Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029
By Market Structure, By End-Users, By Product Type, By Temperature Type, By Mode of Transport and By Region
- Product Code: TDR0336
- Region: Africa
- Published on: September 2025
- Total Pages: 80
Report Summary
The report titled “Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market Outlook to 2029 - By Market Structure, By End-Users, By Product Type, By Temperature Type, By Mode of Transport and By Region.” provides a comprehensive analysis of the cold chain market in Zimbabwe. The report covers an overview and genesis of the industry, overall market size in terms of revenue, market segmentation; trends and developments, regulatory landscape, customer-level profiling, issues and challenges, and comparative landscape including competition scenario, cross comparison, opportunities and bottlenecks, and company profiling of major players in the Cold Chain Market. The report concludes with future market projections based on revenue, by market, application areas, temperature zones, region, cause-and-effect relationship, and success case studies highlighting the major opportunities and cautions.
Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market Overview and Size
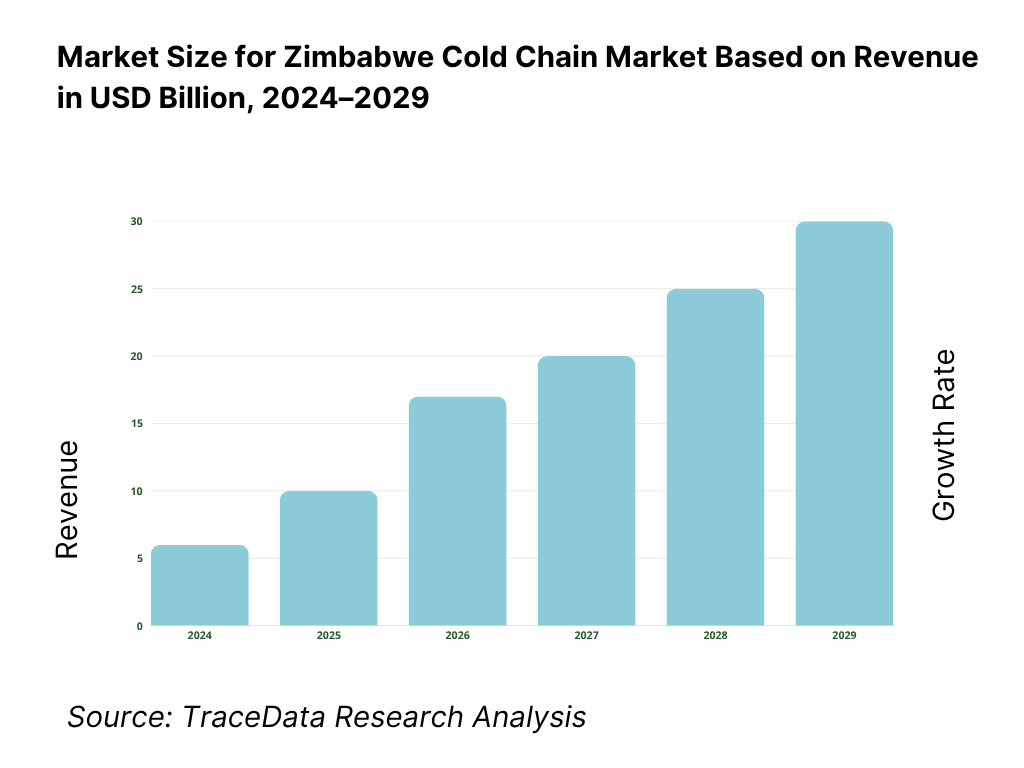
The Zimbabwe cold chain market reached a valuation of USD 150 million in 2023, driven by the rising demand for temperature-controlled logistics in the agriculture, pharmaceutical, and retail sectors. The market is characterized by major players such as Freight World, Swift Transport, Unifreight, and Bak Logistics. These companies are recognized for their regional logistics capabilities, integrated cold storage facilities, and strong B2B networks.
