USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market Outlook to 2035
By Vehicle Type, By Range Extender Technology, By Power Output, By Application, and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0463
- Region: Central and South America
- Published on: January 2026
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market Outlook to 2035 – By Vehicle Type, By Range Extender Technology, By Power Output, By Application, and By Region” provides a comprehensive analysis of the electric vehicle (EV) range extender ecosystem in the United States. The report covers an overview and genesis of the market, overall market size in terms of value, detailed market segmentation; technology trends and developments, regulatory and policy landscape, OEM and fleet-level demand profiling, key issues and challenges, and competitive landscape including competition scenario, cross-comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the USA EV range extender market. The report concludes with future market projections based on EV adoption trajectories, charging infrastructure readiness, commercial fleet electrification, regulatory compliance pathways, regional demand drivers, cause-and-effect relationships, and case-based illustrations highlighting the major opportunities and cautions shaping the market through 2035.
USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market Overview and Size
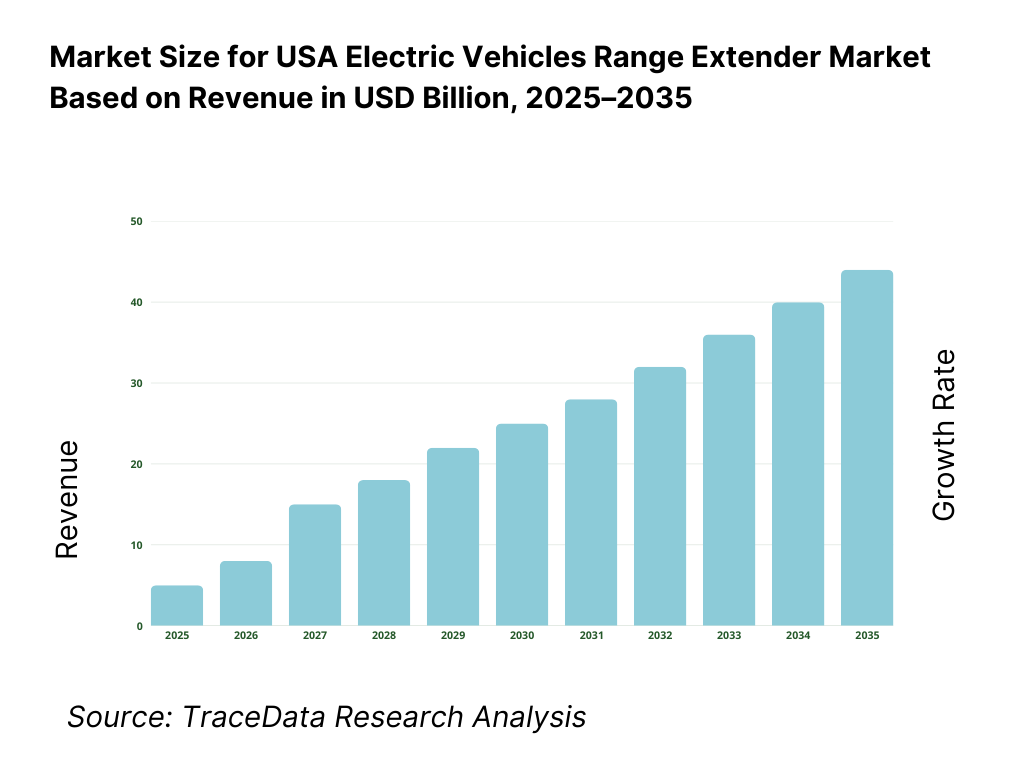
The USA electric vehicles range extender market is valued at approximately ~USD ~ billion, representing the supply of auxiliary power systems integrated into electric vehicles to extend driving range beyond battery-only limits. Range extenders typically comprise compact internal combustion engines, rotary engines, micro-turbines, fuel cells, or advanced generator systems coupled with power electronics, control units, and thermal management components. These systems generate electricity to recharge the battery or directly supply power to the drivetrain without mechanically driving the wheels.
Range extenders are increasingly positioned as a transitional electrification solution, particularly for vehicle segments and use cases where full battery-electric operation remains constrained by charging infrastructure availability, duty cycle intensity, payload requirements, or total cost of ownership considerations. In the US market, adoption is primarily concentrated in commercial vehicles, specialty vehicles, off-highway platforms, and select passenger EV segments that prioritize operational flexibility and uptime.
The market is supported by the United States’ accelerating EV penetration, growing emphasis on fleet electrification, and regulatory push toward emissions reduction, while simultaneously navigating persistent concerns around range anxiety, charging downtime, and grid reliability in certain regions. Range extenders allow OEMs and fleet operators to balance electrification targets with real-world operating constraints, especially in long-distance, rural, and high-utilization environments.
