing preference for outsourced and integrated logistics solutions, adoption of digital platforms, and rising demand for specialized logistics such as cold chain and healthcare logistics.
04 What are the Challenges in the UAE Logistics Market?
Challenges include margin pressure due to intense competition, cost volatility across transport and warehousing, dependence on expatriate labor, and operational complexity across multi-free-zone and multimodal environments. Capacity constraints during peak demand periods and increasing expectations around service quality and visibility can also impact execution consistency. Regulatory compliance across transport, customs, and safety frameworks adds to operational complexity, particularly for smaller logistics operators.