In 2023, Bak Logistics expanded its cold storage capacity in Harare to address growing demand in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Harare and Bulawayo are key markets due to their strategic locations, access to trade routes, and higher concentration of industrial and healthcare facilities.
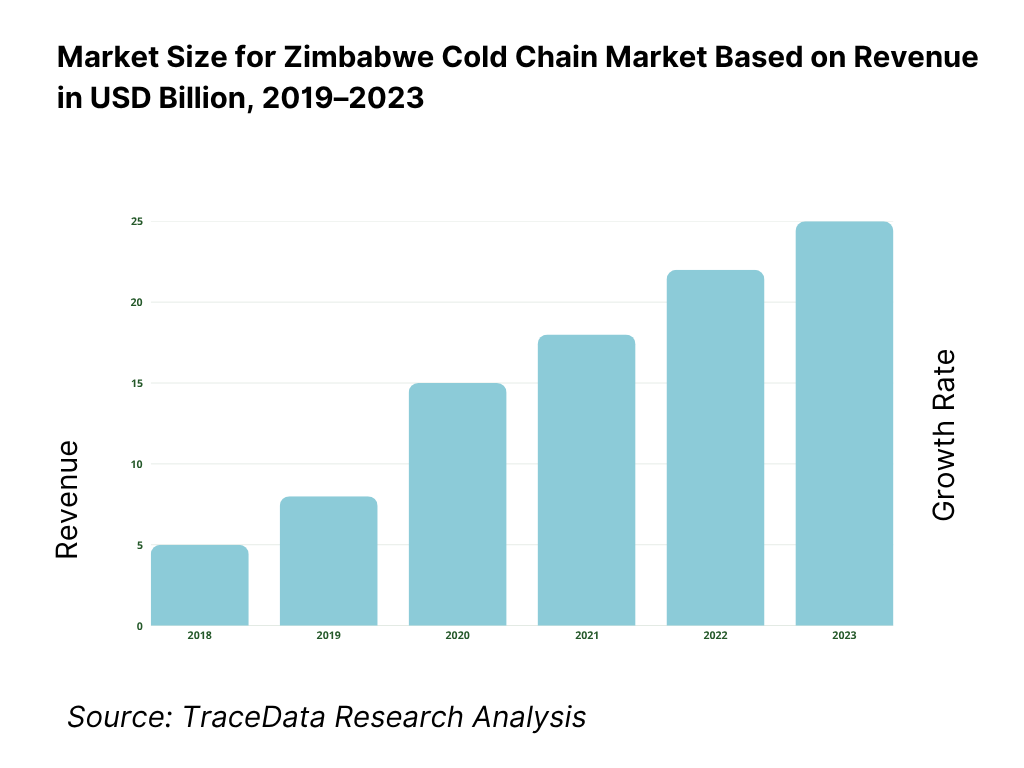
What Factors are Leading to the Growth of Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market:
Agricultural Exports and Food Security: Zimbabwe’s agricultural exports, including perishables such as fruits and vegetables, require efficient cold storage and transport. As the government promotes export diversification, demand for reliable cold chain infrastructure is increasing. In 2023, over 30% of Zimbabwe’s horticultural exports required refrigerated logistics.
Pharmaceutical and Vaccine Demand: The rise in demand for vaccines and temperature-sensitive medicines has led to significant investment in healthcare cold chains. With Zimbabwe expanding immunization programs, especially in rural areas, cold chain logistics have become critical for last-mile delivery. Public-private partnerships are playing a vital role in cold storage enhancements.
Retail and FMCG Sector Expansion: Growth in modern retail chains and quick service restaurants has fueled the need for cold logistics. Zimbabwe's urban retail market grew by approximately 7% in 2023, and retailers are increasingly relying on third-party cold chain service providers to maintain inventory freshness and compliance.
