United Kingdom Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Structure, By Type of Commodities, By Temperature Range, By Mode of Transportation, By End-User Industries, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0333
- Region: Europe
- Published on: September 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “United Kingdom Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029 – By Market Structure, By Type of Commodities, By Temperature Range, By Mode of Transportation, By End-User Industries, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the cold chain industry in the UK. The report covers the genesis and evolution of the market, overall market size in terms of revenue, detailed segmentation, key trends and developments, regulatory environment, customer profiles, challenges and constraints, and competitive landscape. It concludes with future projections for 2029 and insights into major opportunities and risk factors affecting market growth.
United Kingdom Cold Chain Market Overview and Size
The UK cold chain market was valued at GBP 18.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow steadily through 2029, driven by expanding food retail, e-commerce grocery delivery, biopharma distribution, and the demand for temperature-controlled logistics. Major players in the market include Lineage Logistics, NewCold, Gist Limited, Turners (Soham), and Culina Group, known for their advanced infrastructure, nationwide distribution capabilities, and diversified service offerings.
In 2023, Lineage Logistics expanded its cold storage capacity by over 20% in the Midlands and South East regions to cater to the growing demand from foodservice and pharmaceutical sectors. London and Manchester are considered key logistics hubs due to their proximity to ports, airports, and high-density consumer zones.
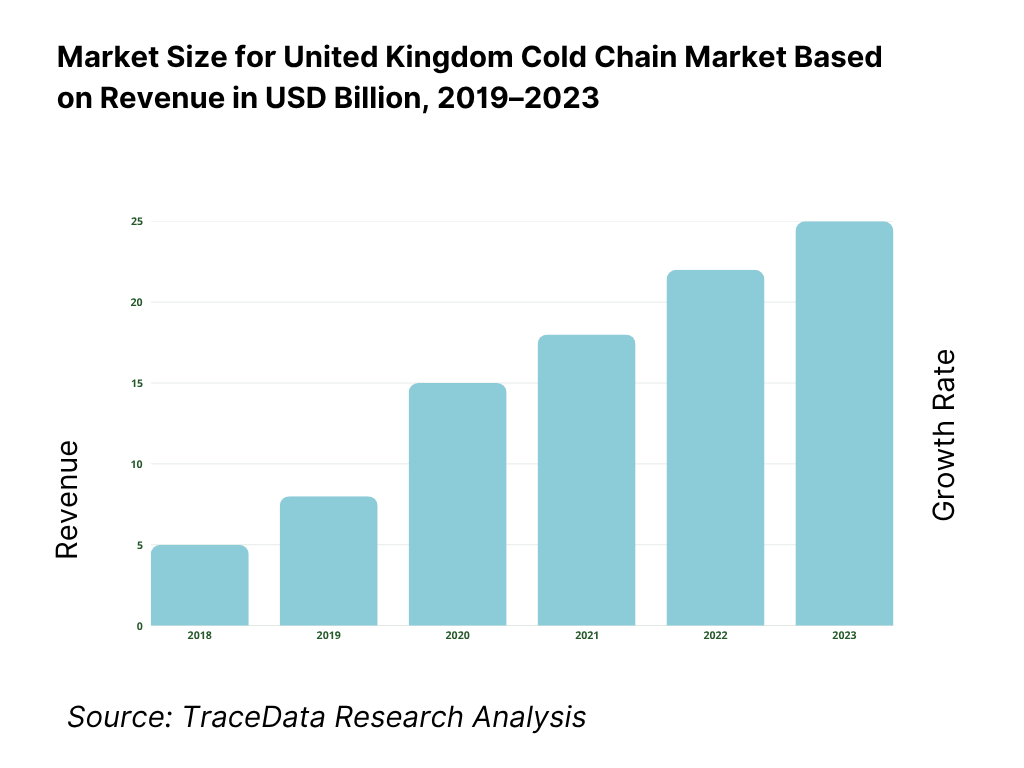
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the United Kingdom Cold Chain Market
Changing Consumer Habits: Increasing consumer preference for fresh, frozen, and perishable food, including online grocery deliveries, is boosting demand for cold storage and temperature-controlled last-mile delivery. In 2023, over 50% of UK households shopped for groceries online at least once a month.