Regionally, the West and South represent the most prominent demand centers for EV range extender systems. Western states lead due to early EV adoption, stringent emissions regulations, and strong innovation ecosystems supporting advanced powertrain development. Southern states show rising adoption driven by logistics fleets, municipal electrification programs, and mixed urban–rural operating profiles where charging access remains uneven. The Midwest serves as a critical manufacturing and engineering hub for range extender components, supported by automotive OEMs, Tier-1 suppliers, and powertrain R&D centers. The Northeast market is comparatively niche, with adoption skewed toward municipal fleets, specialty vehicles, and pilot programs rather than mass deployment.
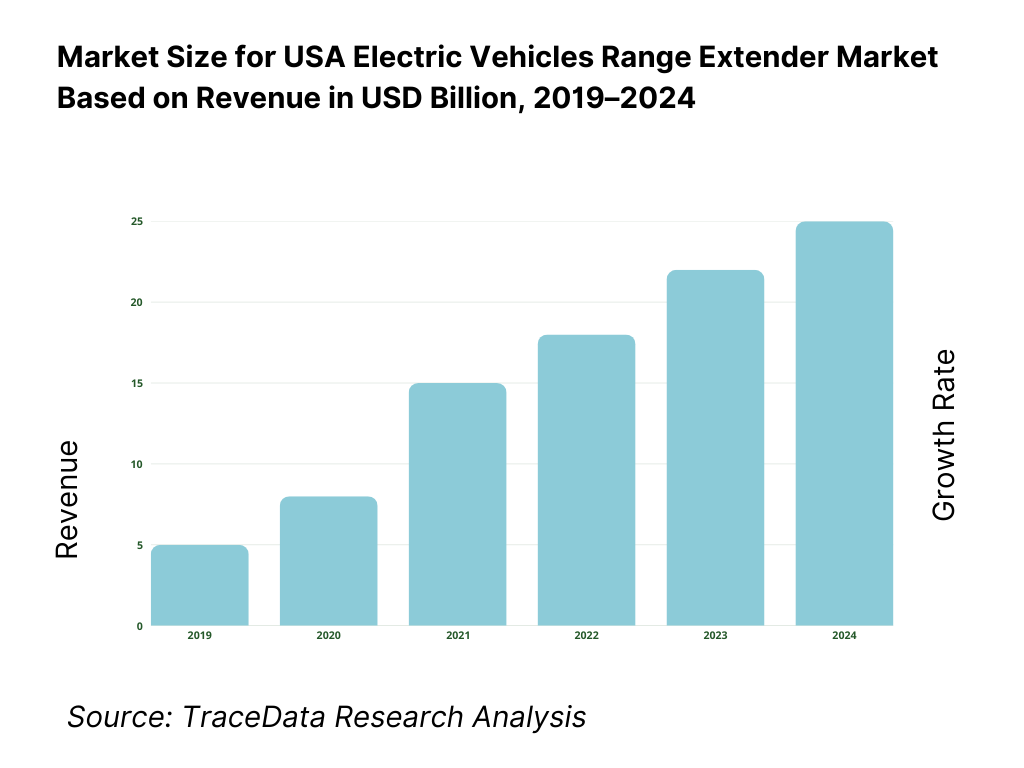
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of the USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market:
Persistent range anxiety and charging infrastructure gaps sustain demand for hybridized EV architectures: Despite rapid growth in public and private charging networks, charging availability, reliability, and dwell time remain key concerns for many EV users—particularly fleets with time-sensitive operations. Range extenders mitigate these limitations by providing on-demand energy generation, enabling vehicles to complete routes without extended charging stops. This capability is especially valuable in regions with sparse fast-charging coverage, extreme weather conditions, or grid capacity constraints. As a result, range extender-equipped EVs are increasingly viewed as a pragmatic bridge between conventional powertrains and fully battery-dependent mobility.
Commercial fleet electrification accelerates adoption in high-utilization vehicle segments: Delivery vans, utility trucks, emergency vehicles, municipal fleets, and specialty service vehicles often operate under demanding duty cycles that challenge battery-only configurations. Range extenders enable these vehicles to electrify propulsion while preserving operational continuity, predictable uptime, and route flexibility. Fleet operators prioritize total cost of ownership, reliability, and service continuity, making range extender systems an attractive solution during the transition toward zero-emission operations. This trend is particularly pronounced among logistics providers, utilities, public agencies, and last-mile delivery operators.