Which Industry Challenges Have Impacted the Growth for Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market
Infrastructure Deficiencies: Zimbabwe's cold chain infrastructure remains underdeveloped, particularly in rural and peri-urban regions. According to a 2023 logistics industry survey, nearly 45% of cold chain operators cited unreliable electricity supply and outdated storage facilities as their biggest operational hurdles. Frequent power outages also lead to increased spoilage rates, reducing trust among clients and limiting market scalability.
High Operating Costs: The costs associated with running refrigerated storage and transport—particularly fuel and generator backup—are disproportionately high in Zimbabwe. Industry experts report that energy expenses alone can account for up to 30–35% of total cold chain operating costs, significantly above regional averages. This reduces the affordability of cold chain services for small-scale producers and businesses.
Limited Skilled Workforce: A shortage of trained professionals in temperature-sensitive logistics and refrigeration engineering has hampered service quality and scalability. In 2023, over 60% of firms reported difficulty in recruiting adequately trained cold chain technicians, leading to inconsistent temperature monitoring and increased product wastage.
What are the Regulations and Initiatives which have Governed the Market
Standards for Perishable Goods Handling: Zimbabwe’s Ministry of Health and the Food Standards Advisory Board enforce regulations on the safe storage and transport of perishable products. These include mandatory temperature thresholds for categories such as dairy, poultry, and vaccines. However, compliance remains inconsistent, especially among informal and small-scale operators.
Import Regulations for Refrigerated Vehicles and Equipment: To address equipment shortages, the Zimbabwe Revenue Authority (ZIMRA) has permitted duty exemptions on certain cold chain equipment, including insulated vans and modular cold rooms. These incentives, initiated in 2022, are aimed at encouraging private investment in modern cold logistics.
Public Health and Pharmaceutical Compliance: The Medicines Control Authority of Zimbabwe (MCAZ) mandates Good Distribution Practice (GDP) compliance for pharmaceutical cold chain logistics. This includes real-time monitoring of temperature logs, audit trails, and calibrated equipment. In 2023, over 70% of urban pharmaceutical distributors were GDP-compliant, though rural penetration remains limited.
Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market Segmentation
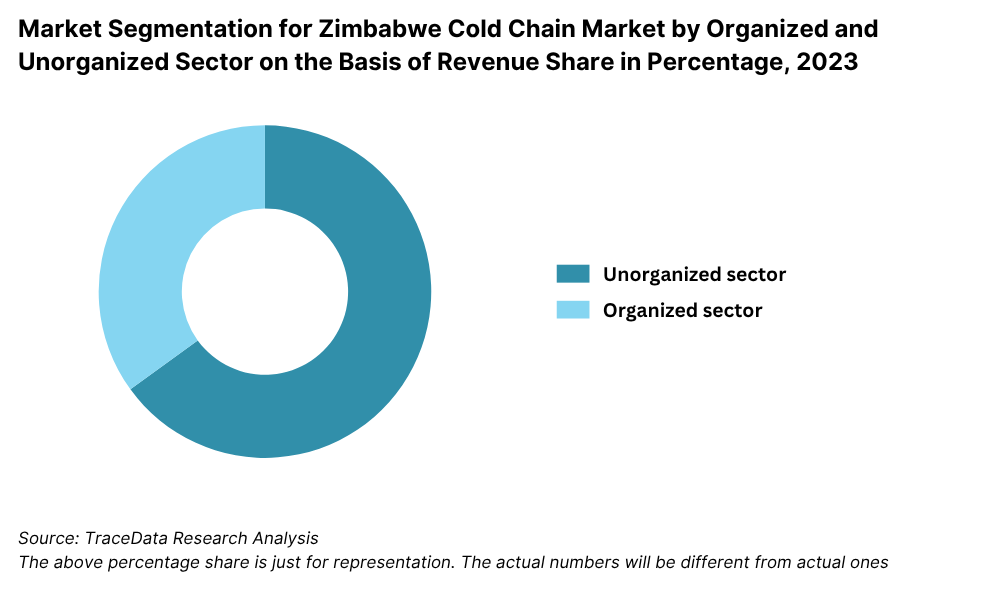
By Market Structure: The unorganized sector continues to dominate Zimbabwe’s cold chain market due to the prevalence of small-scale operators, limited regulatory oversight, and relatively low capital investment requirements. These operators typically cater to local food producers, small retailers, and informal markets. However, the organized sector—comprising established logistics companies and cold storage providers—is gradually expanding, driven by rising demand from large FMCG players, healthcare providers, and exporters seeking consistent quality, traceability, and compliance.