Pharmaceutical and Life Sciences Growth: With the rise of biologics, vaccines, and personalized medicine, the need for specialized cold chain infrastructure has surged. The UK’s biopharma cold chain sector accounted for 18% of total market revenue in 2023.
Regulatory Compliance: Stringent EU and UK regulations on food and drug storage and transport are pushing firms to adopt standardized, high-tech temperature-controlled systems. This is driving upgrades and investment in automation, telematics, and warehouse monitoring systems.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of the United Kingdom Cold Chain Market
High Energy and Operational Costs: Operating cold storage facilities and temperature-controlled transport systems require significant energy consumption. In 2023, it was estimated that energy costs constituted nearly 30% of total operating expenses for cold chain companies in the UK. The rising electricity prices and carbon levies have further strained profit margins, especially for mid-sized logistics providers.
Skilled Labour Shortage and Automation Gaps: The industry faces an acute shortage of skilled technicians and drivers trained in cold chain logistics. According to the UK Logistics Association, around 18% of cold chain logistics firms experienced workforce shortages in 2023, leading to delays and inefficiencies in service delivery. Furthermore, the slow pace of adoption of automation in smaller firms continues to hinder scalability and cost optimization.
Infrastructure Bottlenecks and Urban Access Limitations: Urban delivery restrictions, limited warehousing space in high-demand zones, and outdated infrastructure in some rural cold chain routes are impeding efficiency. In 2023, over 22% of perishable shipments experienced delays due to inadequate last-mile cold chain infrastructure, especially in regions outside London and Manchester.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market
UK Food Safety and Hygiene Regulations (FSA): The Food Standards Agency enforces strict guidelines on temperature control during storage and transport of perishable goods. Cold chain operators must ensure food remains within safe temperature limits throughout the logistics cycle. As of 2023, 89% of cold storage facilities met compliance during audits, reflecting improving industry practices.
MHRA Guidelines for Pharmaceutical Cold Chain: The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) mandates specific protocols for pharmaceutical cold chain logistics, especially for vaccines, biologics, and temperature-sensitive drugs. Compliance with Good Distribution Practice (GDP) standards is compulsory. In 2023, 95% of UK-based pharmaceutical warehouses adhered to GDP audits.
Net-Zero Carbon Mandate and Sustainability Policies: To meet the UK’s 2050 net-zero targets, the government has encouraged the use of low-emission refrigeration units, solar-powered cold storage, and electrified transport fleets. In 2023, 12% of cold chain fleet vehicles were either electric or hybrid, driven by government grants, including the Plug-in Van Grant and the Industrial Energy Transformation Fund (IETF) for sustainable warehousing.
United Kingdom Cold Chain Market Segmentation
By Market Structure: The organized sector dominates the UK cold chain market, driven by large-scale players such as Lineage Logistics, NewCold, and Culina Group. These firms offer end-to-end integrated solutions with real-time monitoring, regulatory compliance, and multi-temperature warehousing services, ensuring high reliability and traceability. The unorganized sector, comprising smaller, regional transporters and storage operators, also plays a notable role, especially in rural or specialized markets. However, challenges such as limited technology adoption and scalability restrict their market share.
%20by%20Revenue%20Share%20(%25)%2C%202023.png)
By Type of Commodities: The food and beverage segment leads the UK cold chain market, accounting for a major share due to rising demand for chilled and frozen foods, dairy, meat, ready-to-eat meals, and online grocery fulfillment. The pharmaceutical sector is the fastest-growing segment, driven by increasing vaccine distribution, biological therapies, and temperature-sensitive drug logistics. The floriculture and chemical industries also utilize cold chains, though at a smaller scale.