OEM strategy to balance regulatory compliance with customer usability supports integration of range extenders: Automotive OEMs face increasing regulatory pressure to reduce fleet-wide emissions while maintaining broad market appeal across diverse customer segments. Range extender architectures allow OEMs to offer electrified vehicles that comply with emissions standards while addressing consumer concerns related to range, charging time, and infrastructure dependence. This approach reduces barriers to EV adoption among conservative or first-time buyers and supports phased electrification strategies without committing to oversized battery packs that increase vehicle cost and weight.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth of the USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market:
Regulatory ambiguity around emissions classification and long-term policy direction impacts OEM investment confidence: While range extender systems support electrification by reducing reliance on grid charging, they often incorporate combustion-based or fuel-dependent energy generation. Regulatory frameworks at the federal and state levels do not always treat extended-range electric vehicles consistently, particularly when distinguishing between battery-electric, plug-in hybrid, and auxiliary power architectures. Uncertainty around future eligibility for incentives, credits, and compliance under zero-emission vehicle mandates creates hesitation among OEMs when committing to large-scale range extender platform development. This ambiguity can delay product roadmaps, limit platform standardization, and restrict adoption primarily to niche or transitional vehicle programs rather than mass-market deployment.
Cost and system complexity compared to larger battery packs affect total cost of ownership calculations: Range extender integration adds mechanical, electrical, thermal, and software complexity to EV platforms, increasing bill-of-materials costs, engineering effort, and long-term maintenance requirements. As battery costs continue to decline and energy density improves, some OEMs and fleet operators reassess whether incremental investment in larger battery packs may offer a simpler pathway to extended range. This dynamic places cost pressure on range extender suppliers to demonstrate clear total cost of ownership advantages through reduced downtime, smaller battery sizing, or improved asset utilization—particularly in price-sensitive commercial and fleet segments.
Packaging, NVH, and vehicle integration challenges limit applicability across vehicle segments: Incorporating a range extender requires additional space for the generator unit, fuel storage, exhaust or ventilation systems, cooling circuits, and power electronics. These requirements can constrain vehicle packaging, reduce cargo capacity, or introduce noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) concerns if not carefully engineered. For passenger vehicles and light commercial platforms with tight packaging envelopes, these trade-offs can reduce customer acceptance. As a result, range extender adoption remains more viable in medium-duty, specialty, and purpose-built vehicles rather than compact or mass-market consumer EVs.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market:
Federal and state emissions regulations influencing extended-range electric vehicle classification and compliance: The USA EV range extender market operates within a complex regulatory environment shaped by EPA emissions standards, fuel economy requirements, and state-level zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) mandates. The classification of extended-range electric vehicles affects how they are counted toward fleet emissions targets and compliance credits. Differences in treatment between battery-electric vehicles, plug-in hybrids, and range extender-equipped EVs influence OEM product strategies and market positioning. Regulatory flexibility for transitional technologies supports near-term deployment, but evolving definitions and compliance thresholds continue to shape investment decisions.
Incentive structures and electrification programs impacting adoption economics for fleets and OEMs: Federal tax credits, state rebates, and utility-supported electrification programs play a role in determining the commercial viability of range extender-equipped vehicles. Eligibility criteria tied to battery capacity, tailpipe emissions, or zero-emission operation can either support or constrain adoption depending on system design. Fleet-focused initiatives—such as clean fleet mandates, public-sector electrification targets, and infrastructure grants—often allow limited flexibility for extended-range solutions, particularly in applications where full battery-electric operation is not yet feasible. These programs influence purchasing decisions, pilot deployments, and scaling timelines.
Fuel, safety, and certification standards governing auxiliary power and energy systems: Range extender systems must comply with safety, fuel handling, emissions, and certification standards applicable to auxiliary power units and onboard energy generation systems. Requirements related to fuel storage integrity, exhaust management, electrical safety, and thermal control add layers of testing and validation. For emerging technologies such as hydrogen fuel-cell range extenders or alternative-fuel generators, evolving certification pathways and infrastructure readiness directly affect commercialization speed. Compliance with these standards shapes system design, supplier qualification, and time-to-market for new range extender solutions.
USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market Segmentation
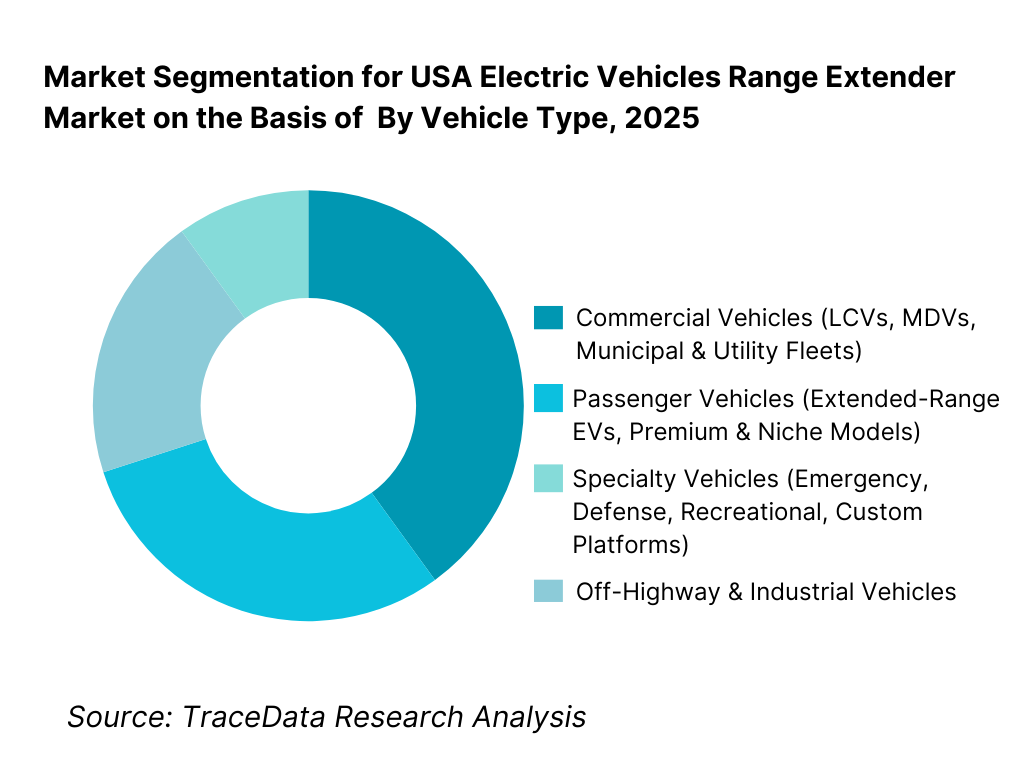
By Vehicle Type: Commercial vehicles hold dominance. This is because commercial and specialty vehicles operate under high-utilization duty cycles where charging downtime, route variability, and uptime requirements directly affect productivity. Delivery vans, utility trucks, municipal service vehicles, and specialty platforms benefit significantly from range extender systems that provide operational flexibility without requiring oversized battery packs. While passenger vehicles and off-highway platforms show selective adoption, the commercial vehicle segment continues to account for the majority of demand due to fleet electrification mandates, predictable route economics, and total cost of ownership optimization.
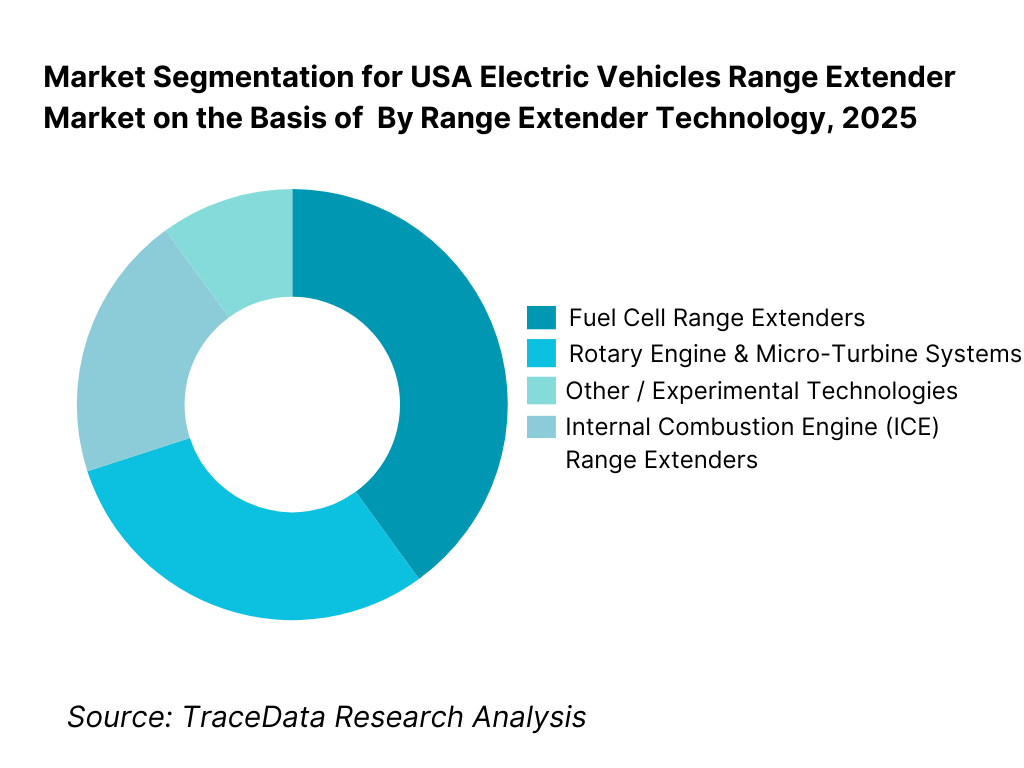
By Range Extender Technology: Internal combustion-based systems remain dominant, while fuel cell systems gain traction. Conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) range extenders continue to dominate due to their maturity, cost competitiveness, established supply chains, and regulatory familiarity. These systems are widely adopted in near-term commercial deployments where reliability and serviceability are prioritized. However, fuel-cell-based range extenders are emerging as a strategic growth segment, particularly for zero-emission-focused fleets and longer-duration applications. Rotary engines and micro-turbines remain niche, primarily in experimental, specialty, or defense-linked applications.