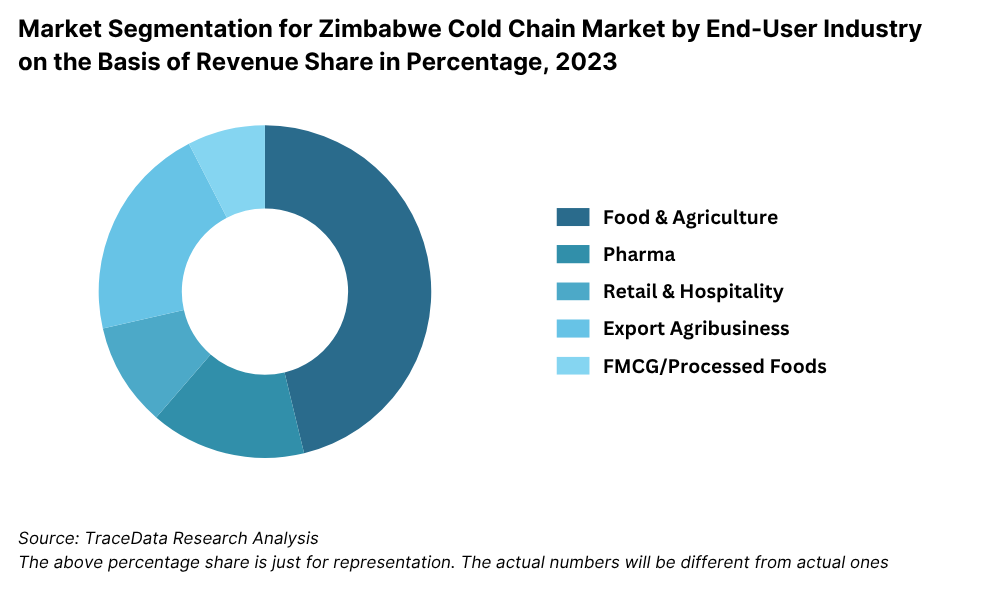
By End-User Industry: The food and agriculture segment is the largest end-user of cold chain services in Zimbabwe, particularly for the storage and transport of fruits, vegetables, meat, and dairy. Pharmaceuticals represent the second-largest segment, largely due to increased vaccine distribution and temperature-sensitive medicines. Retail and hospitality sectors are also growing contributors, driven by urban expansion and changing consumer preferences for fresh and frozen goods.
By Temperature Type: Chilled logistics holds a significant share of the Zimbabwe cold chain market, driven by demand for fresh produce, dairy, and beverages. However, frozen logistics is gaining traction, especially for meat, poultry, and long-distance vaccine transport. Growth in frozen logistics is particularly visible in export corridors and urban supermarkets.
Competitive Landscape in Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market
The Zimbabwe cold chain market is moderately fragmented, with a few organized players holding notable shares while numerous small and medium-sized operators cater to localized and niche demand. The entry of international development programs and partnerships with regional logistics providers have also contributed to capacity expansion and operational improvements. Major players include Bak Logistics, Swift Transport, Freight World, Unifreight Africa, and Cross Country Containers.
Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters |
Bak Logistics | 2005 | Harare, Zimbabwe |
Swift Transport | 1948 | Harare, Zimbabwe |
Freight World | 1998 | Harare, Zimbabwe |
Unifreight Africa | 1970 | Harare, Zimbabwe |
Cross Country Containers | 2004 | Bulawayo, Zimbabwe |
Some of the recent competitor trends and key information about competitors include:
Bak Logistics: A key player in the integrated logistics sector, Bak Logistics expanded its cold storage facilities in Harare in 2023, increasing its capacity by 30%. The company has partnered with agricultural cooperatives and pharmaceutical firms to ensure consistent cold chain delivery in both urban and peri-urban markets.
Swift Transport: Known for its extensive distribution network across Zimbabwe and neighboring countries, Swift has recently invested in a new fleet of refrigerated trucks. In 2023, it signed logistics contracts with two leading supermarket chains to manage frozen and chilled distribution nationwide.
Freight World: Focused on cross-border logistics, Freight World has seen rising demand from horticulture exporters needing reliable cold chain transport to ports in Mozambique and South Africa. The company enhanced its temperature monitoring system in 2023 to meet international compliance standards.
Unifreight Africa: As a publicly listed logistics provider, Unifreight has diversified into cold chain solutions in response to increasing demand from the healthcare and agribusiness sectors. The firm has piloted cold chain container solutions for remote vaccine deliveries in coordination with donor agencies.
Cross Country Containers: With strong presence in Bulawayo and the southern region, Cross Country has built its niche in dairy and meat logistics. In 2023, the company upgraded two cold storage depots and introduced route optimization software, reducing spoilage rates by 18%.
What Lies Ahead for Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market?
The Zimbabwe cold chain market is projected to grow steadily through 2029, with a moderate yet promising CAGR. This growth is expected to be driven by increasing demand for food security, healthcare logistics, modernization of agricultural exports, and improved regulatory alignment with global standards.
Expansion of Agri-Export Cold Chains: With Zimbabwe aiming to boost its horticultural exports to the EU and regional markets, investment in cold chain infrastructure for fresh produce, flowers, and dairy is expected to increase. Exporters are seeking more reliable end-to-end refrigerated logistics to meet stringent international quality standards, especially in high-value crops like blueberries, peas, and citrus.
Strengthening of Pharmaceutical Logistics: Rising healthcare investments, vaccine distribution programs, and growing access to chronic disease treatments will necessitate robust pharmaceutical cold chain systems. By 2029, a significant portion of healthcare logistics is expected to be GDP-compliant, driven by international donor support and government prioritization of public health.
Technology Integration in Cold Chain Monitoring: The adoption of IoT-based temperature tracking, automated storage systems, and mobile-enabled inventory management tools will help reduce wastage and improve traceability. These digital upgrades will enable small and medium players to meet regulatory expectations and reduce spoilage by 20–25% over the next five years.
Rise of Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Providers: Increasing outsourcing of cold chain operations by retailers, QSRs, and pharmaceutical companies will lead to the expansion of 3PL cold chain providers. These players offer end-to-end solutions—transportation, warehousing, and compliance—allowing businesses to focus on core operations while ensuring quality control.
Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market Segmentation
• By Market Structure:
o Organized Sector
o Unorganized Sector
o 3PL Cold Chain Providers
o Owner-Operated Transporters
o Integrated Logistics Companies
• By End-User Industry:
o Agriculture & Horticulture (Fruits, Vegetables, Dairy)
o Pharmaceuticals & Vaccines
o Food Processing & Meat
o Retail & Supermarkets
o Quick Service Restaurants (QSRs)
o Hospitality & Catering Services
• By Temperature Type:
o Chilled (0°C to 10°C)
o Frozen (-18°C and below)
• By Mode of Transport:
o Refrigerated Road Transport
o Cold Chain Air Freight (Imports/Exports)
o Reefer Containers (Sea Transport)
• By Type of Cold Storage Facility:
o Blast Freezers
o Multi-Commodity Cold Stores
o Solar-Powered Cold Rooms
o Modular Cold Storage
• By Region:
o Harare
o Bulawayo
o Manicaland
o Mashonaland West
o Midlands
o Matabeleland
Players Mentioned in the Report:
• Bak Logistics
• Swift Transport
• Freight World
• Unifreight Africa
• Cross Country Containers
• Premier Refrigerated Transport
• Greenspan Refrigeration
• Associated Cold Storage
Key Target Audience:
• Cold Chain Logistics Companies
• Agro-Exporters and Cooperatives
• Pharmaceutical Distributors and Health NGOs
• Food Processors and FMCG Manufacturers
• Government Agencies (e.g., Ministry of Agriculture, MCAZ)
• Development Organizations (e.g., USAID, GAVI, UNICEF)
• Investors and Infrastructure Development Firms
• Research and Technology Providers
Time Period:
• Historical Period: 2018–2023
• Base Year: 2024
• Forecast Period: 2024–2029
Report Coverage
1. Executive Summary
2. Research Methodology
3. Ecosystem of Key Stakeholders in Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market
4. Value Chain Analysis
4.1. Value Chain Process-Role of Entities, Stakeholders, and Challenges They Face
4.2. Revenue Streams for Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market
4.3. Business Model Canvas for Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market
4.4. Cold Chain Decision-Making Process (Demand Side)
4.5. Cold Chain Decision-Making Process (Supply Side)
5. Market Structure
5.1. Agricultural Exports and Cold Chain Dependence, 2018-2024
5.2. Pharmaceutical Distribution Channels, 2018-2024
5.3. Adoption of Solar Cold Storage Solutions in Zimbabwe, 2024
5.4. Number of Cold Chain Operators by Region in Zimbabwe
6. Market Attractiveness for Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market
7. Supply-Demand Gap Analysis
8. Market Size for Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market Basis
8.1. Revenues, 2018-2024
8.2. Cold Storage Capacity and Fleet Size, 2018-2024
9. Market Breakdown for Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market Basis
9.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized Sector), 2023-2024P
9.2. By End-User Industry (Agriculture, Pharma, Retail, QSR, etc.), 2023-2024P
9.3. By Temperature Type (Chilled and Frozen), 2023-2024P
9.4. By Mode of Transport (Road, Air, Sea), 2023-2024P
9.5. By Region (Harare, Bulawayo, Manicaland, etc.), 2023-2024P
9.6. By Type of Cold Storage Facility (Modular, Solar, Blast, etc.), 2023-2024P
10. Demand Side Analysis for Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market
10.1. Customer Landscape and Cohort Analysis
10.2. Customer Journey and Vendor Decision-Making
10.3. Need, Desire, and Pain Point Analysis
10.4. Gap Analysis Framework
11. Industry Analysis
11.1. Trends and Developments for Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market
11.2. Growth Drivers for Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market
11.3. SWOT Analysis for Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market
11.4. Issues and Challenges for Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market
11.5. Government Regulations for Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market
12. Snapshot on Digitalization in Cold Chain Logistics
12.1. Adoption of IoT, GPS, and Monitoring Tools, 2018-2029
12.2. Business Model and Technology Integration Framework
12.3. Cross Comparison of Leading Players Based on Technology Adoption, Fleet Size, Network, Cold Storage, and Services
13. Donor-Funded and Public-Private Cold Chain Initiatives
13.1. Solar-Powered Cold Room Deployment, 2018-2029
13.2. Collaborations with NGOs (e.g., GAVI, USAID, UNICEF)
13.3. Healthcare Supply Chain Resilience Projects
14. Opportunity Matrix for Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market-Presented with the Help of Radar Chart
15. PEAK Matrix Analysis for Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market
16. Competitor Analysis for Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market
16.1. Benchmark of Key Competitors Including Company Overview, Core Focus Areas, Business Strategies, Fleet & Facility Size, Coverage, Recent Developments
16.2. Strengths and Weaknesses
16.3. Operating Model Analysis Framework
16.4. Gartner Magic Quadrant