%20by%20Revenue%20Share%20(%25)%2C%202023.png)
By Temperature Range: Cold chain operations in the UK are segmented into chilled (0°C to 8°C) and frozen (<0°C) ranges. The chilled segment dominates due to the high volume of dairy, fresh produce, and meal kits requiring mild temperature control. Frozen logistics—critical for meat, seafood, and frozen bakery—also hold a significant share. The ultra-cold category (< -20°C), though niche, is gaining traction in the pharma segment for vaccine and biologics logistics.
Competitive Landscape in United Kingdom Cold Chain Market
The UK cold chain market is moderately consolidated, with a mix of established logistics conglomerates and specialized temperature-controlled service providers. Players like Lineage Logistics, NewCold, Gist Limited, Turners (Soham), and Culina Group dominate the space due to their nationwide infrastructure, advanced technology adoption, and strong client base across food and pharma industries. Recent investments in automation, sustainability, and regional expansion have intensified competition in this space.
Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
Lineage Logistics | 2008 (UK operations) | Peterborough, England |
NewCold | 2012 | Wakefield, West Yorkshire |
Gist Limited | 2001 | Basingstoke, Hampshire |
Turners (Soham) | 1930s | Newmarket, Suffolk |
Culina Group | 1994 | Market Drayton, Shropshire |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information include:
Lineage Logistics: One of the largest cold storage providers in the UK, Lineage added over 100,000 pallet positions in 2023 through warehouse expansions in Peterborough and the Midlands. Their use of automated retrieval systems and solar-powered facilities supports both efficiency and sustainability goals.
NewCold: Known for their high-rise, fully automated cold storage sites, NewCold has expanded their Wakefield facility to become one of Europe’s largest. In 2023, they signed long-term contracts with major food manufacturers, increasing their revenue by 18% YoY.
Gist Limited: Specializing in chilled food logistics, Gist handles supply chain operations for major UK supermarkets and foodservice chains. The company introduced AI-based route optimization in 2023, reducing average delivery delays by 12%.
Turners (Soham): A key player in refrigerated haulage, Turners expanded its fleet by 10% in 2023 to support growth in fresh produce transportation across the UK and EU. Their vertically integrated model combines transport and warehousing for efficient cold chain continuity.