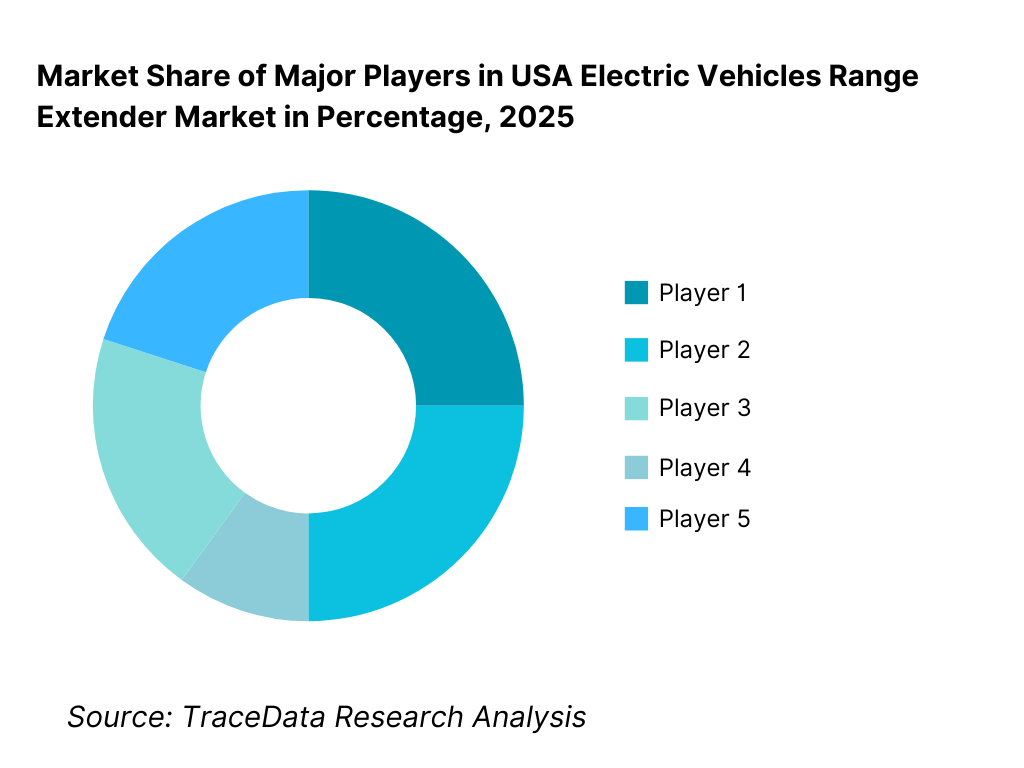
Competitive Landscape in USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market
The USA electric vehicles range extender market exhibits moderate concentration, characterized by a mix of global automotive OEMs, Tier-1 powertrain suppliers, specialized range extender technology providers, and emerging fuel cell developers. Competitive positioning is shaped by system efficiency, emissions compliance, packaging flexibility, integration capability, and long-term OEM partnerships. While large automotive suppliers dominate high-volume commercial and fleet programs, niche technology players remain competitive in specialty, defense, and pilot-scale deployments by offering differentiated architectures and fuel flexibility.
Name | Founding Year | Original Headquarters |
BMW Group | 1916 | Munich, Germany |
General Motors | 1908 | Detroit, Michigan, USA |
Cummins Inc. | 1919 | Columbus, Indiana, USA |
Bosch | 1886 | Stuttgart, Germany |
Ballard Power Systems | 1979 | Burnaby, Canada |
Hyundai Motor Group | 1967 | Seoul, South Korea |
Magna International | 1957 | Aurora, Ontario, Canada |
AVL | 1948 | Graz, Austria |
Roush Industries | 1976 | Livonia, Michigan, USA |
Some of the Recent Competitor Trends and Key Information About Competitors Include:
BMW Group: BMW remains one of the most visible OEMs associated with extended-range EV architecture through its earlier passenger vehicle deployments. The company’s experience continues to influence industry understanding of range extender integration, control strategies, and consumer acceptance, even as its newer platforms shift toward full battery-electric architectures.
General Motors: GM has explored range extender concepts primarily in commercial and military-adjacent applications rather than mainstream consumer vehicles. Its competitive strength lies in system integration, power electronics, and the ability to scale solutions across fleet-oriented platforms where electrification flexibility is essential.
Cummins Inc.: Cummins plays a central role in the commercial and industrial range extender ecosystem, leveraging its expertise in compact engines, generators, and emerging hydrogen and fuel cell technologies. The company’s positioning is particularly strong in medium-duty, heavy-duty, and specialty vehicle applications where durability and service networks matter.