16.5. Bowman’s Strategic Clock for Competitive Advantage
17. Future Market Size for Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market Basis
17.1. Revenues, 2025-2029
17.2. Cold Storage & Reefer Truck Capacity, 2025-2029
18. Market Breakdown for Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market Basis
18.1. By Market Structure (Organized and Unorganized Sector), 2025-2029
18.2. By End-User Industry, 2025-2029
18.3. By Temperature Type, 2025-2029
18.4. By Mode of Transport, 2025-2029
18.5. By Region, 2025-2029
18.6. By Type of Cold Storage Facility, 2025-2029
18.7. Recommendation
18.8. Opportunity Analysis
Research Methodology
Step 1: Ecosystem Creation
Map the ecosystem and identify all the demand side and supply side entities for Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market. Basis this ecosystem, we will shortlist leading 5-6 service providers in the country based upon their infrastructure capacity, service network, and sectoral presence.
Sourcing is made through industry articles, multiple secondary, and proprietary databases to perform desk research around the market to collate industry-level information.
Step 2: Desk Research
Subsequently, we engage in an exhaustive desk research process by referencing diverse secondary and proprietary databases. This approach enables us to conduct a thorough analysis of the market, aggregating industry-level insights. We delve into aspects like the service coverage, number of market players, pricing models, demand patterns, and other variables. We supplement this with detailed examinations of company-level data, relying on sources like press releases, donor reports, development agency publications, and similar documents. This process aims to construct a foundational understanding of both the market and the entities operating within it.
Step 3: Primary Research
We initiate a series of in-depth interviews with C-level executives and other stakeholders representing various Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market companies and end-users. This interview process serves a multi-faceted purpose: to validate market hypotheses, authenticate statistical data, and extract valuable operational and financial insights from these industry representatives. Bottom to top approach is undertaken to evaluate volume serviced by each player thereby aggregating to the overall market.
As part of our validation strategy, our team executes disguised interviews wherein we approach each company under the guise of potential customers. This approach enables us to validate the operational and financial information shared by company executives, corroborating this data against what is available in secondary databases. These interactions also provide us with a comprehensive understanding of revenue streams, value chain, process, pricing, and other factors.
Step 4: Sanity Check
Bottom to top and top to bottom analysis along with market size modeling exercises is undertaken to assess sanity check process.
FAQs
1. What is the potential for the Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market?
The Zimbabwe cold chain market is poised for steady growth, reaching a valuation of USD 150 million in 2023. This growth is driven by increasing demand for perishable food storage, vaccine distribution, and export-oriented agricultural logistics. The market's potential is further strengthened by government initiatives, donor-backed infrastructure development, and growing interest from private logistics companies.
2. Who are the Key Players in the Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market?
The Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market features several key players, including Bak Logistics, Swift Transport, and Freight World. These companies dominate the market due to their established infrastructure, regional logistics networks, and focus on integrated cold storage solutions. Other notable players include Unifreight Africa and Cross Country Containers.
3. What are the Growth Drivers for the Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market?
The primary growth drivers include rising exports of horticultural produce, expanding vaccine and pharmaceutical distribution needs, and growth in modern retail and food processing sectors. Additionally, increased donor investment in healthcare cold chain and solar-powered storage solutions is fueling development, especially in rural and underserved regions.
4. What are the Challenges in the Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market?
The Zimbabwe Cold Chain Market faces several challenges, including unreliable electricity supply, high operational costs for refrigerated transport, and limited skilled workforce in cold chain management. Infrastructure deficiencies in rural areas and fragmented supply chain coordination also restrict service coverage and efficiency, posing barriers to sustained growth.