Culina Group: Culina Group operates an integrated cold and ambient logistics network. In 2023, it acquired Great Bear Distribution and further expanded its cold storage capabilities, enhancing service reach into Scotland and Ireland. The group also introduced ESG-compliant reporting tools for clients in the F&B sector.
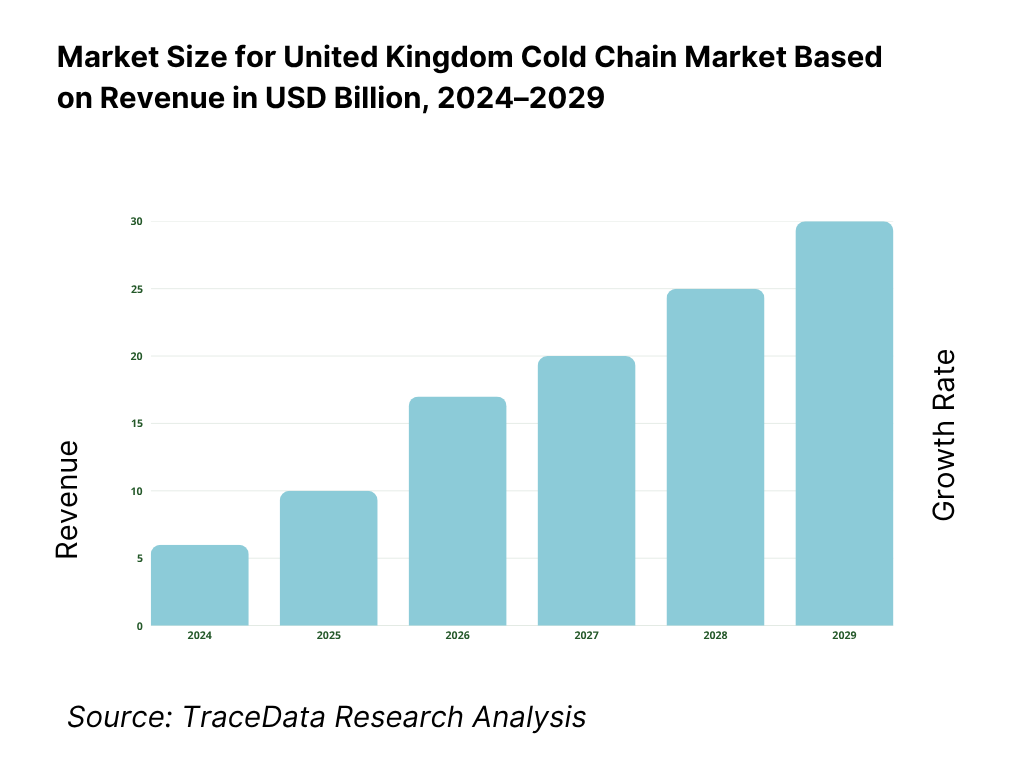
What Lies Ahead for United Kingdom Cold Chain Market?
The UK cold chain market is projected to grow steadily through 2029, demonstrating a healthy CAGR over the forecast period. Growth will be driven by the expansion of online grocery delivery, increasing demand for pharmaceuticals and biologics, regulatory mandates on food safety, and sustainability-focused logistics transformation.
Expansion of E-Grocery and Meal Kit Deliveries: The surge in consumer demand for online grocery platforms such as Tesco, Ocado, and HelloFresh is expected to fuel cold chain infrastructure growth. By 2029, online fresh food and chilled meal deliveries are projected to account for over 25% of the food retail cold chain market, creating strong demand for last-mile temperature-controlled solutions.
Acceleration of Pharma Cold Chain Investments: With the rise in biologics, specialty drugs, and personalized medicine, the UK pharmaceutical sector will increasingly depend on ultra-cold and GDP-compliant logistics. By 2029, the pharma segment is anticipated to represent over 20% of total cold chain revenues, supported by NHS reforms and growing public-private investments in life sciences infrastructure.
Adoption of Sustainable and Carbon-Neutral Technologies: The industry is moving toward net-zero logistics with the adoption of electric reefer trucks, solar-powered warehouses, and low-GWP refrigerants. By 2029, over 30% of new cold chain fleet purchases are expected to be electric or hybrid, aligned with the UK government’s climate roadmap and green logistics funding initiatives.
Integration of IoT and Predictive Analytics: Cold chain players are adopting real-time IoT monitoring systems and AI-driven analytics to enhance temperature visibility, predict spoilage risks, and optimize routes. These digital interventions are expected to lower spoilage rates and reduce fuel costs, making operations more efficient and responsive to compliance audits.