Bosch: Bosch continues to compete through advanced power electronics, energy management software, and modular range extender subsystems rather than complete vehicle solutions. Its strength lies in supplying scalable, OEM-agnostic components that enable integration across multiple vehicle platforms.
Ballard Power Systems: Ballard is a key enabler of fuel-cell-based range extender systems, particularly in zero-emission-focused commercial fleets and long-range applications. Its competitiveness is driven by hydrogen fuel cell stack efficiency, durability, and growing alignment with fleet decarbonization strategies.
Magna International: Magna supports OEMs through flexible powertrain engineering and contract manufacturing capabilities. Its involvement in electrified powertrain systems allows it to participate in range extender programs where OEMs seek outsourced development and scalable integration.
What Lies Ahead for USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market?
The USA electric vehicles range extender market is expected to evolve steadily through 2035, supported by the continued electrification of commercial fleets, uneven charging infrastructure readiness, and the need for operational flexibility across diverse duty cycles. While long-term policy and technology trajectories favor full battery-electric architectures, range extender systems are expected to remain relevant as a transitional and application-specific solution—particularly in commercial, municipal, specialty, and off-highway vehicle segments. Growth momentum will be shaped by fleet uptime requirements, regulatory compliance strategies, and OEM efforts to balance emissions reduction with real-world usability.
Gradual Shift from Transitional Technology to Application-Specific Deployment: Through 2035, the role of range extenders will increasingly shift from broad consumer-facing solutions toward targeted, application-specific deployments. Passenger vehicle adoption is expected to remain limited and selective, while commercial fleets, utilities, emergency services, and specialty vehicle operators will continue to rely on range extender architectures where charging downtime, route uncertainty, or mission-critical operations limit the practicality of battery-only configurations. This evolution will reinforce the positioning of range extenders as a pragmatic electrification bridge rather than a universal solution.
Growing Role of Fleet Electrification and Duty-Cycle-Driven Design: Fleet electrification will remain the primary demand driver for range extender systems in the US market. Operators with high daily mileage, variable routes, or limited access to fast charging will increasingly favor extended-range EV platforms that offer predictable uptime and operational resilience. Range extenders enable optimized battery sizing, reduced charging frequency, and greater asset utilization—factors that directly influence total cost of ownership. Suppliers that align system design with specific fleet duty cycles and service requirements will capture sustained demand.
Transition Toward Low-Emission and Zero-Emission Range Extender Technologies: While internal combustion-based range extenders currently dominate, the medium-to-long-term outlook points toward increased adoption of low-emission and zero-emission alternatives. Fuel-cell-based range extenders, hydrogen-compatible systems, and alternative-fuel generators are expected to gain traction, particularly in regions and fleets facing stricter emissions mandates. Technological progress in fuel cell durability, hydrogen infrastructure pilots, and regulatory clarity will determine the pace at which these solutions move from demonstration to scaled deployment.
Increasing OEM Focus on Modular and Scalable Electrification Platforms: OEMs are expected to prioritize modular vehicle platforms that can support multiple powertrain configurations, including battery-only and extended-range variants. This approach allows manufacturers to address diverse customer needs while managing development costs and regulatory risk. Range extenders will be increasingly integrated as optional or configurable modules rather than standalone architectures, enabling OEMs to tailor offerings by region, application, and customer profile. Suppliers with flexible, platform-agnostic solutions will benefit from this modularization trend.
USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market Segmentation
By Vehicle Type
• Commercial Vehicles (Light, Medium, and Municipal Fleets)
• Passenger Vehicles (Extended-Range EVs, Niche & Premium)
• Specialty Vehicles (Emergency, Defense, Recreational, Custom)
• Off-Highway & Industrial Vehicles
By Range Extender Technology
• Internal Combustion Engine (ICE)-Based Range Extenders
• Fuel Cell-Based Range Extenders
• Rotary Engine & Micro-Turbine Systems
• Alternative Fuel / Experimental Technologies
By Application
• Logistics & Delivery Fleets
• Utilities, Municipal & Public Services
• OEM Passenger Vehicle Programs
• Defense, Specialty & Other Applications
By Power Output
• Low Power (<30 kW)
• Medium Power (30–75 kW)
• High Power (>75 kW)
By Region
• West
• South
• Midwest
• Northeast
Players Mentioned in the Report:
• Automotive OEMs with extended-range EV programs
• Commercial vehicle manufacturers and fleet solution providers
• Tier-1 powertrain and electrification suppliers
• Fuel cell and alternative energy system developers
• Specialized range extender technology companies
• Engineering and system integration firms
Key Target Audience
• Automotive OEMs and commercial vehicle manufacturers
• Fleet operators (logistics, utilities, municipal services)
• Powertrain and electrification system suppliers
• Fuel cell and alternative energy technology providers
• Engineering, testing, and certification service firms
• Infrastructure developers and clean mobility investors
• Policy bodies and public-sector electrification agencies
Time Period:
Historical Period: 2019–2024
Base Year: 2025
Forecast Period: 2025–2035
Report Coverage
Choose individual sections to purchase. Mix and match as you like.
4. 1 Delivery Model Analysis for Range Extender Systems-OEM-Integrated, Tier-1 Supplied, Retrofit/Aftermarket, Modular Platforms [Margins, Preference, Strength & Weakness]
4. 2 Revenue Streams for USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market [System Sales, Licensing, Integration Services, Software & Controls, After-Sales & Maintenance]
4. 3 Business Model Canvas for USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market [Key Partners, Key Activities, Value Propositions, Customer Segments, Cost Structure, Revenue Streams]
5. 1 Local Players vs Global Vendors [US-Based OEMs & Suppliers vs Global Automotive & Powertrain Players]
5. 2 Investment Model in USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market [OEM Capex, Government Grants, VC Funding, PE Investments, Strategic Partnerships]
5. 3 Comparative Analysis of Range Extender Adoption in Commercial vs Passenger Vehicles [Procurement Models, Use Cases, ROI Benchmarks]
5. 4 Budget Allocation by Buyer Type [Large Fleet Operators, Medium Fleets, Specialty Operators, OEM Programs]
8. 1 Revenues (Historical Trend)
9. 1 By Market Structure (OEM-Integrated Systems vs Outsourced / Tier-1 Supplied Systems)
9. 2 By Technology (ICE-Based Range Extenders, Fuel Cell Range Extenders, Rotary Engines, Micro-Turbines, Alternative Fuel Systems)
9. 3 By Vehicle Type (Commercial Vehicles, Passenger Vehicles, Specialty Vehicles, Off-Highway & Industrial Vehicles)
9. 4 By Application (Logistics & Delivery Fleets, Utilities & Municipal Services, OEM Passenger Programs, Defense & Specialty Applications)
9. 5 By Power Output (Low Power, Medium Power, High Power)
9. 6 By Fuel Type (Gasoline, Diesel, Hydrogen, Alternative Fuels)
9. 7 By Integrated vs Modular Range Extender Systems
9. 8 By Region (West, South, Midwest, Northeast)
10. 1 OEM & Fleet Client Landscape and Cohort Analysis
10. 2 Adoption Drivers & Decision-Making Process
10. 3 Operational Effectiveness & Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Analysis
10. 4 Gap Analysis Framework
11. 1 Trends & Developments in USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market
11. 2 Growth Drivers for USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market
11. 3 SWOT Analysis for USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market
11. 4 Issues & Challenges for USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market
11. 5 Government Regulations for USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market
12. 1 Market Size and Future Potential for Fuel Cell & Low-Emission Range Extenders in USA
12. 2 Business Models & Revenue Streams [System Sales, Licensing, Energy-as-a-Service, Maintenance Contracts]
12. 3 Delivery Models & Applications Offered [OEM Platforms, Fleet-Specific Solutions, Modular & Scalable Systems]
15. 1 Market Share of Key Players in USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market (By Revenues)
15. 2 Benchmark of Key Competitors [Company Overview, USP, Business Strategies, Business Model, Engineering Capabilities, Revenues, Pricing Models, Technology Used, Key Range Extender Solutions, Major Clients, Strategic Tie-ups, Marketing Strategy, Recent Developments]
15. 3 Operating Model Analysis Framework
15. 4 Gartner Magic Quadrant for Range Extender & Electrified Powertrain Providers
15. 5 Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
16. 1 Revenues (Projections)
17. 1 By Market Structure (OEM-Integrated and Outsourced Systems)
17. 2 By Technology (ICE-Based, Fuel Cell, Rotary, Micro-Turbine, Alternative Fuel Systems)
17. 3 By Vehicle Type (Commercial, Passenger, Specialty, Off-Highway)
17. 4 By Application (Logistics, Utilities, Passenger OEM Programs, Defense & Specialty)
17. 5 By Power Output (Low, Medium, High)
17. 6 By Fuel Type (Gasoline, Diesel, Hydrogen, Alternative Fuels)
17. 7 By Integrated vs Modular Systems
17. 8 By Region (West, South, Midwest, Northeast)
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
We begin by mapping the complete ecosystem of the USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market across demand-side and supply-side entities. On the demand side, entities include commercial fleet operators (logistics, utilities, municipal services), automotive OEMs, specialty vehicle manufacturers, defense and emergency service operators, off-highway equipment users, and selected premium or niche passenger vehicle buyers. Demand is further segmented by vehicle type (commercial, passenger, specialty, off-highway), duty cycle intensity (urban, mixed, long-range), range requirement, and charging infrastructure access (depot-based, public fast charging, limited-access regions).