United Kingdom Cold Chain Market Segmentation
- By Market Structure:
o Organized Sector
o Unorganized Sector
o Public Cold Storage Facilities
o Private/Contract Logistics Providers
o Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Providers
o Dedicated In-house Cold Chain Operations - By Type of Commodities:
o Fruits & Vegetables
o Meat & Seafood
o Dairy Products
o Frozen Foods & Ready Meals
o Pharmaceuticals & Vaccines
o Specialty Chemicals & Others - By Temperature Range:
o Chilled (0°C to 8°C)
o Frozen (Below 0°C)
o Ultra-Cold (Below -20°C) - By Mode of Transportation:
o Road Transport (Refrigerated Trucks, Vans)
o Air Freight
o Sea Freight
o Rail Logistics - By End-User Industries:
o Food & Beverage Retailers
o E-commerce & Online Grocery Platforms
o Foodservice & Hospitality Chains
o Pharmaceutical Manufacturers & Distributors
o Chemical & Biotech Companies
o Export-Import Houses - By Region:
o South East England
o Greater London
o Midlands
o North West England
o Scotland
o Wales & Northern Ireland
Players Mentioned in the Report
- Lineage Logistics
- NewCold
- Gist Limited
- Turners (Soham)
- Culina Group
- NFT Distribution
- Frocester Group
- Magnavale
- Reed Boardall Group
Key Target Audience
- Cold Chain Logistics Providers
- Food and Pharma Manufacturers
- Supermarket and Grocery Retail Chains
- Healthcare and Biotech Companies
- Temperature-Controlled Equipment Suppliers
- Policy Makers and Regulatory Bodies (e.g., DEFRA, MHRA)
- Supply Chain Technology Providers
- Investment and Infrastructure Development Firms
Time Period
- Historical Period: 2018–2023
- Base Year: 2024
- Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
1. Executive Summary
2. Research Methodology
3. Ecosystem of Key Stakeholders in the United Kingdom Cold Chain Market
4. Value Chain Analysis
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and Challenges They Face
4.2. Revenue Streams for the United Kingdom Cold Chain Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for the United Kingdom Cold Chain Market
4.4. Cold Chain Logistics Decision-Making Process-Demand and Supply Side
5. Market Structure
5.1. Cold Chain Infrastructure in the UK-Warehouse & Transport Capacity, 2018-2024
5.2. Cold Chain Penetration Rate in Food and Pharma Sectors, 2018-2024
5.3. GDP-Compliant Facilities Distribution by Region
5.4. Number of Cold Chain Operators in the UK by Size and Specialization
6. Market Attractiveness for the United Kingdom Cold Chain Market
7. Supply-Demand Gap Analysis
8. Market Size for the United Kingdom Cold Chain Market Basis
8.1. Revenues, 2018-2024
8.2. Storage and Transportation Capacity, 2018-2024
9. Market Breakdown for the United Kingdom Cold Chain Market Basis
9.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized), 2023-2024P
9.2. By Type of Commodity (Food, Pharma, Others), 2023-2024P
9.3. By Temperature Range (Chilled, Frozen, Ultra-Cold), 2023-2024P
9.4. By Transportation Mode (Road, Air, Rail, Sea), 2023-2024P
9.5. By End-User Industry (Retail, Foodservice, Pharma, Others), 2023-2024P
9.6. By Region (South East, London, Midlands, North West, Scotland, etc.), 2023-2024P
10. Demand Side Analysis for the United Kingdom Cold Chain Market
10.1. Customer Segments and Buyer Profiles
10.2. Buyer Journey and Partner Decision Framework
10.3. Needs, Preferences, and Pain Point Analysis
10.4. Cold Chain Compliance Expectations by Sector
11. Industry Analysis
11.1. Trends and Developments for the United Kingdom Cold Chain Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for the United Kingdom Cold Chain Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for the United Kingdom Cold Chain Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges for the United Kingdom Cold Chain Market
11.5. Regulatory Landscape (DEFRA, MHRA, FSA Guidelines)
12. Snapshot on Digital Cold Chain and Telematics Adoption
12.1. Market Size and Trends in Cold Chain Monitoring Technology, 2018-2029
12.2. Business Models and Technology Providers
12.3. Comparative Analysis of Key Players in Cold Chain Automation and IoT
13. UK Cold Chain Financing and Infrastructure Investment Trends
13.1. Investment Trends and Key Infrastructure Projects, 2018-2024
13.2. Government Grants and Carbon Neutral Incentives
13.3. Financing Models for Cold Chain Warehousing and Transport
14. Opportunity Matrix for the UK Cold Chain Market-Radar Chart View
15. PEAK Matrix Analysis for Cold Chain Logistics Providers in the UK
16. Competitor Analysis for the United Kingdom Cold Chain Market
16.1. Benchmarking of Key Players: Lineage, NewCold, Gist, Culina, Turners
16.2. Strengths and Weaknesses
16.3. Operating Model Comparison Framework
16.4. Gartner Magic Quadrant (Cold Chain Tech & Logistics)
16.5. Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Positioning
17. Future Market Size for the UK Cold Chain Market Basis
17.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
17.2. Storage and Transport Expansion Capacity, 2025-2029
18. Market Breakdown for the UK Cold Chain Market Basis
18.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized), 2025-2029
18.2. By Commodity Type (Food, Pharma, Others), 2025-2029
18.3. By Temperature Range (Chilled, Frozen, Ultra-Cold), 2025-2029
18.4. By Region, 2025-2029
18.5. By End-User Sector, 2025-2029
18.6. By Transportation Mode, 2025-2029
18.7. By Cold Storage Ownership (Public, Private, Contract), 2025-2029
18.8. Strategic Recommendations
18.9. Opportunity Analysis and Investment Hotspots
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand-side and supply-side entities for the United Kingdom Cold Chain Market. Based on this ecosystem, we shortlisted 5–6 key players in the country by evaluating their financial data, storage and transport capacity, client segments, and infrastructure footprint.