On the supply side, the ecosystem includes automotive OEMs with extended-range EV platforms, Tier-1 powertrain and electrification suppliers, range extender system developers, fuel cell technology providers, power electronics and energy management software vendors, integration and calibration specialists, testing and certification bodies, and fuel or hydrogen infrastructure partners. From this mapped ecosystem, we shortlist 6–10 leading OEMs and system suppliers based on deployment scale, technology maturity, OEM partnerships, regulatory readiness, and relevance to commercial and fleet-oriented applications. This step establishes how value is created and captured across system design, integration, vehicle deployment, operation, and lifecycle support.
Step 2: Desk Research
An exhaustive desk research process is undertaken to analyze the structure and evolution of the USA EV range extender market. This includes reviewing EV adoption trends, commercial fleet electrification pipelines, charging infrastructure development, and regulatory frameworks influencing extended-range architectures. We assess buyer behavior related to range anxiety, uptime requirements, total cost of ownership, and emissions compliance strategies.
Company-level analysis includes review of OEM product strategies, range extender technology roadmaps, system specifications, deployment case studies, and partnerships between vehicle manufacturers and technology providers. We also examine federal and state policy dynamics, incentive structures, and emissions classification frameworks that influence adoption by region and vehicle segment. The outcome of this stage is a comprehensive industry foundation that defines segmentation logic and establishes the assumptions required for market estimation and long-term outlook modeling.
Step 3: Primary Research
We conduct structured interviews with automotive OEMs, commercial vehicle manufacturers, fleet operators, Tier-1 suppliers, range extender technology providers, and powertrain engineers. The objectives are threefold: (a) validate assumptions around demand concentration across vehicle types and applications, (b) authenticate segment splits by technology, power output, and end-use application, and (c) gather qualitative insights on system costs, integration challenges, maintenance considerations, regulatory hurdles, and buyer acceptance.
A bottom-to-top approach is applied by estimating vehicle deployment volumes across key fleet and specialty segments and mapping typical range extender system values by power class and technology type. These are aggregated to develop the overall market view. In selected cases, disguised buyer-style interactions are conducted with fleet solution providers and OEM sales teams to validate real-world decision drivers such as uptime sensitivity, charging constraints, and procurement trade-offs between larger batteries and extended-range configurations.
Step 4: Sanity Check
The final stage integrates bottom-to-top and top-to-down approaches to cross-validate the market size, segmentation splits, and forecast assumptions. Demand estimates are reconciled with macro indicators such as EV penetration rates, fleet electrification mandates, infrastructure rollout timelines, and emissions reduction targets. Assumptions around battery cost declines, charging availability improvements, and regulatory treatment of extended-range EVs are stress-tested to assess their impact on adoption through 2035.
Sensitivity analysis is conducted across key variables including infrastructure readiness by region, fuel cell commercialization pace, fleet utilization intensity, and policy shifts toward stricter zero-emission definitions. Market models are refined until alignment is achieved between OEM deployment strategies, supplier capacity, and fleet purchasing behavior, ensuring internal consistency and robust directional forecasting.
FAQs
01 What is the potential for the USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market?
The USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market holds moderate but strategically important potential, primarily as a transitional and application-specific electrification solution. Demand is supported by commercial fleet electrification, uneven charging infrastructure availability, and the need for operational flexibility in high-utilization and mission-critical vehicle segments. While long-term growth of battery-electric vehicles may limit mass-market adoption, range extenders are expected to remain relevant in commercial, municipal, specialty, and off-highway applications through 2035.
02 Who are the Key Players in the USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market?
The market features a mix of automotive OEMs, Tier-1 powertrain suppliers, specialized range extender system developers, and emerging fuel cell technology providers. Competition is shaped by system efficiency, regulatory compliance, integration capability, and long-term OEM or fleet partnerships. OEM-led platforms dominate large-scale deployments, while niche technology players remain active in specialty and pilot-driven applications.
03 What are the Growth Drivers for the USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market?
Key growth drivers include commercial fleet electrification mandates, persistent range anxiety in regions with limited charging access, and fleet operator focus on uptime and total cost of ownership. Range extenders enable optimized battery sizing, reduced charging downtime, and compliance with emissions targets without fully relying on charging infrastructure. Additional momentum comes from modular vehicle platforms and emerging low-emission range extender technologies such as fuel cells.
04 What are the Challenges in the USA Electric Vehicles Range Extender Market?
Challenges include regulatory uncertainty around emissions classification, system cost and complexity relative to declining battery prices, and packaging and integration constraints across certain vehicle platforms. As charging infrastructure expands and battery performance improves, the addressable market for range extenders may narrow to specific use cases. Managing long-term relevance while aligning with evolving zero-emission policies remains a critical challenge for market participants.