Sourcing is conducted through industry reports, government publications (DEFRA, MHRA), company databases, and secondary sources such as trade articles, cold chain associations (e.g., Cold Chain Federation UK), and proprietary research platforms to capture market-level data.
Step 2: Desk Research
We then conduct an exhaustive desk research phase by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This includes analyzing market-level indicators such as total cold storage capacity, refrigerated fleet size, revenue generation by sub-segments (food, pharma, etc.), and technological integration across the value chain.
Additionally, we examine detailed company-level data, utilizing annual reports, corporate press releases, sustainability disclosures, investment reports, and industry publications. This provides the foundational structure for segment-level analysis and historical trend assessment.
Step 3: Primary Research
A structured set of in-depth interviews is conducted with senior executives, operations heads, and supply chain managers representing major UK cold chain companies and key end-users across food, pharma, and retail sectors. These interviews help validate market assumptions, confirm data accuracy, and gather on-ground insights related to price models, logistics constraints, and regulatory compliance.
As part of our validation process, we employ disguised interviews by posing as prospective clients or logistics partners. This allows for cross-verification of operational metrics, price structures, warehousing timelines, and capacity utilization rates. These discussions enrich our understanding of competitive dynamics and real-time market bottlenecks.
Step 4: Sanity Check
A combination of bottom-up (player-wise capacity and revenue estimation) and top-down (industry benchmarks, import/export data, cold chain demand models) approaches is applied to estimate the market size. These modeling exercises are complemented by triangulation and sensitivity analysis to ensure internal consistency and validation across datasets.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the United Kingdom Cold Chain Market?
The United Kingdom cold chain market holds strong growth potential, reaching a valuation of GBP 18.5 billion in 2023. Growth is driven by rising demand for temperature-controlled logistics in food retail, online grocery delivery, and the pharmaceutical sector. The market is further supported by increasing regulatory oversight, sustainability initiatives, and investment in cold chain infrastructure and automation.
2. Who are the Key Players in the United Kingdom Cold Chain Market?
Key players in the UK cold chain market include Lineage Logistics, NewCold, Gist Limited, Turners (Soham), and Culina Group. These companies are recognized for their extensive cold storage capacity, advanced technology usage, and integrated temperature-controlled transport services across multiple industries.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the United Kingdom Cold Chain Market?
Growth in the UK cold chain market is driven by expanding e-grocery services, increasing pharmaceutical distribution needs, and heightened food safety regulations. Other drivers include the post-Brexit realignment of logistics routes, rising consumer expectations for fresh and frozen delivery, and investments in sustainable and electric-powered cold transport systems.
4. What are the Challenges in the United Kingdom Cold Chain Market?
The market faces several challenges, including high operational and energy costs, a shortage of skilled cold chain workforce, and outdated infrastructure in certain regions. Additional constraints include compliance with evolving regulatory standards (e.g., MHRA, FSA), limited urban warehousing space, and the need for greater adoption of digital and IoT-based temperature monitoring systems.